Evaluation of the Costs and Outcomes of COVID-19 Therapeutic Regimens in Hospitalized Patients in Shiraz
et al., Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions A: Science, doi:10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0, Sep 2022
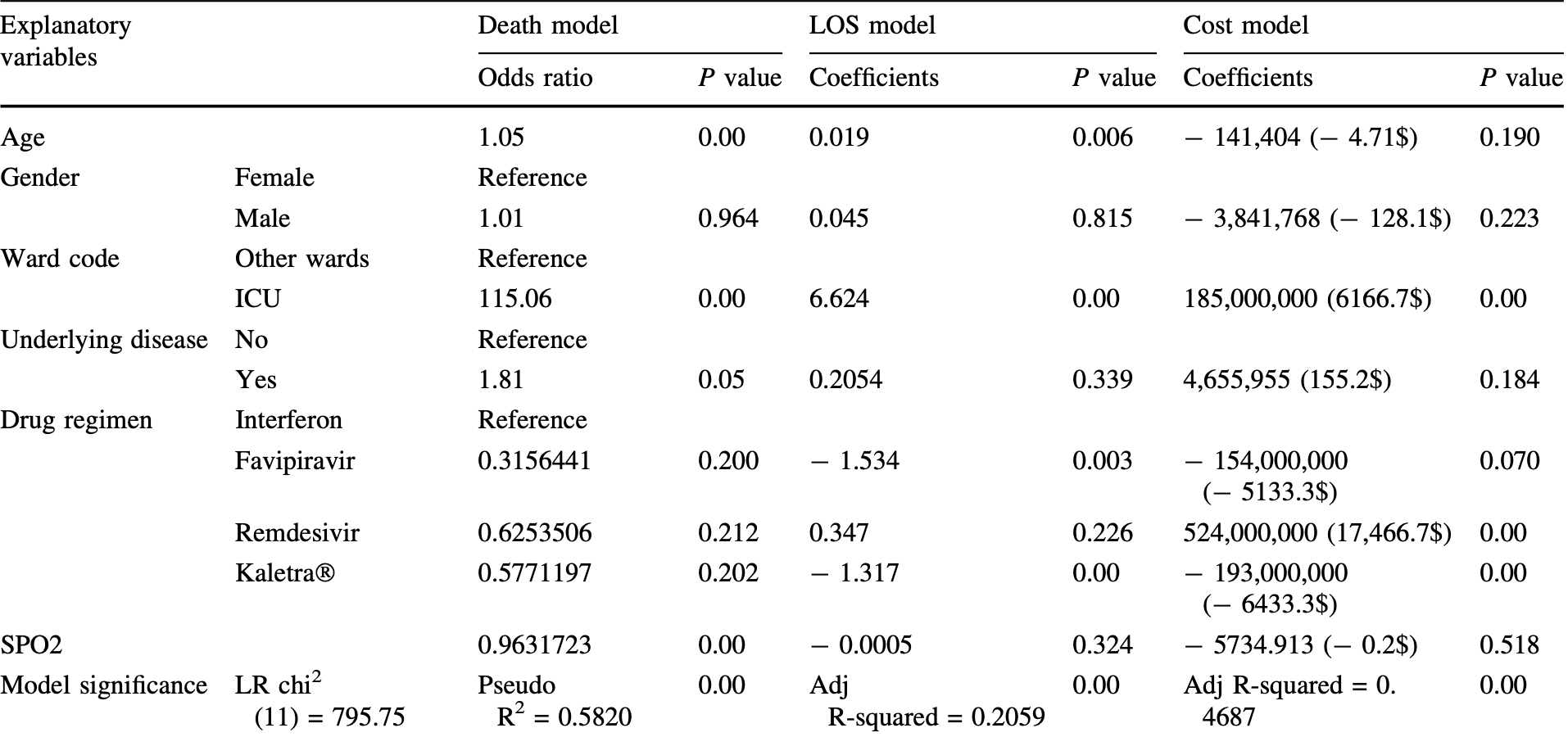
Retrospective 2,174 hospitalized patients showing significantly shorter length of stay with favipiravir treatment.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
Study covers remdesivir and favipiravir.
|
risk of death, 68.5% lower, OR 0.32, p = 0.20, treatment 95, control 2,079, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Behboodikhah et al., 15 Sep 2022, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Evaluation of the Costs and Outcomes of COVID-19 Therapeutic Regimens in Hospitalized Patients in Shiraz
doi:10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0(
patients in critical conditions are hospitalized and treated with various protocols including antiviral drugs, which have been updated repeatedly. This study was aimed to analyze the demographics, costs, and outcomes of drug regimens in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in ''Ali Asghar'' hospital, affiliated with Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, from March 2019 to December 2020 as a retrospective study, approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (IR.SUMS.REC.1399.1003) on Dec. 28, 2020. Using hospital information system (HIS) data, 2174 patients receiving favipiravir, remdesivir, interferon-b, and Kaletra Ò were analyzed. Descriptive, univariate, and regression analyses were used. The costs and consequences of different drug regimens were significantly different (P value \ 0.05); the highest and lowest costs belonged to remdesivir and Kaletra Ò , respectively. The highest and lowest mean length of stay and mortality were related to remdesivir and favipiravir, respectively. Mortality did not differ significantly with various regimens. Length of stay was significantly shorter with favipiravir and Kaletra Ò than interferon-b. Remdesivir had significantly the highest cost. Age presented a significantly positive relationship with mortality and length of stay. Besides, ICU admission significantly increased mortality, length of stay, and costs. Underlying diseases and low blood oxygen saturation contributed to mortality. COVID-19 correlation with age and underlying diseases is accordant with the published data. Given the highest costs and broad usage of remdesivir, besides controversies regarding its outcomes and side effects, a stricter evaluation of remdesivir benefits seems essential. Totally, COVID-19 therapeutic protocols should be selected carefully to optimize costs and outcomes.
Author Contributions KHK and MN: contributed to the study conception and design. HB, KHK, and MN: were involved in data colstatistical analysis, interpretation, manuscript drafting, and final review of the manuscript. MM, ESH, and IK: helped with the research idea, providing the data, and supervision of the research. JSH: helped in data collecting and data cleaning. MB: helped in statistical analysis and interpretation. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Authors and Affiliations
References
Bagheri, Moezzi, Mosaddeghi, Interferoninducer antivirals: potential candidates to combat COVID-19, Int Immunopharmacol
Barbarawi, Jabri, Kumar, Fashanu, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Contemp Clin Trials
Bartsch, Ferguson, Mckinnell, Shea, Wedlock, The potential health care costs and resource use associated with COVID-19 in the United States, Health Aff
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, New Eng J Med
Cai, Yang, Liu, Chen, Shu, Experimental treatment with favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study, Engineering
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang, A trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, New Eng J Med
Chen, Dai, Mo, Li, Ma, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of older patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, Retrosp Study J Gerontol: Series A
Dawoud, Soliman, Cost-effectiveness of antiviral treatments for pandemics and outbreaks of respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19: a systematic review of published economic evaluations, Value Health
Doggrell, Remdesivir, a remedy or a ripple in severe COVID-19?, Expert Opin Investig Drugs
Dro_, Rosik, Lechowicz, Machaj, Szostak et al., An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment, Drug Resist Updat
Elshabrawy, SARS-CoV-2: an update on potential antivirals in light of SARS-CoV antiviral drug discoveries, Vaccines
Ghaffaridarab, Keshavarz, Sadeghi, Shahmohamadi, Kavosi, The economic burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from Iran, BMC Health Serv Res
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Diaz, Asperges, Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19, N Eng J Med
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Liang, Chen, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Res J
Hashemian, Pourhanifeh, Hamblin, Shahrzad, Mirzaei, Rd inhibitors and COVID-19: Is molnupiravir a good option?, Biomed Pharmacother
Jo, Jamieson, Edoka, Long, Silal, Costeffectiveness of remdesivir and dexamethasone for COVID-19 treatment in South Africa, Open Forum Inf Diss, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab040
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19, J Pharm Anal
Lotfi, Rezaei, SARS-CoV-2: a comprehensive review from pathogenicity of the virus to clinical consequences, J Med Virol
Mahase, Covid-19: Pfizer's paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports, BMJ
Martines, Ritter, Matkovic, Gary, Bollweg, Pathology and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 associated with fatal coronavirus disease, United States, Emerg Infect Dis
Molina, Seow, Heng, Chong, Ho, Outcomes of direct and indirect medical intensive care unit admissions from the emergency department of an acute care hospital: a retrospective cohort study, BMJ Open
Monk, Marsden, Tear, Brookes, Batten, Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial, Lancet Resp Med
Mosaddeghi, Shahabinezhad, Dehghani, Farahmandnejad, Taghipour et al., Therapeutic approaches for COVID-19 based on the interferon-mediated immune responses, Curr Signal Transduct Ther
Nasir, Perveen, Murshed, Nazneen, Talha, Survival and biomarkers of COVID-19 patients treated with remdesivir and favipiravir in ICU during the peak of pandemic: a single center study in Bangladesh, JPRI
Negahdaripour, Post-COVID-19 hyperglycemia: a concern in selection of therapeutic regimens, Iran J Med Sci
Negahdaripour, The rise and fall in therapeutic candidates for COVID-19, Iran J Med Sci
Owji, Negahdaripour, Hajighahramani, Immunotherapeutic approaches to curtail COVID-19, Int Immunopharmacol
Parashkouhi, Mosaddeghi, Bagheri, Moezzi, Hoseini, The dual sides of interferon induction in COVID-19 treatment, Trend Pharm Sci
Park, Iwasaki, Type I and Type III interferons-induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe
Perlman, Another decade, another coronavirus, N Eng J Med
Sanchez-Felipe, Vercruysse, Sharma, Ma, Lemmens, A single-dose live-attenuated YF17D-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate, Nature
Sepandi, Taghdir, Alimohamadi, Afrashteh, Hosamirudsari, Factors associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Iran J Public Health
Shen, Yang, Zhao, Jiang, Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children: experts' consensus statement, W J Pediatr
Singh, COVID-19 and its impact on society, Electron Res J Soc Sci
Singh, Chugh, Khera, Chugh, Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Open
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Arribaslo ´pez Jr, Cattelan, Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Srinivas, Sacha, Koval, Antivirals for COVID-19, Cleve Clin J Med, doi:10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc030
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol
Walmsley, Bernstein, King, Arribas, Beall, Lopinavir-ritonavir versus nelfinavir for the initial treatment of HIV infection, N Eng J Med
Wise, Covid-19: remdesivir is recommended for authorisation by European Medicines Agency
Yamamura, Matsuura, Nakagawa, Fukuoka, Domi, Effect of favipiravir and an anti-inflammatory strategy for COVID-19, Crit Care
Zhang, Lu, Wang, Jia, Li, Do underlying cardiovascular diseases have any impact on hospitalised patients with COVID-19?, Heart
Zhou, Chen, Shannon, Wei, Xiang, Interferon-a2b treatment for COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01061
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0",
"ISSN": [
"1028-6276",
"2364-1819"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0",
"alternative-id": [
"1351"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "18 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "20 August 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "15 September 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of Interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Behboodikhah",
"given": "Hooman",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shorafa",
"given": "Eslam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karimzadeh",
"given": "Iman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moghadami",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahmohammadi",
"given": "Javad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bayati",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keshavarz",
"given": "Khosro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4265-1499",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Negahdaripour",
"given": "Manica",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions A: Science",
"container-title-short": "Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-15T14:27:56Z",
"timestamp": 1663252076000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-15T17:42:53Z",
"timestamp": 1663263773000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013041",
"award": [
"22409"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Vice-Chancellor for Research, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-16T06:14:06Z",
"timestamp": 1663308846727
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1663200000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1663200000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cct.2021.106272",
"author": "ABA Al-Abdouh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106272",
"journal-title": "Contemp Clin Trials",
"key": "1351_CR1",
"unstructured": "Al-Abdouh ABA, Barbarawi M, Jabri A, Kumar A, Fashanu OE et al (2021) Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Contemp Clin Trials 101:106272",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107245",
"author": "A Bagheri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107245",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "1351_CR2",
"unstructured": "Bagheri A, Moezzi SMI, Mosaddeghi P et al (2021) Interferon-inducer antivirals: potential candidates to combat COVID-19. Int Immunopharmacol 91:107245",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00426",
"author": "SM Bartsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "927",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Health Aff",
"key": "1351_CR3",
"unstructured": "Bartsch SM, Ferguson MC, McKinnell JA, O’Shea KJ, Wedlock PT (2020) The potential health care costs and resource use associated with COVID-19 in the United States. Health Aff 39(6):927–935",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "New Eng J Med",
"key": "1351_CR4",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC et al (2020) Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report. New Eng J Med 383(19):1813–1826",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.007",
"author": "Q Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1192",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Engineering",
"key": "1351_CR5",
"unstructured": "Cai Q, Yang M, Liu D, Chen J, Shu D et al (2020) Experimental treatment with favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study. Engineering 6(10):1192–1198",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"author": "B Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "New Eng J Med",
"key": "1351_CR6",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J et al (2020) A trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. New Eng J Med 382(19):1787–1799",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glaa089",
"author": "T Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1788",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Retrosp Study J Gerontol: Series A",
"key": "1351_CR7",
"unstructured": "Chen T, Dai Z, Mo P, Li X, Ma Z et al (2020) Clinical characteristics and outcomes of older patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: a single-centered. Retrosp Study J Gerontol: Series A 75(9):1788–1795",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2020.07.002",
"author": "DM Dawoud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1409",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Value Health",
"key": "1351_CR8",
"unstructured": "Dawoud DM, Soliman KY (2020) Cost-effectiveness of antiviral treatments for pandemics and outbreaks of respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19: a systematic review of published economic evaluations. Value Health 23(11):1409–1422",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13543784.2020.1821645",
"author": "SA Doggrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Investig Drugs",
"key": "1351_CR9",
"unstructured": "Doggrell SA (2020) Remdesivir, a remedy or a ripple in severe COVID-19? Expert Opin Investig Drugs 29:1195–1198",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drup.2021.100794",
"author": "S Drożdżal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100794",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist Updat",
"key": "1351_CR10",
"unstructured": "Drożdżal S, Rosik J, Lechowicz K, Machaj F, Szostak B, Przybyciński J et al (2021) An update on drugs with therapeutic potential for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment. Drug Resist Updat 59:100794",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines8020335",
"author": "HA Elshabrawy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "335",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "1351_CR11",
"unstructured": "Elshabrawy HA (2020) SARS-CoV-2: an update on potential antivirals in light of SARS-CoV antiviral drug discoveries. Vaccines 8:335",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12913-021-06126-8",
"author": "M GhaffariDarab",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "132",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Health Serv Res",
"key": "1351_CR12",
"unstructured": "GhaffariDarab M, Keshavarz K, Sadeghi E, Shahmohamadi J, Kavosi Z (2021) The economic burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from Iran. BMC Health Serv Res 21(1):132",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007016",
"author": "J Grein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2327",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "N Eng J Med",
"key": "1351_CR13",
"unstructured": "Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G, Asperges E et al (2020) Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19. N Eng J Med 382(24):2327–2336",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547-2020",
"author": "WJ Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2000547",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur Res J",
"key": "1351_CR14",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Liang WH, Zhao Y, Liang HR, Chen ZS et al (2020) Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Res J 55(5):2000547",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112517",
"author": "SMR Hashemian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "1351_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hashemian SMR, Pourhanifeh MH, Hamblin MR, Shahrzad MK, Mirzaei H (2022) Rd inhibitors and COVID-19: Is molnupiravir a good option? Biomed Pharmacother 146:112517",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab040",
"author": "Y Jo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Inf Diss",
"key": "1351_CR16",
"unstructured": "Jo Y, Jamieson L, Edoka I, Long L, Silal S et al (2021) Cost-effectiveness of remdesivir and dexamethasone for COVID-19 treatment in South Africa. Open Forum Inf Diss. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab040",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"author": "X Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Anal",
"key": "1351_CR17",
"unstructured": "Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S (2020) Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J Pharm Anal 10(2):102–108",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26123",
"author": "M Lotfi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1864",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1351_CR18",
"unstructured": "Lotfi M, Rezaei N (2020) SARS-CoV-2: a comprehensive review from pathogenicity of the virus to clinical consequences. J Med Virol 92:1864–1874",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n2713",
"author": "E Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "n2713",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1351_CR19",
"unstructured": "Mahase E (2021) Covid-19: Pfizer’s paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports. BMJ 375:n2713",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2609.202095",
"author": "RB Martines",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2005",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "1351_CR20",
"unstructured": "Martines RB, Ritter JM, Matkovic E, Gary J, Bollweg BC et al (2020) Pathology and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 associated with fatal coronavirus disease, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 26:2005–2015",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005553",
"author": "JAD Molina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e005553",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "1351_CR21",
"unstructured": "Molina JAD, Seow E, Heng BH, Chong WF, Ho B (2014) Outcomes of direct and indirect medical intensive care unit admissions from the emergency department of an acute care hospital: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 4:e005553",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30511-7",
"author": "PD Monk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "196",
"journal-title": "Lancet Resp Med",
"key": "1351_CR22",
"unstructured": "Monk PD, Marsden RJ, Tear VJ, Brookes J, Batten TN et al (2021) Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Resp Med 9:196–206",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1574362416666210120104636",
"author": "P Mosaddeghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Signal Transduct Ther",
"key": "1351_CR23",
"unstructured": "Mosaddeghi P, Shahabinezhad F, Dehghani Z, Farahmandnejad M, Taghipour MJ, Moghadami M, Nezafat N, Masoompour SM, Negahdaripour M (2021) Therapeutic approaches for COVID-19 based on the interferon-mediated immune responses. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 16:1",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.9734/jpri/2020/v32i4531088",
"author": "M Nasir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"issue": "45",
"journal-title": "JPRI",
"key": "1351_CR25",
"unstructured": "Nasir M, Perveen RA, Murshed M, Nazneen R, Talha KA (2021) Survival and biomarkers of COVID-19 patients treated with remdesivir and favipiravir in ICU during the peak of pandemic: a single center study in Bangladesh. JPRI 32(45):14–22",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "M Negahdaripour",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "Iran J Med Sci",
"key": "1351_CR26",
"unstructured": "Negahdaripour M (2020) The rise and fall in therapeutic candidates for COVID-19. Iran J Med Sci 45:231–232",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "M Negahdaripour",
"first-page": "235",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Iran J Med Sci",
"key": "1351_CR27",
"unstructured": "Negahdaripour M (2021) Post-COVID-19 hyperglycemia: a concern in selection of therapeutic regimens. Iran J Med Sci 46(4):235–236",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106924",
"author": "H Owji",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106924",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "1351_CR28",
"unstructured": "Owji H, Negahdaripour M, Hajighahramani N (2020) Immunotherapeutic approaches to curtail COVID-19. Int Immunopharmacol 88:106924",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "SN Parashkouhi",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trend Pharm Sci",
"key": "1351_CR24",
"unstructured": "Parashkouhi SN, Mosaddeghi P, Bagheri A, Moezzi SMI, Hoseini SMF et al (2021) The dual sides of interferon induction in COVID-19 treatment. Trend Pharm Sci 7(1):9–14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008",
"author": "A Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "1351_CR29",
"unstructured": "Park A, Iwasaki A (2020) Type I and Type III interferons–induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 27:870–878",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2001126",
"author": "S Perlman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "760",
"journal-title": "N Eng J Med",
"key": "1351_CR30",
"unstructured": "Perlman S (2020) Another decade, another coronavirus. N Eng J Med 382:760–762",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-3035-9",
"author": "L Sanchez-Felipe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1351_CR31",
"unstructured": "Sanchez-Felipe L, Vercruysse T, Sharma S, Ma J, Lemmens V et al (2020) A single-dose live-attenuated YF17D-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate. Nature 590:320–325",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "M Sepandi",
"first-page": "1211",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Iran J Public Health",
"key": "1351_CR32",
"unstructured": "Sepandi M, Taghdir M, Alimohamadi Y, Afrashteh S, Hosamirudsari H (2020) Factors associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Public Health 49(7):1211–1221",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12519-020-00343-7",
"author": "K Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "223",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "W J Pediatr",
"key": "1351_CR33",
"unstructured": "Shen K, Yang Y, Wang T, Zhao D, Jiang Y et al (2020) Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children: experts’ consensus statement. W J Pediatr 16(3):223–231",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1351_CR34",
"unstructured": "Singh J (2020) COVID-19 and its impact on society. Electron Res J Soc Sci. 2(I) Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3567837"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048416",
"author": "SKD Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e048416",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "1351_CR35",
"unstructured": "Singh SKD, Chugh A, Khera PS, Chugh VK (2021) Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 11:e048416",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"author": "CD Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1048",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1351_CR36",
"unstructured": "Spinner CD, Gottlieb RL, Criner GJ, ArribasLópez JR, Cattelan AM et al (2020) Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(11):1048–1057",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc030",
"author": "P Srinivas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cleve Clin J Med",
"key": "1351_CR37",
"unstructured": "Srinivas P, Sacha GL, Koval C (2020) Antivirals for COVID-19. Cleve Clin J Med. https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc030",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"author": "P V'Kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "1351_CR38",
"unstructured": "V’Kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H, Thiel V (2021) Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol 19(3):155–170",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa012354",
"author": "S Walmsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2039",
"journal-title": "N Eng J Med",
"key": "1351_CR39",
"unstructured": "Walmsley S, Bernstein B, King M, Arribas J, Beall G et al (2002) Lopinavir-ritonavir versus nelfinavir for the initial treatment of HIV infection. N Eng J Med 346:2039–2046",
"volume": "346",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m2610",
"author": "J Wise",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m2610",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1351_CR40",
"unstructured": "Wise J (2020) Covid-19: remdesivir is recommended for authorisation by European Medicines Agency. BMJ 369:m2610",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1351_CR41",
"unstructured": "World Bank (2020) PPP conversion factor, GDP (LCU per international $) - Iran, Islamic Rep. Available at https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/PA.NUS.PPP?locations=IR, Accessed at 22 May 2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03137-5",
"author": "H Yamamura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "1351_CR42",
"unstructured": "Yamamura H, Matsuura H, Nakagawa J, Fukuoka H, Domi H et al (2020) Effect of favipiravir and an anti-inflammatory strategy for COVID-19. Crit Care 24(1):413",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/heartjnl-2020-316909",
"author": "J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1148",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Heart",
"key": "1351_CR44",
"unstructured": "Zhang J, Lu S, Wang X, Jia X, Li J et al (2020) Do underlying cardiovascular diseases have any impact on hospitalised patients with COVID-19? Heart 106(15):1148",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01061",
"author": "Q Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1351_CR45",
"unstructured": "Zhou Q, Chen V, Shannon CP, Wei XS, Xiang X et al (2020) Interferon-α2b treatment for COVID-19. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01061",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40995-022-01351-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Physics and Astronomy",
"General Mathematics",
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Agricultural and Biological Sciences",
"General Chemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of the Costs and Outcomes of COVID-19 Therapeutic Regimens in Hospitalized Patients in Shiraz",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}