DNA damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes of severely ill COVID-19 patients in relation to inflammatory markers and parameters of hemostasis
et al., Mutagenesis, doi:10.1093/mutage/geac011, May 2022
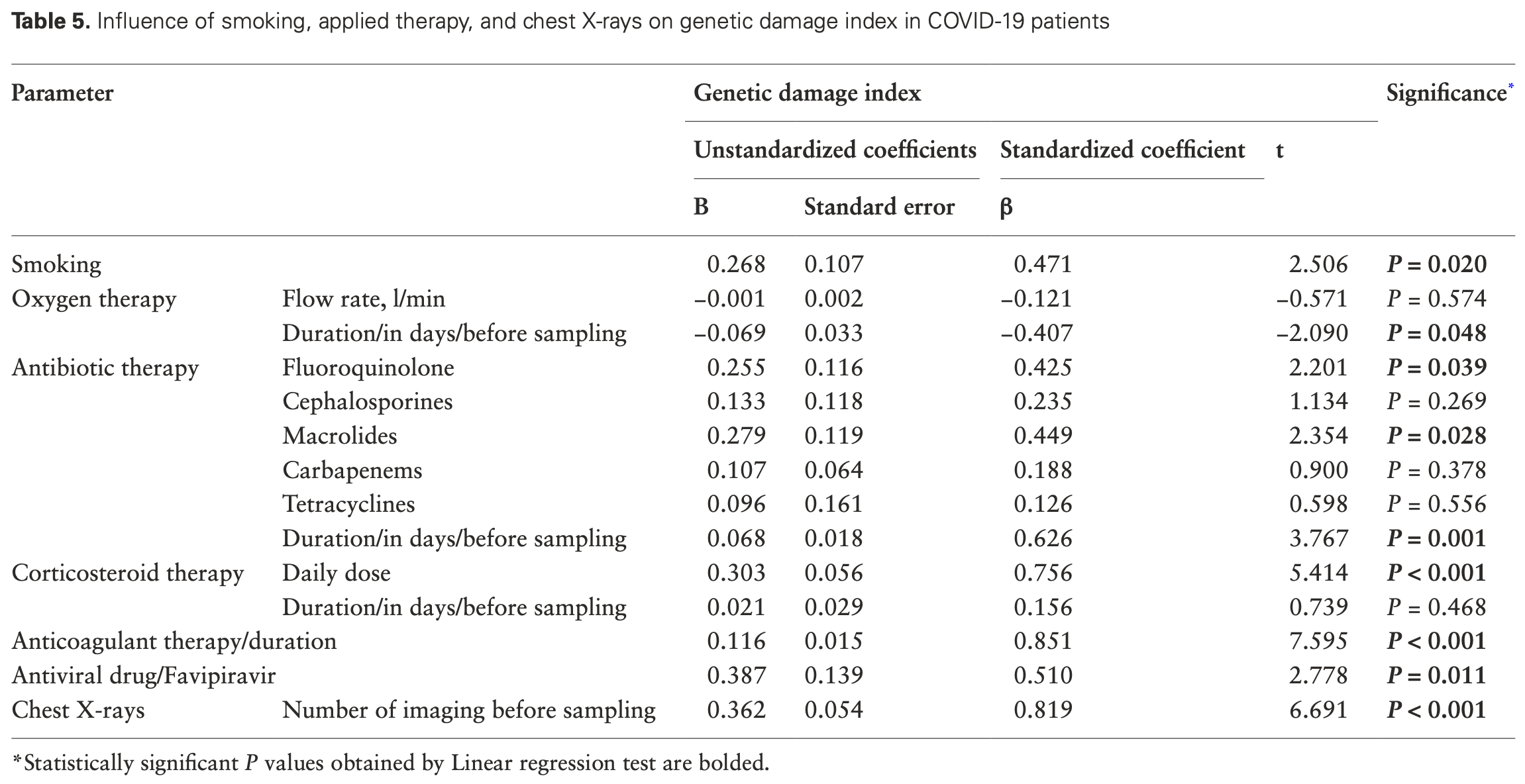
Observational study of 24 severely ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significantly higher DNA damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes compared to 15 healthy controls. Favipiravir was associated with increased DNA damage.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Mihaljevic et al., 1 May 2022, Serbia, peer-reviewed, mean age 55.8, 8 authors.
Contact: vrndic07@yahoo.com.
DNA damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes of severely ill COVID-19 patients in relation to inflammatory markers and parameters of hemostasis
Mutagenesis, doi:10.1093/mutage/geac011
Bearing in the mind that a variety of agents can contribute to genome instability, including viral infections, the aim of this study was to analyze DNA damage in hospitalized COVID-19 patients and its relationship with certain laboratory parameters. The potential impact of applied therapy and chest X-rays on DNA damage was also estimated. The study population included 24 severely COVID-19 patients and 15 healthy control subjects. The level of DNA damage was measured as genetic damage index (GDI) by comet assay. The standard laboratory methods and certified enzymatic reagents for the appropriate autoanalyzers were performed for the determination of the biochemical and hematological parameters. COVID-19 patients had significantly higher level of DNA damage compared with control subjects. The absolute number of neutrophil leukocytes was statistically higher, while the absolute number of lymphocytes was statistically lower in COVID-19 patients than in healthy controls. The analysis of the relationship between DNA damage and laboratory parameters indicated that GDI was positively correlated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) concentration and negatively with platelet count in COVID-19 patients. The level of DNA damage was slightly higher in female patients, in whom it was demonstrated a positive correlation of GDI with C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin. Likewise, there was a negative relationship of GDI and platelet count, and positive relationship of GDI and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) in female population. The applied therapy (antibiotics, corticosteroid, anticoagulant, and antiviral therapy) as well as chest X rays has been shown to have genotoxic potential. The level of DNA damage significantly corresponds to the inflammatory markers and parameters of hemostasis in COVID-19 patients. In conclusion, inflammation, smoking habit, applied therapy, and chest X rays contribute to a higher level of DNA damage in COVID-19 patients.
209 LDH, AST, ALT, CK, pro-BNP, urea, and creatinine. This is in line with the results of previous studies that dealt with the diagnostic and prognostic value of laboratory findings in COVID-19 patients [8, 47, 48] . The aggrevated inflammatory response in SARS-CoV-2 infection causes multiorgan dysfunction that is reflected through a remarkable increase in different laboratory parameters. However, the mentioned parameters did not show a significant relationship with DNA damage, nor the hemostasis parameters. Namely, we found that lower values of platelet count, as well as the higher values of aPTT correspond to a more pronounced DNA damage in females. It is assumed that hemostasis abnormalities in
Conflict of Interest Statement None declared.
References
Adil, Baig, Amir, Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio vs platelets to lymphocyte ratio: biomarkers to predict severity of disease and their comparasion in patients of COVID-19, Pak Armed Forces Med J
Aguilera, Gómez-González, Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences, Nat Rev Genet
Ahmed, Alkhatip, Kamel, The diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophilto-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Expert Rev Mol Diagn
Ashok, Rita, Jaskaran, Wuhan to world: the COVID-19 pandemic, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Cecchini, Cecchini, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression, Med Hypotheses
Chapple, Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in inflammatory diseases, J Clin Periodontol
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Ciaccio, Agnello, Biochemical biomarkers alterations in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Diagnosis
Collins, Dušinská, Oxidation of cellular DNA measured with the comet assay, Methods Mol Biol
Fa, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyteto-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, Med Virol
Garcia-Olivé, Sintes, Radua, D-dimer in patients infected with COVID-19 and suspected pulmonary embolism, Respir Med
Guan, Liang, Zhao, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for COVID-19. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with Covid-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir, doi:10.1183/13993003.00547-2020
Hayes, Doherty, Coulson, Micronucleus induction in the bone marrow of rats by pharmacological mechanisms. I: glucocorticoid receptor agonism, Mutagenesis
He, Chen, Jin, Comparative evaluation of the in vitro micronucleus test and the comet assay for the detection of genotoxic effects of X-ray radiation, Mutat Res
Hr, Grand, Activation of the DNA damage response by RNA viruses, Biomolecules
Huang, Fs, Liu, Coronavirus infection induces DNA replication stress partly through interaction of its nonstructural protein 13 with the p125 subunit of DNA polymerase delta, J Biol Chem
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Husseina, Rahala, The role of viral infections in the development of autoimmune diseases, Crit Rev Microbiol
Iba, Levy, Inflammation and thrombosis: roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis, J Thromb Haemost
Jackson, Bartek, The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease, Nature
Jiang, Mei, SARS-CoV-2 spike impairs DNA damage repair and inhibits V(D)J recombination in vitro, Viruses
Katsuyama, NOX/NADPH oxidase, the superoxide generating enzyme: its transcriptional regulation and physiological roles, J Pharmacol Sci
Kuchařová, Hronek, Rybáková, Comet assay and its use for evaluating oxidative dna damage in some pathological states, Physiol Res
Laforge, Elbim, Frère, Tissue damage from neutrophilinduced oxidative stress in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Li, Ma, Yokota, Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic changes of vital organs in SARS-CoV-2 induced systemic toxicity, JCI Insight
Liu, Du, Chen, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent risk factor for mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Infect
Lorente, Martín, González-Rivero, DNA and RNA oxidative damage and mortality of patients with COVID-19, Am J Med Sci
Luftig, Viruses and the DNA damage response: activation and antagonism, Annu Rev Virol
Malik, Patel, Mehta, Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Evid Based Med
Micco, Krizhanovsky, Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Miesbach, Makris, COVID-19: coagulopathy, risk of thrombosis, and the rationale for anticoagulation, Clin Appl Thromb Hemost
Mihaljevic, Zivancevic-Simonovic, Milosevic-Djordjevic, Apoptosis and genome instability in children with autoimmune diseases, Mutagenesis
Milkovic, Garaj-Vrhovac, Ranogajec-Komor, Primary DNA damage assessed with the comet assay and comparison to the absorbed dose of diagnostic X-rays in children, Int J Toxicol
Moorthy, Koshy, Kumar, Role of inflammatory and liver function markers in assessing the prognosis of patients with COVID-19, World Acad Sci J
Munster, Koopmans, Van Doremalen, A novel coronavirus emerging in China-key questions for impact assessment, N Engl J Med
Møller, Stopper, Collins, Measurement of DNA damage with the comet assay in high-prevalence diseases: current status and future directions, Mutagenesi
Nasi, Mcardle, Gaudernack, Reactive oxygen species as an initiator of toxic innate immune responses in retort to SARS-CoV-2 in an ageing population, consider N-acetylcysteine as early therapeutic intervention, Toxicol Rep
Pinto, Alpire, Ribeiro, Cytogenetic biomonitoring in buccal mucosa cells of COVID-19 patients: preliminary findings, Vivo
Pitarque, Vaglenov, Nosko, Evaluation of DNA damage by the comet assay in shoe workers exposed to toluene and other organic solvents, Mutat Res
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Rocco, Peluso, Stingo, Micronucleus test and comet assay for the evaluation of zebrafish genomic damage induced by erythromycin and lincomycin, Environ Toxicol
Ré, Evaluation of the genotoxic activity of metronidazole and dimetridazole in human lymphocytes by the comet assay, Mutat Res
Schwarz, Oxidative stress during viral infection: a review, Free Radical Biol Med
Singh, Mccoy, Tice, A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells, Exp Cell Res
Su, Hong, RNA viruses: ROS-mediated cell death, Int J Cell Biol
Terpos, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Elalamy, Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19, Am J Hematol
Ulanowska, Olas, Modulation of hemostasis in COVID-19; blood platelets may be important pieces in the COVID-19 puzzle, Pathogens
Valko, Leibfritz, Moncol, Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease, Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Vijg, Dong, Milholland, Genome instability: a conserved mechanism of ageing?, Essays Biochem
Wahby, Elwassif, Magdy, Association between DNA damage and serum levels of copper, zinc, and selenium in full-term neonates with late-onset sepsis, J Pediatr Infect Dis
Waters, Warren, Hughes, Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environ Mol Mutagen
Wingert, Arbo, Göethel, In vitro toxicity assessment of rivaroxaban degradation products and kinetic evaluation to decay process, Drug Chem Toxicol
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Wu, Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19, Nitric Oxide
Xu, Ghosal, Chen, DNA damage tolerance: a double-edged sword guarding the genome, Transl Cancer Res
Yang, Li, Tao, Infection with SARS-CoV-2 causes abnormal laboratory results of multiple organs in patients, Aging
Yao, Zheng, Wu, Immune environment modulation in pneumonia patients caused by coronavirus: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, Aging
Zhanataev, Moroz, Durnev, DNA damage and cell death assessment in patients with severe multiple trauma using comet assay, Health
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy
Zhang, Dong, Lee, Single-cell whole-genome sequencing reveals the functional landscape of somatic mutations in B lymphocytes across the human lifespan, Proc Natl Acad Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/mutage/geac011",
"ISSN": [
"0267-8357",
"1464-3804"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geac011",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Bearing in the mind that a variety of agents can contribute to genome instability, including viral infections, the aim of this study was to analyze DNA damage in hospitalized COVID-19 patients and its relationship with certain laboratory parameters. The potential impact of applied therapy and chest X-rays on DNA damage was also estimated. The study population included 24 severely COVID-19 patients and 15 healthy control subjects. The level of DNA damage was measured as genetic damage index (GDI) by comet assay. The standard laboratory methods and certified enzymatic reagents for the appropriate autoanalyzers were performed for the determination of the biochemical and hematological parameters. COVID-19 patients had significantly higher level of DNA damage compared with control subjects. The absolute number of neutrophil leukocytes was statistically higher, while the absolute number of lymphocytes was statistically lower in COVID-19 patients than in healthy controls. The analysis of the relationship between DNA damage and laboratory parameters indicated that GDI was positively correlated with interleukin 6 (IL-6) concentration and negatively with platelet count in COVID-19 patients. The level of DNA damage was slightly higher in female patients, in whom it was demonstrated a positive correlation of GDI with C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin. Likewise, there was a negative relationship of GDI and platelet count, and positive relationship of GDI and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) in female population. The applied therapy (antibiotics, corticosteroid, anticoagulant, and antiviral therapy) as well as chest X rays has been shown to have genotoxic potential. The level of DNA damage significantly corresponds to the inflammatory markers and parameters of hemostasis in COVID-19 patients. In conclusion, inflammation, smoking habit, applied therapy, and chest X rays contribute to a higher level of DNA damage in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5614-210X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathophysiology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mihaljevic",
"given": "Olgica",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathophysiology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Zivancevic-Simonovic",
"given": "Snezana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal medicine, University Clinical Center Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Cupurdija",
"given": "Vojislav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal medicine, University Clinical Center Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Marinkovic",
"given": "Milos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Tubic Vukajlovic",
"given": "Jovana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Markovic",
"given": "Aleksandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Stanojevic-Pirkovic",
"given": "Marijana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Genetics, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Kragujevac , Kragujevac , Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Milosevic-Djordjevic",
"given": "Olivera",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Mutagenesis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-14T11:10:24Z",
"timestamp": 1649934624000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-26T15:32:21Z",
"timestamp": 1666798341000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004564",
"award": [
"III41010",
"ON175069"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100004564",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-20T04:04:23Z",
"timestamp": 1752984263263,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 10,
"issue": "3-4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3-4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1651363200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mutage/article-pdf/37/3-4/203/46647702/geac011.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mutage/article-pdf/37/3-4/203/46647702/geac011.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "203-212",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
7
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrg2268",
"article-title": "Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences",
"author": "Aguilera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "204",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Genet",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0001",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature08467",
"article-title": "The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0002",
"volume": "461",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0891-5849(96)00131-1",
"article-title": "Oxidative stress during viral infection: a review",
"author": "Schwarz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "641",
"journal-title": "Free Radical Biol Med",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0003",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"article-title": "DNA damage tolerance: a double-edged sword guarding the genome",
"author": "Xu",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Transl Cancer Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0004",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "RNA viruses: ROS-mediated cell death",
"author": "Su",
"first-page": "467452",
"journal-title": "Int J Cell Biol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0005",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Wuhan to world: the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Ashok",
"first-page": "242",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0006",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.145027",
"article-title": "Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic changes of vital organs in SARS-CoV-2 induced systemic toxicity",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e145027",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0007",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103255",
"article-title": "Infection with SARS-CoV-2 causes abnormal laboratory results of multiple organs in patients",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10059",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0008",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/dx-2020-0057",
"article-title": "Biochemical biomarkers alterations in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Ciaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Diagnosis",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0009",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom6010002",
"article-title": "Activation of the DNA damage response by RNA viruses",
"author": "Ryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0010",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/EBC20160082",
"article-title": "Genome instability: a conserved mechanism of ageing?",
"author": "Vijg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "Essays Biochem",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0011",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-051X.1997.tb00760.x",
"article-title": "Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in inflammatory diseases",
"author": "Chapple",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "J Clin Periodontol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0012",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001",
"article-title": "Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease",
"author": "Valko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Int J Biochem Cell Biol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0013",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1254/jphs.10R01CR",
"article-title": "NOX/NADPH oxidase, the superoxide generating enzyme: its transcriptional regulation and physiological roles",
"author": "Katsuyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0014",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13102056",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike impairs DNA damage repair and inhibits V(D)J recombination in vitro",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2056",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0015",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.242206",
"article-title": "Coronavirus infection induces DNA replication stress partly through interaction of its nonstructural protein 13 with the p125 subunit of DNA polymerase delta",
"author": "Huang M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39546",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0016",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0017",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4236/health.2010.25062",
"article-title": "DNA damage and cell death assessment in patients with severe multiple trauma using comet assay",
"author": "Zhanataev",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "Health",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0018",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0",
"article-title": "A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Exp Cell Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0019",
"volume": "175",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"article-title": "Oxidation of cellular DNA measured with the comet assay",
"author": "Collins",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0020",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1383-5718(99)00042-X",
"article-title": "Evaluation of DNA damage by the comet assay in shoe workers exposed to toluene and other organic solvents",
"author": "Pitarque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Mutat Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0021",
"volume": "441",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0022",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0023",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with Covid-19 in China: a nationwide analysis",
"author": "Guan",
"first-page": "547",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0024",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0025",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2000929",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus emerging in China—key questions for impact assessment",
"author": "Munster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0026",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25829",
"article-title": "Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19",
"author": "Terpos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "834",
"journal-title": "Am J Hematol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0027",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103101",
"article-title": "Immune environment modulation in pneumonia patients caused by coronavirus: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7639",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0028",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0029",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.003",
"article-title": "Reactive oxygen species as an initiator of toxic innate immune responses in retort to SARS-CoV-2 in an ageing population, consider N-acetylcysteine as early therapeutic intervention",
"author": "Nasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Rep",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0030",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2020.06.002",
"article-title": "Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0031",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110102",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression",
"author": "Cecchini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110102",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0032",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0033",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-020-00314-w",
"article-title": "Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities",
"author": "Di Micco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0034",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1902510116",
"article-title": "Single-cell whole-genome sequencing reveals the functional landscape of somatic mutations in B lymphocytes across the human lifespan",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9014",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0035",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/mutage/gey037",
"article-title": "Apoptosis and genome instability in children with autoimmune diseases",
"author": "Mihaljevic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Mutagenesis",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0036",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-031413-085548",
"article-title": "Viruses and the DNA damage response: activation and antagonism",
"author": "Luftig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "605",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Virol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0037",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1040841X.2019.1614904",
"article-title": "The role of viral infections in the development of autoimmune diseases",
"author": "Husseina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "394",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Microbiol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0038",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2021.02.012",
"article-title": "DNA and RNA oxidative damage and mortality of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Lorente",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Am J Med Sci",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0039",
"volume": "361",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0040-1717126",
"article-title": "Association between DNA damage and serum levels of copper, zinc, and selenium in full-term neonates with late-onset sepsis",
"author": "Wahby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "299",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Infect Dis",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0040",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/invivo.12651",
"article-title": "Cytogenetic biomonitoring in buccal mucosa cells of COVID-19 patients: preliminary findings",
"author": "Pinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3495",
"journal-title": "In Vivo",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0041",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent risk factor for mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0042",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25819",
"article-title": "Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Lagunas-Rangel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1733",
"journal-title": "Med Virol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0043",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.51253/pafmj.v70i6.5010",
"article-title": "Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio vs platelets to lymphocyte ratio: biomarkers to predict severity of disease and their comparasion in patients of COVID-19",
"author": "Adil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1609",
"journal-title": "Pak Armed Forces Med J",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0044",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1",
"article-title": "Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19",
"author": "Laforge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0045",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14737159.2021.1915773",
"article-title": "The diagnostic and prognostic role of neutrophilto-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Abdelaal Ahmed Mahmoud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Mol Diagn",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0046",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111536",
"article-title": "Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Malik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "BMJ Evid Based Med",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0047",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/wasj.2021.123",
"article-title": "Role of inflammatory and liver function markers in assessing the prognosis of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Moorthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "World Acad Sci J",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0048",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10030370",
"article-title": "Modulation of hemostasis in COVID-19; blood platelets may be important pieces in the COVID-19 puzzle",
"author": "Ulanowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0049",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1076029620938149",
"article-title": "COVID-19: coagulopathy, risk of thrombosis, and the rationale for anticoagulation",
"author": "Miesbach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Appl Thromb Hemost",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0050",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.13911",
"article-title": "Inflammation and thrombosis: roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis",
"author": "Iba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0051",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106023",
"article-title": "D-dimer in patients infected with COVID-19 and suspected pulmonary embolism",
"author": "Garcia-Olivé",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106023",
"journal-title": "Respir Med",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0052",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33549/physiolres.933901",
"article-title": "Comet assay and its use for evaluating oxidative dna damage in some pathological states",
"author": "Kuchařová",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Physiol Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0053",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Measurement of DNA damage with the comet assay in high-prevalence diseases: current status and future directions",
"author": "Møller",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Mutagenesi",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0054",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/tox.20685",
"article-title": "Micronucleus test and comet assay for the evaluation of zebrafish genomic damage induced by erythromycin and lincomycin",
"author": "Rocco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "598",
"journal-title": "Environ Toxicol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0055",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00010-9",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the genotoxic activity of metronidazole and dimetridazole in human lymphocytes by the comet assay",
"author": "Ré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "Mutat Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0056",
"volume": "375",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/mutage/ges076",
"article-title": "Micronucleus induction in the bone marrow of rats by pharmacological mechanisms. I: glucocorticoid receptor agonism",
"author": "Hayes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Mutagenesis",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0057",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01480545.2018.1452931",
"article-title": "In vitro toxicity assessment of rivaroxaban degradation products and kinetic evaluation to decay process",
"author": "Wingert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Drug Chem Toxicol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0058",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/em.22471",
"article-title": "Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir",
"author": "Waters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Environ Mol Mutagen",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0059",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1091581809344775",
"article-title": "Primary DNA damage assessed with the comet assay and comparison to the absorbed dose of diagnostic X-rays in children",
"author": "Milkovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "Int J Toxicol",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0060",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1383-5718(00)00077-2",
"article-title": "Comparative evaluation of the in vitro micronucleus test and the comet assay for the detection of genotoxic effects of X-ray radiation",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Mutat Res",
"key": "2022102614310244600_CIT0061",
"volume": "469",
"year": "2000"
}
],
"reference-count": 61,
"references-count": 61,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/mutage/article/37/3-4/203/6582305"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "DNA damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes of severely ill COVID-19 patients in relation to inflammatory markers and parameters of hemostasis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "37"
}