Lactoferrin Binds through Its N-Terminus to the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
et al., Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17081021, Aug 2024
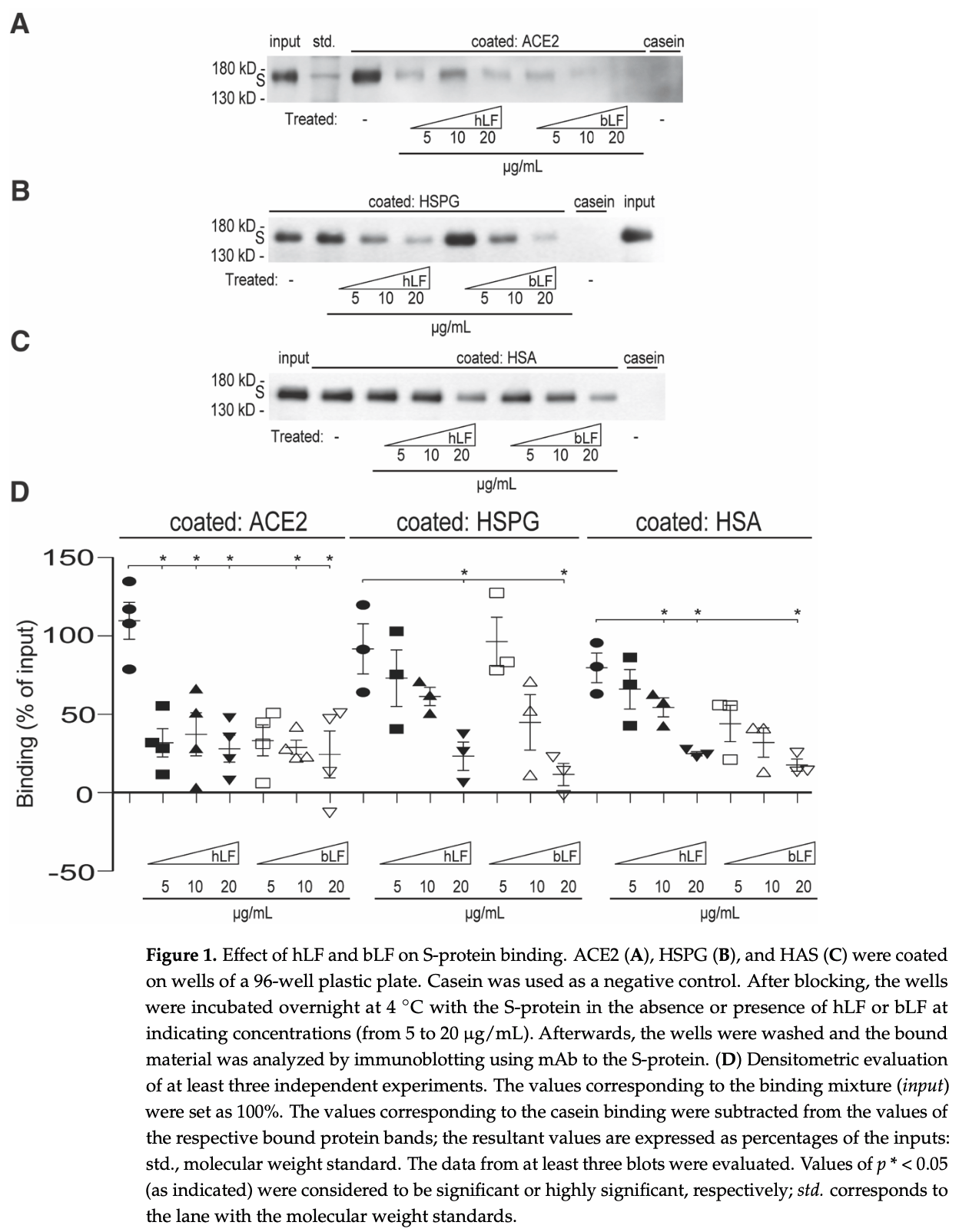
In vitro study showing that lactoferrin directly binds to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, potentially explaining lactoferrin's observed protective effects against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Authors found that both human and bovine lactoferrin inhibited spike protein binding to ACE2, heparan sulfate proteoglycans, and human serum albumin in a concentration-dependent manner. Mapping studies identified the N-terminal region of lactoferrin and the RBD of the spike protein as the binding sites involved in this interaction. Surface plasmon resonance confirmed lactoferrin binding to the spike protein and RBD with nanomolar affinity.
18 preclinical studies support the efficacy of lactoferrin for COVID-19:
1.
da Silva et al., Immunomodulatory effect of bovine lactoferrin during SARS-CoV-2 infection, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456634.
2.
Cutone et al., Lactoferrin binding to Sars-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein protects host from infection, inflammation and iron dysregulation., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1605740/v1.
3.
Miotto et al., Molecular Mechanisms Behind Anti SARS-CoV-2 Action of Lactoferrin, Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.607443.
4.
Babulic et al., Lactoferrin Binds through Its N-Terminus to the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17081021.
5.
Yathindranath et al., Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Host Cell Infection, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S448005.
6.
Alves et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vero Cells by Bovine Lactoferrin under Different Iron-Saturation States, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16101352.
7.
Kobayashi-Sakamoto et al., Bovine lactoferrin suppresses the cathepsin-dependent pathway of SARS-CoV-2 entry in vitro, International Dairy Journal, doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2023.105805.
8.
Andreu et al., Liposomal Lactoferrin Exerts Antiviral Activity against HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15040972.
9.
Yazawa et al., Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 isolation in cell culture from nasal/nasopharyngeal swabs or saliva specimens of patients with COVID-19, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2676422/v1.
10.
Piacentini et al., Lactoferrin Inhibition of the Complex Formation between ACE2 Receptor and SARS CoV-2 Recognition Binding Domain, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23105436.
11.
Ostrov et al., Highly Specific Sigma Receptor Ligands Exhibit Anti-Viral Properties in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Cells, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10111514.
12.
Mirabelli et al., Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2105815118.
13.
Salaris et al., Protective Effects of Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020328.
Babulic et al., 4 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: rostislav.skrabana@savba.sk (corresponding author), patrik.babulic@savba.sk, gabriela.ondrovicova@savba.sk, shunyascience@ukr.net, ondrej.cehlar@savba.sk, vladimir.leksa@savba.sk.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Lactoferrin Binds through Its N-Terminus to the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17081021
Since Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) still presents a considerable threat, it is beneficial to provide therapeutic supplements against it. In this respect, glycoprotein lactoferrin (LF) and lactoferricin (LFC), a natural bioactive peptide yielded upon digestion from the N-terminus of LF, are of utmost interest, since both have been shown to reduce infections of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for COVID-19, in particular via blockade of the virus priming and binding. Here, we, by means of biochemical and biophysical methods, reveal that LF directly binds to the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. We determined thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of the complex formation and mapped the mutual binding sites involved in this interaction, namely the N-terminal region of LF and the receptor-binding domain of the S-protein (RBD). These results may not only explain many of the observed protective effects of LF and LFC in SARS-CoV-2 infection but may also be instrumental in proposing potent and cost-effective supplemental tools in the management of COVID-19.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, V.L. and R.S.; methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, P.B., O.C., G.O., T.M., R.S., and V.L.; validation, R.S. and V.L.; writing-original draft preparation, V.L.; writing-review and editing, P.B., O.C., G.O., T.M., R.S., and V.L.; visualization, supervision, project administration, V.L.; resources; funding acquisition, V.L., R.S., T.M., and P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement: Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations Angiotensin converting enzyme-2, ACE2; antibody, Ab; Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19; heparan sulphate proteoglycans, HSPG; (human/bovine) lactoferricin, (h/b)LFC; (human/bovine) lactoferrin, (h/b)LF; human serum albumin (HSA); mAb, monoclonal antibody; receptor-binding domain (RBD); severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, SARS-CoV-2; sodium dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE; blue native PAGE, BN-PAGE; surface plasmon resonance, SPR; TEMED, N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine; transmembrane protease serine 2, TMPRSS2; synthetic peptides, pLF1, pLF3, pLF2 and pCTR.
References
Alves, Azevedo, Dias, Horbach, Setatino et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vero Cells by Bovine Lactoferrin under Different Iron-Saturation States, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph16101352
Andersen, Jenssen, Sandvik, Gutteberg, Anti-HSV Activity of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin Is Dependent on the Presence of Heparan Sulphate at the Cell Surface, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.20171
Andersen, Osbakk, Vorland, Traavik, Gutteberg, Lactoferrin and Cyclic Lactoferricin Inhibit the Entry of Human Cytomegalovirus into Human Fibroblasts, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/S0166-3542(01)00146-2
Arredondo-Beltran, Ramirez-Sanchez, Zazueta-Garcia, Canizalez-Roman, Angulo-Zamudio et al., Antitumor Activity of Bovine Lactoferrin and Its Derived Peptides against HepG2 Liver Cancer Cells and Jurkat Leukemia Cells, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-022-00484-4
Baker, Baker, A Structural Framework for Understanding the Multifunctional Character of Lactoferrin, Biochimie, doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2008.05.006
Campione, Lanna, Cosio, Rosa, Conte et al., Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2: In Vitro and In Silico Evidences, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.666600
Carthagena, Becquart, Hocini, Kazatchkine, Bouhlal et al., Modulation of HIV Binding to Epithelial Cells and HIV Transfer from Immature Dendritic Cells to CD4 T Lymphocytes by Human Lactoferrin and Its Major Exposed LF-33 Peptide, Open Virol. J, doi:10.2174/1874357901105010027
Chen, Fan, Lin, Chen, Hsu et al., Bovine Lactoferrin Inhibits Dengue Virus Infectivity by Interacting with Heparan Sulfate, Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor, and DC-SIGN, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18091957
Cutone, Rosa, Bonaccorsi Di Patti, Iacovelli, Conte et al., Lactoferrin Binding to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Blocks Pseudoviral Entry and Relieves Iron Protein Dysregulation in Several In Vitro Models, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14102111
Dessie, Malik, Role of Serine Proteases and Host Cell Receptors Involved in Proteolytic Activation, Entry of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Current Therapeutic Options, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S308176
El-Baky, Elkhawaga, Abdelkhalek, Sharaf, Redwan et al., De Novo Expression and Antibacterial Potential of Four Lactoferricin Peptides in Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System, Biotechnol. Rep, doi:10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00583
El-Fakharany, Nanoformulation of Lactoferrin Potentiates Its Activity and Enhances Novel Biotechnological Applications, Int. J. Biol. Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.235
Eliassen, Berge, Sveinbjornsson, Svendsen, Vorland et al., Evidence for a Direct Antitumor Mechanism of Action of Bovine Lactoferricin, Anticancer Res
Fuentes-Prior, Priming of SARS-CoV-2 S Protein by Several Membrane-Bound Serine Proteinases Could Explain Enhanced Viral Infectivity and Systemic COVID-19 Infection, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.REV120.015980
Giansanti, Panella, Leboffe, Antonini, Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph9040061
Gifford, Hunter, Vogel, Lactoferricin: A Lactoferrin-Derived Peptide with Antimicrobial, Antiviral, Antitumor and Immunological Properties, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5373-z
Gonzalez-Chavez, Arevalo-Gallegos, Rascon-Cruz, Lactoferrin: Structure, Function and Applications, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.07.020
Groot, Geijtenbeek, Sanders, Baldwin, Sanchez-Hernandez et al., Lactoferrin Prevents Dendritic Cell-Mediated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Transmission by Blocking the DC-SIGN-gp120 Interaction, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.5.3009-3015.2005
Han, Gao, Luan, Xie, Liu et al., Comparing Bacterial Membrane Interactions and Antimicrobial Activity of Porcine Lactoferricin-Derived Peptides, J. Dairy Sci, doi:10.3168/jds.2012-6104
Haque, Ashwaq, Sarief, Azad John Mohamed, A Comprehensive Review about SARS-CoV-2, Future Virol, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0124
He, Qin, Guan, Liu, Hong et al., Bovine Lactoferrin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 by Targeting the RdRp Complex and Alleviates Viral Infection in the Hamster Model, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28281
Hu, Meng, Zhang, Xiang, Wang, The In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Lactoferrin against Common Human Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 is Mediated by Targeting the Heparan Sulfate Co-Receptor, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2021.1888660
Hunter, Demcoe, Jenssen, Gutteberg, Vogel, Human Lactoferricin is Partially Folded in Aqueous Solution and Is Better Stabilized in a Membrane Mimetic Solvent, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.49.8.3387-3395.2005
Hwang, Kruzel, Actor, Immunomodulatory Effects of Recombinant Lactoferrin during MRSA Infection, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.029
Iles, Zmuidinaite, Sadee, Gardiner, Lacey et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding of Glycated Serum Albumin-Its Potential Role in the Pathogenesis of the COVID-19 Clinical Syndromes and Bias Towards Individuals with Pre-Diabetes/Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23084126
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Koch, Uckeley, Doldan, Stanifer, Boulant et al., TMPRSS2 Expression Dictates the Entry Route Used by SARS-CoV-2 to Infect Host Cells, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2021107821
Kovacech, Fialova, Filipcik, Skrabana, Zilkova et al., Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Two Immunodominant Epitopes on the Spike Protein Neutralize Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103818
Kowalczyk, Kaczynska, Kleczkowska, Bukowska-Osko, Kramkowski et al., The Lactoferrin Phenomenon-A Miracle Molecule, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27092941
Kruzel, Zimecki, Actor, Lactoferrin in a Context of Inflammation-Induced Pathology, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01438
Lai, Yu, Xian, Ye, Ju et al., Identified Human Breast Milk Compositions Effectively Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and Variants Infection and Replication, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104136
Lambert, Molecular Evolution of the Transferrin Family and Associated Receptors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.06.002
Lang, Yang, Deng, Liu, Yang et al., Inhibition of SARS Pseudovirus Cell Entry by Lactoferrin Binding to Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023710
Legrand, Mazurier, A Critical Review of the Roles of Host Lactoferrin in Immunity, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-010-9297-1
Leksa, Pfisterer, Ondrovicova, Binder, Lakatosova et al., Dissecting Mannose 6-Phosphate-Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 Receptor Complexes That Control Activation and Uptake of Plasminogen in Cells, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.339663
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Is a Functional Receptor for the SARS Coronavirus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature02145
Makhluf, Madany, Kim, Long COVID: Long-Term Impact of SARS-CoV2, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics14070711
Myszka, Improving Biosensor Analysis, J. Mol. Recognit, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199909/10)12:5%3C279::AID-JMR473%3E3.0.CO;2-3
Ohradanova-Repic, Prazenicova, Gebetsberger, Moskalets, Skrabana et al., Time to Kill and Time to Heal: The Multifaceted Role of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin in Host Defense, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15041056
Ohradanova-Repic, Skrabana, Gebetsberger, Tajti, Barath et al., Blockade of TMPRSS2-Mediated Priming of SARS-CoV-2 by Lactoferricin, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.958581
Patil, Chen, Fogliano, Madadlou, Hydrolysis Improves the Inhibition Efficacy of Bovine Lactoferrin against Infection by SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus, Int. Dairy J, doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2022.105488
Prieto-Fernandez, Egia-Mendikute, Vila-Vecilla, Bosch, Barreira-Manrique et al., Hypoxia Reduces Cell Attachment of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Modulating the Expression of ACE2, Neuropilin-1, Syndecan-1 and Cellular Heparan Sulfate, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2021.1932607
Rosa, Cutone, Conte, Campione, Bianchi et al., An Overview on In Vitro and In Vivo Antiviral Activity of Lactoferrin: Its Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-022-00427-z
Shestakov, Jenssen, Nordstrom, Eriksson, Lactoferricin but Not Lactoferrin Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Infection in Mice, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.01.003
Stax, Mouser, Van Montfort, Sanders, De Vries et al., Colorectal Mucus Binds DC-SIGN and Inhibits HIV-1 Trans-Infection of CD4+ T-Lymphocytes, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122020
Takayama, Aoki, Uchida, Tajima, Aoki-Yoshida, Role of CXC Chemokine Receptor Type 4 as a Lactoferrin Receptor, Biochem. Cell Biol, doi:10.1139/bcb-2016-0039
Van Berkel, Geerts, Van Veen, Mericskay, De Boer et al., N-Terminal Stretch Arg2, Arg3, Arg4 and Arg5 of Human Lactoferrin Is Essential for Binding to Heparin, Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, Human Lysozyme and DNA, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/bj3280145
Vogel, Lactoferrin, a Bird's Eye View, Biochem. Cell Biol, doi:10.1139/o2012-016
Vorland, Ulvatne, Andersen, Haukland, Rekdal et al., Lactoferricin of Bovine Origin Is More Active than Lactoferricins of Human, Murine and Caprine Origin, Scand. J. Infect. Dis
Wang, Liu, Groopman, The Alpha-Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 is Expressed on the Megakaryocytic Lineage from Progenitor to Platelets and Modulates Migration and Adhesion, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.V92.3.756
Yazidi-Belkoura, Legrand, Nuijens, Slomianny, Van Berkel et al., The Binding of Lactoferrin to Glycosaminoglycans on Enterocyte-Like HT29-18-C1 Cells is Mediated through Basic Residues Located in the N-Terminus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj, doi:10.1016/S0304-4165(01)00222-7
Zarzosa-Moreno, Avalos-Gomez, Ramirez-Texcalco, Torres-Lopez, Ramirez-Mondragon et al., Lactoferrin and Its Derived Peptides: An Alternative for Combating Virulence Mechanisms Developed by Pathogens, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25245763
Zekri-Nechar, Zamorano-Leon, Segura-Fragoso, Alcaide, Reche et al., Albumin Binds COVID-19 Spike 1 Subunit and Predicts in-Hospital Survival of Infected Patients-Possible Alteration by Glucose, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11030587
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
Zwirzitz, Reiter, Skrabana, Ohradanova-Repic, Majdic et al., Lactoferrin Is a Natural Inhibitor of Plasminogen Activation, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA118.003145
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph17081021",
"ISSN": [
"1424-8247"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ph17081021",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Since Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) still presents a considerable threat, it is beneficial to provide therapeutic supplements against it. In this respect, glycoprotein lactoferrin (LF) and lactoferricin (LFC), a natural bioactive peptide yielded upon digestion from the N-terminus of LF, are of utmost interest, since both have been shown to reduce infections of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for COVID-19, in particular via blockade of the virus priming and binding. Here, we, by means of biochemical and biophysical methods, reveal that LF directly binds to the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. We determined thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of the complex formation and mapped the mutual binding sites involved in this interaction, namely the N-terminal region of LF and the receptor-binding domain of the S-protein (RBD). These results may not only explain many of the observed protective effects of LF and LFC in SARS-CoV-2 infection but may also be instrumental in proposing potent and cost-effective supplemental tools in the management of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ph17081021"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0001-3798-6729",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 51 Bratislava, Slovakia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Genetics, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Comenius University, 842 15 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Babulic",
"given": "Patrik",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1996-6812",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Structural Biology of Neurodegeneration, Institute of Neuroimmunology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 10 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cehlar",
"given": "Ondrej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6281-2931",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 51 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ondrovičová",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 51 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"family": "Moskalets",
"given": "Tetiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8200-5275",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Structural Biology of Neurodegeneration, Institute of Neuroimmunology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 10 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Skrabana",
"given": "Rostislav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 845 51 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"family": "Leksa",
"given": "Vladimir",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"container-title-short": "Pharmaceuticals",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T11:37:30Z",
"timestamp": 1722857850000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-05T11:54:17Z",
"timestamp": 1722858857000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"APVV-16-0452",
"APVV-20-0513",
"APVV-21-0479"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Assistance Agency of the Slovak Republic"
},
{
"award": [
"2/0020/17",
"2/0152/21"
],
"name": "Slovak Grant Agency VEGA"
},
{
"award": [
"09I03-03-V01-00113",
"09I03-03-V02-00047"
],
"name": "Recovery plan for Europe"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T00:22:06Z",
"timestamp": 1722903726128
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722729600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/17/8/1021/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1021",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics14070711",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Makhluf, H., Madany, H., and Kim, K. (2024). Long COVID: Long-Term Impact of SARS-CoV2. Diagnostics, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics15041056",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Ohradanova-Repic, A., Prazenicova, R., Gebetsberger, L., Moskalets, T., Skrabana, R., Cehlar, O., Tajti, G., Stockinger, H., and Leksa, V. (2023). Time to Kill and Time to Heal: The Multifaceted Role of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin in Host Defense. Pharmaceutics, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Is a Functional Receptor for the SARS Coronavirus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.REV120.015980",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Fuentes-Prior, P. (2021). Priming of SARS-CoV-2 S Protein by Several Membrane-Bound Serine Proteinases Could Explain Enhanced Viral Infectivity and Systemic COVID-19 Infection. J. Biol. Chem., 296."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S308176",
"article-title": "Role of Serine Proteases and Host Cell Receptors Involved in Proteolytic Activation, Entry of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Current Therapeutic Options",
"author": "Dessie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1883",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021107821",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 Expression Dictates the Entry Route Used by SARS-CoV-2 to Infect Host Cells",
"author": "Koch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e107821",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0124",
"article-title": "A Comprehensive Review about SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Haque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "625",
"journal-title": "Future Virol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Nanoformulation of Lactoferrin Potentiates Its Activity and Enhances Novel Biotechnological Applications",
"first-page": "970",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Macromol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "165 Pt A",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biochi.2008.05.006",
"article-title": "A Structural Framework for Understanding the Multifunctional Character of Lactoferrin",
"author": "Baker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Biochimie",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.06.002",
"article-title": "Molecular Evolution of the Transferrin Family and Associated Receptors",
"author": "Lambert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "244",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "1820",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.01438",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Kruzel, M.L., Zimecki, M., and Actor, J.K. (2017). Lactoferrin in a Context of Inflammation-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-010-9297-1",
"article-title": "A Critical Review of the Roles of Host Lactoferrin in Immunity",
"author": "Legrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1139/o2012-016",
"article-title": "Lactoferrin, a Bird’s Eye View",
"author": "Vogel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27092941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Kowalczyk, P., Kaczynska, K., Kleczkowska, P., Bukowska-Osko, I., Kramkowski, K., and Sulejczak, D. (2022). The Lactoferrin Phenomenon—A Miracle Molecule. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25245763",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Zarzosa-Moreno, D., Avalos-Gomez, C., Ramirez-Texcalco, L.S., Torres-Lopez, E., Ramirez-Mondragon, R., Hernandez-Ramirez, J.O., Serrano-Luna, J., and de la Garza, M. (2020). Lactoferrin and Its Derived Peptides: An Alternative for Combating Virulence Mechanisms Developed by Pathogens. Molecules, 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.1932607",
"article-title": "Hypoxia Reduces Cell Attachment of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Modulating the Expression of ACE2, Neuropilin-1, Syndecan-1 and Cellular Heparan Sulfate",
"author": "Bosch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1065",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.1888660",
"article-title": "The In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Lactoferrin against Common Human Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 is Mediated by Targeting the Heparan Sulfate Co-Receptor",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.idairyj.2022.105488",
"article-title": "Hydrolysis Improves the Inhibition Efficacy of Bovine Lactoferrin against Infection by SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus",
"author": "Patil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105488",
"journal-title": "Int. Dairy J.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.958581",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Ohradanova-Repic, A., Skrabana, R., Gebetsberger, L., Tajti, G., Barath, P., Ondrovicova, G., Prazenicova, R., Jantova, N., Hrasnova, P., and Stockinger, H. (2022). Blockade of TMPRSS2-Mediated Priming of SARS-CoV-2 by Lactoferricin. Front. Immunol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2022.104136",
"article-title": "Identified Human Breast Milk Compositions Effectively Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and Variants Infection and Replication",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104136",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28281",
"article-title": "Bovine Lactoferrin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 by Targeting the RdRp Complex and Alleviates Viral Infection in the Hamster Model",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28281",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023710",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Lang, J., Yang, N., Deng, J., Liu, K., Yang, P., Zhang, G., and Jiang, C. (2011). Inhibition of SARS Pseudovirus Cell Entry by Lactoferrin Binding to Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. PLoS ONE, 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23084126",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Iles, J., Zmuidinaite, R., Sadee, C., Gardiner, A., Lacey, J., Harding, S., Ule, J., Roblett, D., Heeney, J., and Baxendale, H. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding of Glycated Serum Albumin-Its Potential Role in the Pathogenesis of the COVID-19 Clinical Syndromes and Bias Towards Individuals with Pre-Diabetes/Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11030587",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Zekri-Nechar, K., Zamorano-Leon, J.J., Segura-Fragoso, A., Alcaide, J.R., Reche, C., Andres-Castillo, A., Martinez-Martinez, C.H., Giner, M., Jimenez-Garcia, R., and Lopez-de-Andres, A. (2022). Albumin Binds COVID-19 Spike 1 Subunit and Predicts in-Hospital Survival of Infected Patients-Possible Alteration by Glucose. J. Clin. Med., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA118.003145",
"article-title": "Lactoferrin Is a Natural Inhibitor of Plasminogen Activation",
"author": "Zwirzitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8600",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "293",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.20171",
"article-title": "Anti-HSV Activity of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin Is Dependent on the Presence of Heparan Sulphate at the Cell Surface",
"author": "Andersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "262",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.01.003",
"article-title": "Lactoferricin but Not Lactoferrin Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Infection in Mice",
"author": "Shestakov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "340",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.5.3009-3015.2005",
"article-title": "Lactoferrin Prevents Dendritic Cell-Mediated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Transmission by Blocking the DC-SIGN—gp120 Interaction",
"author": "Groot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3009",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1139/bcb-2016-0039",
"article-title": "Role of CXC Chemokine Receptor Type 4 as a Lactoferrin Receptor",
"author": "Takayama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1874357901105010027",
"article-title": "Modulation of HIV Binding to Epithelial Cells and HIV Transfer from Immature Dendritic Cells to CD4 T Lymphocytes by Human Lactoferrin and Its Major Exposed LF-33 Peptide",
"author": "Carthagena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Open Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0122020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Stax, M.J., Mouser, E.E., van Montfort, T., Sanders, R.W., de Vries, H.J., Dekker, H.L., Herrera, C., Speijer, D., Pollakis, G., and Paxton, W.A. (2015). Colorectal Mucus Binds DC-SIGN and Inhibits HIV-1 Trans-Infection of CD4+ T-Lymphocytes. PLoS ONE, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.V92.3.756",
"article-title": "The Alpha-Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 is Expressed on the Megakaryocytic Lineage from Progenitor to Platelets and Modulates Migration and Adhesion",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "756",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "92",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18091957",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Chen, J.M., Fan, Y.C., Lin, J.W., Chen, Y.Y., Hsu, W.L., and Chiou, S.S. (2017). Bovine Lactoferrin Inhibits Dengue Virus Infectivity by Interacting with Heparan Sulfate, Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor, and DC-SIGN. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18."
},
{
"article-title": "Lactoferrin: Structure, Function and Applications",
"first-page": "301.e1",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3280145",
"article-title": "N-Terminal Stretch Arg2, Arg3, Arg4 and Arg5 of Human Lactoferrin Is Essential for Binding to Heparin, Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, Human Lysozyme and DNA",
"author": "Geerts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "328",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-022-00427-z",
"article-title": "An Overview on In Vitro and In Vivo Antiviral Activity of Lactoferrin: Its Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Rosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "417",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0304-4165(01)00222-7",
"article-title": "The Binding of Lactoferrin to Glycosaminoglycans on Enterocyte-Like HT29-18-C1 Cells is Mediated through Basic Residues Located in the N-Terminus",
"author": "Legrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "197",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "1568",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-005-5373-z",
"article-title": "Lactoferricin: A Lactoferrin-Derived Peptide with Antimicrobial, Antiviral, Antitumor and Immunological Properties",
"author": "Gifford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2588",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.49.8.3387-3395.2005",
"article-title": "Human Lactoferricin is Partially Folded in Aqueous Solution and Is Better Stabilized in a Membrane Mimetic Solvent",
"author": "Hunter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3387",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph9040061",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Giansanti, F., Panella, G., Leboffe, L., and Antonini, G. (2016). Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties. Pharmaceuticals, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00365549850161557",
"article-title": "Lactoferricin of Bovine Origin Is More Active than Lactoferricins of Human, Murine and Caprine Origin",
"author": "Vorland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "30",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-022-00484-4",
"article-title": "Antitumor Activity of Bovine Lactoferrin and Its Derived Peptides against HepG2 Liver Cancer Cells and Jurkat Leukemia Cells",
"author": "Bolscher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2012-6104",
"article-title": "Comparing Bacterial Membrane Interactions and Antimicrobial Activity of Porcine Lactoferricin-Derived Peptides",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3471",
"journal-title": "J. Dairy Sci.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Evidence for a Direct Antitumor Mechanism of Action of Bovine Lactoferricin",
"author": "Eliassen",
"first-page": "2703",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00583",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "El-Baky, N.A., Elkhawaga, M.A., Abdelkhalek, E.S., Sharaf, M.M., Redwan, E.M., and Kholef, H.R. (2021). De Novo Expression and Antibacterial Potential of Four Lactoferricin Peptides in Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System. Biotechnol. Rep., 29."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0166-3542(01)00146-2",
"article-title": "Lactoferrin and Cyclic Lactoferricin Inhibit the Entry of Human Cytomegalovirus into Human Fibroblasts",
"author": "Andersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.029",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory Effects of Recombinant Lactoferrin during MRSA Infection",
"author": "Hwang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph16101352",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Alves, N.S., Azevedo, A.S., Dias, B.M., Horbach, I.S., Setatino, B.P., Denani, C.B., Schwarcz, W.D., Lima, S.M.B., Missailidis, S., and Ano Bom, A.P.D. (2023). Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vero Cells by Bovine Lactoferrin under Different Iron-Saturation States. Pharmaceuticals, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1605740/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_51",
"unstructured": "Cutone, A., Rosa, L., Bonaccorsi di Patti, M.C., Iacovelli, F., Conte, M.P., Ianiro, G., Romeo, A., Campione, E., Bianchi, L., and Valenti, P. (2022). Lactoferrin Binding to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Blocks Pseudoviral Entry and Relieves Iron Protein Dysregulation in Several In Vitro Models. Pharmaceutics, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.666600",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Campione, E., Lanna, C., Cosio, T., Rosa, L., Conte, M.P., Iacovelli, F., Romeo, A., Falconi, M., Del Vecchio, C., and Franchin, E. (2021). Lactoferrin against SARS-CoV-2: In Vitro and In Silico Evidences. Front. Pharmacol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103818",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_53",
"unstructured": "Kovacech, B., Fialova, L., Filipcik, P., Skrabana, R., Zilkova, M., Paulenka-Ivanovova, N., Kovac, A., Palova, D., Rolkova, G.P., and Tomkova, K. (2022). Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Two Immunodominant Epitopes on the Spike Protein Neutralize Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. EBioMedicine, 76."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199909/10)12:5<279::AID-JMR473>3.0.CO;2-3",
"article-title": "Improving Biosensor Analysis",
"author": "Myszka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Recognit.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M112.339663",
"article-title": "Dissecting Mannose 6-Phosphate-Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 Receptor Complexes That Control Activation and Uptake of Plasminogen in Cells",
"author": "Leksa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22450",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2012"
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/17/8/1021"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Lactoferrin Binds through Its N-Terminus to the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}