Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
et al., Obesity and metabolism, doi:10.14341/omet12801, Jun 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
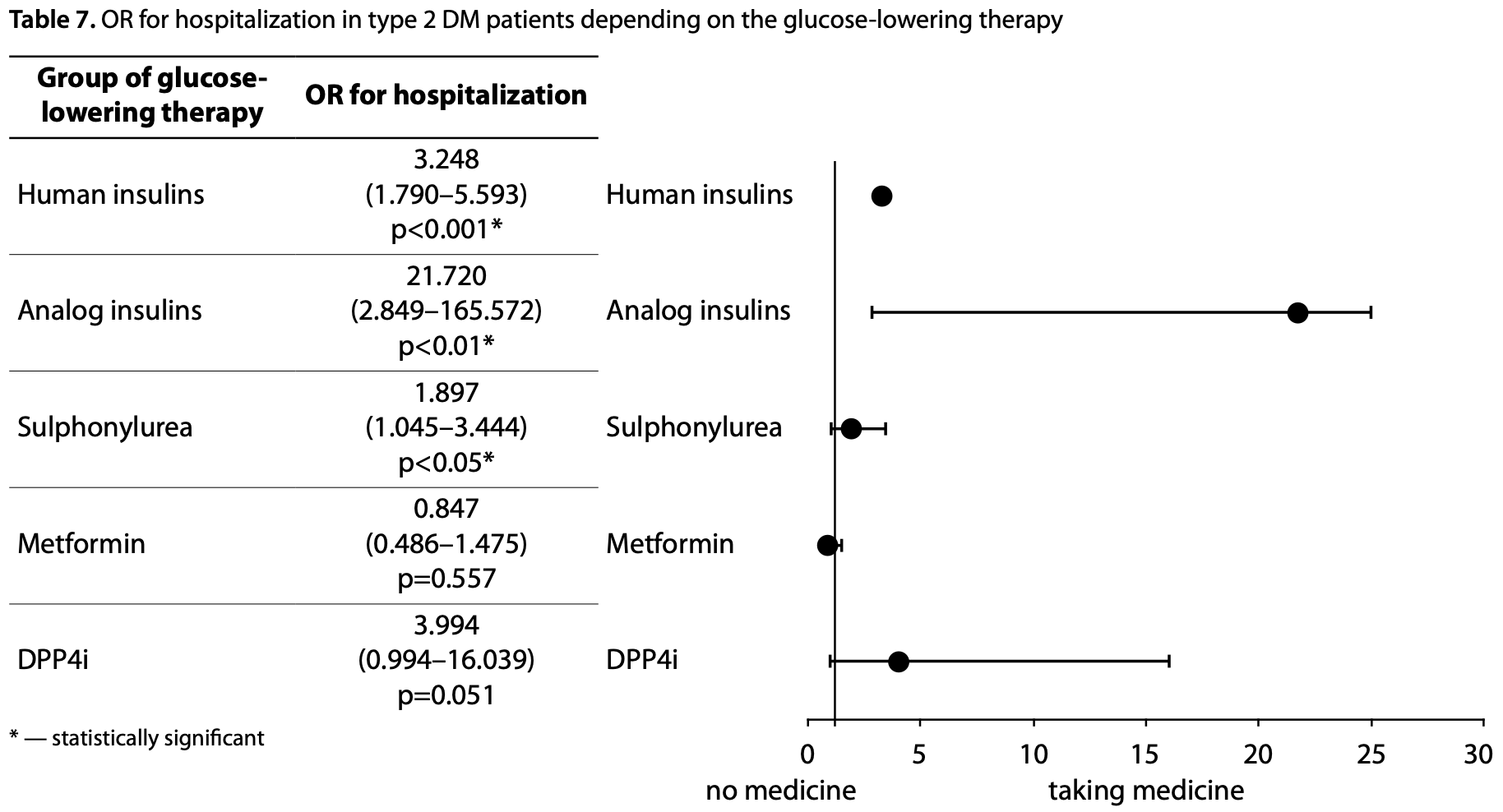
Retrospective 763 COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes in Uzbekistan, showing lower hospitalization with metformin use in unadjusted results, without statistical significance.
Although the 15% lower hospitalization is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 17% lower hospitalization [11‑23%] from meta-analysis of the 25 hospitalization results to date.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of hospitalization, 15.3% lower, OR 0.85, p = 0.56, treatment 375, control 388, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Alieva et al., 6 Jun 2023, retrospective, Uzbekistan, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period April 2020 - December 2020.
Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
Obesity and metabolism, doi:10.14341/omet12801
Tashkent city health department, Uzbekistan BACKGROUND: Since the very first outbreak, scientists have been trying to determine the most critical pathogenetic mechanisms for the development of COVID-19 and related complications, analyze individual subpopulations of patients with chronic diseases and develop optimal tactics to combat not only the infection itself but also its acute and chronic complications. AIM: to assess the COVID-19 course among patients with Type 1 and Type 2 DM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective cohort study of Tashkent inhabitants, who had COVID-19 from April to December 2020, was performed. The data were obtained from the single electronic database of registered cases of COVID-19. All data were analyzed using a logistic regression in STATA 17.0 software. Further, the matched case-control study was performed for patients with type 2 DM and no DM based on age, gender, and BMI. RESULTS: Of the 5023 analyzed subjects, 72.63% had no diabetes mellitus (DM), 4.24% had type 1 DM, 15.19% had type 2 DM, and 7.94% was diagnosed with DM during the COVID-19 infection. DM, overweight, and obesity were associated with severe COVID-19; the most significant risk of a severe course was found in persons with type 2 DM. The risk of a lethal outcome and the need for prescription of glucocorticoids did not show a significant association with diabetes in Tashkent. The clinical features of COVID-19 were more common in patients with type 2 DM, especially for shortness of breath, chest pain, and arrhythmia. The persons receiving SU have complained of dyspnea significantly more often than matched patients without DM. Metformin and DPP4i were the groups of drugs that were not associated with significantly increased risk of hospitalization of patients because of COVID-19. The matched case-control study did not reveal statistically significant differences in the disease course severity, need for hospitalization and glucocorticoids, and death depending on the glucose-lowering therapy preceding the onset of COVID-19. CONCLUSION: Diabetes, age and overweight/obesity were associated with severe course of COVID-19 in Tashkent. There was no statistical difference in COVID-19 severity depending on initial glucose-lowering therapy.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Funding. This study was funded by the grant by the Ministry of Innovation of the Republic of Uzbekistan A-CC-2021-139.
Conflict of interest
References
Abu-Jamous, Anisimovich, Baxter, Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID-19 outcome: a retrospective analysis of real-world evidence data. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.20.20174169
Alieva, Djalilov, Khaydarova, Alimov, Khalilova et al., Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study, Obesity and metabolism
Alieva, Ismailov, Rahimova, Epidemiology of diabetes and prediabetes in Uzbekistan: Screening results, Health Sci J, doi:10.21767/1791-809X.1000609
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a wholepopulation study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Heal Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Anti-Inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Casqueiro, Casqueiro, Alves, Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review of pathogenesis, Indian J Endocrinol Metabol, doi:10.4103/2230-8210.94253
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-0660
Cheng, Liu, Li, Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in Individuals with COVID-19 and Pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013
Crouse, Grimes, Li, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes, Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.600439
Dalan, Ang, Tan, The association of Hypertension and Diabetes Pharmacotherapy with COVID-19 severity and immune signatures: an observational study, Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, doi:10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098.pvaa098
Fadini, Morieri, Longato, Exposure to dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors and COVID-19 among people with type 2 diabetes: A case-control study, Diabetes, Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14097
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Risk of metformin in type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Grant, The effects of metformin on the fibrinolytic system in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects, Diabete metab
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J
Guo, Li, Dong, Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3319
Gupta, Ghosh, Singh, Misra, Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002
Ho, Huang, Tsai, Metformin use mitigates the adverse prognostic effect of diabetes mellitus in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-019-1035-9
Holman, Knighton, Kar, Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0
Hughes, Smith-Mccain, Effects of sulfonylurea compounds on pneumocystis carinii, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/153.5.944
Izzi-Engbeaya, Distaso, Amin, Severe COVID-19 and diabetes e a retrospective cohort study from three London 2 teaching hospitals. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.07.20160275
Jiang, Chen, Liu, Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619
Kim, Jeon, Kim, The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in Daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab J, doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
Li, Wei, Li, Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: Effects on mortality in Covid-19, Endocr Pract, doi:10.4158/EP-2020-0466
Liang, Ding, Li, Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Mendy, Gopal, Alcorn, Forno, Reduced mortality from lower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patients treated with metformin, Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.13486
Orcid, -mail: endocrin@uzsci.net Халилова Диловар Захириддиновна, Dilovar Z. Khalilova
Orcid, None
Orcid, alimovna@mail.ru Алимов Анвар Валиевич, д.м.н., профессор [Anvar V
Peleg, Weerarathna, Mccarthy, Davis, Common infections in diabetes: pathogenesis, management and relationship to glycaemic control, Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.682
Philipose, Smati, Wong, Obesity, old age, and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID-19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.12.20156257
Raj, Mou, Smits, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature12005
Sinclair, Dhatariya, Burr, Guidelines for the management of diabetes in care homes during the Covid-19 pandemic, Diabet Med, doi:10.1111/dme.14317
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations, Diabetes Metab Synd, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004
Singh, Khunti, Assessment of risk, severity, mortality, glycemic control and antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: a narrative review, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108266
Singh, Singh, Saboo, Misra, Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A critical appraisal of literature, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.026
Tsoyi, Jang, Nizamutdinova, Metformin inhibits HMGB1 release in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells and increases survival rate of endotoxaemic mice, Br J Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01126.x
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk Factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus Disease, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Xin, Wei, Ji, Metformin uniquely prevents thrombosis by inhibiting platelet activation and mtDNA release, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep36222
You, Lee, Chun, Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: A populationbased study in Korea, Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.3803/EnM.2020.787
Yuan, Qi, Peng, Molecular basis of binding between Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus and CD26 from seven bat species, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01387-19
Zhang, He, Impacts of metformin on tuberculosis incidence and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00228-019-02786-y
Акида Саттаровна, Phd, Akida, Sadikova, Phd et al., -mail: akidahon@yandex.ru *Автор, ответственный за переписку / Corresponding author, doi:10.14341/omet12801TOCITETHISARTICLE
Алиева, Валерьевна, Anna, Alieva, Md, адрес: Республика Узбекистан, 100125, Ташкент, ул. Мирзо Улугбека, д. 56 [address: 56, M. Ulugbek str
Информация Об Авторах, None
Малика Дильшадовна, Md [malika, Aripova, Orcid, None
Насиба, None, PhD [Nasiba U. Alimova, PhD
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.14341/omet12801",
"ISSN": [
"2306-5524",
"2071-8713"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14341/omet12801",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>BACKGROUND: </jats:bold>Since the very first outbreak, scientists have been trying to determine the most critical pathogenetic mechanisms for the development of COVID-19 and related complications, analyze individual subpopulations of patients with chronic diseases and develop optimal tactics to combat not only the infection itself but also its acute and chronic complications.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>AIM:</jats:bold> to assess the COVID-19 course among patients with Type 1 and Type 2 DM.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>MATERIALS AND METHODS: </jats:bold>A retrospective cohort study of Tashkent inhabitants, who had COVID-19 from April to D ecember 2020, was performed. The data were obtained from the single electronic database of registered cases of COVID-19. All data were analyzed using a logistic regression in STATA 17.0 software. Further, the matched case-control study was performed for patients with type 2 DM and no DM based on age, gender, and BMI.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>RESULTS: </jats:bold>Of the 5023 analyzed subjects, 72.63% had no diabetes mellitus (DM), 4.24% had type 1 DM, 15.19% had type 2 DM, and 7.94% was diagnosed with DM during the COVID-19 infection. DM, overweight, and obesity were associated with severe COVID-19; the most significant risk of a severe course was found in persons with type 2 DM. The risk of a lethal outcome and the need for prescription of glucocorticoids did not show a significant association with diabetes in Tashkent. The clinical features of COVID-19 were more common in patients with type 2 DM, especially for shortness of breath, chest pain, and arrhythmia. The persons receiving SU have complained of dyspnea significantly more often than matched patients without DM. Metformin and DPP4i were the groups of drugs that were not associated with significantly increased risk of hospitalization of patients because of COVID-19. The matched case-control study did not reveal statistically significant differences in the disease course severity, need for hospitalization and glucocorticoids, and death depending on the glucose-lowering therapy preceding the onset of COVID-19.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>CONCLUSION: </jats:bold>Diabetes, age and overweight/obesity were associated with severe course of COVID-19 in Tashkent. There was no statistical difference in COVID-19 severity depending on initial glucose-lowering therapy.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4921-4494",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Alieva",
"given": "A. V.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2865-5186",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Westminster International University in Tashkent"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Djalilov",
"given": "A. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0926-0306",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Khaydarova",
"given": "F. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8422-9803",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tashkent city health department"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Alimov",
"given": "A. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4121-4462",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Khalilova",
"given": "D. Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4121-4462",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Talenova",
"given": "V. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2809-9834",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Alimova",
"given": "N. U.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4683-1435",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Aripova",
"given": "M. D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4708-0306",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Republican Specialized Scientific-and-Practical Medical Centre of Endocrinology named after academician Ya.Kh.Turakulov"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Sadikova",
"given": "A. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Obesity and metabolism",
"container-title-short": "Obes. metabol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.omet-endojournals.ru"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-26T13:54:47Z",
"timestamp": 1690379687000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-26T13:55:21Z",
"timestamp": 1690379721000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-27T04:30:03Z",
"timestamp": 1690432203862
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
26
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.omet-endojournals.ru/jour/about/editorialPolicies#openAccessPolicy",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1686009600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.omet-endojournals.ru/jour/article/viewFile/12801/10061",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "5458",
"original-title": [],
"page": "92-103",
"prefix": "10.14341",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Endocrinology Research Centre",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S et al. Risk Factors Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(7):934-943. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2230-8210.94253",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Casqueiro J, Casqueiro J, Alves C. Infections in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Pathogenesis. Indian J Endocrinol Metabol. 2012. 16(Suppl1):S27-S36. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.94253."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.682",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Peleg Y, Weerarathna T, McCarthy JS, Davis T. Common Infections in Diabetes: Pathogenesis, Management and Relationship to Glycaemic Control. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2007 Jan;23(1):3-13. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.682"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3319",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Guo W, Li M, Dong Y, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Tian C, et al. Dia-betes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2020;36:e3319"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01227-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Liang WH, Zhao Y, Liang HR, Chen ZS, Li YM, et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with CO-VID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J 2020; 55:2000547."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Barron E., Bakhai Ch., Kar P., Weaver A., Bradley D., Ismail H., et al. Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study. www.thelancet.com/diabetes-endocrinology Vol 8 October 2020 813-822 doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Holman N., Knighton P., Kar P., O’Keefe J., Curley M., Weaver A., Barron E., Bakhai Ch., Khunti K., Wareham N.J., Sattar N., Young B., Jonathan Valabhji et al. Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study. www.thelancet.com/diabetes-endocrinology Vol 8 October 2020 P.823-833. doi.org/10.1016/ S2213-8587(20)30271-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Singh R, Saboo B, Misra A. Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A Critical Appraisal of Literature. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan-Feb;15(1):159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.026. Epub 2020 Dec 15. PMID: 33352455; PMCID: PMC7832723."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Gupta R, Ghosh A, Singh AK, Misra A. Clinical considerations for patients with diabetes in times of COVID-19 epidemic. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2020;14(3): 211e2. 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Bornstein SR, Rubino F, Khunti K, Mingrone G, Hopkins D, Birkenfeld A, et al. Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19 Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Jun;8(6):546-550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Gupta R, Ghosh A, Misra A. Diabetes in COVID-19: prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations. Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome: Clin Res Rev 2020;14:303e10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dme.14317",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Sinclair A, Dhatariya K, Burr O, Nagi D, Higgins K, Hopkins D, et al. Guidelines for the management of diabetes in care homes during the Covid-19 pandemic. Diabet Med. 2020 Jul;37(7):1090-1093. doi: 10.1111/dme.14317."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108266",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Khunti K. Assessment of risk, severity, mortality, glycemic control and antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: a narrative review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020 Jul;165:108266."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3803/EnM.2020.787",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "You J.H., Lee S.A., Chun S.Y., Song S.O., Lee B.W., Kim D.J., Boyko E.J. Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:901-908."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4093/dmj.2020.0146",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Kim MK, Jeon JH, Kim SW, et al. The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in Daegu, South Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):602-613. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0146."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Luo P, Qiu L, Liu Y, Liu XL, Zheng JL, Xue HY, et al. Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2020:1e4. https://doi.org/10.4269/ ajtmh.20-0375."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108146",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Pal R, Bhadada SK. Should anti-diabetic medications be reconsidered amid COVID-19 pandemic? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020;163:108146."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajprenal.00516.2013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Salem ESB, Grobe N, Elased KM. Insulin treatment attenuates renal ADAM17 and ACE2 shedding in diabetic Akita mice. Am J Physiol-Ren Physiol 2014;306:F629–39."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000047811",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Kaloyianni M, Bourikas D, Koliakos G. The effect of insulin on Na+-H+ antiport activity of obese and normal subjects erythrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 2001;11:253–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Cariou B, Hadjadj S, Wargny M, Pichelin M, Al-Salameh A, Allix I, et al. Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study. Diabetologia. 2020;63(8):1500-15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Chen Y, Yang D, Cheng B, Chen J, Peng A, Yang C, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication. Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul;43(7):1399-1407. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0660."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.12.20156257",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Philipose Z, Smati N, Wong CSJ, Aspey K, Mendall M. Obesity, old age, and frailty are the true risk factors for COVID-19 mortality and not chronic disease or ethnicity. medRxiv 2020.08.12.20156257; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.12.20156257"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.07.20160275",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Izzi-Engbeaya C, Distaso W, Amin A, Yang W, Idowu O, Kenkre JS et al. Severe COVID-19 and diabetes e a retrospective cohort study from three London 2 teaching hospitals. medRxiv 2020.08.07.20160275; https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.07.20160275"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Gao Y, Liu T, Zhong W, Liu R, Zhou H, Huang W, et al. Risk of metformin in type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report. Clin Transl Sci 2020 Sep 21. Vol 13, Issue6: 1055-1059. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12897."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.20.20174169",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Abu-Jamous B, Anisimovich A, Baxter J, Mackillop L, Vizcaychipi MP, McCarthy A. et al. Associations of comorbidities and medications with COVID-19 outcome: a retrospective analysis of real-world evidence data. medRxiv 2020.08.20.20174169; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.20.20174169."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.600439",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Crouse AB, Grimes T, Li P, Might M, Ovalle F, Shalev A. Metformin Use Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in a Diverse Population With COVID-19 and Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021;11:600439. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.600439."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Ingraham NE, Murray TA, Marmor S., Hovertsen S., Gronski J., et al. Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalized with Covid-19: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021;2:e34-41 Published on line December 2020;3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Jiang N, Chen Z, Liu L, Yin X, Yang H, Tan X, et al. Association of metformin with mortality or ARDS in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021 Mar;173:108619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108619."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Cheng X, Liu YM, Li H, Xin X, Lei F, Qin JJ, et al. Metformin use is associated with increased incidence of acidosis but not mortality in individuals with COVID-19 and preexisting type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabol 2020. 32. 537-547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.013."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Wargny M, Potier L, Gourdy P, Pichelin M, Amadou C, Benhamou PY, et al. Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study. Diabetologia. 2021 Apr;64(4):778-794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP-2020-0466",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Li J., Wei Q., Li W.X., McCowen K.C., Xiong W., Liu J., Jiang W., et al. Metformin use in diabetes prior to hospitalization: effects on mortality in COVID-19. Endocrine practice 2020;26(10):1166-1172"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2346-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "Liang H, Ding X, Li L, Wang T, Kan Q, Wang L, et al.Association of preadmission metformin use and mortality inpatients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematicreview and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Crit Care 2019;23(1):50."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-019-02786-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Zhang M, He J. Impacts of metformin on tuberculosisincidence and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes: asystematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2020;76:149–59."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.13486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Mendy A, Gopal R, Alcorn JF, Forno E. Reduced mortality fromlower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patientstreated with metformin. Respirology 2019;24(7):646e51."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-019-1035-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Ho T, Huang C, Tsai Y, Shin-Yu Lien A, Lai F, Yu CJ. Metformin use mitigates theadverse prognostic effect of diabetes mellitus in chronicobstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res 2019;20:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-019-1035-9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Zhu L, She ZG, Cheng X, Guo J, Zhang BH, Li H. Association ofblood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing Type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 2020;31:1–10.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021."
},
{
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Grant PJ. The effects of metformin on the fibrinolytic system in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabete & metabolisme. 1991;17(1 Pt 2):168-73."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep36222",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Xin G, Wei Z, Ji C, Zheng H, Gu J, Ma L, et al. Metformin Uniquely Prevents Thrombosis by Inhibiting Platelet Activation and mtDNA Release. Scientific reports. 2016;6:36222."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Cameron AR, Morrison VL, Levin D, Mohan M, Forteath C, Beall C, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status. Circulation research. 2016;119(5):652-65."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01126.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref40",
"unstructured": "Tsoyi K, Jang HJ, Nizamutdinova IT, Kim YM, Lee YS, Kim HJ, et al. Metformin inhibits HMGB1 release in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells and increases survival rate of endotoxaemic mice. British journal of pharmacology. 2011;162(7):1498-508."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref41",
"unstructured": "Ghany R, Palacio A, Dawkins E, Chen G, McCarter D, Forbes E, et al. Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical research and Reviews. 2021;15(2): 513-518. doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02/022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/680213",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "Huetsch J, Shimoda LA. Na + /H + exchange and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ 2015;5:228–43."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/diacare.27.7.1791",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref43",
"unstructured": "Misbin RI. The phantom of lactic acidosis due to metformin in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1791–3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-015-1180-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref44",
"unstructured": "Keren D.B., Ilia B., Ronit M., Shai E. Lactic acidosis and severe septic shock in metformin users: a cohort study. Crit Care 2015;20(1). https://doi.org/ 10.1186/s13054-015-1180-6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref45",
"unstructured": "Xian H, Liu Y, Nilsson AR, Gatchalian R, Crother TR, Tourtellotte WG, et al. Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation. Immunity 2021;54:1-15. doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.05.004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389450118666170613081730",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref46",
"unstructured": "Schuiveling M, Vazirpanah N, Radstake T, Zimmermann M, Broen JCA. Metformin, a new era for an old drug in the treatment of immune mediated disease? Curr Drug Targets 2018;19:945e59."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tube.2019.02.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref47",
"unstructured": "Yew WW, Chang KC, Chan DP, Zhang Y. Metformin as a host-directed therapeutic in tuberculosis: is there a promise? Tuberculosis 2019;115:76e80."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12981-020-00267-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref48",
"unstructured": "Ouyang J, Isnard S, Lin J, Fombuena B, Marette A, Routy B, et al. Metformin effect on gut microbiota: insights for HIV-related inflammation. AIDS Res Ther 2020;17:10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD002967.pub4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref49",
"unstructured": "Salpeter SR, Greyber E, Pasternak GA, Salpeter EE. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;2010(4):CD002967."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047164",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref50",
"unstructured": "Fried JA, Ramasubbu K, Bhatt R, Topkara VK, Clerkin KJ, Horn E, et al. The variety of cardiovascular presentations of COVID-19. Circulation 2020;141(23):1930-6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.01.20185850",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref51",
"unstructured": "Bramante C, Tignanelli CJ, Dutta N, Jones E, Tamariz L, Clark JM, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and risk of hospitalization for Covid-19. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 2:2020.09.01.20185850. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.01.20185850. PMID: 32909011; PMCID: PMC7480063."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref52",
"unstructured": "Scheen AJ. Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality. Diabetes Metabol 2020;46:423e6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref53",
"unstructured": "Lukito AA, Pranata R, Henrina J, Lim MA, Lawrensia S, Suastika K. The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Diabetes Metabolic SyndromeDiabetes Metab Syndr. Nov-Dec 2020;14(6):2177-2183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/153.5.944",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref54",
"unstructured": "Hughes WT, Smith-McCain. Effects of sulfonylurea compounds on Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis 1986;153:944e7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref55",
"unstructured": "Dalan R, Ang LW, Tan WY, Fong SW, Tay WC, Chan YH, et al. The association of Hypertension and Diabetes Pharmacotherapy with COVID-19 severity and immune signatures: an observational study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2021;7(3): e48–e51. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa098. pvaa098."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01387-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref56",
"unstructured": "Yuan Y, Qi J, Peng R, Li C, Lu G, Yan J, et al. Molecular ba-sis of binding between Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus and CD26 from seven bat species. J Virol 2020; 94:e01387-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref57",
"unstructured": "Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DH, Muller MA, Dijkman R, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013; 495:251-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2019.00080",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref58",
"unstructured": "Deacon, C.F. Physiology and Pharmacology of DPP-4 in Glucose Homeostasis and the Treatment of Type 2Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)2019,10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref59",
"unstructured": "Vankadari, N., Wilce, J.A. Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure predictionof spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26.Emerg. Microbes Infect.2020;9:601–604. https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref60",
"unstructured": "Letko, M.; Marzi, A.; Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol.2020;5:562–569."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsr2005760",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref61",
"unstructured": "Vaduganathan M., Vardeny O, Michel T, McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med.2020;382:1653–1659."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref62",
"unstructured": "Tai W, He L, Zhang X, Pu J, Voronin D, Jiang S, et al. Characterization of the receptor-bindingdomain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell Mol. Immunol.2020;17: 613–620."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.13955",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref63",
"unstructured": "Seong JM, Yee J, Gwak HS. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors lower the risk of autoimmune disease inpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.2019;85:1719–1727."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205216",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref64",
"unstructured": "Kim SC, Schneeweiss S, Glynn RJ, Doherty M, Goldfine AB, Solomon DH. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4inhibitors in type 2 diabetes may reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases: A population-based cohort study.Ann. Rheum. Dis.2015;74:1968–1975."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mco.2018.1766",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref65",
"unstructured": "Ali A, Fuentes A, Skelton WP, Wang Y, McGorray S, Shah C, et al. A multi-center retrospective analysis of the effect of DPP4 inhibitors on progression-free survival in advance dairway and colorectal cancers. Mol. Clin. Oncol.2019;10:118–124."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70696-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref66",
"unstructured": "Reinhold D, Brocke S. DPP4-directed therapeutic strategies for MERS-CoV. Lancet. Infect. Dis.2014;14:100–101."
},
{
"key": "ref67",
"unstructured": "Kritas SK, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Ross R, Conti P. Mast cells contribute to coronavirus-induced inflammation: New anti-inflammatory strategy. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2020;34(1):9-14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000053693",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref68",
"unstructured": "Lin TJ, Issekutz TB, Marshall JS. SDF-1 induces IL-8 production and transendothelial migration of humancord blood-derived mast cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:142–145."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref69",
"unstructured": "Chillo O, Kleinert EC, Lautz T, Lasch M, Pagel JI, Heun Y, et al. Perivascular Mast Cells Govern Shear Stress-Induced Arteriogenesis by Orchestrating Leukocyte Function. Cell Rep.2016;23:2197–2207."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/343741",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref70",
"unstructured": "Soriano A, Martínez C, García F, Plana M, Palou E, Lejeune M, et al. Plasma stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1 levels, SDF1-3’A genotype, and expression of CXCR4 on T lymphocytes: Their impact on resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and its progression. J. Infect. Dis.2002;186:922–931."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.112.003277",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref71",
"unstructured": "Ayaori M, Iwakami N, Uto-Kondo H, Sato H, Sasaki M, Komatsu T, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors attenuate endothelial function as evaluated by flow-mediated vasodilatation in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc.2013;2:1-10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1358863X16681486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref72",
"unstructured": "Widlansky ME, Puppala VK, Suboc TM, Malik M, Branum A, Signorelli K, et al. Impact of DPP-4 inhibition on acute and chronic endothelial function in humans with type 2 diabetes on background metformin therapy. Vasc. Med.2017;22:189–196."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2741/2849",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref73",
"unstructured": "Reinhold D, Bank U, Tager M. DP IV/ CD26, APN/CD13 and related enzymes as regulators of T cell immunity: implications for experimental encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Front Biosci 2008;13:2356-63."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14097",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref74",
"unstructured": "Fadini GP, Morieri ML, Longato E, Bonora BM, Pinelli S, Selin E, et al. Exposure to DPP-4 inhibitors and COVID-19 among people with type 2 diabetes. A case-control study. Diabetes Obes. 2020;22(10):1946-1950."
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.omet-endojournals.ru/jour/article/view/12801"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14341/crossmarkpolicy2018",
"volume": "20"
}
