Corticosteroids for hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19: a retrospective study in Chongqing, China
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-75926-9, Oct 2024
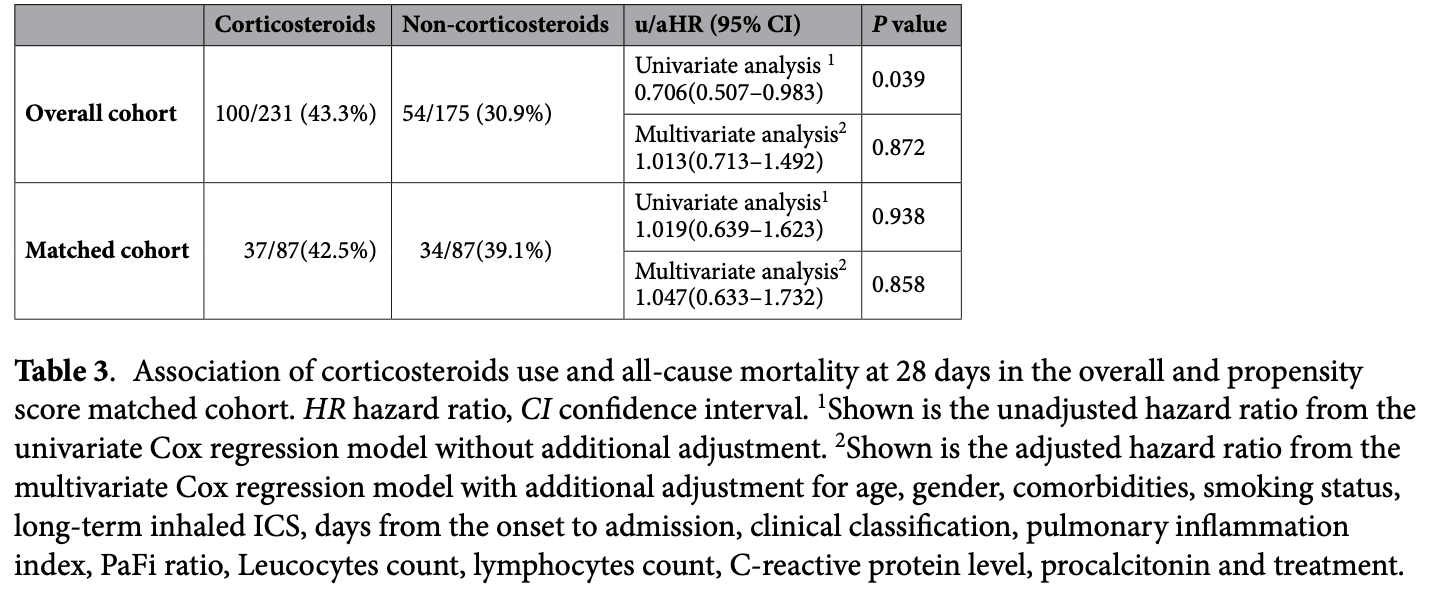
Retrospective 406 hospitalized severe/critical COVID-19 patients in China showing no significant difference in 28-day mortality with corticosteroid treatment (methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, or both). Corticosteroids were associated with a longer survival time among non-survivors. The study found high overall mortality of 33% in-hospital and 38% at 28 days in this severe/critical, mostly elderly population with high comorbidities during the omicron wave in 2022-2023. Authors hypothesize that the potential benefits of corticosteroids may be limited by the timing of administration and the biphasic effects of suppressing both viral replication and inflammation.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
|
risk of death, 4.7% higher, HR 1.05, p = 0.86, treatment 37 of 87 (42.5%), control 34 of 87 (39.1%), adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhuang et al., 16 Oct 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 76.0, 13 authors, study period December 2022 - January 2023.
Contact: guoshul666@163.com.
Corticosteroids for hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19: a retrospective study in Chongqing, China
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-75926-9
Corticosteroids have always been recommended for severe cases of COVID-19. However, the efficacy of treatment with corticosteroids for COVID-19 during the SARS-CoV-2 omicron outbreak in China has not been reported. Clinical data from 406 patients hospitalized for severe/critical COVID-19 from December 2022 to January 2023 at six hospitals in Chongqing were retrospectively analyzed. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality at 28 days in the groups with and without corticosteroids treatment after propensity score matching (PSM). Secondary outcomes were to compare in-hospital mortality and length of survival time with corticosteroids and those without corticosteroids. This study included 406 patients with severe or critical COVID-19, divided into the corticosteroids group (231, 56.9%) and non-corticosteroids group (175, 43.1%). After PSM, the use of corticosteroids did not reduce all-cause mortality at 28 days (42.5% vs. 39.1%). Univariate analysis showed that corticosteroids were not associated with improved all-cause mortality at 28 days [hazard ratio (HR), 1.019; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.639-1.623; p = 0.938]. Multivariate analysis showed similar results (HR, 1.047; 95% CI, 0.633-1.732; p = 0.858). Among non-survivors, the survival time was significantly larger in those who received corticosteroids compared with the non-corticosteroid users [median 13 (IQR 6.5-15.5) vs. 6 (4-11.25), p = 0.007]. The use of systemic corticosteroids in severe/critical COVID-19 may provide certain potential survival benefits but does not improve prognosis.
Author contributions R.Z. and H.X. participated in the study design. Z.L., K.Z., H.P., B.L., H.W., L.H., H.Y., C.L., and Y.Y. collected the epidemiological and clinical data. R.Z. and H.X. performed the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. L.X. Conducted the literature search and data extraction. S.G. revised the final manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (K2023-066). The institutional review board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Jinshan Campus of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, The Seventh People's Hospital of Chongqing, People's Hospital of Shapingba District, Affiliated University Town Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and Chongqing University Three Gorges Hospital approved the analysis of patients' clinical and radiological data. Because of the retrospective nature of the study, the requirement for informed consent was waived by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. The data were deidentified and only then transferred for analysis.
Consent for publication All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and..
References
Angus, Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama
Chaudhuri, Corticosteroids in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 ARDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Intensive Care Med
Chen, Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study, BMJ (Clinical Res. ed
China, Of, Medicine, Translation: diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 (Trial Version 10), Infect. Microbes Dis
China, Of, Medicine, Translation: diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 (Trial Version 9), Infect. Microbes Dis
Corral-Gudino, Effect of intravenous pulses of methylprednisolone 250 mg versus dexamethasone 6 mg in hospitalised adults with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label randomised trial, Eur. J. Clin. Invest
Corral-Gudino, Methylprednisolone in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label randomized trial (GLUCOCOVID), Wien Klin. Wochenschr
De Luca, GM-CSF blockade with mavrilimumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia and systemic hyperinflammation: a single-centre, prospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
De Mélo, Júnior, De Souza, Dutra, De Valente et al., Review on therapeutic targets for COVID-19: insights from cytokine storm, Postgrad. Med. J
Dequin, Effect of hydrocortisone on 21-Day mortality or respiratory support among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama
Edalatifard, Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial, Eur. Respir J
Ezeokoli, Gcilitshana, Pohl, Risk factors for fungal co-infections in critically ill COVID-19 patients, with a focus on immunosuppressants, J. Fungi
Granholm, Long-term outcomes of dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia, Intensive Care Med
Jalali, Increased household transmission and immune escape of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron compared to Delta variants, Nat. Commun
Jeronimo, Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a Randomized, Double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial, Clin. Infect. Dis
Jianping, Expert consensus on the use of corticosteroid in patients with 2019-nCoV pneumonia, Chin. J. Tuberculosis Respiratory Dis
Keller, Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on mortality or mechanical ventilation in patients with COVID-19, J. Hosp. Med
Liu, Zheng, Huang, Shan, Huang, Successful use of methylprednisolone for treating severe COVID-19, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol
Mager, Lin, Blum, Lates, Jusko, Dose equivalency evaluation of major corticosteroids: pharmacokinetics and cell trafficking and cortisol dynamics, J. Clin. Pharmacol
Markov, Katzourakis, Stilianakis, Antigenic evolution will lead to new SARS-CoV-2 variants with unpredictable severity, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Maskin, High-Versus Low-Dose Dexamethasone for the treatment of COVID-19-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: a Multicenter, Randomized Open-label clinical trial, J. Intensive Care Med
Mcmenamin, Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study, Lancet Infect. Dis
Mehta, Mazer-Amirshahi, Alkindi, Pourmand, Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19; a narrative review for emergency providers, Am. J. Emerg. Med
Mohanty, Meher, Biswa, Padhy, Effectiveness of pulse dose methyl prednisolone in management of COVID 19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences: A Publication of the Canadian Society for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Societe Canadienne Des Sciences Pharmaceutiques
Moreno, Corticosteroid treatment and mortality in mechanically ventilated COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients: a multicentre cohort study, Ann. Intensiv. Care
Morton, Griffiths, Loeffler, Orr, White, Defective antifungal immunity in patients with COVID-19, Front. Immunol
Papamanoli, High-dose methylprednisolone in nonintubated patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia, Eur. J. Clin. Invest
Park, Corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19 infections? Too early to conclude, Korean J. Intern. Med
Patoulias, Dimosiari, Intravenous pulse methylprednisolone for the treatment of severe COVID-19, Eur. J. Intern. Med. S, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2023.02.008
Pei, Antiviral agents, glucocorticoids, antibiotics, and intravenous immunoglobulin in 1142 patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pol. Archives Intern. Med
Ranjbar, Methylprednisolone or dexamethasone, which one is superior corticosteroid in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a triple-blinded randomized controlled trial, BMC Infect. Dis
Remmington, Steroid exposure and outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia, BJA Open
Russell, Millar, Baillie, Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury, Lancet
Smith, COVID-19 Mortality and Vaccine Coverage -Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep
Uraki, Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, Nature
Vanderbeke, Monocyte-driven atypical cytokine storm and aberrant neutrophil activation as key mediators of COVID-19 disease severity, Nat. Commun
Wan, Relationships among lymphocyte subsets, cytokines, and the pulmonary inflammation index in coronavirus (COVID-19) infected patients, Br. J. Haematol
Wang, Effect of corticosteroids in patients with COVID-19: a bayesian network meta-analysis, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Williamson, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature
Wu, Risk factors Associated with Acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern. Med
Xiang, Glucocorticoids improve severe or critical COVID-19 by activating ACE2 and reducing IL-6 levels, Int. J. Biol. Sci
Zhan, Shang, Gu, Huang, Xie, Efficacy of corticosteroid in patients with COVID-19: a multi-center retrospective study and meta-analysis, J. Med. Virol
Zhou, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Effect of methylprednisolone in severe and critical COVID-19: analysis of 102 cases, World J. Clin. Cases
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-75926-9",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-75926-9",
"alternative-id": [
"75926"
],
"article-number": "24317",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "18 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "9 October 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "16 October 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (K2023-066). The institutional review board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Jinshan Campus of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, The Seventh People’s Hospital of Chongqing, People’s Hospital of Shapingba District, Affiliated University Town Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and Chongqing University Three Gorges Hospital approved the analysis of patients’ clinical and radiological data. Because of the retrospective nature of the study, the requirement for informed consent was waived by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. The data were de-identified and only then transferred for analysis."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhuang",
"given": "Rongjuan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Hongli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Zhiqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zong",
"given": "Kaican",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Hailang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Huizi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Lan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Hongwei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Chun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yin",
"given": "Yuting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Shuliang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T20:31:04Z",
"timestamp": 1729110664000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T21:02:34Z",
"timestamp": 1729112554000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-17T04:32:17Z",
"timestamp": 1729139537750,
"version": "3.27.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729036800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729036800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-75926-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-75926-9",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-75926-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00722-z",
"author": "PV Markov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "251",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "75926_CR1",
"unstructured": "Markov, P. V., Katzourakis, A. & Stilianakis, N. I. Antigenic evolution will lead to new SARS-CoV-2 variants with unpredictable severity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 251–252 (2022).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33233-9",
"author": "N Jalali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5706",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "75926_CR2",
"unstructured": "Jalali, N. et al. Increased household transmission and immune escape of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron compared to Delta variants. Nat. Commun. 13, 5706 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "75926_CR3",
"unstructured": "WHO & Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR4",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl. J. Med. 384, 693–704 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.47652",
"author": "Z Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2382",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "75926_CR5",
"unstructured": "Xiang, Z. et al. Glucocorticoids improve severe or critical COVID-19 by activating ACE2 and reducing IL-6 levels. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 16, 2382–2391 (2020).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06045-3",
"author": "K Ranjbar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR6",
"unstructured": "Ranjbar, K. et al. Methylprednisolone or dexamethasone, which one is superior corticosteroid in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a triple-blinded randomized controlled trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 21, 337 (2021).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26914",
"author": "Y Zhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4292",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "75926_CR7",
"unstructured": "Zhan, Y., Shang, J., Gu, Y., Huang, Q. & Xie, J. Efficacy of corticosteroid in patients with COVID-19: a multi-center retrospective study and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 93, 4292–4302 (2021).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.10.021",
"author": "X Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR8",
"unstructured": "Wang, X. et al. Effect of corticosteroids in patients with COVID-19: a bayesian network meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 125, 84–92 (2022).",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24360-w",
"author": "L Vanderbeke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4117",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "75926_CR9",
"unstructured": "Vanderbeke, L. et al. Monocyte-driven atypical cytokine storm and aberrant neutrophil activation as key mediators of COVID-19 disease severity. Nat. Commun. 12, 4117 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bjao.2023.100128",
"author": "C Remmington",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100128",
"journal-title": "BJA Open.",
"key": "75926_CR10",
"unstructured": "Remmington, C. et al. Steroid exposure and outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia. BJA Open. 5, 100128 (2023).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2023.02.008",
"author": "D Patoulias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "00048",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR11",
"unstructured": "Patoulias, D. & Dimosiari, A. Intravenous pulse methylprednisolone for the treatment of severe COVID-19. Eur. J. Intern. Med. S0953-6205 (23), 00048–00041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2023.02.008 (2023).",
"volume": "S0953-6205",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3904/kjim.2023.046",
"author": "S Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "144",
"journal-title": "Korean J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR12",
"unstructured": "Park, S. Corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19 infections? Too early to conclude. Korean J. Intern. Med. 38, 144–146 (2023).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "75926_CR13",
"unstructured": "Zhou, F. et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 395, 1054–1062 (2020).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "T Chen",
"first-page": "m1091",
"journal-title": "BMJ (Clinical Res. ed.)",
"key": "75926_CR14",
"unstructured": "Chen, T. et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ (Clinical Res. ed.). 368, m1091 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "NH China",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "Infect. Microbes Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR15",
"unstructured": "China, N. H. C. of the P. R. of & Medicine, N. A. of T. C. Translation: diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 (Trial Version 9). Infect. Microbes Dis. 4, 94 (2022).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/IM9.0000000000000112",
"author": "NH China",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Infect. Microbes Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR16",
"unstructured": "China, N. H. C. of the P. R. of & Medicine, N. A. of T. C. Translation: diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 (Trial Version 10). Infect. Microbes Dis. 5, 3 (2023).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "Z Jianping",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Chin. J. Tuberculosis Respiratory Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR17",
"unstructured": "Jianping, Z. et al. Expert consensus on the use of corticosteroid in patients with 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Chin. J. Tuberculosis Respiratory Dis. 43, 183–184 (2020).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.16659",
"author": "S Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Haematol.",
"key": "75926_CR18",
"unstructured": "Wan, S. et al. Relationships among lymphocyte subsets, cytokines, and the pulmonary inflammation index in coronavirus (COVID-19) infected patients. Br. J. Haematol. 189, 428–437 (2020).",
"volume": "189",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0091270003258651",
"author": "DE Mager",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1216",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "75926_CR19",
"unstructured": "Mager, D. E., Lin, S. X., Blum, R. A., Lates, C. D. & Jusko, W. J. Dose equivalency evaluation of major corticosteroids: pharmacokinetics and cell trafficking and cortisol dynamics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 43, 1216–1227 (2003).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"key": "75926_CR20",
"unstructured": "Overview of national treatment. and surveillance data for novel coronavirus infection. https://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/zl/szkb_11803/jszl_13141/202301/t20230125_263519.html.<published in 25 January 2023>."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1",
"author": "R Uraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "75926_CR21",
"unstructured": "Uraki, R. et al. Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2. Nature. 607, 119–127 (2022).",
"volume": "607",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"author": "EJ Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "75926_CR22",
"unstructured": "Williamson, E. J. et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 584, 430–436 (2020).",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7115e1",
"author": "DJ Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep.",
"key": "75926_CR23",
"unstructured": "Smith, D. J. et al. COVID-19 Mortality and Vaccine Coverage - Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China, January 6, 2022-March 21, 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 71, 545–548 (2022).",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00345-0",
"author": "ME McMenamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1435",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR24",
"unstructured": "McMenamin, M. E. et al. Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, 1435–1443 (2022).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138791",
"author": "ML de Mélo Silva Júnior",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "75926_CR25",
"unstructured": "de Mélo Silva Júnior, M. L., de Souza, L. M. A., Dutra, R. E. M. C., de Valente, R. G., Melo, T. S. & M. & Review on therapeutic targets for COVID-19: insights from cytokine storm. Postgrad. Med. J. 97, 391–398 (2021).",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.035",
"author": "N Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1488",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR26",
"unstructured": "Mehta, N., Mazer-Amirshahi, M., Alkindi, N. & Pourmand, A. Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19; a narrative review for emergency providers. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 38, 1488–1493 (2020).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12788/jhm.3497",
"author": "MJ Keller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "489",
"journal-title": "J. Hosp. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR27",
"unstructured": "Keller, M. J. et al. Effect of systemic glucocorticoids on mortality or mechanical ventilation in patients with COVID-19. J. Hosp. Med. 15, 489–493 (2020).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16761",
"author": "PF Dequin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1298",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "75926_CR28",
"unstructured": "Dequin, P. F. et al. Effect of hydrocortisone on 21-Day mortality or respiratory support among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 324, 1298–1306 (2020).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "L Pei",
"first-page": "726",
"journal-title": "Pol. Archives Intern. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR29",
"unstructured": "Pei, L. et al. Antiviral agents, glucocorticoids, antibiotics, and intravenous immunoglobulin in 1142 patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pol. Archives Intern. Med. 130, 726–733 (2020).",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5952",
"author": "HM Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5952",
"journal-title": "World J. Clin. Cases",
"key": "75926_CR30",
"unstructured": "Zhu, H. M. et al. Effect of methylprednisolone in severe and critical COVID-19: analysis of 102 cases. World J. Clin. Cases. 8, 5952–5961 (2020).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1177",
"author": "CMP Jeronimo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e373",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "75926_CR31",
"unstructured": "Jeronimo, C. M. P. et al. Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a Randomized, Double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 72, e373–e381 (2021).",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-021-00951-0",
"author": "G Moreno",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensiv. Care.",
"key": "75926_CR32",
"unstructured": "Moreno, G. et al. Corticosteroid treatment and mortality in mechanically ventilated COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients: a multicentre cohort study. Ann. Intensiv. Care. 11, 159 (2021).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.021",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "75926_CR33",
"unstructured": "Liu, J., Zheng, X., Huang, Y., Shan, H. & Huang, J. Successful use of methylprednisolone for treating severe COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 146, 325–327 (2020).",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13458",
"author": "A Papamanoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13458",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "75926_CR34",
"unstructured": "Papamanoli, A. et al. High-dose methylprednisolone in nonintubated patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 51, e13458 (2021).",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00508-020-01805-8",
"author": "L Corral-Gudino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Wien Klin. Wochenschr",
"key": "75926_CR35",
"unstructured": "Corral-Gudino, L. et al. Methylprednisolone in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label randomized trial (GLUCOCOVID). Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 133, 303–311 (2021).",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"author": "C Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "75926_CR36",
"unstructured": "Wu, C. et al. Risk factors Associated with Acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 180, 934–943 (2020).",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02808-2020",
"author": "M Edalatifard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2002808",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir J.",
"key": "75926_CR37",
"unstructured": "Edalatifard, M. et al. Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial. Eur. Respir J. 56, 2002808 (2020).",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps32430",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "75926_CR38",
"unstructured": "Mohanty, R. R. & Meher, B. R. Biswa Mohan Padhy, null Effectiveness of pulse dose methyl prednisolone in management of COVID 19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences: A Publication of the Canadian Society for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Societe Canadienne Des Sciences Pharmaceutiques 25, 110–123 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13881",
"author": "L Corral-Gudino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13881",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "75926_CR39",
"unstructured": "Corral-Gudino, L. et al. Effect of intravenous pulses of methylprednisolone 250 mg versus dexamethasone 6 mg in hospitalised adults with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-label randomised trial. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 53, e13881 (2023).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-022-06677-2",
"author": "A Granholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "580",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "75926_CR40",
"unstructured": "Granholm, A. et al. Long-term outcomes of dexamethasone 12 mg versus 6 mg in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxaemia. Intensive Care Med. 48, 580–589 (2022).",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/08850666211066799",
"author": "LP Maskin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "J. Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "75926_CR41",
"unstructured": "Maskin, L. P. et al. High- Versus Low-Dose Dexamethasone for the treatment of COVID-19-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: a Multicenter, Randomized Open-label clinical trial. J. Intensive Care Med. 37, 491–499 (2022).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17022",
"author": "DC Angus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1317",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "75926_CR42",
"unstructured": "Angus, D. C. et al. Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 324, 1317–1329 (2020).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"author": "WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "75926_CR43",
"unstructured": "WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group. Association between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a Meta-analysis. Jama. 324, 1330–1341 (2020).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-021-06394-2",
"author": "D Chaudhuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "521",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "75926_CR44",
"unstructured": "Chaudhuri, D. et al. Corticosteroids in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 ARDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 47, 521–537 (2021).",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30317-2",
"author": "CD Russell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London England)",
"key": "75926_CR45",
"unstructured": "Russell, C. D., Millar, J. E. & Baillie, J. K. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury. Lancet (London England). 395, 473–475 (2020).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "OT Ezeokoli",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "J. Fungi (Basel Switzerland)",
"key": "75926_CR46",
"unstructured": "Ezeokoli, O. T., Gcilitshana, O. & Pohl, C. H. Risk factors for fungal co-infections in critically ill COVID-19 patients, with a focus on immunosuppressants. J. Fungi (Basel Switzerland). 7, 545 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1080822",
"author": "CO Morton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1080822",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "75926_CR47",
"unstructured": "Morton, C. O., Griffiths, J. S., Loeffler, J., Orr, S. & White, P. L. Defective antifungal immunity in patients with COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 13, 1080822 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30170-3",
"author": "G De Luca",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e465",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "75926_CR48",
"unstructured": "De Luca, G. et al. GM-CSF blockade with mavrilimumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia and systemic hyperinflammation: a single-centre, prospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2, e465–e473 (2020).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-75926-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Corticosteroids for hospitalized patients with severe/critical COVID-19: a retrospective study in Chongqing, China",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}