Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding and impact of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment in hospitalised non-critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection
et al., European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.00799-2020, May 2020
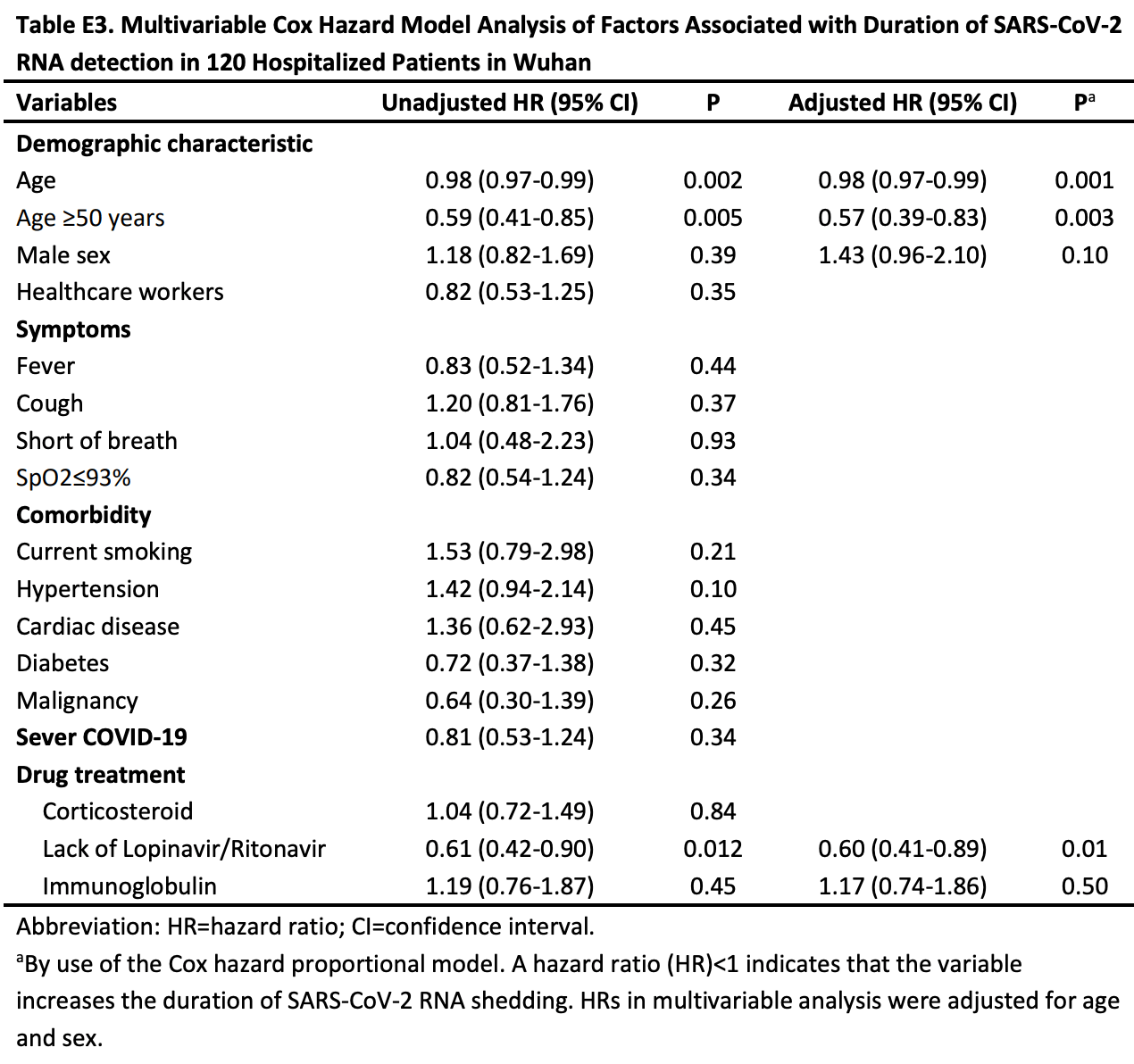
Retrospective 120 hospitalized non-critically ill COVID-19 patients showing that early administration of lopinavir/ritonavir was associated with shorter duration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
prolonged viral shedding, 40.0% lower, HR 0.60, p = 0.010, treatment 78, control 42, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yan et al., 19 May 2020, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 52.0, 7 authors, study period 31 January, 2020 - 9 March, 2020.
Contact: gaoyonghuahust@163.com.
Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding and impact of lopinavir/ ritonavir treatment in hospitalised non-critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection
doi:10.1183/13993003.00799-2020].
Risk factors for prolonged SARS-CoV-2 shedding include older age and the lack of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment. Earlier administration of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment could shorten the duration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding.
Conflict of interest: None declared.
References
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Chan, Yao, Yeung, Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-β1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset, J Infect Dis
Chen, Yang, Lin, Nasopharyngeal shedding of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus is associated with genetic polymorphisms, Clin Infect Dis
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax
De Wilde, Jochmans, Posthuma, Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1183/13993003.00799-2020
Killerby, Biggs, Midgley, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus transmission, Emerg Infect Dis
Opal, Girard, Ely, The immunopathogenesis of sepsis in elderly patients, Clin Infect Dis
Sheahan, Sims, Leist, Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV, Nat Comm
Wang, Gao, Lou, The clinical dynamics of 18 cases of COVID-19 outside of Wuhan, China, Eur Respir J
Wang, Guo, Yan, Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding in patients with avian influenza A (H7N9) virus infection, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1183/13993003.00799-2020
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Young, Ong, Kalimuddin, Epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore, JAMA
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00799-2020",
"ISSN": [
"0903-1936",
"1399-3003"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00799-2020",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The duration of viral shedding is central to the guidance of decisions about isolation precautions and antiviral treatment. However, studies regarding the risk factors associated with prolonged shedding of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the impact of lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) treatment on viral shedding remain scarce.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Data were collected from all SARS-CoV-2 infected patients who were admitted to isolation wards and had reverse transcription PCR conversion at the No. 3 People's Hospital of Hubei province, China, between 31 January and 9 March 2020. We compared clinical characteristics and SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding between patients initiated with LPV/r treatment and those without. Logistic regression analysis was employed to evaluate the risk factors associated with prolonged viral shedding.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Of 120 patients, the median age was 52 years, 54 (45%) were male and 78 (65%) received LPV/r treatment. The median duration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection from symptom onset was 23 days (interquartile range 18–32 days). Older age (OR 1.03, 95% CI 1.00–1.05; p=0.03) and the lack of LPV/r treatment (OR 2.42, 95% CI 1.10–5.36; p=0.029) were independent risk factors for prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding. Patients who initiated LPV/r treatment within 10 days from symptom onset, but not initiated from day 11 onwards, had significantly shorter viral shedding duration compared with those without LPV/r treatment (median 19 days<jats:italic>versus</jats:italic>28.5 days; log-rank p<0.001).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Older age and the lack of LPV/r treatment were independently associated with prolonged SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Earlier administration of LPV/r treatment could shorten viral shedding duration.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
8
]
]
},
"alternative-id": [
"10.1183/13993003.00799-2020"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xiao-Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Ya-nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dan",
"given": "Bi-tang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Guo-jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Yong-hua",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Respiratory Journal",
"container-title-short": "Eur Respir J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"publications.ersnet.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-19T20:37:04Z",
"timestamp": 1589920624000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-24T07:33:55Z",
"timestamp": 1740382435000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-22T16:47:48Z",
"timestamp": 1747932468200,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 112,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1589846400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1183/13993003.00799-2020",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "81",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2000799",
"prefix": "10.1183",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "European Respiratory Society (ERS)",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report – 94 . www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200423-sitrep-94-covid-19.pdf Date last updated: 23 April 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4372",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00398-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.9"
},
{
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.10",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Chinese management guideline for COVID-19 (version 6.0). www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202002/8334a8326dd94d329df351d7da8aefc2/files/b218cfeb1bc54639af227f922bf6b817.pdf Date last updated: 19 February 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2602.190697",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.12",
"unstructured": "Wu C , Chen X , Cai Y , et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med 2020; in press [ https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994 ]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/432007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/503843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6",
"article-title": "Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Nat Comm",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03011-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiv392",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiy115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024102101415435000_56.1.2000799.19"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.03.22.20040832",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://publications.ersnet.org/lookup/doi/10.1183/13993003.00799-2020"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding and impact of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment in hospitalised non-critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1183/ers-crossmark-policy",
"volume": "56"
}