Slower Recovery with Early Lopinavir/Ritonavir use in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study
et al., Pediatric Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7, Apr 2022
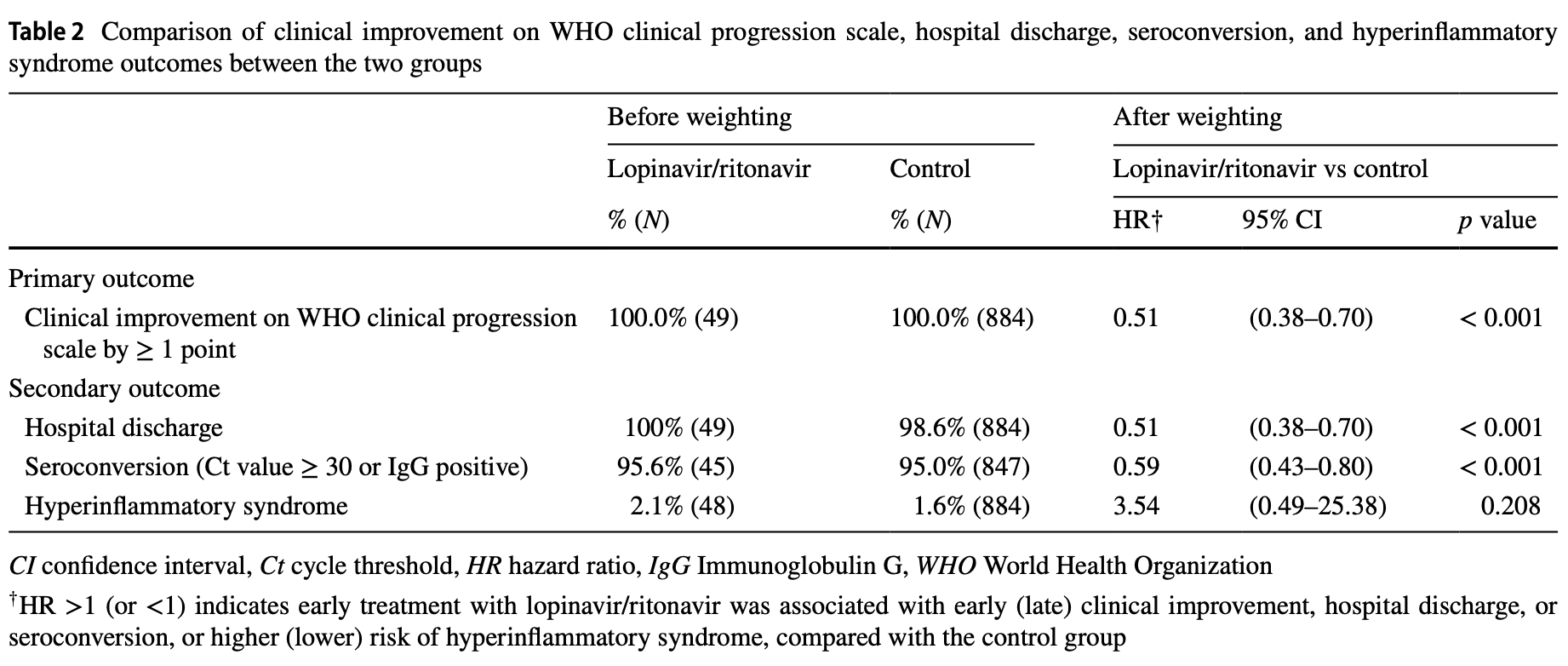
Retrospective 933 pediatric COVID-19 patients in Hong Kong showing worse outcomes with early lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) use.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 96.1% higher, HR 1.96, p < 0.001, treatment 49, control 884, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score weighting.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 96.1% higher, HR 1.96, p < 0.001, treatment 49, control 884, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score weighting.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wong et al., 16 Apr 2022, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 21 January, 2020 - 31 January, 2021.
Contact: carlosho@hku.hk.
Slower Recovery with Early Lopinavir/Ritonavir use in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study
Pediatric Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7
Objectives There was initially insufficient understanding regarding suitable pharmacological treatment for pediatric Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Lopinavir-ritonavir (LPV/r) was originally used for the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infection. It was also used in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) with positive results. Nonetheless, results from recent randomized controlled trials and observational studies on COVID-19 patients were unfavorable. We sought to evaluate the clinical outcomes associated with early treatment with LPV/r for pediatric COVID-19 patients. Study Design A total of 933 COVID-19 patients aged ≤ 18 years were admitted between 21 January 2020 and 31 January 2021 in Hong Kong. Exposure was receiving LPV/r within the first two days of admission. Time to clinical improvement, hospital discharge, seroconversion and hyperinflammatory syndrome, cumulative costs, and hospital length of stay were assessed. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard and linear models were performed to estimate hazard ratios (HR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) of time-to-event and continuous outcomes, respectively. Results LPV/r users were associated with longer time to clinical improvement (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.38-0.70; p < 0.001), hospital discharge (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.38-0.70; p < 0.001) and seroconversion (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.43-0.80; p < 0.001) when compared with controls. LPV/r users were also associated with prolonged hospital length of stay (6.99 days, 95% CI 6.23-7.76; p < 0.001) and higher costs at 30 days (US$11,709 vs US$8270; p < 0.001) as opposed to controls. Conclusion Early treatment with LPV/r for pediatric COVID-19 patients was associated with longer time to clinical improvement. Our study advocates the recommendation against LPV/r use for pediatric patients across age groups.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s40272-022-00500-7 .
Declarations Author Contributors' Statement Dr CKHW conceptualized, designed the study, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Mr MCHL, Miss ACYK and Miss AYCL searched literatures, drafted the initial manuscript, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Miss KTKL reviewed and revised the manuscript. Mr ICHA and Mr SHC conducted data analysis, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Miss XX, Mr EHYL and Prof. BJC reviewed and revised the manuscript. Dr MYWK provided clinical input.
Conflict of interest
Ethical approval and informed consent The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (Reference No. UW . Given the extraordinary nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, individual patient informed consent was not required for this retrospective cohort study using anonymized data.
Data sharing statement The data that support the findings of this study were provided by the Hong Kong Hospital Authority. Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study. Deidentified individual participant data will not be made available.
Availability of Data and Material The data that supported the findings of this study were provided by the Hong Kong Hospital Authority but restrictions apply to the availability of these..
References
Aitken, Morgan, Gene-specific effects of inflammatory cytokines on cytochrome P450 2C, 2B6 and 3A4 mRNA levels in human hepatocytes, Drug Metab Dispos, doi:10.1124/dmd.107.015511
Austin, Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations, Biometr J J Math Methods Biosci
Barragan, Podzamczer, Lopinavir/ritonavir: a protease inhibitor for HIV-1 treatment, Expert Opin Pharmacother, doi:10.1517/14656566.9.13.2363
Boffito, Back, Blaschke, Protein binding in antiretroviral therapies, AIDS Res Hum Retrovirus
Bourgeois, Gutiérrez-Sacristán, Keller, International analysis of electronic health records of children and youth hospitalized with COVID-19 infection in 6 countries, JAMA Netw Open
Cao, Wang, Wen, A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Chandwani, Shuter, Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: a review, Ther Clin Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/tcrm.s3285
Cheng, Morgan, Hepatic cytochrome P450 regulation in disease states, Curr Drug Metab, doi:10.2174/1389200013338676
Chiotos, Hayes, Kimberlin, Multicenter initial guidance on use of antivirals for children with coronavirus disease 2019/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax
Chua, Wong, Lam, Clinical characteristics and transmission of COVID-19 in children and youths during 3 waves of outbreaks in Hong Kong, JAMA Netw Open
Croxtall, Perry, Lopinavir/Ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV-1 infection, Drugs, doi:10.2165/11204950-000000000-00000
De Souza, Nadal, Nogueira, Pereira, Brandão, Clinical manifestations of children with COVID-19: a systematic review, Pediatr Pulmonol
Deb, Arrighi, Potential effects of COVID-19 on cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism and disposition in infected patients, Eur J Drug Metabol Pharmacokinet
Dong, Mo, Hu, Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China, Pediatrics
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med
Gao, Wang, Wang, Brief report: retrospective evaluation on the efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine to treat nonsevere COVID-19 patients, J Acquir Immune Def Syndromes
Goldman, Aldrich, Hagmann, Compassionate use of remdesivir in children with severe COVID-19, Pediatrics
Gupta, Wang, Hayek, Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252
Henry, Benoit, De Oliveira, Laboratory abnormalities in children with mild and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pooled analysis and review, Clin Biochem
Horby, Mafham, Bell, Lopinavir-ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol
Hung, Lung, Tso, Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial, Lancet
Karolyi, Omid, Pawelka, High dose lopinavir/ritonavir does not lead to sufficient plasma levels to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Original research, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.704767
Kaushik, Aydin, Derespina, Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multi-institutional study from New York City, J Pediatr
Lim, Jeon, Shin, Case of the index patient who caused tertiary transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea: the application of lopinavir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia monitored by quantitative RT-PCR, J Korean Med Sci
Lin, Niu, Zhang, Influence of lncRNA MALAT1 on septic lung injury in mice through p38 MAPK/p65 NF-κB pathway, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Lu, Zhou, Zhang, Safety and efficacy of oral lopinavir/ritonavir in pediatric patients with coronavirus disease: a nationwide comparative analysis, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Ludvigsson, Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults, Acta Paediatr
Maciorowski, Idrissi, Gupta, A review of the preclinical and clinical efficacy of Remdesivir, Hydroxychloroquine, and Lopinavir-Ritonavir treatments against COVID-19, SLAS Discov Adv Sci Drug Discov
Meini, Pagotto, Longo, Vendramin, Pecori et al., Role of Lopinavir/Ritonavir in the treatment of Covid-19: a review of current evidence, guideline recommendations, and perspectives, J Clin Med
Monedero, Gea, Castro, Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03422-3
Nutho, Mahalapbutr, Hengphasatporn, Why are lopinavir and ritonavir effective against the newly emerged coronavirus 2019? Atomistic insights into the inhibitory mechanisms, Biochemistry
Renoux, Azoulay, Suissa, Biases in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: designing real-world evidence studies, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwab028
Rubens, Akindele, Tschudy, Sick-Samuels, Acute covid-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, Bmj
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA
Sevilla-Castillo, Roque-Reyes, Romero-Lechuga, Both chloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir are ineffective for COVID-19 treatment and combined worsen the pathology: a single-center experience with severely ill patients, BioMed Res Int
Shane, Sato, Kao, A pediatric infectious diseases perspective of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children, J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc
Shehu, Lu, Wang, Pregnane X receptor activation potentiates ritonavir hepatotoxicity, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/jci128274
Venturini, Montagnani, Garazzino, Treatment of children with COVID-19: position paper of the Italian Society of Pediatric Infectious Disease, Ital J Pediatr
Webb, Peltan, Jensen, Clinical criteria for COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: a cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Wilde, Jochmans, Posthuma, Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Wong, Au, Cheng, Remdesivir use and risks of acute kidney injury and acute liver injury among patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a self-controlled case series study, Aliment Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.16894
Wong, Lau, Au, Optimal timing of remdesivir initiation in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) administered with dexamethasone, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab728
Wong, Lau, Au, Xiong, Lau et al., Clinical improvement, outcomes, antiviral activity, and costs associated with early treatment with remdesivir for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab631
Wood, Flexner, HIV-protease inhibitors, N Engl J Med
Wu, Ma, Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Ye, Luo, Xia, Clinical efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7",
"ISSN": [
"1174-5878",
"1179-2019"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7",
"alternative-id": [
"500"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "13 March 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 2,
"value": "16 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Author Contributors’ Statement",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Dr CKHW conceptualized, designed the study, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Mr MCHL, Miss ACYK and Miss AYCL searched literatures, drafted the initial manuscript, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Miss KTKL reviewed and revised the manuscript. Mr ICHA and Mr SHC conducted data analysis, reviewed and revised the manuscript. Miss XX, Mr EHYL and Prof. BJC reviewed and revised the manuscript. Dr MYWK provided clinical input."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Funding/Support",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "We received financial support from the Health and Medical Research Fund, Food and Health Bureau, Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (Grant no. COVID190210)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Dr Wong, Mr Low, Miss Kwok, Miss Lui, Miss Lau, Mr Au, Mr Chung, Miss Xiong, Mr Lau, Prof. Cowling and Dr Kwan have no conflicts of interest to disclose."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval and informed consent",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (Reference No. UW 20-493). Given the extraordinary nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, individual patient informed consent was not required for this retrospective cohort study using anonymized data."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Data sharing statement",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 6,
"value": "The data that support the findings of this study were provided by the Hong Kong Hospital Authority. Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study. Deidentified individual participant data will not be made available."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Availability of Data and Material",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 7,
"value": "The data that supported the findings of this study were provided by the Hong Kong Hospital Authority but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Hong Kong Hospital Authority."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 8,
"value": "All authors contributed to the interpretation of the analysis, critically reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Code availability",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 9,
"value": "All statistical analyses were performed using STATA Version 16 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX)."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6895-6071",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Carlos K. H.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Low",
"given": "Marshall C. H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kwok",
"given": "Ashley C. Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lui",
"given": "Angel Y. C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4412-2969",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Kristy T. K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5904-8322",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Au",
"given": "Ivan C. H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9418-7448",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Xi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1669-4479",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Matthew S. H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1476-9625",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kwan",
"given": "Mike Y. W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6688-9637",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Eric H. Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6297-7154",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cowling",
"given": "Benjamin J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pediatric Drugs",
"container-title-short": "Pediatr Drugs",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-16T03:33:01Z",
"timestamp": 1650079981000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-05T01:11:39Z",
"timestamp": 1651713099000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100005847",
"award": [
"COVID190210"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100005847",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Health and Medical Research Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T13:22:50Z",
"timestamp": 1740144170456,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1650067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1650067200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "269-280",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "500_CR1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 23 Feb 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15270",
"author": "JF Ludvigsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1088",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr",
"key": "500_CR2",
"unstructured": "Ludvigsson JF. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1088–95.",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n385",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "500_CR3",
"unstructured": "Rubens JH, Akindele NP, Tschudy MM, Sick-Samuels AC. Acute covid-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Bmj. 2021;372"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8824",
"author": "GT Chua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e218824",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "500_CR4",
"unstructured": "Chua GT, Wong JSC, Lam I, et al. Clinical characteristics and transmission of COVID-19 in children and youths during 3 waves of outbreaks in Hong Kong. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(5):e218824–e218824.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13052-020-00900-w",
"author": "E Venturini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ital J Pediatr",
"key": "500_CR5",
"unstructured": "Venturini E, Montagnani C, Garazzino S, et al. Treatment of children with COVID-19: position paper of the Italian Society of Pediatric Infectious Disease. Ital J Pediatr. 2020;46(1):1–11.",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.06.045",
"author": "S Kaushik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr",
"key": "500_CR6",
"unstructured": "Kaushik S, Aydin SI, Derespina KR, et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multi-institutional study from New York City. J Pediatr. 2020;224:24.",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26232",
"author": "B Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "250",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "500_CR7",
"unstructured": "Hu B, Huang S, Yin L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2021;93(1):250–6.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00160",
"author": "B Nutho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1769",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "500_CR8",
"unstructured": "Nutho B, Mahalapbutr P, Hengphasatporn K, et al. Why are lopinavir and ritonavir effective against the newly emerged coronavirus 2019? Atomistic insights into the inhibitory mechanisms. Biochemistry. 2020;59(18):1769–79.",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"author": "WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "500_CR9",
"unstructured": "WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19—interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(6):497–511.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/8821318",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "500_CR10",
"unstructured": "Sevilla-Castillo F, Roque-Reyes OJ, Romero-Lechuga F, et al. Both chloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir are ineffective for COVID-19 treatment and combined worsen the pathology: a single-center experience with severely ill patients. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAI.0000000000002452",
"author": "G Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "239",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Acquir Immune Def Syndromes.",
"key": "500_CR11",
"unstructured": "Gao G, Wang A, Wang S, et al. Brief report: retrospective evaluation on the efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine to treat nonsevere COVID-19 patients. J Acquir Immune Def Syndromes. 2020;85(2):239.",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2472555220958385",
"author": "D Maciorowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1108",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "SLAS Discov Adv Sci Drug Discov",
"key": "500_CR12",
"unstructured": "Maciorowski D, Idrissi SZE, Gupta Y, et al. A review of the preclinical and clinical efficacy of Remdesivir, Hydroxychloroquine, and Lopinavir-Ritonavir treatments against COVID-19. SLAS Discov Adv Sci Drug Discov. 2020;25(10):1108–22.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03011-14",
"author": "AH De Wilde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4875",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "500_CR13",
"unstructured": "De Wilde AH, Jochmans D, Posthuma CC, et al. Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(8):4875–84.",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "JM Sanders",
"first-page": "1824",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "500_CR14",
"unstructured": "Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824–36.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "500_CR15",
"unstructured": "Lopinavir/Ritonavir and Other HIV Protease Inhibitors. Updated 11/02/2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/antiviral-therapy/lopinavir-ritonavir-and-other-hiv-protease-inhibitors/. Accessed 13 Aug 2021."
},
{
"key": "500_CR16",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living Guideline (World Health Organization). 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4",
"author": "PW Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "10259",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "500_CR17",
"unstructured": "Horby PW, Mafham M, Bell JL, et al. Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2020;396(10259):1345–52.",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"author": "B Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "500_CR18",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, et al. A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(19):1787–99.",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e79",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "500_CR19",
"unstructured": "Lim J, Jeon S, Shin H-Y, et al. Case of the index patient who caused tertiary transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea: the application of lopinavir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia monitored by quantitative RT-PCR. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(6)"
},
{
"author": "XT Ye",
"first-page": "3390",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "500_CR20",
"unstructured": "Ye XT, Luo YL, Xia SC, et al. Clinical efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):3390–6.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "L Lin",
"first-page": "1296",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "500_CR21",
"unstructured": "Lin L, Niu G, Zhang X. Influence of lncRNA MALAT1 on septic lung injury in mice through p38 MAPK/p65 NF-κB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3):1296–304.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jpids/piaa099",
"author": "AL Shane",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "596",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc.",
"key": "500_CR22",
"unstructured": "Shane AL, Sato AI, Kao C, et al. A pediatric infectious diseases perspective of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children. J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc. 2020;9(5):596–608.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-047803",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "500_CR23",
"unstructured": "Goldman DL, Aldrich ML, Hagmann SH, et al. Compassionate use of remdesivir in children with severe COVID-19. Pediatrics. 2021;147(5)."
},
{
"key": "500_CR24",
"unstructured": "Interim Drug Treatment Handbook for COVID-19. Department of Pharmacy, Queen Mary Hospital, Hospital Authority, Hong Kong. 2021."
},
{
"key": "500_CR25",
"unstructured": "Updated Consensus Recommendations on Criteria for Releasing Confirmed COVID-19 Patients from Isolation (July 29, 2020) In: Scientific Committee on Emerging and Zoonotic Diseases. Centre for Health Protection, Department of Health, Hong Kong. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252",
"author": "S Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "500_CR26",
"unstructured": "Gupta S, Wang W, Hayek SS, et al. Association between early treatment with tocilizumab and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181(1):41–51. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6252.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03422-3",
"author": "P Monedero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "500_CR27",
"unstructured": "Monedero P, Gea A, Castro P, et al. Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03422-3.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwab028",
"author": "C Renoux",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1452",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "500_CR28",
"unstructured": "Renoux C, Azoulay L, Suissa S. Biases in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19: designing real-world evidence studies. Am J Epidemiol. 2021;190(8):1452–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwab028.",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "500_CR29",
"unstructured": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(8):e192–e197. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30483-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30343-X",
"author": "BJ Webb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e754",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "500_CR30",
"unstructured": "Webb BJ, Peltan ID, Jensen P, et al. Clinical criteria for COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: a cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(12):e754–63.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "PC Austin",
"first-page": "171",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biometr J J Math Methods Biosci.",
"key": "500_CR31",
"unstructured": "Austin PC. Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations. Biometr J J Math Methods Biosci. 2009;51(1):171–84.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jpids/piaa045",
"author": "K Chiotos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "701",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc.",
"key": "500_CR32",
"unstructured": "Chiotos K, Hayes M, Kimberlin DW, et al. Multicenter initial guidance on use of antivirals for children with coronavirus disease 2019/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc. 2020;9(6):701–15.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-0702",
"author": "Y Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics.",
"key": "500_CR33",
"unstructured": "Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, et al. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics. 2020;145(6):e20200702.",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.24885",
"author": "TH de Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1892",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Pulmonol",
"key": "500_CR34",
"unstructured": "de Souza TH, Nadal JA, Nogueira RJ, Pereira RM, Brandão MB. Clinical manifestations of children with COVID-19: a systematic review. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55(8):1892–9.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12596",
"author": "FT Bourgeois",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2112596",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "500_CR35",
"unstructured": "Bourgeois FT, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Keller MS, et al. International analysis of electronic health records of children and youth hospitalized with COVID-19 infection in 6 countries. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(6):e2112596–e2112596.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.05.012",
"author": "BM Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Biochem",
"key": "500_CR36",
"unstructured": "Henry BM, Benoit SW, de Oliveira MHS, et al. Laboratory abnormalities in children with mild and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pooled analysis and review. Clin Biochem. 2020;81:1–8.",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199804303381808",
"author": "AJJMD Wood",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1281",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "500_CR37",
"unstructured": "Wood AJJMD, Flexner CMD. HIV-protease inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(18):1281–1293.",
"volume": "338",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/tcrm.s3285",
"author": "A Chandwani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1023",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ther Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "500_CR38",
"unstructured": "Chandwani A, Shuter J. Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: a review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008;4(5):1023–33. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s3285.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/14656566.9.13.2363",
"author": "P Barragan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2363",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Pharmacother",
"key": "500_CR39",
"unstructured": "Barragan P, Podzamczer D. Lopinavir/ritonavir: a protease inhibitor for HIV-1 treatment. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(13):2363–75. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.9.13.2363.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"author": "C Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "252",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "500_CR40",
"unstructured": "Chu C, Cheng V, Hung I, et al. Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings. Thorax. 2004;59(3):252–6.",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4",
"author": "IFN Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1695",
"issue": "10238",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "500_CR41",
"unstructured": "Hung IF-N, Lung K-C, Tso EY-K, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10238):1695–1704.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab631",
"author": "CKH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"key": "500_CR42",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Lau KTK, Au ICH, Xiong X, Lau EHY, Cowling BJ. Clinical improvement, outcomes, antiviral activity, and costs associated with early treatment with remdesivir for patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin Infect Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab631.",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.16894",
"author": "CKH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther.",
"key": "500_CR43",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Au ICH, Cheng WY, et al. Remdesivir use and risks of acute kidney injury and acute liver injury among patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a self-controlled case series study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.16894.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab728",
"author": "CKH Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"key": "500_CR44",
"unstructured": "Wong CKH, Lau KTK, Au ICH, et al. Optimal timing of remdesivir initiation in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) administered with dexamethasone. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab728.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "500_CR45",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. Therapeutic management of hospitalized adults with COVID-19. Updated 16/12/2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management/hospitalized-adults--therapeutic-management/. Accessed 07 Feb 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9072050",
"author": "S Meini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2050",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "500_CR46",
"unstructured": "Meini S, Pagotto A, Longo B, Vendramin I, Pecori D, Tascini C. Role of Lopinavir/Ritonavir in the treatment of Covid-19: a review of current evidence, guideline recommendations, and perspectives. J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2050.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"author": "L Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e21",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med.",
"key": "500_CR47",
"unstructured": "Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e21.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "J Lu",
"first-page": "549",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "500_CR48",
"unstructured": "Lu J, Zhou A, Zhang X, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral lopinavir/ritonavir in pediatric patients with coronavirus disease: a nationwide comparative analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(1):549–55.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.704767",
"author": "M Karolyi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Original research. Front Pharmacol.",
"key": "500_CR49",
"unstructured": "Karolyi M, Omid S, Pawelka E, et al. High dose lopinavir/ritonavir does not lead to sufficient plasma levels to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Original research. Front Pharmacol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.704767.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0403596101",
"author": "C-Y Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10012",
"issue": "27",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "500_CR50",
"unstructured": "Wu C-Y, Jan J-T, Ma S-H, et al. Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101(27):10012–7.",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/088922203769232629",
"author": "M Boffito",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "825",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "AIDS Res Hum Retrovirus",
"key": "500_CR51",
"unstructured": "Boffito M, Back DJ, Blaschke TF, et al. Protein binding in antiretroviral therapies. AIDS Res Hum Retrovirus. 2003;19(9):825–35.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/11204950-000000000-00000",
"author": "JD Croxtall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1885",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "500_CR52",
"unstructured": "Croxtall JD, Perry CM. Lopinavir/Ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV-1 infection. Drugs. 2010;70(14):1885–915. https://doi.org/10.2165/11204950-000000000-00000.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.107.015511",
"author": "AE Aitken",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1687",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab Dispos",
"key": "500_CR53",
"unstructured": "Aitken AE, Morgan ET. Gene-specific effects of inflammatory cytokines on cytochrome P450 2C, 2B6 and 3A4 mRNA levels in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007;35(9):1687–93. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.107.015511.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389200013338676",
"author": "PY Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Drug Metab",
"key": "500_CR54",
"unstructured": "Cheng PY, Morgan ET. Hepatic cytochrome P450 regulation in disease states. Curr Drug Metab. 2001;2(2):165–83. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200013338676.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci128274",
"author": "AI Shehu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2898",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "500_CR55",
"unstructured": "Shehu AI, Lu J, Wang P, et al. Pregnane X receptor activation potentiates ritonavir hepatotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(7):2898–903. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci128274.",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13318-020-00668-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "500_CR56",
"unstructured": "Deb S, Arrighi S. Potential effects of COVID-19 on cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism and disposition in infected patients. Eur J Drug Metabol Pharmacokinet. 2021:1–19."
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40272-022-00500-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Slower Recovery with Early Lopinavir/Ritonavir use in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "24"
}