Real World Outcomes of Cancer Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection Receiving Monoclonal Antibodies
et al., Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, doi:10.6004/jnccn.2021.7309, Mar 2022
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
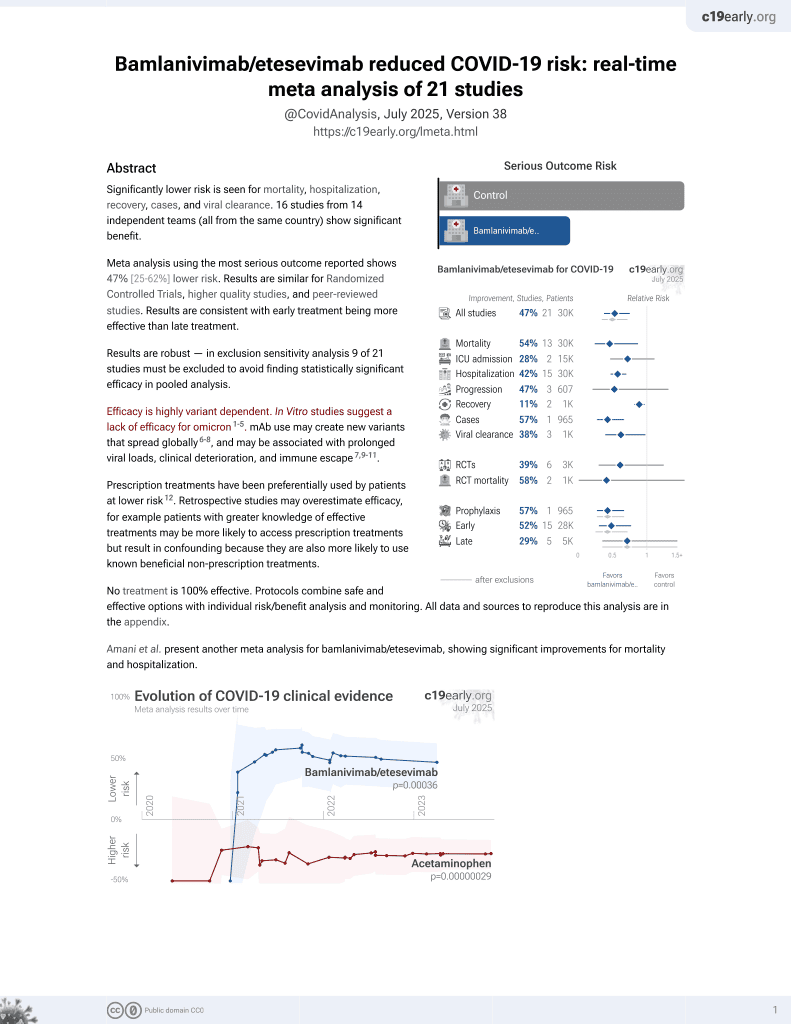
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
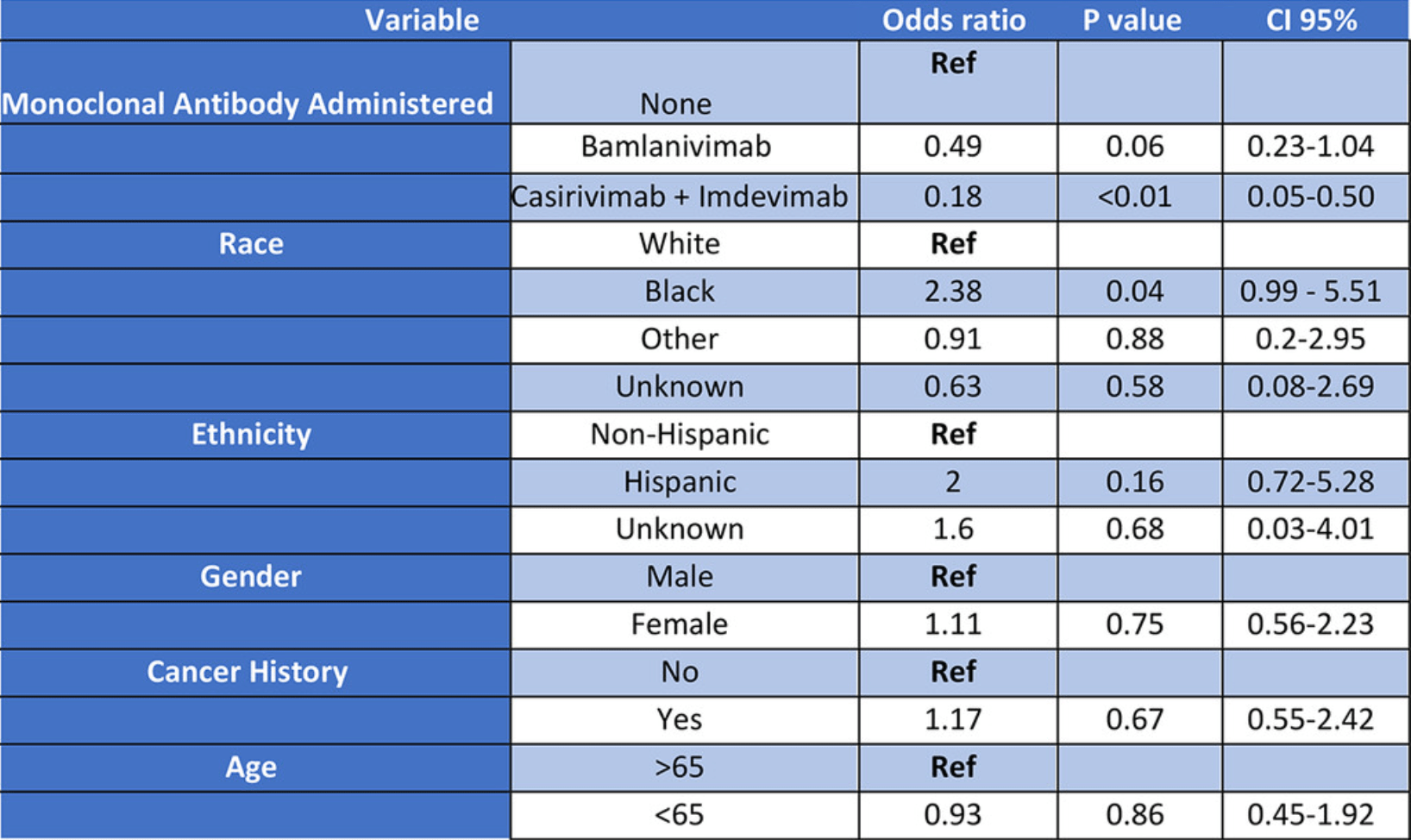
Retrospective 395 patients in the USA receiving casirivimab/imdevimab or bamlanivimab, showing lower risk of hospitalization with treatment, statistically significant for casirivimab/imdevimab.
Although the 51% lower hospitalization is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 42% lower hospitalization [30‑53%] from meta-analysis of the 15 hospitalization results to date.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers bamlanivimab/etesevimab and casirivimab/imdevimab.
|
risk of hospitalization, 51.0% lower, OR 0.49, p = 0.06, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Wilden et al., 31 Mar 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period December 2020 - July 2021.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.6004/jnccn.2021.7309",
"ISSN": [
"1540-1405",
"1540-1413"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2021.7309",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Wilden",
"given": "Alexa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Sannareddy",
"given": "Aishwarya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Hetal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Kansagra",
"given": "Shraddha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "Gurbakhash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Ramakrishnan",
"given": "Praveen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Prapti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "2 Jacobi Medical Center, Bronx, NY"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Ansh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "1 UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX"
}
],
"family": "Kansagra",
"given": "Ankit",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-31T11:49:36Z",
"timestamp": 1648727376000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-31T11:50:05Z",
"timestamp": 1648727405000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-04T00:56:40Z",
"timestamp": 1649033800757
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1540-1405"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1540-1413"
}
],
"issue": "3.5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3.5"
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/20/3.5/article-pHSR22-178.xml",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/20/3.5/article-pHSR22-178.xml",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4047",
"original-title": [],
"page": "HSR22-178",
"prefix": "10.6004",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Harborside Press, LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/20/3.5/article-pHSR22-178.xml"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Oncology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"HSR22-178: Real World Outcomes of Cancer Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection Receiving Monoclonal Antibodies"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "20"
}
wilden