Efficacy of Remdesivir in Covid-19 Patients; Multicenter Study in Lahore
et al., International Journal of Sciences, doi:10.18483/ijSci.2417, Nov 2020
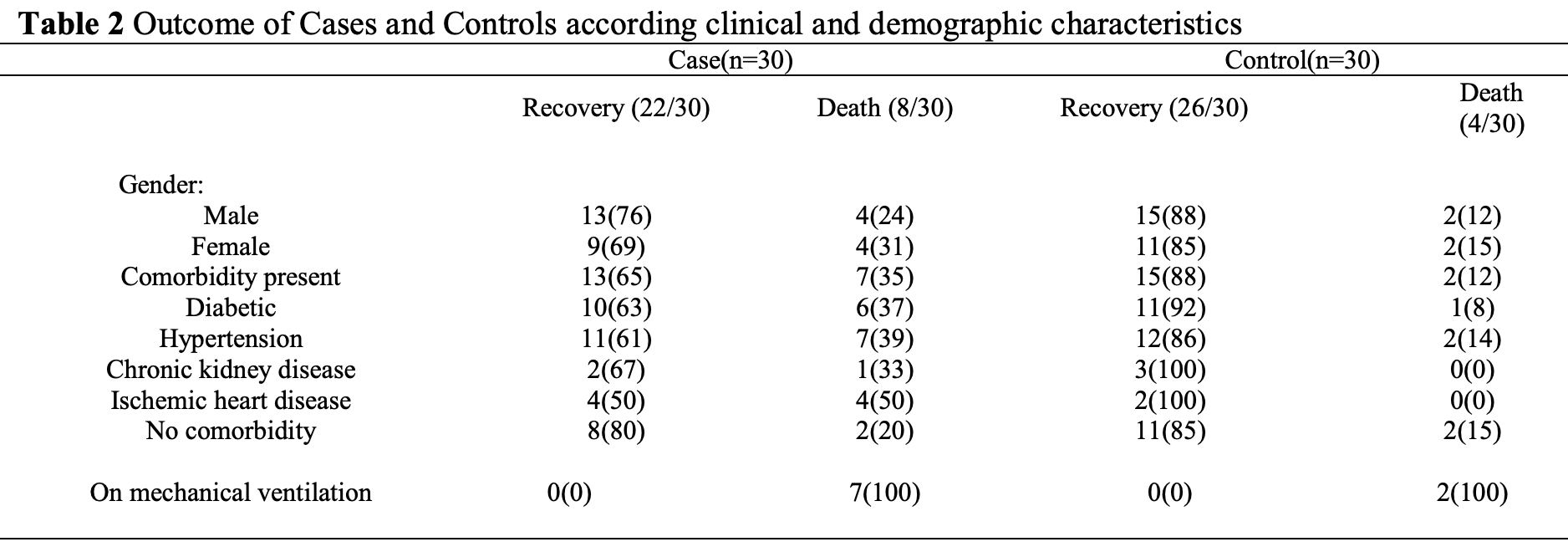
Small late stage (hospitalized, <12 days symptoms) remdesivir study showing non-statistically significant higher mortality with treatment.
No adjustments were made for differences in the groups. Remdesivir mean age was 49 vs. control 57. Baseline oxygen requirement was 13.4 liters treatment vs. 10.8 control. Potential confounding by indication.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.33, treatment 8 of 30 (26.7%), control 4 of 30 (13.3%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 250.0% higher, RR 3.50, p = 0.15, treatment 7 of 30 (23.3%), control 2 of 30 (6.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Ullah et al., 29 Nov 2020, retrospective, Pakistan, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Efficacy of Remdesivir in Covid-19 Patients; Multicenter Study in Lahore
International Journal of Sciences, doi:10.18483/ijsci.2417
Introduction: This Pandemic of Covid-19 has shaken the world and devastating and unpredictable nature of the disease and scenario becomes worse when we see limited treatment options for this disease. Objectives: The objective of the study was to assess the efficacy of Remdesivir in patients having early phase of the disease. Methodology: Study Settings: The study was conducted in two major tertiary care hospitals, Fatima Memorial Hospital, Bahria international Hospital, Lahore. Sample size & Sampling Technique: A total of 60 patients were selected for this study who were suffering from COVID 19, out of which 30 were given Remdesivir and 30 patients were kept in control group. Participants were enrolled in the study after fulfilling inclusion and exclusion criteria. It was Probability sampling. Study design: Non-randomized control interventional study. Data Analysis: Data was analyzed with respect to demographics and clinical characteristics. Outcome was observed in terms of recovery and death. Also, the oxygen requirement and respiratory rate was measured on presentation and on 14 th day of admission. Furthermore, coexisting conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, ischemic heart disease and chronic kidney disease were also considered regarding outcome in case group and control group. Results: Mean age of the study participants was 53.2 with standard deviation (SD)±14.6 years, whereas average age of cases was 49.2±15.1 and control 57.1±13.1 years. Male were 60% of the patients and 40% were females, whereas both cases and control had 57% males. The most common co existing disease was hypertension which attributed to 53% of the total sample size followed by diabetes which was present in 47% of the study participants. 23 (38%) participants did not have any coexisting disease. The data did not show any promises with Remdesivir therapy in patients with or without ventilatory support in comparison with participants who did not receive Remdesivir.
References
Adamsick, Remdesivir in patients with acute or chronic kidney disease and COVID-19, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, doi:.org/10.1681/asn.2020050589
Agostini, Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease, MBio, doi:.org/10.1128/mbio.00221-18
Beigel, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-preliminary report, The New England journal of medicine, doi:.org/10.1056/nejmc2022236
Brown, Broad spectrum antiviral Remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic delta coronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase, Antiviral research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2019
Cao, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:.org/10.1056/nejmc2008043
Goldman, Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:.org/10.1056/nejmc2022236
Grant, Geoghegan, Arbyn, Mohammed, Mcguinness et al., The Prevalence of Symptoms in 24,410 Adults Infected by the Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 148 Studies from 9 Countries, doi:org/10.2139/ssrn.3582819
Helmy, Fawzy, Elaswad, Sobieh, Kenney, The COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive review of taxonomy, genetics, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:1225./doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041225
Madsen, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report, The New England Journal of Medicine, doi:.org/10.1056/nejmc2022236
Rathore, Ghosh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a newly emerged pathogen: an overview, Pathogens and disease, doi:ftaa042.doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftaa042
Wang, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, The Lancet, doi:.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31022-9
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18483/ijsci.2417",
"ISSN": [
"2305-3925",
"2410-4477"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18483/ijSci.2417",
"alternative-id": [
"92020112417"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ullah",
"given": "Najeeb",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmad Khan",
"given": "Khurshid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "Javeid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rana",
"given": "Asim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bin Younis",
"given": "Bilal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asif",
"given": "Mohsin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeeshan Khan Chachar",
"given": "Aijaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "shan",
"given": "Falak",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Sciences",
"container-title-short": "ijSciences",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-26T15:46:49Z",
"timestamp": 1606405609000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-26T15:46:49Z",
"timestamp": 1606405609000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-03T18:11:39Z",
"timestamp": 1649009499856
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"member": "7748",
"original-title": [],
"page": "31-34",
"prefix": "10.18483",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"publisher": "Alkhaer Publications",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.ijsciences.com/pub/article/2417"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Materials Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of Remdesivir in Covid-19 Patients; Multicenter Study in Lahore",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "9"
}