Dose-dependent Oxidative Damage of Molnupiravir (Antiviral Drug for Treatment of COVID-19) in Lung, Liver, Heart, and Kidney Tissues in Rats
et al., Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, doi:10.33696/Pharmacol.4.044, Nov 2023
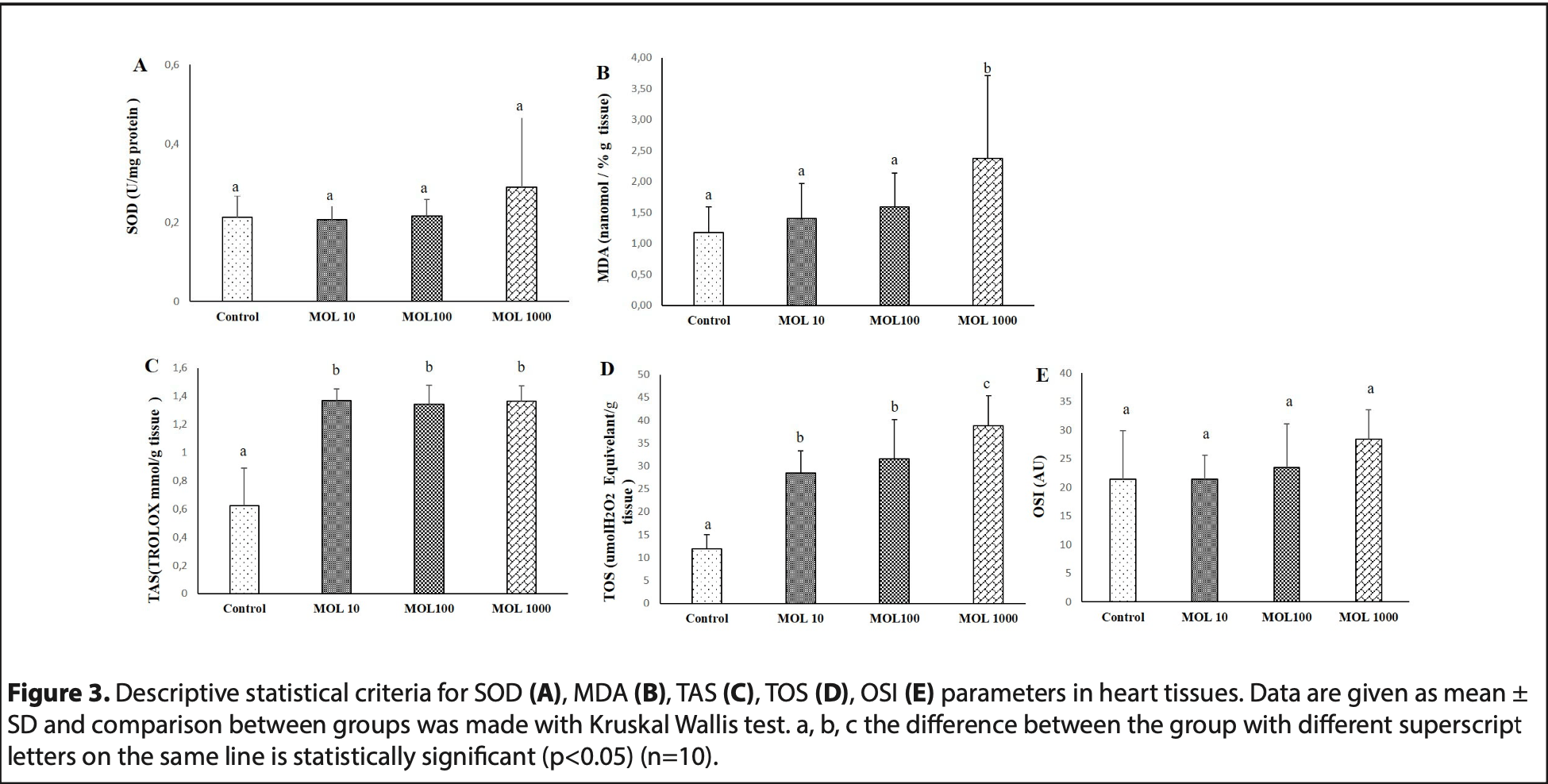
Rat study showing dose-dependent oxidative damage with molnupiravir in lung, liver, heart, and kidney tissues. Authors found that molnupiravir decreased SOD activity and increased MDA, TOS, and OSI levels in multiple tissues, indicating oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. ALT levels also increased in liver tissue at higher doses. The study suggests molnupiravir may cause tissue damage by disrupting oxidant/antioxidant balance in a dose-dependent manner. Lower doses, shorter treatment, or co-administration with antioxidants may reduce potential adverse effects.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Tanbek et al., 4 Nov 2023, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Contact: suleyman.sandal@inonu.edu.tr.
Dose-dependent Oxidative Damage of Molnupiravir (Antiviral Drug for Treatment of COVID-19) in Lung, Liver, Heart, and Kidney Tissues in Rats
did not respond to treatment and vaccines, which emerged in Wuhan, the capital of China's Hubei region, in December 2019. The virus isolated as the cause of the disease was determined as SARS-CoV2. A global epidemic was declared
Confict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval This study was carried out with approval of Ethical Committee of Experimental Animals of the Faculty of Medicine in Inonu University (2022/7-3). The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose.
Author Contributions Conceptualization, K.T.; methodology, K.T. software, K.T.;
References
Abdi, Jalilian, Sarbarzeh, Zjdr, Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences
Adams, Franco, Agjeb, Medicine, Reactive nitrogen species in cellular signaling
Antelmann, Helmann, Thiol-based redox switches and gene regulation
Arslan, Yaşar, Çolak, Yoloğlu, WSSPAS: an interactive web application for sample size and power analysis with R using shiny
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med
Cecchini, Aljmh, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression
Delgado-Roche, Fjaomr, Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection
Demirbag, Yilmaz, Erel, Gultekin, Asci et al., The relationship between potency of oxidative stress and severity of dilated cardiomyopathy, Can J Cardiol
Ekici, Temelli, Parlakpinar, Samdanci, Polat et al., Beneficial effects of aminoguanidine on radiotherapy-induced kidney and testis injury, Andrologia
Erel, A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status, Clinical biochemistry
Erel, A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cation, Clinical biochemistry
Erel, A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions, Clinical biochemistry
Esterbauer, Cheeseman, Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal, Methods Enzymol
Fischer, Eron, Holman, Cohen, Fang et al., Molnupiravir, an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19
Fischer, Eron, Holman, Cohen, Fang et al., an Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19, medRxiv
Focosi, Molnupiravir: From Hope to Epic Fail?, Viruses
Gordon, Tchesnokov, Schinazi, Gotte, Molnupiravir promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis via the RNA template, J Biol Chem
Khoo, Fitzgerald, Fletcher, Ewings, Jaki et al., Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a Phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study, J Antimicrob Chemother
Ks, Aa, Kalala, Pm, Sabarathinam, Drug interaction risk between cardioprotective drugs and drugs used in treatment of COVID-19: A evidence-based review from six databases, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Lavillette, Barbouche, Yao, Boson, Cosset et al., Significant redox insensitivity of the functions of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein: comparison with HIV envelope
Law, Ho, Law, Cheung, Gastrointestinal and hepatic side effects of potential treatment for COVID-19 and vaccination in patients with chronic liver diseases, World J Hepatol
Mihalopoulos, Dogra, Mohamed, Badani, Njeuf, COVID-19 and kidney disease: molecular determinants and clinical implications in renal cancer
Ntyonga-Pono, COVID-19 infection and oxidative stress: an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment
Ozdemir, Gokce, Taslidere, Tanbek, Gul et al., Does Chrysin prevent severe lung damage in Hyperoxia-Induced lung injury Model?, International immunopharmacology
Painter, Natchus, Cohen, Holman, Painter, Developing a direct acting, orally available antiviral agent in a pandemic: the evolution of molnupiravir as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Curr Opin Virol
Pourkarim, Pourtaghi-Anvarian, Rezaee, Molnupiravir: A new candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Pharmacol Res Perspect
Prasad, Muralidhara, Protective effects of geraniol (a monoterpene) in a diabetic neuropathy rat model: attenuation of behavioral impairments and biochemical perturbations, J Neurosci Res
Reedy, Loo, Levine, AST/ALT ratio > or = 1 is not diagnostic of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C, Dig Dis Sci
Schafer, Martinez, Won, Moreira, Brown et al., Therapeutic efficacy of an oral nucleoside analog of remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis in mice, bioRxiv
Schieber, Nsjcb, ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress
Schou, Joca, Wegener, Richter, Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 -A systematic review, Brain Behav Immun
Singh, Singh, Singh, Misra, Molnupiravir in COVID-19: A systematic review of literature, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Sun, Oberley, Li, A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase, Clin Chem
Tanbek, Ozerol, Bilgic, Iraz, Sahin et al., Protective effect of Nigella sativa oil against thioacetamide-induced liver injury in rats
Tanbek, Ozerol, Yilmaz, Yilmaz, Gul et al., Alpha lipoic acid decreases neuronal damage on brain tissue of STZ-induced diabetic rats, Physiol Behav
Tarnawski, Ahluwalia, Endothelial cells and blood vessels are major targets for COVID-19-induced tissue injury and spreading to various organs, World J Gastroenterol
Wen, Chen, Tang, Wang, Zhou et al., Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Ann Med
Yoshikawa, Yjjmaj, What is oxidative stress?
Çolak, Hjjotomc, Hayvan deneyleri: in vivo denemelerin bildirimi: ARRIVE Kılavuzu-Derleme
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.33696/pharmacol.4.044",
"ISSN": [
"2688-9609"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.33696/Pharmacol.4.044",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Molnupiravir (MOL) is an orally absorbed prodrug of the ribonucleoside analogue N-hydroxycytidine, which has in vitro activity against several coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and 2. It remains to be seen whether long term MOL has serious side effects. The side effects of MOL, which was the first to be allowed for oral use during the pandemic process, are not yet fully known. In this study, it was aimed to investigate the the mechanisms of possible dose-dependent damage on liver, lung, heart, and kidney tissues. \nFourty male Wistar albino rats were separated into four groups as Control, MOL10, MOL100, MOL1000. For five days, MOL (10-100-1000 mg/kg/day) was administered by oral gavaj. At the end of the five days rats were sacrificed and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and total bilirubin (TB) levels in serum were measured. Collected tissues (liver, lung, heart, and kidney) were evaluated to the malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant state (TAS), and total oxidant state (TOS), and oxidative stress indexes (OSI) were calculated. MOL administration showed significant improvement in liver, heart, and kidney in rats (p<0.05). SOD activities which were decreased in the MOL group, while MDA level increased in the MOL groups compared to the control group in all tissue (p<0.05). ALT was increased in the MOL group compared to the control group (p<0.05). Increase of TOS and OSI is statistically significant, but TAS was decreased in the MOL group compared to the control group (p<0.05). MOL used in virus treatment is dose-dependently effective on the oxidant/antioxidant system in tissues. For this reason, the use of antioxidants may be beneficial to reduce tissue damage that may occur in the use of MOL.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Inonu University, 44280 Malatya, Turkey,Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Inonu University, 44280 Malatya, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "TANBEK",
"given": "Kevser",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Inonu University, 44280 Malatya, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "SANDAL",
"given": "Suleyman",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Archives of Pharmacology and Therapeutics",
"container-title-short": "Arch Pharmacol Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-04T06:47:39Z",
"timestamp": 1699080459000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-04T06:47:40Z",
"timestamp": 1699080460000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-09T15:18:27Z",
"timestamp": 1725895107781
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.scientificarchives.com/about-us",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1699056000000
}
}
],
"member": "18993",
"original-title": [],
"page": "44-52",
"prefix": "10.33696",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Scientific Archives LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.scientificarchives.com/article/dose-dependent-oxidative-damage-of-molnupiravir-%28antiviral-drug-for-treatment-of-covid-19%29-in-lung-%2C-liver-%2C-heart-%2C-and-kidney-tissues-in-rats"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Dose-dependent Oxidative Damage of Molnupiravir (Antiviral Drug for Treatment of COVID-19) in Lung, Liver, Heart, and Kidney Tissues in Rats",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "5"
}