Cohort study to evaluate the effect of combination Vitamin D, Magnesium and Vitamin B12 (DMB) on progression to severe outcome in older COVID-19 patients
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017, Jun 2020 (preprint)
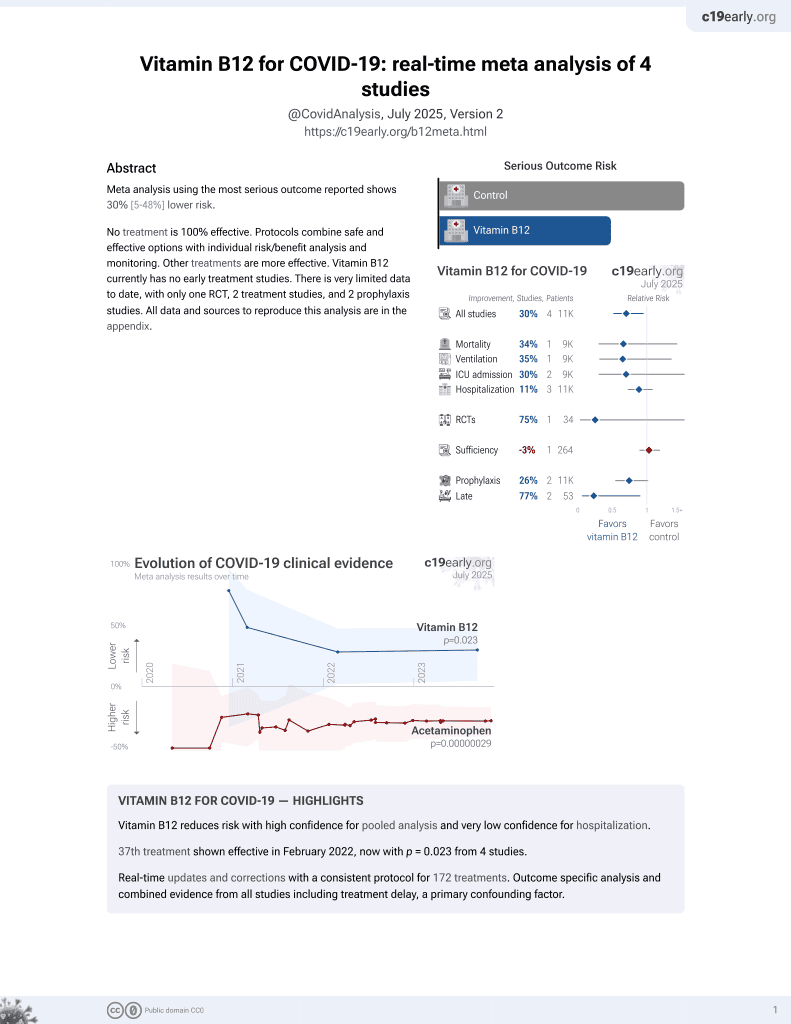
38th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2022, now with p = 0.023 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Observational study of 43 patients ≥50 years old, with 17 patients receiving vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 (DMB); and 26 control patients, showing a significantly lower need for oxygen therapy and ICU admission with treatment. DMB OR 0.20 [0.04-0.93] for oxygen therapy and/or intensive care support with multivariate analysis.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
combined treatments may contribute more to the effect seen.
Study covers vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 80.5% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.04, treatment 3 of 17 (17.6%), control 16 of 26 (61.5%), NNT 2.3, adjusted per study, multivariate.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 80.9% lower, RR 0.19, p = 0.07, treatment 1 of 17 (5.9%), control 8 of 26 (30.8%), NNT 4.0, no adjusted result available.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tan et al., 10 Jun 2020, retrospective, Singapore, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with magnesium and vitamin B12) - results of individual treatments may vary.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900720303002"
],
"article-number": "111017",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19)"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Chuen Wen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ho",
"given": "Liam Pock",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalimuddin",
"given": "Shirin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherng",
"given": "Benjamin Pei Zhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teh",
"given": "Yii Ean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thien",
"given": "Siew Yee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Hei Man",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tern",
"given": "Paul Jie Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandran",
"given": "Manju",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chay",
"given": "Jason Wai Mun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagarajan",
"given": "Chandramouli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sultana",
"given": "Rehena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Low",
"given": "Jenny Guek Hong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Heng Joo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-08T15:28:19Z",
"timestamp": 1599578899000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-05T21:44:17Z",
"timestamp": 1604612657000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-25T04:38:37Z",
"timestamp": 1711341517725
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 149,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900720303002?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900720303002?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111017",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0001",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"article-title": "Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis",
"author": "Verity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0002",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systemic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0003",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqy274",
"article-title": "Magnesium status and supplementation influence vitamin D status and metabolism: results from a randomized trial",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1258",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0004",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9149(99)00225-8",
"article-title": "Oral magnesium supplementation inhibits platelet-dependent thrombosis in patients with coronary artery disease",
"author": "Shechter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Am J Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0005",
"volume": "84",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2014.10.002",
"article-title": "Vitamin B12 as a modulator of gut microbial ecology",
"author": "Degnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "769",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0006",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency is prevalent in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Lau",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0007",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02441",
"article-title": "Potential role of gut microbiota in induction and regulation of innate immune memory",
"author": "Negi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2441",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0008",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota and Covid-19—possible link and implications",
"author": "Dhar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0009",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization [Epub ahead of print]",
"author": "Zuo",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111017_bib0010",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.06.01.20112334",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900720303002"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Cohort study to evaluate the effect of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 in combination on progression to severe outcomes in older patients with coronavirus (COVID-19)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "79-80"
}