A randomised, open-label trial of nebulised unfractionated heparin in patients mechanically ventilated for COVID-19
et al., Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, doi:10.1177/0310057X251322783, Mar 2025
59th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2025, now with p = 0.0077 from 3 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
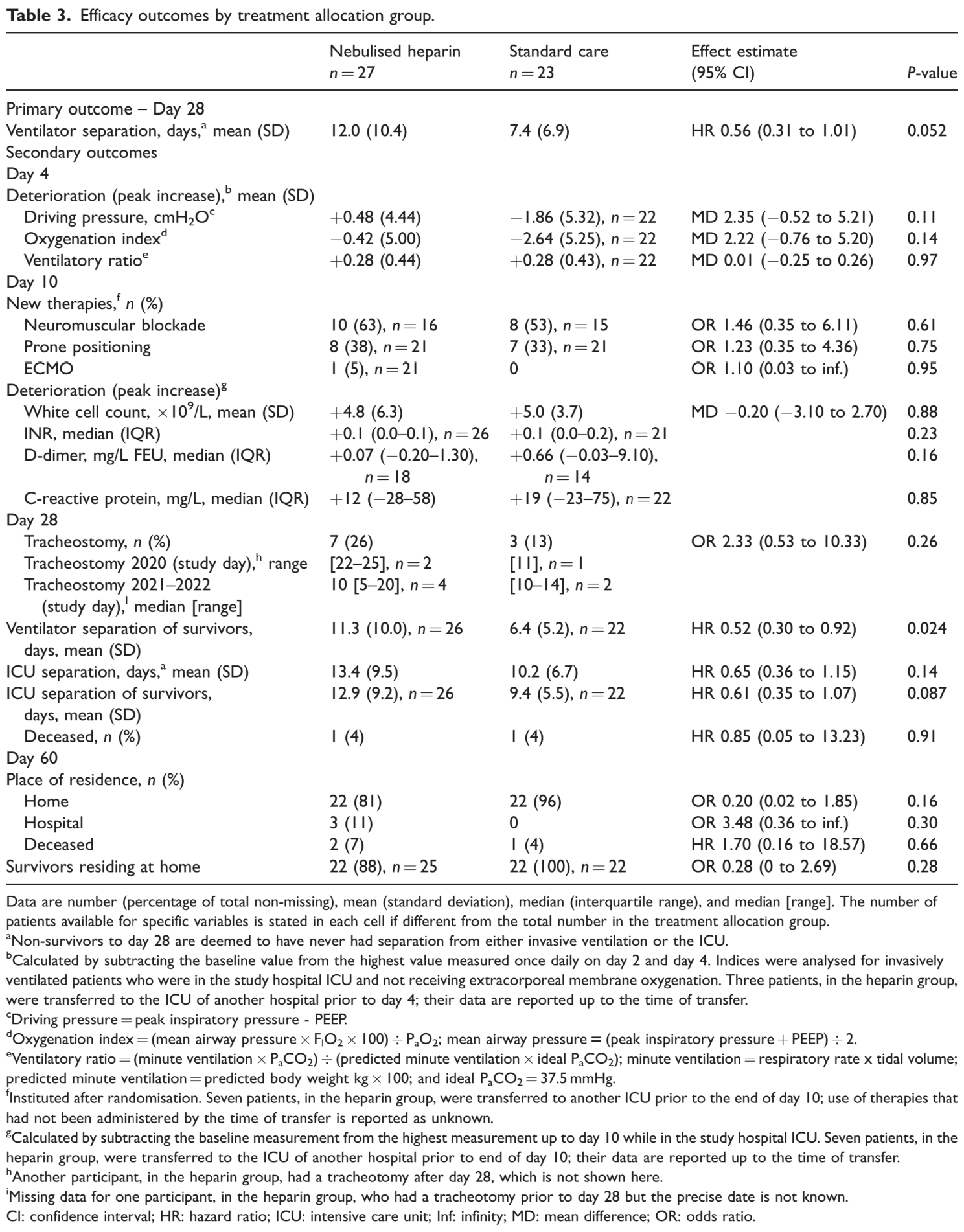
RCT 50 intubated COVID-19 patients showing no improvement with inhaled nebulized unfractionated heparin. Time to separation
from invasive ventilation among survivors to day 28 was significantly slower in the heparin group.
from invasive ventilation among survivors to day 28 was significantly slower in the heparin group.
|
risk of death, 70.4% higher, RR 1.70, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 27 (7.4%), control 1 of 23 (4.3%), day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 14.8% lower, RR 0.85, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 27 (3.7%), control 1 of 23 (4.3%), NNT 155, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Smith et al., 27 Mar 2025, Randomized Controlled Trial, Australia, peer-reviewed, median age 55.0, 8 authors, study period 1 July, 2020 - 23 March, 2022, average treatment delay 8.0 days.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0310057x251322783",
"ISSN": [
"0310-057X",
"1448-0271"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0310057X251322783",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n Nebulised unfractionated heparin (UFH) might reduce time to ventilator separation in patients with COVID-19 by reducing virus infectivity, pulmonary coagulopathy, and inflammation, but clinical trial data are limited. Between 1 July 2020 and 23 March 2022, we conducted, at two hospitals in Victoria, Australia, a randomised, parallel-group, open-label, controlled trial of nebulised UFH. Eligible patients were aged 18 years or more, intubated, under intensive care unit management, had a P\n <jats:sub>a</jats:sub>\n O\n <jats:sub>2</jats:sub>\n to F\n <jats:sub>I</jats:sub>\n O\n <jats:sub>2</jats:sub>\n ratio of 300 or less, had acute opacities affecting at least one lung quadrant and attributed to COVID-19, and were polymerase chain reaction-positive for SARS-CoV-2 or had further testing planned. The target sample size was 270, however, the trial was stopped due to slow recruitment. There were 50 enrolments, all of whom were analysed. The median age was 55 (interquartile range (IQR) 46–64) years, 28 (56%) were males, and 46 (92%) had acute respiratory distress syndrome. Twenty-seven (54%) were randomised to nebulised heparin and 23 (46%) to standard care. Nebulised UFH was administered to the heparin group on 6 (IQR 4–10) days; median daily dose of 83 (IQR 75–88) kIU. The primary outcome, time to separation from invasive ventilation to day 28 adjusted for the competing risk of death, was not significantly different between groups but took numerically longer in the nebulised heparin group (12.0, standard deviation (SD) 10.4 days versus 7.4, SD 6.9 days; hazard ratio (HR) 0.56, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.31 to 1.01,\n <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>\n = 0.052). One patient died by day 28 in each group, fewer than expected. Time to separation from invasive ventilation among survivors to day 28 occurred more quickly than expected in the standard care group and was, without correction for multiple comparisons, significantly slower in the heparin group (11.3, SD 10.0 days,\n <jats:italic>n</jats:italic>\n = 26 versus 6.4, SD 5.2 days,\n <jats:italic>n</jats:italic>\n = 22; HR 0.52, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.92,\n <jats:italic>P</jats:italic>\n = 0.024). Nebulised heparin did not reduce time to ventilator separation in intubated adult patients with COVID-19. The study is limited by the small sample size and potential for sampling bias. Further study is required.\n </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/0310057X251322783"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9356-2285",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Fitzroy VIC, Australia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Roger J",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2067-7276",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, Northern Hospital, Epping, VIC, Australia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "Angajendra N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, Northern Hospital, Epping, VIC, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Said",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, Australia"
}
],
"family": "van Haren",
"given": "Frank MP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine, Galway University Hospitals and University of Galway, Galway, Ireland"
}
],
"family": "Laffey",
"given": "John G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Northern Clinical School Intensive Care Research Unit, University of Sydney, St Leonards, NSW, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Doig",
"given": "Gordon S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7106-5141",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Fitzroy VIC, Australia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Santamaria",
"given": "John D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Fitzroy VIC, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "Barry",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Anaesthesia and Intensive Care",
"container-title-short": "Anaesth Intensive Care",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-28T02:14:42Z",
"timestamp": 1743128082000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-03T07:56:16Z",
"timestamp": 1751529376000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-30T13:26:55Z",
"timestamp": 1753882015130,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/page/policies/text-and-data-mining-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743033600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0310057X251322783",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/0310057X251322783",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0310057X251322783",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "238-252",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-00192-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0040-1721319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0038-1650241",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0037-1614530",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2007-996081",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0049-3848(89)90308-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/pr.115.011247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph16040584",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03148-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0351",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30513-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2609.201353",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-2003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7790",
"article-title": "Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19",
"author": "D’Agnillo F",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "e_1_3_4_16_2",
"unstructured": "D’Agnillo F, Walters KA, Xiao Y, et al. Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19. Sci Transl Med 2021; 13: eabj7790. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7790.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc6894",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc9269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc9286",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0310057X1604400106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30470-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_21_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_22_2",
"unstructured": "Dixon B Smith RJ Artigas A et al. Protocol of the can nebulised heparin reduce time to extubation in SARS-CoV-2 (CHARTER) study. medRxiv preprint https://www.medrxiv.org/content/medrxiv/early/2020/05/12/2020.04.28.20082552.full.pdf (2020 accessed 18 July 2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.720",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_23_2"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition",
"author": "Force ADT",
"first-page": "2526",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "e_1_3_4_24_2",
"unstructured": "Force ADT, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012; 307: 2526–2533. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5669.",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_25_2",
"unstructured": "Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care Therapeutic Goods Administration. Australian product information – heparin injection 25000IU/5mL heparin sodium injection (porcine mucous) version date 05 March 2021. Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd Sydney NSW (Australia) https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/artg/49236 (2000 accessed 18 July 2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01204.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.14-2843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1472-6963-6-163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000005844",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000005874",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000001295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201804-0692OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_32_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_33_2",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines Updated July 8 2021. National Institutes of Health (United States) https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (2021 accessed 18 July 2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.50883",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201810-2050CP",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_37_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_38_2",
"unstructured": "Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. COVID-19 Vaccination – geographic vaccination rates – SA4 – 28 February 2022. https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/covid-19-vaccination-geographic-vaccination-rates-sa4-28-february-2022 (2022 accessed 18 July 2023)."
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_39_2",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines updated March 2 2022. National Institutes of Health (United States) https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (2022 accessed 18 July 2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.51590",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30459-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cti2.1365",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac957",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/08850666211022613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-021-00841-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.51917",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15212",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102212",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105911",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14122620",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-022-03191-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_53_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_4_54_2",
"unstructured": "Murdoch Children’s Research Institute. Intranasal heparin treatment to reduce transmission among household contacts of COVID-19 positive adults and children (INHERIT). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05204550 https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05204550 (2022 accessed 30 July 2023)."
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0310057X251322783"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A randomised, open-label trial of nebulised unfractionated heparin in patients mechanically ventilated for COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "53"
}