Mar 1 |
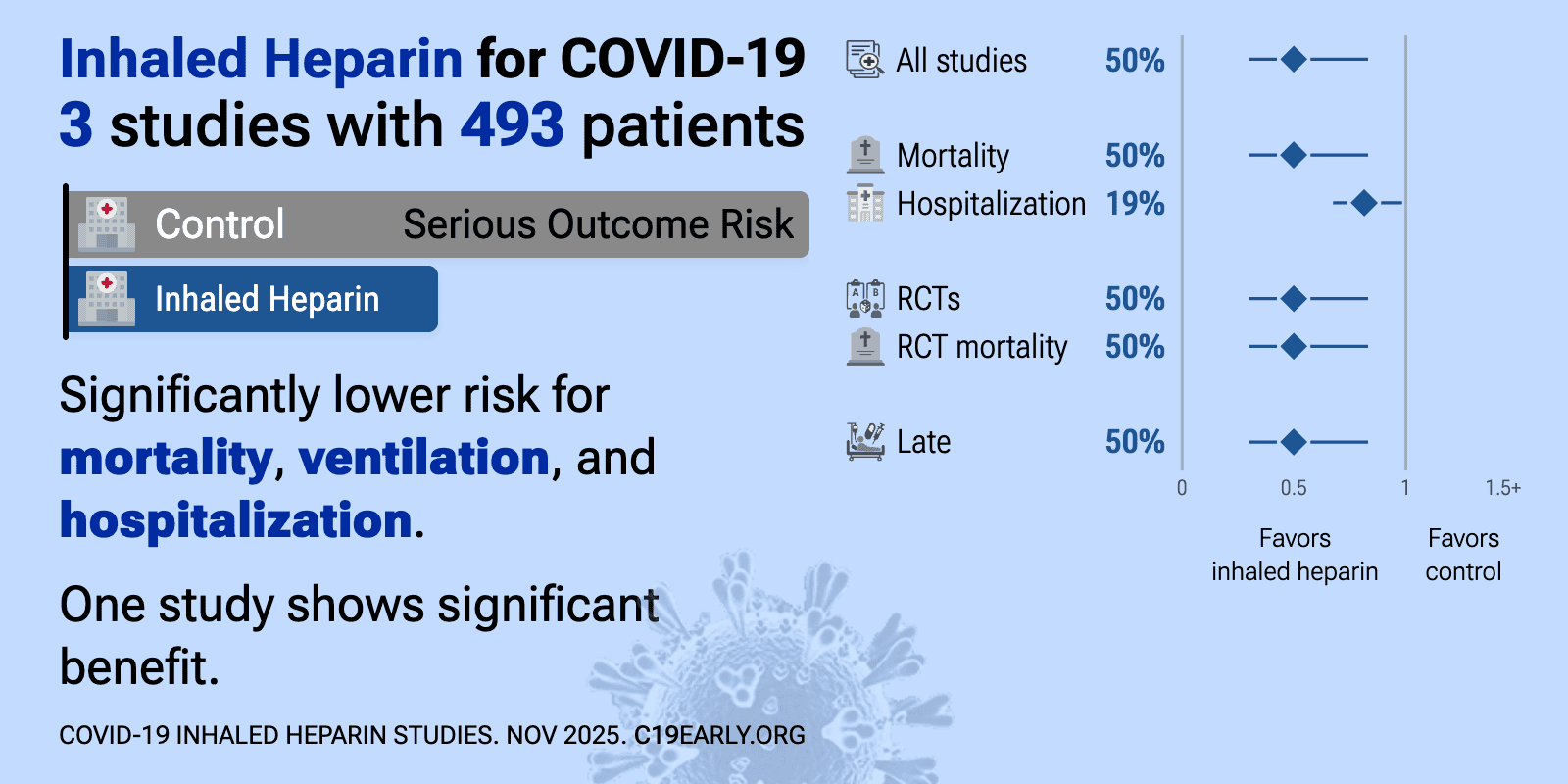
Inhaled Heparin reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta-analysis of 3 studies | |
| Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, and hospitalization. One study shows significant benefit. Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 50% [17‑70%] lower risk. Currently all studies a.. | ||
Oct 31 2025 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103339 | Efficacy of inhaled nebulised unfractionated heparin to prevent intubation or death in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: an investigator-initiated international meta-trial of randomised clinical studies |
| 58% lower mortality (p=0.01), 47% lower ventilation (p=0.01), and 23% lower hospitalization (p=0.02). Meta-trial of 6 RCTs with 478 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significant benefit with inhaled nebulized unfractionated heparin (UFH). Patients receiving nebulized UFH had lower rates of intubation or death at longest follow-up (11.. | ||
Mar 27 2025 |
et al., Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, doi:10.1177/0310057X251322783 | A randomised, open-label trial of nebulised unfractionated heparin in patients mechanically ventilated for COVID-19 |
| 70% higher mortality (p=1). RCT 50 intubated COVID-19 patients showing no improvement with inhaled nebulized unfractionated heparin. Time to separation from invasive ventilation among survivors to day 28 was significantly slower in the heparin group. | ||
Jun 30 2023 |
et al., Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102212 | Inhaled nebulised unfractionated heparin (UFH) for the treatment of hospitalised patients with COVID-19: A randomised controlled pilot study |
| 42% lower mortality (p=0.27), 42% lower ventilation (p=0.27), and 5% shorter hospitalization (p=0.8). RCT 75 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 showing reduced mortality with inhaled nebulized unfractionated heparin (UFH). | ||