Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2
et al., Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626, Apr 2021
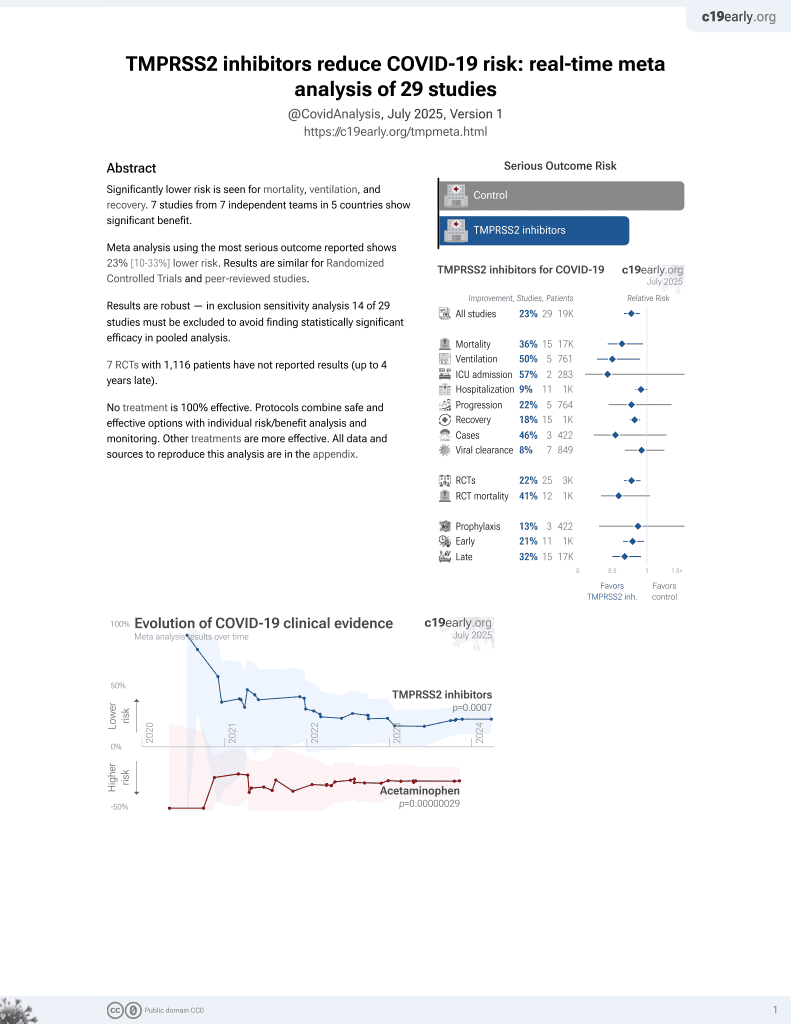
22nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.00063 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In silico study of TMPRSS2 inhibition by camostat, nafamostat, and bromhexine, suggesting allosteric binding for bromhexine, compared to camostat and nafamostat which bind to the active site of TMPRSS2 forming covalent adducts.
13 preclinical studies support the efficacy of TMPRSS2 inhibitors for COVID-19:
1.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
2.
González-Paz et al., Biophysical Analysis of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Recognition and Their Effect on Viral Dynamics in Different Cell Types: A Computational Prediction from In Vitro Experimental Data, ACS Omega, doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c06968.
3.
Umar et al., Inhibitory potentials of ivermectin, nafamostat, and camostat on spike protein and some nonstructural proteins of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening approach, Jurnal Teknologi Laboratorium, doi:10.29238/teknolabjournal.v11i1.344.
4.
Unal et al., Favipiravir, umifenovir and camostat mesylate: a comparative study against SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.11.475889.
5.
Sgrignani et al., Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2, Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626.
6.
Yathindranath et al., Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Host Cell Infection, International Journal of Nanomedicine, doi:10.2147/IJN.S448005.
7.
Martins et al., In Vitro Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Bromhexine hydrochloride, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.23.521817.
8.
Schultz et al., Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x.
9.
Hempel et al., Synergistic inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry by otamixaban and covalent protease inhibitors: pre-clinical assessment of pharmacological and molecular properties, Chemical Science, doi:10.1039/D1SC01494C.
Sgrignani et al., 30 Apr 2021, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626
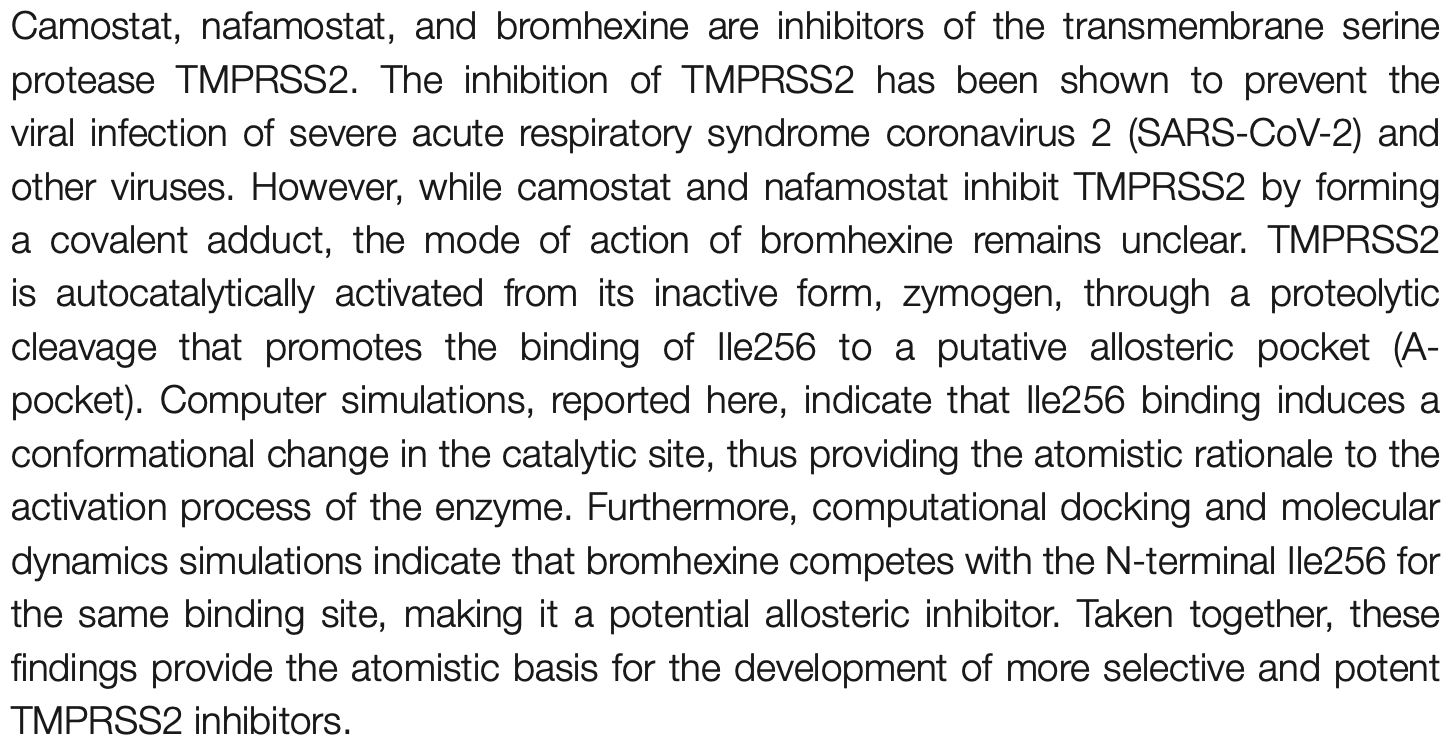
Camostat, nafamostat, and bromhexine are inhibitors of the transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2. The inhibition of TMPRSS2 has been shown to prevent the viral infection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and other viruses. However, while camostat and nafamostat inhibit TMPRSS2 by forming a covalent adduct, the mode of action of bromhexine remains unclear. TMPRSS2 is autocatalytically activated from its inactive form, zymogen, through a proteolytic cleavage that promotes the binding of Ile256 to a putative allosteric pocket (Apocket). Computer simulations, reported here, indicate that Ile256 binding induces a conformational change in the catalytic site, thus providing the atomistic rationale to the activation process of the enzyme. Furthermore, computational docking and molecular dynamics simulations indicate that bromhexine competes with the N-terminal Ile256 for the same binding site, making it a potential allosteric inhibitor. Taken together, these findings provide the atomistic basis for the development of more selective and potent TMPRSS2 inhibitors.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS JS designed the study, performed and analyzed simulations and experiments, and wrote and revised the manuscript. AC designed the study, analyzed the results of simulations and experiments, and wrote and revised the manuscript. Both authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb. 2021.666626/full#supplementary-material
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Afar, Vivanco, Hubert, Kuo, Chen et al., Catalytic cleavage of the androgen-regulated TMPRSS2 protease results in its secretion by prostate and prostate cancer epithelia, Cancer Res
Amaro, Baron, Mccammon, An improved relaxed complex scheme for receptor flexibility in computer-aided drug design, J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des, doi:10.1007/s10822-007-9159-2
Amaro, Baudry, Chodera, Demir, Mccammon et al., Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a randomized clinical trial, Biophys. J, doi:10.34172/bi.2020.27
Bertram, Glowacka, Blazejewska, Soilleux, Allen et al., TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 facilitate trypsin-independent spread of influenza virus in Caco-2 cells, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.00239-10
Bestle, Heindl, Limburg, Van Lam Van, Pilgram et al., TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells, Life Sci. Alliance, doi:10.26508/lsa.202000786
Cavasotto, Phatak, Homology modeling in drug discovery: current trends and applications, Drug Discov. Today, doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2009.04.006
Chen, Lee, Lucht, Chou, Huang et al., TMPRSS2, a serine protease expressed in the prostate on the apical surface of luminal epithelial cells and released into semen in prostasomes, is misregulated in prostate cancer cells, Am. J. Pathol, doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090665
Depfenhart, De Villiers, Lemperle, Meyer, Somma, Potential new treatment strategies for COVID-19: is there a role for bromhexine as add-on therapy?, Intern. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02383-3
Fassi, Sgrignani, D'agostino, Cecchinato, Garofalo et al., Oxidation state dependent conformational changes of HMGB1 regulate the formation of the CXCL12/HMGB1 Heterocomplex, Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.06.020
Friesner, Banks, Murphy, Halgren, Klicic et al., Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring
Fu, Sahakyan, Camilloni, Tartaglia, Paci et al., ALMOST: an all atom molecular simulation toolkit for protein structure determination, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.23588
Guarnera, Berezovsky, Toward comprehensive allosteric control over protein activity, Structure
Habtemariam, Nabavi, Ghavami, Cismaru, Berindan-Neagoe et al., Possible use of the mucolytic drug, bromhexine hydrochloride, as a prophylactic agent against SARS-CoV-2 infection based on its action on the Transmembrane Serine Protease 2, Pharmacol. Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104853
Halgren, Halgren, New method for fast and accurate binding-site identification and analysis, J. Chem. Inform. Modell, doi:10.1021/ci800324m
Hammamy, Haase, Hammami, Hilgenfeld, Steinmetzer, Development and characterization of new peptidomimetic inhibitors of the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease, ChemMedChem, doi:10.1002/cmdc.201200497
Harder, Damm, Maple, Wu, Reboul et al., OPLS3: a force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins, J. Chem. Theory Comput, doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00864
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Huber, How I chose research on proteases or, more correctly, how it chose me, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl, doi:10.1002/anie.201205629
Ishida, Kato, Theoretical perspectives on the reaction mechanism of serine proteases: the reaction free energy profiles of the acylation process, J. Am. Chem. Soc, doi:10.1021/ja021369m
Ivanova, Hardes, Kallis, Dahms, Than et al., Optimization of substrate-analogue furin inhibitors, ChemMedChem, doi:10.1002/cmdc.201700596
Jerabek-Willemsen, André, Wanner, Roth, Duhr et al., MicroScale thermophoresis: interaction analysis and beyond, J. Mol. Struct, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.03.009
Jerabek-Willemsen, Wienken, Braun, Baaske, Duhr, Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis, Assay Drug. Dev. Technol, doi:10.1089/adt.2011.0380
Jiménez, Doerr, Martínez-Rosell, Rose, De Fabritiis, DeepSite: protein-binding site predictor using 3D-convolutional neural networks, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btx350
Jorgensen, Chandrasekhar, Madura, Impey, Klein, Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water, J. Chem. Phys, doi:10.1063/1.445869
Kots, Lushchekina, Varfolomeev, Nemukhin, Role of protein dimeric interface in allosteric inhibition of N-Acetyl-aspartate hydrolysis by human aspartoacylase, J. Chem. Inform. Modell, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00133
Kozakov, Grove, Hall, Bohnuud, Mottarella et al., The FTMap family of web servers for determining and characterizing ligand-binding hot spots of proteins, Nat. Protoc, doi:10.1038/nprot.2015.043
Laporte, Naesens, Airway proteases: an emerging drug target for influenza and other respiratory virus infections, Curr. Opin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2017.03.018
Li, Sun, Zhang, Zheng, Jiang et al., Bromhexine hydrochloride tablets for the treatment of moderate COVID-19: an open-label randomized controlled pilot study, Clin. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12881
Lucas, Heinlein, Kim, Hernandez, Malik et al., The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis, Cancer Discov, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-13-1010
Maggio, Corsini, Repurposing the mucolytic cough suppressant and TMPRSS2 protease inhibitor bromhexine for the prevention and management of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Pharmacol. Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104837
Martyna, Klein, Tuckerman, Nosé-hoover chains: the canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics, J. Chem. Phys, doi:10.1063/1.463940
Martyna, Tobias, Klein, Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms, J. Chem. Phys, doi:10.1063/1.467468
Meyer, Sielaff, Hammami, Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, Garten et al., Identification of the first synthetic inhibitors of the type II transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 suitable for inhibition of influenza virus activation, Biochem. J, doi:10.1042/bj20130101
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Rugge, Zorzi et al., Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532), Ann. Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479
Olsson, Sondergaard, Rostkowski, Jensen, PROPKA3: consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions, J. Chem. Theory Comput, doi:10.1021/ct100578z
Panjkovich, Daura, PARS: a web server for the prediction of protein allosteric and regulatory sites, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu002
Partridge, Choy, Silva-Garcia, Yu, Li et al., Structures of full-length plasma kallikrein bound to highly specific inhibitors describe a new mode of targeted inhibition, J. Struct. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2019.03.001
Pászti-Gere, Czimmermann, Ujhelyi, Balla, Maiwald et al., In vitro characterization of TMPRSS2 inhibition in IPEC-J2 cells, J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem, doi:10.1080/14756366.2016.1193732
Sanchez-Martin, Moroni, Ferraro, Laquatra, Cannino et al., Rational design of allosteric and selective inhibitors of the molecular chaperone TRAP1, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107531
Schmaier, Chapter 638 -prekallikrein and plasma kallikrein, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-382219-2.00638-4
Sgrignani, Bon, Colombo, Magistrato, Computational approaches elucidate the allosteric mechanism of human aromatase inhibition: a novel possible route to small-molecule regulation of CYP450s activities?, J. Chem. Inf. Mod, doi:10.1021/ci500425y
Sgrignani, Bonaccini, Grazioso, Chioccioli, Cavalli et al., Insights into docking and scoring neuronal alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor agonists using molecular dynamics simulations and QM/MM calculations, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.21251
Sgrignani, Garofalo, Matkovic, Merulla, Catapano et al., Structural biology of STAT3 and its implications for anticancer therapies development, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19061591
Shen, Mao, Wu, Tanaka, Zhang, TMPRSS2: a potential target for treatment of influenza virus and coronavirus infections, Biochimie, doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016
Sherman, Day, Jacobson, Friesner, Farid, Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/jm050540c
Shrimp, Kales, Sanderson, Simeonov, Shen et al., An enzymatic TMPRSS2 assay for assessment of clinical candidates and discovery of inhibitors as potential treatment of COVID-19, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00106
Singh, Decroly, Khatib, Villoutreix, Structurebased drug repositioning over the human TMPRSS2 protease domain: search for chemical probes able to repress SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein cleavages, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105495
Stubbs, Renatus, Bode, An active zymogen: unravelling the mystery of tissue-type plasminogen activator, Biol. Chem
Sungnak, Huang, Becavin, Berg, Queen et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6
Szabo, Wu, Dickson, Netzel-Arnett, Antalis et al., Type II transmembrane serine proteases, Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1160/th03-02-0071
Thunders, Delahunt, Gene of the month: TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2), J. Clin. Pathol, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206987
Tibshirani, Walther, Hastie, Estimating the number of clusters in a data set via the gap statistic, R. Stat. Soc, doi:10.1111/1467-9868.00293
Tubiana, Carvaillo, Boulard, Bressanelli, TTClust: a versatile molecular simulation trajectory clustering program with graphical summaries, J. Chem. Inform. Modell, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00512
Waterhouse, Bertoni, Bienert, Studer, Tauriello et al., SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes, Nucleic Acids Res
Wiederstein, Sippl, ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins, Nucl. Acids Res
Xiang, Advances in homology protein structure modeling, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci, doi:10.2174/138920306777452312
Xu, Wang, Hu, Gao, Ma et al., CavityPlus: a web server for protein cavity detection with pharmacophore modelling, allosteric site identification and covalent ligand binding ability prediction, Nucleic Acids Res
Yamamoto, Matsuyama, Li, Takeda, Kawaguchi et al., Identification of nafamostat as a potent inhibitor of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein-mediated membrane fusion using the split-protein-based cell-cell fusion assay, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.01043-16
Yu, Zhou, Tanaka, Yao, Roll: a new algorithm for the detection of protein pockets and cavities with a rolling probe sphere, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp599
Zang, Gomez Castro, Mccune, Zeng, Rothlauf et al., TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes, Sci. Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626",
"ISSN": [
"2296-889X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Camostat, nafamostat, and bromhexine are inhibitors of the transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2. The inhibition of TMPRSS2 has been shown to prevent the viral infection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and other viruses. However, while camostat and nafamostat inhibit TMPRSS2 by forming a covalent adduct, the mode of action of bromhexine remains unclear. TMPRSS2 is autocatalytically activated from its inactive form, zymogen, through a proteolytic cleavage that promotes the binding of Ile256 to a putative allosteric pocket (A-pocket). Computer simulations, reported here, indicate that Ile256 binding induces a conformational change in the catalytic site, thus providing the atomistic rationale to the activation process of the enzyme. Furthermore, computational docking and molecular dynamics simulations indicate that bromhexine competes with the N-terminal Ile256 for the same binding site, making it a potential allosteric inhibitor. Taken together, these findings provide the atomistic basis for the development of more selective and potent TMPRSS2 inhibitors.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sgrignani",
"given": "Jacopo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cavalli",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences",
"container-title-short": "Front. Mol. Biosci.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-30T05:33:57Z",
"timestamp": 1619760837000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-30T05:34:09Z",
"timestamp": 1619760849000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-18T19:56:40Z",
"timestamp": 1713470200179
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1619740800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Catalytic cleavage of the androgen-regulated TMPRSS2 protease results in its secretion by prostate and prostate cancer epithelia.",
"author": "Afar",
"first-page": "1686",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10822-007-9159-2",
"article-title": "An improved relaxed complex scheme for receptor flexibility in computer-aided drug design.",
"author": "Amaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.038",
"article-title": "Ensemble docking in drug discovery.",
"author": "Amaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2271",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/bi.2020.27",
"article-title": "Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Ansarin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "209",
"journal-title": "Bioimpacts",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00239-10",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 facilitate trypsin-independent spread of influenza virus in Caco-2 cells.",
"author": "Bertram",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10016",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202000786",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells.",
"author": "Bestle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Life Sci. Alliance",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2009.04.006",
"article-title": "Homology modeling in drug discovery: current trends and applications.",
"author": "Cavasotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov. Today",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2353/ajpath.2010.090665",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2, a serine protease expressed in the prostate on the apical surface of luminal epithelial cells and released into semen in prostasomes, is misregulated in prostate cancer cells.",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2986",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02383-3",
"article-title": "Potential new treatment strategies for COVID-19: is there a role for bromhexine as add-on therapy?",
"author": "Depfenhart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "Intern. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2019.06.020",
"article-title": "Oxidation state dependent conformational changes of HMGB1 regulate the formation of the CXCL12/HMGB1 Heterocomplex.",
"author": "Fassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "886",
"journal-title": "Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm0306430",
"article-title": "Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. method and assessment of docking accuracy.",
"author": "Friesner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1739",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.23588",
"article-title": "ALMOST: an all atom molecular simulation toolkit for protein structure determination.",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1101",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2019.01.014",
"article-title": "Toward comprehensive allosteric control over protein activity.",
"author": "Guarnera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "866",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104853",
"article-title": "Possible use of the mucolytic drug, bromhexine hydrochloride, as a prophylactic agent against SARS-CoV-2 infection based on its action on the Transmembrane Serine Protease 2.",
"author": "Habtemariam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1747-0285.2007.00483.x",
"article-title": "New method for fast and accurate binding-site identification and analysis.",
"author": "Halgren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol. Drug Des.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci800324m",
"article-title": "Identifying and characterizing binding sites and assessing druggability.",
"author": "Halgren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inform. Modell.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cmdc.201200497",
"article-title": "Development and characterization of new peptidomimetic inhibitors of the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease.",
"author": "Hammamy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "ChemMedChem",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00864",
"article-title": "OPLS3: a force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins.",
"author": "Harder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Theory Comput.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor.",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/anie.201205629",
"article-title": "How I chose research on proteases or, more correctly, how it chose me.",
"author": "Huber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "68",
"journal-title": "Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ja021369m",
"article-title": "Theoretical perspectives on the reaction mechanism of serine proteases: the reaction free energy profiles of the acylation process.",
"author": "Ishida",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12035",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Chem. Soc.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cmdc.201700596",
"article-title": "Optimization of substrate-analogue furin inhibitors.",
"author": "Ivanova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1953",
"journal-title": "ChemMedChem",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.03.009",
"article-title": "MicroScale thermophoresis: interaction analysis and beyond.",
"author": "Jerabek-Willemsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Struct.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "1077",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/adt.2011.0380",
"article-title": "Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis.",
"author": "Jerabek-Willemsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "Assay Drug. Dev. Technol.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btx350",
"article-title": "DeepSite: protein-binding site predictor using 3D-convolutional neural networks.",
"author": "Jiménez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3036",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.445869",
"article-title": "Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water.",
"author": "Jorgensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "926",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00133",
"article-title": "Role of protein dimeric interface in allosteric inhibition of N-Acetyl-aspartate hydrolysis by human aspartoacylase.",
"author": "Kots",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1999",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inform. Modell.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nprot.2015.043",
"article-title": "The FTMap family of web servers for determining and characterizing ligand-binding hot spots of proteins.",
"author": "Kozakov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "733",
"journal-title": "Nat. Protoc.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2017.03.018",
"article-title": "Airway proteases: an emerging drug target for influenza and other respiratory virus infections.",
"author": "Laporte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Virol.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12881",
"article-title": "Bromhexine hydrochloride tablets for the treatment of moderate COVID-19: an open-label randomized controlled pilot study.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1096",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.cd-13-1010",
"article-title": "The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis.",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1310",
"journal-title": "Cancer Discov.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104837",
"article-title": "Repurposing the mucolytic cough suppressant and TMPRSS2 protease inhibitor bromhexine for the prevention and management of SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Maggio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.463940",
"article-title": "Nosé–hoover chains: the canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics.",
"author": "Martyna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2635",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "97",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/1.467468",
"article-title": "Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms.",
"author": "Martyna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4177",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "101",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj20130101",
"article-title": "Identification of the first synthetic inhibitors of the type II transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 suitable for inhibition of influenza virus activation.",
"author": "Meyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "331",
"journal-title": "Biochem. J.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "452",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"article-title": "Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532).",
"author": "Montopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1040",
"journal-title": "Ann. Oncol.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ct100578z",
"article-title": "PROPKA3: consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions.",
"author": "Olsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "525",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Theory Comput.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btu002",
"article-title": "PARS: a web server for the prediction of protein allosteric and regulatory sites.",
"author": "Panjkovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1314",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2019.03.001",
"article-title": "Structures of full-length plasma kallikrein bound to highly specific inhibitors describe a new mode of targeted inhibition.",
"author": "Partridge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "J. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "206",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14756366.2016.1193732",
"article-title": "In vitro characterization of TMPRSS2 inhibition in IPEC-J2 cells.",
"author": "Pászti-Gere",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107531",
"article-title": "Rational design of allosteric and selective inhibitors of the molecular chaperone TRAP1.",
"author": "Sanchez-Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/b978-0-12-382219-2.00638-4",
"article-title": "Chapter 638 - prekallikrein and plasma kallikrein",
"author": "Schmaier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2885",
"journal-title": "Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes",
"key": "B42",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci500425y",
"article-title": "Computational approaches elucidate the allosteric mechanism of human aromatase inhibition: a novel possible route to small-molecule regulation of CYP450s activities?",
"author": "Sgrignani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2856",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Mod.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.21251",
"article-title": "Insights into docking and scoring neuronal alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor agonists using molecular dynamics simulations and QM/MM calculations.",
"author": "Sgrignani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2443",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19061591",
"article-title": "Structural biology of STAT3 and its implications for anticancer therapies development.",
"author": "Sgrignani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2: a potential target for treatment of influenza virus and coronavirus infections.",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Biochimie",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm050540c",
"article-title": "Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects.",
"author": "Sherman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "534",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.0c00106",
"article-title": "An enzymatic TMPRSS2 assay for assessment of clinical candidates and discovery of inhibitors as potential treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Shrimp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "997",
"journal-title": "ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105495",
"article-title": "Structure-based drug repositioning over the human TMPRSS2 protease domain: search for chemical probes able to repress SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein cleavages.",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105495",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An active zymogen: unravelling the mystery of tissue-type plasminogen activator.",
"author": "Stubbs",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "379",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes.",
"author": "Sungnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1160/th03-02-0071",
"article-title": "Type II transmembrane serine proteases.",
"author": "Szabo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "185",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206987",
"article-title": "Gene of the month: TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2).",
"author": "Thunders",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "773",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Pathol.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1467-9868.00293",
"article-title": "Estimating the number of clusters in a data set via the gap statistic.",
"author": "Tibshirani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "R. Stat. Soc.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00512",
"article-title": "TTClust: a versatile molecular simulation trajectory clustering program with graphical summaries.",
"author": "Tubiana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2178",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inform. Modell.",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gky427",
"article-title": "SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes.",
"author": "Waterhouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W296",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkm290",
"article-title": "ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins.",
"author": "Wiederstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W407",
"journal-title": "Nucl. Acids Res.",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138920306777452312",
"article-title": "Advances in homology protein structure modeling.",
"author": "Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "217",
"journal-title": "Curr. Protein Pept. Sci.",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gky380",
"article-title": "CavityPlus: a web server for protein cavity detection with pharmacophore modelling, allosteric site identification and covalent ligand binding ability prediction.",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W374",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.01043-16",
"article-title": "Identification of nafamostat as a potent inhibitor of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein-mediated membrane fusion using the split-protein-based cell-cell fusion assay.",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6532",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btp599",
"article-title": "Roll: a new algorithm for the detection of protein pockets and cavities with a rolling probe sphere.",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes.",
"author": "Zang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci. Immunol.",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 62,
"references-count": 62,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "8"
}