Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial
et al., Bioimpacts, doi:10.34172/bi.2020.27, Jul 2020
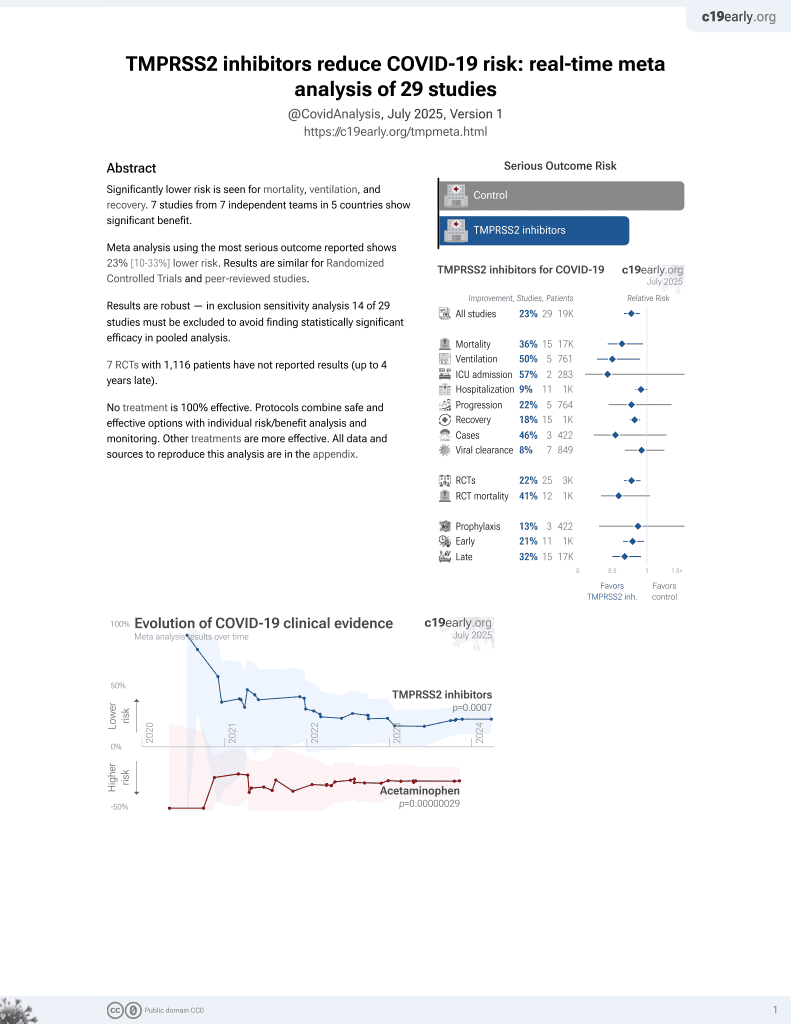
22nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.00063 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
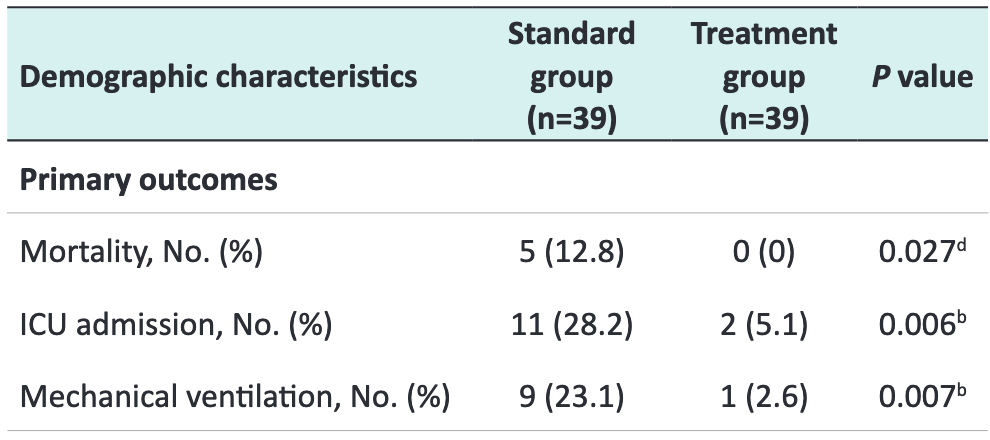
RCT with 39 bromhexine and 39 control patients showing lower mortality, intubation, and ICU admission with treatment. The treatment group received bromhexine hydrochloride 8 mg three times a day for two weeks. All patients received SOC including HCQ.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and bromhexine.
|
risk of death, 90.9% lower, RR 0.09, p = 0.05, treatment 0 of 39 (0.0%), control 5 of 39 (12.8%), NNT 7.8, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.01, treatment 1 of 39 (2.6%), control 9 of 39 (23.1%), NNT 4.9.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 81.8% lower, RR 0.18, p = 0.01, treatment 2 of 39 (5.1%), control 11 of 39 (28.2%), NNT 4.3.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ansarin et al., 19 Jul 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 18 April, 2020 - 19 May, 2020.
Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial
BioImpacts, doi:10.34172/bi.2020.27
Introduction: Bromhexine is a potential therapeutic option in COVID-19, but no data from a randomized clinical trial has been available. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of bromhexine in intensive care unit (ICU) admission, mechanical ventilation, and mortality in patients with COVID-19. Methods: An open-label randomized clinical trial study was performed in Tabriz, North-West of Iran. They were randomized to either the treatment with the bromhexine group or the control group, in a 1:1 ratio with 39 patients in each arm. Standard therapy was used in both groups and those patients in the treatment group received oral bromhexine 8 mg three times a day additionally. The primary outcome was a decrease in the rate of ICU admissions, intubation/ mechanical ventilation, and mortality. Results: A total of 78 patients with similar demographic and disease characteristics were enrolled. There was a significant reduction in ICU admissions (2 out of 39 vs. 11 out of 39, P = 0.006), intubation (1 out of 39 vs. 9 out of 39, P = 0.007) and death (0 vs. 5, P = 0.027) in the bromhexine treated group compared to the standard group. No patients were withdrawn from the study because of adverse effects.
Conclusion: The early administration of oral bromhexine reduces the ICU transfer, intubation, and the mortality rate in patients with COVID-19. This affordable medication can easily be administered everywhere with a huge positive impact(s) on public health and the world economy. Altogether, the verification of our results on a larger scale and different medical centers is strongly recommended. Trial Registration: IRCT202003117046797N4; https://irct.ir/trial/46969.
BioImpacts, 2020, 10(4), 209-215 215 administered in remote and underserved areas. Despite the relatively small sample size and a single-center experience, our results are very encouraging, highlighting a potential breakthrough point in the management of patients with COVID-19 disease if confirmed after verification in largescale clinical trials. Considering the current state of the pandemic, it may be a game-changer and can have a huge positive impact on resolving public health issues as well as on the world economy.
Ethical statement The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran (IR.TBZMED.REC.1399.013).
Competing interests The authors declare no conflict of interest in publishing this paper. This study not supported by any grant money from a pharmaceutical company or for-profit organization. Authors' contribution KA, MRA and SS designed the study. KA, RT, MRA, AT, ST and SS contributed to the protocol development. KA, MRA, AT, MV, ST, TV, HV and PS collected the data. Data analysis and interpretation were conducted by KA, MRA and SS. The initial manuscript was drafted by KA, MRA, RT, SS and KRC. All authors critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved it for submission.
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015432
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Berger, Bölke, Seidelmann, Beger, Time-scale of interleukin-6, myeloid related proteins (MRP), C reactive protein (CRP), and endotoxin plasma levels during the postoperative acute phase reaction, Shock, doi:10.1097/00024382-199706000-00006
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Kim, Jerome et al., Covid-19 in Critically Ill Patients in the Seattle Region -Case Series, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004500
Bm, Benoit, Vikse, Plebani, Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis, Am J Emerg Med, doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073
Depfenhart, De Villiers, Lemperle, Meyer, Somma, Potential new treatment strategies for COVID-19: is there a role for bromhexine as add-on therapy?, Intern Emerg Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02383-3
Grein, Myers, Brainard, Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Covid-19. Reply, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2015312
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Kashani, Hypoxia in COVID-19: Sign of Severity or Cause for Poor Outcomes, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.021
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370
Lucas, Heinlein, Kim, Hernandez, Malik et al., The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis, Cancer Discov, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-13-1010
Marini, Gattinoni, Management of COVID-19 Respiratory Distress, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6825
Meng, Qiu, Ai, Xue, Guo, Intubation and Ventilation amid the COVID-19 Outbreak: Wuhan's Experience, Anesthesiology, doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000003296
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/jci137647
Sa, Respiratory support for patients with COVID-19 infection, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30110-7
Shen, Mao, Wu, Tanaka, Zhang, TMPRSS2: A potential target for treatment of influenza virus and coronavirus infections, Biochimie, doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Yang, Liu, Tao, Li, The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504
Zhou, Vedantham, Lu, Agudelo, Carrion et al., Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.34172/bi.2020.27",
"ISSN": [
"2228-5660",
"2228-5652"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/bi.2020.27",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n <jats:bold>\n <jats:italic>Introduction:</jats:italic>\n </jats:bold> Bromhexine is a potential therapeutic option in COVID-19, but no data from a randomized clinical trial has been available. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of bromhexine in intensive care unit (ICU) admission, mechanical ventilation, and mortality in patients with COVID-19. <jats:italic><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold></jats:italic> An open-label randomized clinical trial study was performed in Tabriz, North-West of Iran. They were randomized to either the treatment with the bromhexine group or the control group, in a 1:1 ratio with 39 patients in each arm. Standard therapy was used in both groups and those patients in the treatment group received oral bromhexine 8 mg three times a day additionally. The primary outcome was a decrease in the rate of ICU admissions, intubation/mechanical ventilation, and mortality. <jats:italic><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold></jats:italic> A total of 78 patients with similar demographic and disease characteristics were enrolled. There was a significant reduction in ICU admissions (2 out of 39 vs. 11 out of 39, <jats:italic>P </jats:italic>= 0.006), intubation (1 out of 39 vs. 9 out of 39, <jats:italic>P </jats:italic>= 0.007) and death (0 vs. 5, <jats:italic>P </jats:italic>= 0.027) in the bromhexine treated group compared to the standard group. No patients were withdrawn from the study because of adverse effects. <jats:italic><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold></jats:italic> The early administration of oral bromhexine reduces the ICU transfer, intubation, and the mortality rate in patients with COVID-19. This affordable medication can easily be administered everywhere with a huge positive impact(s) on public health and the world economy. Altogether, the verification of our results on a larger scale and different medical centers is strongly recommended. <jats:italic><jats:bold>Trial Registration:</jats:bold></jats:italic> IRCT202003117046797N4; https://irct.ir/trial/46969.</jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Journal Owner",
"name": "journal_owner",
"value": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
},
{
"label": "Journal Publisher",
"name": "journal_publisher",
"value": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3114-5224",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Rahat Breath and Sleep Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Tuberculosis and Lung Disease Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ansarin",
"given": "Khalil",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Nephrology, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA"
}
],
"family": "Tolouian",
"given": "Ramin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6851-5460",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Kidney Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ardalan",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis and Lung Disease Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Taghizadieh",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Varshochi",
"given": "Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Teimouri",
"given": "Soheil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Vaezi",
"given": "Tahere",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuberculosis and Lung Disease Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Valizadeh",
"given": "Hamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Kidney Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Saleh",
"given": "Parviz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7986-9072",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Community Medicine, School of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Research Center, Aging Research Institute, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Safiri",
"given": "Saeid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2498-9859",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Asthma and Airway Center, University Health Network, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "Kenneth R.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BioImpacts",
"container-title-short": "Bioimpacts",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"bi.tbzmed.ac.ir"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-14T03:24:41Z",
"timestamp": 1600053881000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-14T03:24:43Z",
"timestamp": 1600053883000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-24T07:33:12Z",
"timestamp": 1711265592154
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 84,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://bi.tbzmed.ac.ir/PDF/bi-10-209.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://bi.tbzmed.ac.ir/PDF/bi-10-209.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "20123",
"original-title": [],
"page": "209-215",
"prefix": "10.34172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Maad Rayan Publishing Company",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci137647",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2015312",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02383-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.cd-13-1010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6825",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30110-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ALN.0000000000003296",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00024382-199706000-00006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "R20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "R21",
"unstructured": "BM H, G A, J W, Benoit S, Vikse J, Plebani M, et al. Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis Am J Emerg Med 2020. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073."
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bi.tbzmed.ac.ir/Article/bi-23240"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}