Remdesivir and molnupiravir had comparable efficacy in lung transplant recipients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a single center experience
et al., Frontiers in Transplantation, doi:10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289, Jul 2024
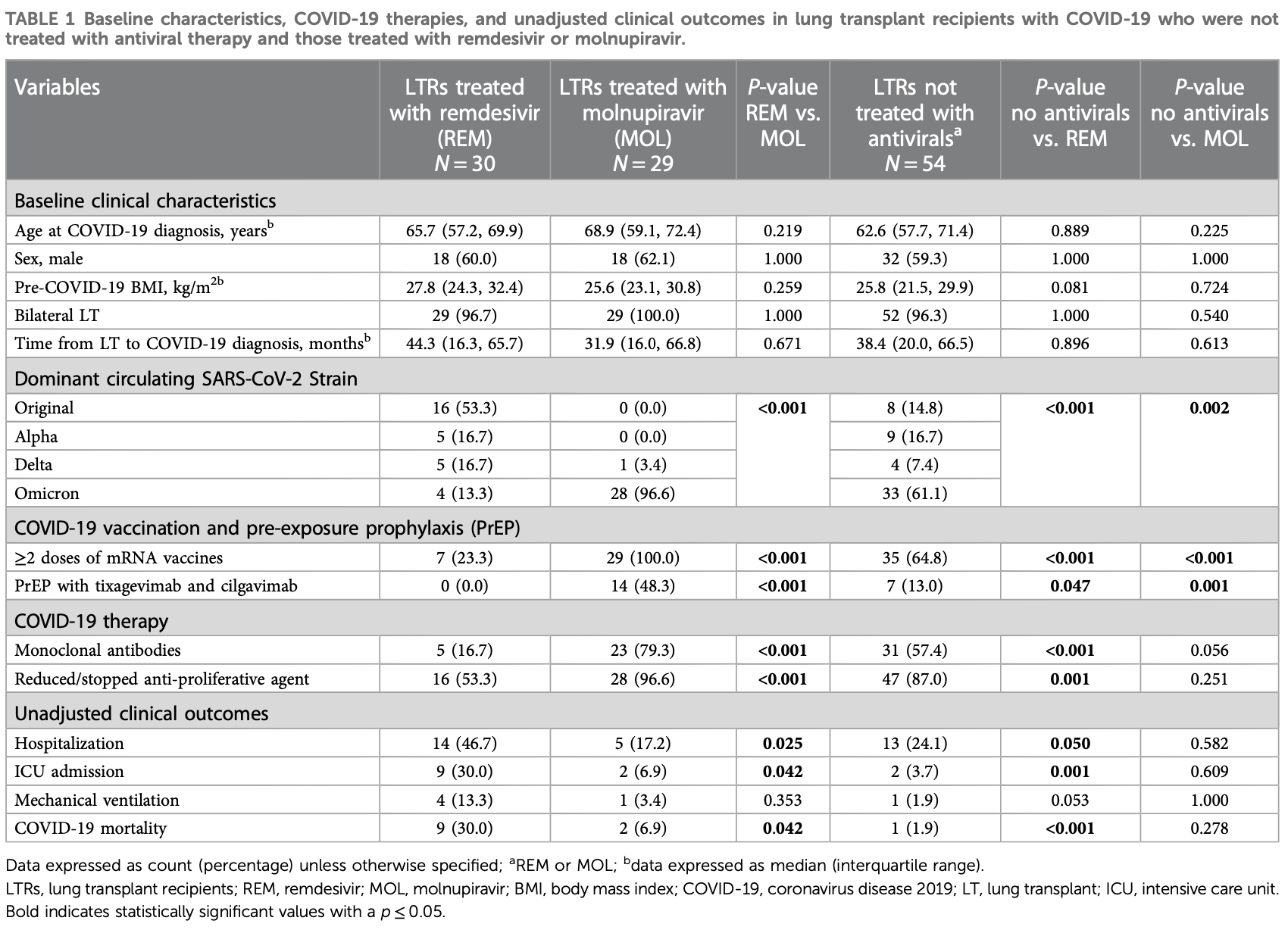
Retrospective 113 lung transplant recipients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 showing higher mortality with remdesivir and molnupiravir in unadjusted analysis, with statistical significance for remdesivir. mAb PrEP and treatment and the dominant variant favored molnupiravir compared with the control group, however they favored the control group compared with remdesivir.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
Study covers molnupiravir and remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 1520.0% higher, RR 16.20, p < 0.001, treatment 9 of 30 (30.0%), control 1 of 54 (1.9%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 620.0% higher, RR 7.20, p = 0.05, treatment 4 of 30 (13.3%), control 1 of 54 (1.9%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 710.0% higher, RR 8.10, p = 0.001, treatment 9 of 30 (30.0%), control 2 of 54 (3.7%).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 93.8% higher, RR 1.94, p = 0.05, treatment 14 of 30 (46.7%), control 13 of 54 (24.1%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Razia et al., 4 Jul 2024, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period March 2020 - August 2022.
Contact: sofya.tokman@dignityhealth.org.
Remdesivir and molnupiravir had comparable efficacy in lung transplant recipients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a single center experience
Frontiers in Transplantation, doi:10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289
Introduction: Remdesivir (REM) and molnupiravir (MOL) are commonly used to treat lung transplant recipients (LTRs) with COVID-19; however, the clinical efficacy of these medications is yet to be compared. In this retrospective cohort study, we compared the clinical outcomes between LTRs with mild-tomoderate COVID-19 treated with REM and those treated with MOL. Methods and Results: Between March 2020 and August 2022, 195 LTRs developed COVID-19 at our center. After excluding 82 who presented with severe disease requiring hospitalization, the remaining 113 were included in the analysis: 54 did not receive antiviral treatment, 30 were treated with REM, and 29 were treated with MOL. Adjusted multivariable logistic regression analysis showed similar rates of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.169, [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.105-12.997, p = 0.899], ICU admission (aOR 0.822, 95% CI 0.042-16.220, p = 0.898), mechanical ventilation (aOR 0.903, 95% CI 0.015-55.124, p = 0.961), and COVID-19related mortality (aOR 0.822, 95% CI 0.042-16.220, p = 0.898) between LTRs treated with REM and those treated with MOL for mild-to-moderate COVID-19, irrespective of SARS-CoV-2 strain. Conclusion: MOL may be a suitable alternative to REM to treat LTRs with mildto-moderate COVID-19, and the choice of antiviral therapy can be driven by practical considerations such as route of administration and drug availability.
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by The Institutional Review Board of St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The Ethics Committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin because the study was a retrospective data analysis study with no identifiable patient information.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Baden, Cheng et al., Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac724
Dauriat, Beaumont, Nguyen, Picard, Penhouet et al., Efficacy of three COVID-19 vaccine doses in lung transplant recipients: a multicentre cohort study, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00502-2022
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Mera, Webb et al., Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
Hallett, Greenberg, Boyarsky, Shah, Ou et al., SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine antibody response and reactogenicity in heart and lung transplant recipients, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2021.07.026
Havlin, Svorcova, Dvorackova, Lastovicka, Lischke et al., Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and SARS-CoV-2 infection in lung transplant recipients, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2021.05.004
Lo, Jordan, Arvey, Sudhamsu, Shrivastava-Ranjan et al., GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit filo-, pneumo-, and paramyxoviruses, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep43395
Narasimhan, Mahimainathan, Clark, Usmani, Cao et al., Serological response in lung transplant recipients after two doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines9070708
Peled, Lavee, Sternik, Segev, Wieder-Finesod, BNT162b2 vaccination in heart transplant recipients: clinical experience and antibody response, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2021.04.003
Razia, None
Sheahan, Sims, Graham, Menachery, Gralinski et al., Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653
Sindu, Razia, Bay, Padiyar, Grief et al., Evolving impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on lung transplant recipients: a single-center experience, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2023.10.010
Warren, Jordan, Lo, Ray, Mackman et al., Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature17180
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289",
"ISSN": [
"2813-2440"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Remdesivir (REM) and molnupiravir (MOL) are commonly used to treat lung transplant recipients (LTRs) with COVID-19; however, the clinical efficacy of these medications is yet to be compared. In this retrospective cohort study, we compared the clinical outcomes between LTRs with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 treated with REM and those treated with MOL.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods and Results</jats:title><jats:p>Between March 2020 and August 2022, 195 LTRs developed COVID-19 at our center. After excluding 82 who presented with severe disease requiring hospitalization, the remaining 113 were included in the analysis: 54 did not receive antiviral treatment, 30 were treated with REM, and 29 were treated with MOL. Adjusted multivariable logistic regression analysis showed similar rates of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.169, [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.105–12.997, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.899], ICU admission (aOR 0.822, 95% CI 0.042–16.220, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.898), mechanical ventilation (aOR 0.903, 95% CI 0.015–55.124, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.961), and COVID-19-related mortality (aOR 0.822, 95% CI 0.042–16.220, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.898) between LTRs treated with REM and those treated with MOL for mild-to-moderate COVID-19, irrespective of SARS-CoV-2 strain.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>MOL may be a suitable alternative to REM to treat LTRs with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, and the choice of antiviral therapy can be driven by practical considerations such as route of administration and drug availability.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razia",
"given": "Deepika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sindu",
"given": "Devika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherrier",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grief",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walia",
"given": "Rajat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tokman",
"given": "Sofya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Transplantation",
"container-title-short": "Front. Transplant.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-04T04:48:50Z",
"timestamp": 1720068530000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-04T04:48:54Z",
"timestamp": 1720068534000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-05T00:16:51Z",
"timestamp": 1720138611512
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1720051200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2023.10.010",
"article-title": "Evolving impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on lung transplant recipients: a single-center experience",
"author": "Sindu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00502-2022",
"article-title": "Efficacy of three COVID-19 vaccine doses in lung transplant recipients: a multicentre cohort study",
"author": "Dauriat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2200502",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2021.07.026",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine antibody response and reactogenicity in heart and lung transplant recipients",
"author": "Hallett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1579",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2021.05.004",
"article-title": "Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and SARS-CoV-2 infection in lung transplant recipients",
"author": "Havlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "754",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines9070708",
"article-title": "Serological response in lung transplant recipients after two doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines",
"author": "Narasimhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2021.04.003",
"article-title": "BNT162b2 vaccination in heart transplant recipients: clinical experience and antibody response",
"author": "Peled",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "759",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Bhimraj",
"first-page": "e250",
"key": "B7",
"volume-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep43395",
"article-title": "GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit filo-, pneumo-, and paramyxoviruses",
"author": "Lo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "43395",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653",
"article-title": "Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature17180",
"article-title": "Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys",
"author": "Warren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "531",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B12",
"volume-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frtra.2024.1408289/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Remdesivir and molnupiravir had comparable efficacy in lung transplant recipients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a single center experience",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "3"
}
razia