Effect of amubarvimab-romlusevimab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in intensive care units: A retrospective cohort study
et al., Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663, Sep 2024
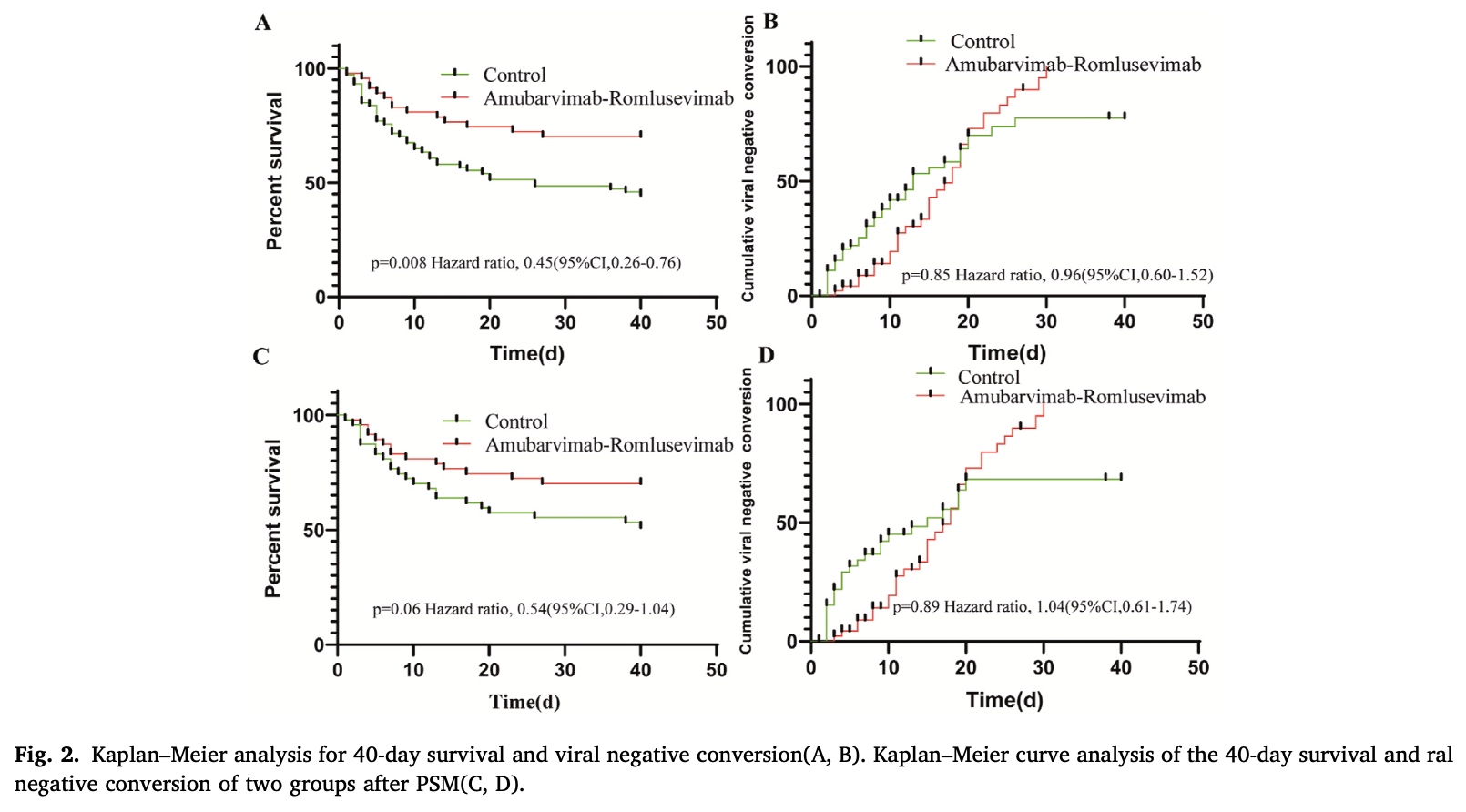
Retrospective 121 severe ICU COVID-19 patients in China showing lower 28-day mortality and ICU mortality with amubarvimab-romlusevimab treatment compared to no antiviral treatment. No significant differences were found in viral conversion rate or thromboembolic events. After propensity score matching to balance baseline characteristics, the mortality differences were no longer statistically significant.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
Viral load measured by PCR may not accurately reflect infectious virus measured by viral culture. Porter et al. show that viral load early in infection was correlated with infectious virus, but viral load late in infection could be high even with low or undetectable infectious virus. Assessing viral load later in infection may underestimate reductions in infectious virus with treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments2.
|
risk of death, 46.0% lower, HR 0.54, p = 0.06, treatment 47, control 47, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier, day 40.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 3.8% lower, HR 0.96, p = 0.89, treatment 47, control 47, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, propensity score matching, Kaplan-Meier, day 40.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Qu et al., 30 Sep 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period December 2022 - March 2023.
Contact: qp136896991@163.com, mylx99@163.com, cc17702067789@outlook.com.
Effect of amubarvimab-romlusevimab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in intensive care units: A retrospective cohort study
Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663
Amubarvimab-romlusevimab is a commonly recommended antiviral treatment in China for adult patients with mild or moderate SARS-CoV-2 infections, especially for patients with a high risk factor for progression to severe COVID-19. However, its exact efficacy in patients with severe Covid-19 is not yet known.This is a single-center retrospective cohort study, in which we collected the general data, laboratory tests, radiological characteristics, viral conversion status, and prognosis of the disease from patients with COVID-19 hospitalized, from December 2022 to March 2023 in the Department of Critical Care Medicine. The amubarvimab-romlusevimab therapy can reduce the 28-day mortality (29.79 % vs 51.35 %, p = 0.02), and ICU mortality (29.79 % vs 55.41 %, p = 0.006) of severe COVID-19.A 1:1 PSM (Propensity Score Matching) was performed to reduce bias, in order to ensure the two groups were balanced and comparable. In the matched population (n = 47), there were no statistically significant differences between the mAbs (monoclonal antibody)group and the Non-antiviral group in 28-day, and thromboembolic events in COVID-19 patients. The 40-day survival analysis shows that mAbs therapy can improve patient prognosis (HR = 0.45, 95%CI = 0.26-0.76, p = 0.008). However, no significant intergroup difference in the 40-day cumulative viral conversion rate. In a univariate Cox regression analysis, The Amubarvimab -romlusevimab therapy(HR:0.464; CI:[0.252-0.853]; p:0.013) is a protective factor and CRP, PCT, PLT, Lactate, PT, PT-INR, and pt% level at admission were risk factors for clinical prognosis. After including the above covariates, Multifactorial COX regression shows that the Amubarvimab -romlusevimab therapy(HR:0.392; CI:[0.211-0.729]; p:0.003), CRP, Lactate and PT-INR at admission are independent factors for mortality of severe COVID-19. Based on the current data, we conclude that amubarvimab-romlusevimab therapy is beneficial for patients with severe COVID-19.
Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Baiyun Branch, Nanfang Hospital (2023004).
Consent for publication All authors approved the final manuscript and the submission to this journal.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Bajema, Berry, Streja, Effectiveness of COVID-19 treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir among U.S. Veterans: target trial emulation studies with one-month and six-month outcomes, Ann. Intern. Med
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation, Blood
Cuker, Tseng, Nieuwlaat, American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis in patients with COVID-19, Blood Adv
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Evering, Chew, Giganti, Safety and efficacy of combination SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies amubarvimab plus romlusevimab in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, Ann. Intern. Med
Ferrando, Mellado-Artigas, Gea, Patient characteristics, clinical course and factors associated to ICU mortality in critically ill patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Spain: a prospective, cohort, multicentre study, Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim
Focosi, Franchini, Maggi, Shoham, COVID-19 therapeutics, Clin. Microbiol. Rev
Godoy, Goligher, Lawler, Slutsky, Zarychanski, Anticipating and managing coagulopathy and thrombotic manifestations of severe COVID-19, CMAJ (Can. Med. Assoc. J.)
Goligher, Bradbury, Mcverry, Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern. Med
Hao, Zhang, Ma, Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind phase 1 studies of the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of BRII-196 and BRII-198, SARS-CoV-2 spike-targeting monoclonal antibodies with an extended half-life in healthy adults, Front. Pharmacol
Hoy, Amubarvimab/romlusevimab: first approval, Drugs
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol
Ji, Zhang, Cheng, Preclinical characterization of amubarvimab and romlusevimab, a pair of non-competing neutralizing monoclonal antibody cocktail, against SARS-CoV-2, Front. Immunol
Jin, Zhan, Peng, Chemoprophylaxis, diagnosis, treatments, and discharge management of COVID-19: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline (updated version), Mil Med Res
Ju, Zhang, Ge, Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nature
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19, Thromb. Res
Lawler, Goligher, Berger, Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Liao, Li, Liu, Neutralizing monoclonal antibody in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: an observational study, Virol. J
Middeldorp, Coppens, Van Haaps, Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Montgomery, Hobbs, Padilla, Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab-cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Respir. Med
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature
Qu, Xie, Qiu, Characterizing infections in two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants: a cohort study in Guangzhou, China, Viruses
Reis, Metzendorf, Kuehn, Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev
Stone, Farkouh, Lala, Randomized trial of anticoagulation strategies for noncritically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol
Taylor, Marson, Elhadi, Factors associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Anaesthesia
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA
Zhang, Yang, Chen, When and how will the epidemic of COVID-19 end?, Aging Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663",
"ISSN": [
"2405-8440"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405844024136948"
],
"article-number": "e37663",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of amubarvimab-romlusevimab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in intensive care units: A retrospective cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Heliyon"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5339-8946",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Peng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lou",
"given": "Anni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rong",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Canmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Qinglei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cui",
"given": "Wanfu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gong",
"given": "Jiacheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Qihan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Zhuoer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bathaiian",
"given": "Luqman Sadat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Cheng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Heliyon",
"container-title-short": "Heliyon",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-11T06:56:15Z",
"timestamp": 1726037775000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-17T06:44:59Z",
"timestamp": 1729147499000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-18T04:19:19Z",
"timestamp": 1729225159886,
"version": "3.27.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1725148800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1725148800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 6,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1725667200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405844024136948?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405844024136948?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e37663",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib1",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16040649",
"article-title": "Characterizing infections in two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants: a cohort study in Guangzhou, China",
"author": "Qu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib2",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14336/AD.2021.1120",
"article-title": "When and how will the epidemic of COVID-19 end?",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "641",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Aging Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib3",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "782",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib4",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/cmr.00119-23",
"article-title": "COVID-19 therapeutics",
"author": "Focosi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib5",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib6",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01759-3",
"article-title": "Amubarvimab/romlusevimab: first approval",
"author": "Hoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib7",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Chemoprophylaxis, diagnosis, treatments, and discharge management of COVID-19: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline (updated version)",
"author": "Jin",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib9",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redar.2020.07.003",
"article-title": "Patient characteristics, clinical course and factors associated to ICU mortality in critically ill patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Spain: a prospective, cohort, multicentre study",
"author": "Ferrando",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib10",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00180-1",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of intramuscular administration of tixagevimab-cilgavimab for early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Montgomery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "985",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate covid-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib12",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19",
"author": "Reis",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3565",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir among U.S. Veterans: target trial emulation studies with one-month and six-month outcomes",
"author": "Bajema",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "807",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib14",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1213",
"issue": "10359",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib15",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00751-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): a randomised controlled trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "622",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib16",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2380-z",
"article-title": "Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Ju",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"issue": "7819",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib17",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01944-6",
"article-title": "Neutralizing monoclonal antibody in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: an observational study",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "218",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib18",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.983505",
"article-title": "Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind phase 1 studies of the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of BRII-196 and BRII-198, SARS-CoV-2 spike-targeting monoclonal antibodies with an extended half-life in healthy adults",
"author": "Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib19",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.980435",
"article-title": "Preclinical characterization of amubarvimab and romlusevimab, a pair of non-competing neutralizing monoclonal antibody cocktail, against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Ji",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3428",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of combination SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies amubarvimab plus romlusevimab in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Evering",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "658",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib21",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z",
"article-title": "Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization",
"author": "Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "671",
"issue": "7898",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib22",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006000",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation",
"author": "Connors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2033",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib23",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.201240",
"article-title": "Anticipating and managing coagulopathy and thrombotic manifestations of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Godoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E1156",
"issue": "40",
"journal-title": "CMAJ (Can. Med. Assoc. J.)",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib24",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013",
"article-title": "Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Klok",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib25",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14888",
"article-title": "Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Middeldorp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1995",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003763",
"article-title": "American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Cuker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "872",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib27",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with covid-19",
"author": "Goligher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib28",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105911",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with covid-19",
"author": "Lawler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib29",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2023.02.041",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of anticoagulation strategies for noncritically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1747",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib30",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/anae.15532",
"article-title": "Factors associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1224",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Anaesthesia",
"key": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37663_bib31",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405844024136948"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of amubarvimab-romlusevimab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in intensive care units: A retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "10"
}