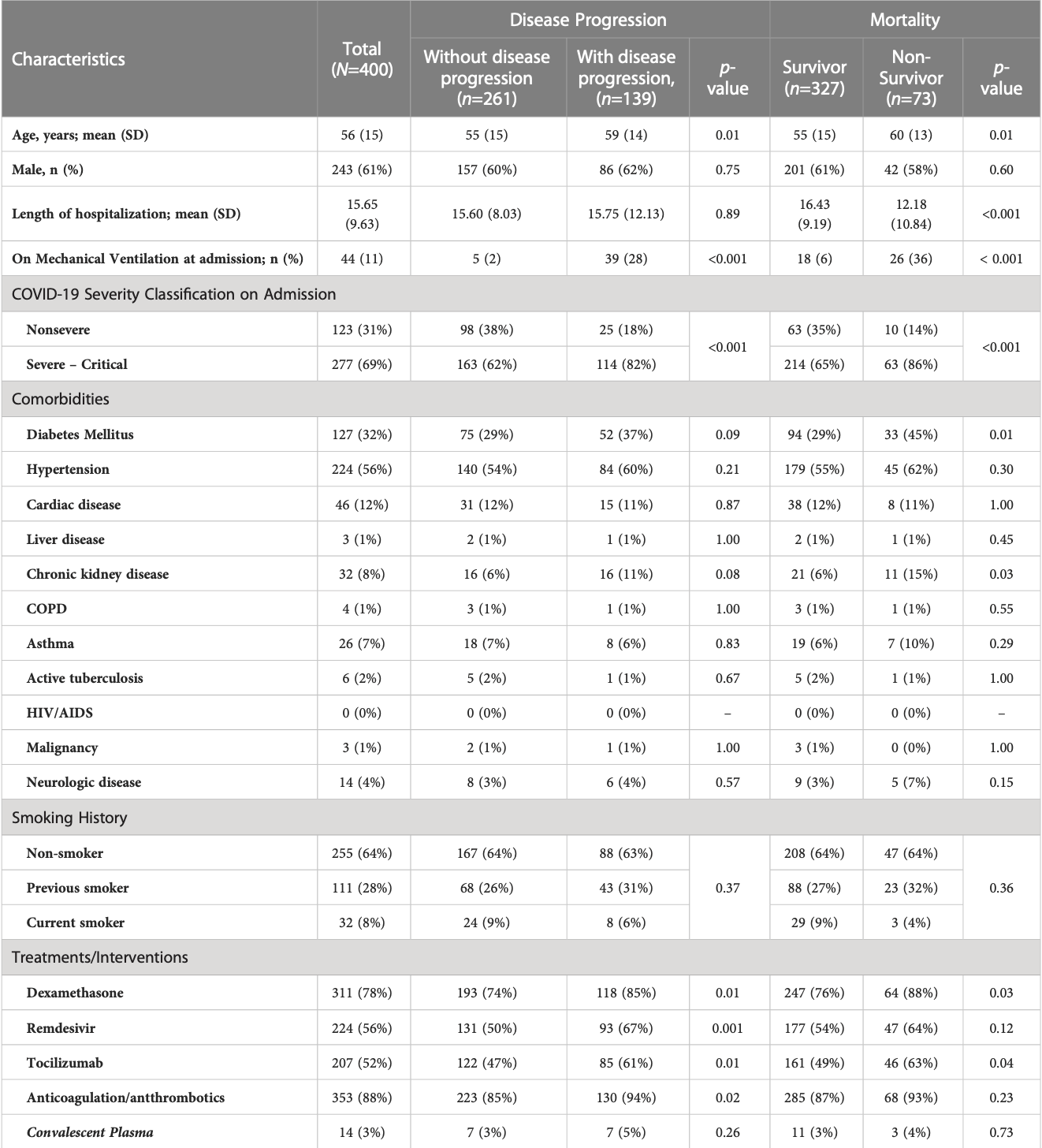
Utility of laboratory and immune biomarkers in predicting disease progression and mortality among patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease at a Philippine tertiary hospital
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497, Feb 2023
Prospective study of 400 hospitalized patients in the Philippines, showing higher progression with remdesivir in unadjusted results, without statistical significance.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 42.0% higher, RR 1.42, p = 0.12, treatment 47 of 224 (21.0%), control 26 of 176 (14.8%).
|
|
risk of progression, 58.9% higher, RR 1.59, p = 0.001, treatment 93 of 224 (41.5%), control 46 of 176 (26.1%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Punzalan et al., 28 Feb 2023, prospective, Philippines, peer-reviewed, mean age 56.0, 17 authors, study period October 2020 - September 2021.
Contact: jimbz11@gmail.com.
Utility of laboratory and immune biomarkers in predicting disease progression and mortality among patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease at a Philippine tertiary hospital
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497
Purpose: This study was performed to determine the clinical biomarkers and cytokines that may be associated with disease progression and in-hospital mortality in a cohort of hospitalized patients with RT-PCR confirmed moderate to severe COVID-19 infection from October 2020 to September 2021, during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic before the advent of vaccination. Patients and methods: Clinical profile was obtained from the medical records. Laboratory parameters (complete blood count [CBC], albumin, LDH, CRP, ferritin, D-dimer, and procalcitonin) and serum concentrations of cytokines (IL-1b, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, IFN-g, IP-10, TNF-a) were measured on Days 0-3, 4-10, 11-14 and beyond Day 14 from the onset of illness. Regression analysis was done to determine the association of the clinical laboratory biomarkers and cytokines with the primary outcomes of disease progression and mortality. ROC curves were generated to determine the predictive performance of the cytokines. Results: We included 400 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection, 69% had severe to critical COVID-19 on admission. Disease progression occurred in Frontiers in Immunology frontiersin.org 01
Ethics statement This study was approved by the UP Manila Research Ethics Board (UPMREB 2020-251-01). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions Conceptualization: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, AD-W, and MA. Methodology: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, MM, KA, JP, AD-W, and MA. Formal analysis: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, MM, KA, AA, AD-W, and MA. Investigation: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, MM, KA, AD-W, and MA. Resources: FP, SP-S, and MA. Data curation: JA, SP-S, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, MM, KA, and JP. Writingoriginal draft preparation: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, and MM. Writingreview & editing: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, OT, MM, and MA. Supervision: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, AD-W, and MA. Project administration: FP, JA, SP-S, AD-W, and MA. Funding acquisition: FP, JA, SP-S, AMo, AMa, JT, OT, EQ, MU, RL, JR, AD-W, and MA. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any..
References
Abani, Abbas, Abbas, Abbas, Abbasi et al., Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0
Abou-Ismail, Diamond, Kapoor, Arafah, Nayak, The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management, Thromb Res, doi:10.1016/J.THROMRES.2020.06.029
Buja, Wolf, Zhao, Akkanti, Mcdonald et al., The emerging spectrum of cardiopulmonary pathology of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 autopsies from Houston, Texas, and review of autopsy findings from other united states cities, Cardiovasc Pathol Off J Soc Cardiovasc Pathol, doi:10.1134/S0006297920100065
Chen, Wang, Liu, Su, Zhang et al., IP-10 and MCP-1 as biomarkers associated with disease severity of COVID-19, Mol Med, doi:10.1186/S10020-020-00230-X
Chen, Zhao, Qu, Chen, Xiong et al., Detectable serum severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 viral load (RNAemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 level in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/CID/CIAA449
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Coutinho, Oliveira, Albuquerque, Mota, Meneses et al., Elevated IL-18 predicts poor prognosis in critically ill COVID-19 patients at a Brazilian hospital in 2020-21, Future Microbiol, doi:10.2217/FMB-2022-0057
Cruz, Mendes-Frias, Oliveira, Dias, Matos et al., Interleukin-6 is a biomarker for the development of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2021.613422
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Goligher, Bradbury, Mcverry, Lawler, Berger et al., Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with covid-19, BioMed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/893106
Gong, Dong, Xia, Huang, Dk et al., Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/S12879-020-05681-5
Gorham, Moreau, Corazza, Peluso, Ponthieux et al., IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.3390/IJMS20030649
Guo, Wang, Xia, Shi, Chen et al., Cytokine signature associated with disease severity in COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.3389/FIMMU.2021.681516
Hadjadj, Yatim, Barnabei, Corneau, Boussier et al., Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients, Science, doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.ABC6027
Han, Ma, Li, Liu, Zhao et al., Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
Herold, Jurinovic, Arnreich, Lipworth, Hellmuth et al., Comparative replication and immune activation profiles of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV in human lungs: An ex vivo study with implications for the pathogenesis of COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1093/CID/CIAA410
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/JMV.26232
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Ichikawa, Kuba, Morita, Chida, Tezuka et al., CXCL10-CXCR3 enhances the development of neutrophil-mediated fulminant lung injury of viral and nonviral origin, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/RCCM.201203-0508OC
Jones, Hunter, Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/S41577-021-00553-8
Lampart, Zellweger, Bassetti, Tschudin-Sutter, Rentsch et al., Clinical utility of inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19 in direct comparison to other respiratory infections-a prospective cohort study, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0269005
Lawler, Goligher, Berger, Neal, Mcverry et al., Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2105911
Li, To, Biomarkers for severe COVID-19, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103405
Li, Ye, Chen, Hu, Wang et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of the first 500 confirmed COVID-19 inpatients in a tertiary infectious disease referral hospital in Manila, Philippines, Trop Med Health, doi:10.1186/S41182-021-00340-0
Liu, Li, Liu, Liang, Wang et al., Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients, EBioMedicine, doi:10.15252/EMMM.202012421
Liu, Tao, Wang, Yuan, Liu et al., Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease, Chin Med J (Engl), doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000775
Lq, Huang, Yq, Zp, Liang et al., COVID-19 patients' clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/JMV.25757
Lu, Zhu, Tan, Zhou, Hu et al., Changes of serum IL-10, IL-1b, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-a, IP-10 and IL-4 in COVID-19 patients, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/IJCP.14462
Lucas, Wong, Klein, Castro, Silva et al., Early differences in cytokine production by severity of coronavirus disease 2019, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/INFDIS/JIAB005
Lupieri, Smirnova, Solinhac, Malet, Benamar et al., Smooth muscle cells-derived CXCL10 prevents endothelial healing through PI3Kg-dependent T cells response, Cardiovasc Res, doi:10.1093/CVR/CVZ122
Malik, Patel, Mehta, Patel, Kelkar et al., Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: Systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Evidence-Based Med, doi:10.1136/BMJEBM-2020-111536
Malundo, Abad, Salamat, Sandejas, Planta et al., Clinical characteristics of patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19 admitted to a tertiary referral centre in the Philippines, IJID Reg, doi:10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.02.002
Martha, Wibowo, Pranata, Prognostic value of elevated lactate dehydrogenase in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Middleton, He, Denorme, Campbell, Ng et al., Efficacy and safety of therapeutic-dose heparin vs standard prophylactic or intermediate-dose heparins for thromboprophylaxis in high-risk hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The HEP-COVID randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6203
Niu, Sareli, Mayer, Visbal, Sareli, Lymphopenia as a predictor for adverse clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A single center retrospective study of 4485 cases, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/JCM11030700
Omland, Mills, Mueller, Care the SG on b of the EA for AC. cardiovascular biomarkers in COVID-19, Eur Hear J Acute Cardiovasc Care, doi:10.1093/EHJACC/ZUAB037
Ozger, Karakus, Kuscu, Bagriacik, Oruklu et al., Serial measurement of cytokines strongly predict COVID-19 outcome, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0260623
Patridge, Bardyn, Research electronic data capture (REDCap), J Med Libr Assoc, doi:10.5195/JMLA.2018.319
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: A storm is raging, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137647
Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson, Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin definition, JAMA, doi:10.1001/JAMA.2012.5669
Rizzi, Costanzo, Tonello, Matino, Casciaro et al., Prognostic markers in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: The role of IP-10 and creactive protein, Dis Markers, doi:10.1155/2022/3528312
Sabaka, Kosčǎĺováa, Straka, Hodosy, Liptaḱ et al., Role of interleukin 6 as a predictive factor for a severe course of covid-19: Retrospective data analysis of patients from a long-term care facility during covid-19 outbreak, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/S12879-021-05945-8
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Patidar, Younis et al., Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN Compr Clin Med, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4
Satışh, Hs, Yıldız, Hızel, Gulbahar et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-18 and its association with other inflammatory markers and disease severity in COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/IJMS22157914
Segundo, De Las Revillas, Lamadrid-Perojo, Comins-Boo, Gonzaĺez-Rico et al., Innate and adaptive immune assessment at admission to predict clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/BIOMEDICINES9080917
Shi, Wang, Ye, Gu, Wang et al., Predictors of mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/S12879-021-06369-0
Wang, Li, Yin, Zhang, Cao et al., Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.02063
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/JAMAINTERNMED.2020.0994
Xia, Wang, Pan, Cheng, Ji et al., Why is the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant milder?, Innov, doi:10.1016/J.XINN.2022.100251
Xu, Yang, Wang, Li, Xue et al., Serum albumin levels are a predictor of COVID-19 patient prognosis: Evidence from a single cohort in chongqing, China, Int J Gen Med, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S312521
Yanez, Weiss, Romand, Treggiari, COVID-19 mortality risk for older men and women, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/S12889-020-09826-8
Yang, Shen, Li, Yuan, Wei et al., Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID
Zhan, Chen, Liu, Cheng, Yan et al., Diagnostic value of d-dimer in COVID-19: A meta-analysis and meta-regression, Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, doi:10.1177/10760296211010976
Zhang, Wang, Jia, Li, Hu et al., Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in wuhan, China, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.47895/amp.v54i0.1561
Zhou, Fu, Zheng, Wang, Zhao et al., Pathogenic T-cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storms in severe COVID-19 patients, Natl Sci Rev, doi:10.1093/NSR/NWAA041
Zhou, He, Liang, Wang, Yu et al., Association of interleukin-6 levels with morbidity and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Jpn J Infect Dis, doi:10.7883/YOKEN.JJID.2020.463
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Gockman, Zuo et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.138999
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Purpose</jats:title><jats:p>This study was performed to determine the clinical biomarkers and cytokines that may be associated with disease progression and in-hospital mortality in a cohort of hospitalized patients with RT-PCR confirmed moderate to severe COVID-19 infection from October 2020 to September 2021, during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic before the advent of vaccination.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Patients and methods</jats:title><jats:p>Clinical profile was obtained from the medical records. Laboratory parameters (complete blood count [CBC], albumin, LDH, CRP, ferritin, D-dimer, and procalcitonin) and serum concentrations of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, IFN-γ, IP-10, TNF-α) were measured on Days 0-3, 4-10, 11-14 and beyond Day 14 from the onset of illness. Regression analysis was done to determine the association of the clinical laboratory biomarkers and cytokines with the primary outcomes of disease progression and mortality. ROC curves were generated to determine the predictive performance of the cytokines.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>We included 400 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection, 69% had severe to critical COVID-19 on admission. Disease progression occurred in 139 (35%) patients, while 18% of the total cohort died (73 out of 400). High D-dimer &gt;1 µg/mL (RR 3.5 95%CI 1.83–6.69), elevated LDH &gt;359.5 U/L (RR 1.85 95%CI 1.05–3.25), lymphopenia (RR 1.91 95%CI 1.14–3.19), and hypoalbuminemia (RR 2.67, 95%CI 1.05–6.78) were significantly associated with disease progression. High D-dimer (RR 3.95, 95%CI 1.62–9.61) and high LDH (RR 5.43, 95%CI 2.39–12.37) were also significantly associated with increased risk of in-hospital mortality. Nonsurvivors had significantly higher IP-10 levels at 0 to 3, 4 to 10, and 11 to 14 days from illness onset (<jats:italic>p&lt;</jats:italic>0.01), IL-6 levels at 0 to 3 days of illness (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>=0.03) and IL-18 levels at days 11-14 of illness (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>&lt;0.001) compared to survivors. IP-10 had the best predictive performance for disease progression at days 0-3 (AUC 0.81, 95%CI: 0.68–0.95), followed by IL-6 at 11-14 days of illness (AUC 0.67, 95%CI: 0.61–0.73). IP-10 predicted mortality at 11-14 days of illness (AUC 0.77, 95%CI: 0.70–0.84), and IL-6 beyond 14 days of illness (AUC 0.75, 95%CI: 0.68–0.82).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Elevated D-dimer, elevated LDH, lymphopenia and hypoalbuminemia are prognostic markers of disease progression. High IP-10 and IL-6 within the 14 days of illness herald disease progression. Additionally, elevated D-dimer and LDH, high IP-10, IL-6 and IL-18 were also associated with mortality. Timely utilization of these biomarkers can guide clinical monitoring and management decisions for COVID-19 patients in the Philippines.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Punzalan",
"given": "Felix Eduardo R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aherrera",
"given": "Jaime Alfonso M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Paz-Silava",
"given": "Sheriah Laine M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mondragon",
"given": "Alric V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malundo",
"given": "Anna Flor G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Joanne Jennifer E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tantengco",
"given": "Ourlad Alzeus G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quebral",
"given": "Elgin Paul B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uy",
"given": "Mary Nadine Alessandra R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lintao",
"given": "Ryan C. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dela Rosa",
"given": "Jared Gabriel L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mercado",
"given": "Maria Elizabeth P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avenilla",
"given": "Krisha Camille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poblete",
"given": "Jonnel B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albay",
"given": "Albert B.",
"sequence": "additional",
"suffix": "Jr."
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "David-Wang",
"given": "Aileen S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alejandria",
"given": "Marissa M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T16:58:18Z",
"timestamp": 1678121898000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T16:58:24Z",
"timestamp": 1678121904000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100011096",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Philippine Council for Health Research and Development"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-07T05:38:44Z",
"timestamp": 1678167524422
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
28
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677542400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London England)",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients",
"author": "Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Sanyaolu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "SN Compr Clin Med",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"article-title": "Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JMV.25757",
"article-title": "COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103405",
"article-title": "Biomarkers for severe COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/BMJEBM-2020-111536",
"article-title": "Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: Systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Malik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Evidence-Based Med",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/EHJACC/ZUAB037",
"article-title": "Care the SG on b of the EA for AC. cardiovascular biomarkers in COVID-19",
"author": "Omland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Hear J Acute Cardiovasc Care",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/BIOMEDICINES9080917",
"article-title": "Innate and adaptive immune assessment at admission to predict clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Segundo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "917",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12879-021-06369-0",
"article-title": "Predictors of mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "663",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.02.002",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19 admitted to a tertiary referral centre in the Philippines",
"author": "Malundo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "IJID Reg",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/CID/CIAA449",
"article-title": "Detectable serum severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 viral load (RNAemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 level in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12879-020-05681-5",
"article-title": "Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study",
"author": "Gong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "963",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/SCIENCE.ABC6027",
"article-title": "Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Hadjadj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.EBIOM.2020.102763",
"article-title": "Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102763",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/EMMM.202012421",
"article-title": "The role of interleukin-6 in monitoring severe case of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137647",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2: A storm is raging",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMAINTERNMED.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/NSR/NWAA041",
"article-title": "Pathogenic T-cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storms in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "998",
"journal-title": "Natl Sci Rev",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0269005",
"article-title": "Clinical utility of inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19 in direct comparison to other respiratory infections–a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Lampart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.008",
"article-title": "Elevated levels of IL-6 and CRP predict the need for mechanical ventilation in COVID-19",
"author": "Herold",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CELL.2020.04.026",
"article-title": "Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19",
"author": "Blanco-Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1036",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/CID/CIAA410",
"article-title": "Comparative replication and immune activation profiles of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV in human lungs: An ex vivo study with implications for the pathogenesis of COVID-19",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JMV.26232",
"article-title": "The cytokine storm and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B25",
"unstructured": "Philippines COVID-19 tracker2022"
},
{
"key": "B26",
"unstructured": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMA.2012.5669",
"article-title": "Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin definition",
"author": "Ranieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "B28",
"volume-title": "UP-PGH COVID-19 daily report",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CMI.2020.04.012",
"article-title": "Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47895/amp.v54i0.1561",
"article-title": "Should laboratory markers be used for early prediction of severe and possibly fatal COVID-19",
"author": "Salido",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Acta Med Philipp",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5195/JMLA.2018.319",
"article-title": "Research electronic data capture (REDCap)",
"author": "Patridge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "J Med Libr Assoc",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London England)",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/AGING.103770",
"article-title": "Elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level as an independent risk factor for the severity and mortality of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S41182-021-00340-0",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of the first 500 confirmed COVID-19 inpatients in a tertiary infectious disease referral hospital in Manila, Philippines",
"author": "Agrupis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Trop Med Health",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000775",
"article-title": "Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Chin Med J (Engl)",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12889-020-09826-8",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality risk for older men and women",
"author": "Yanez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1742",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B38",
"unstructured": "Interim guidance on the clinical management of adult patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection2020"
},
{
"key": "B39",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living guideline2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "Abani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London England)",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/POSTGRADMEDJ-2020-139542",
"article-title": "Prognostic value of elevated lactate dehydrogenase in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Martha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Postgrad Med J",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S312521",
"article-title": "Serum albumin levels are a predictor of COVID-19 patient prognosis: Evidence from a single cohort in chongqing, China",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10760296211010976",
"article-title": "Diagnostic value of d-dimer in COVID-19: A meta-analysis and meta-regression",
"author": "Zhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Appl Thromb Hemost",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/JCM11030700",
"article-title": "Lymphopenia as a predictor for adverse clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A single center retrospective study of 4485 cases",
"author": "Niu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "700",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.THROMRES.2020.06.029",
"article-title": "The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management",
"author": "Abou-Ismail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007008",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Middleton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6203",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of therapeutic-dose heparin vs standard prophylactic or intermediate-dose heparins for thromboprophylaxis in high-risk hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The HEP-COVID randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Spyropoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105911",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with covid-19",
"author": "Lawler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with covid-19",
"author": "Goligher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/893106",
"article-title": "The multifaceted functions of CXCL10 in cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Van Den Borne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "893106",
"journal-title": "BioMed Res Int",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/CVR/CVZ122",
"article-title": "Smooth muscle cells-derived CXCL10 prevents endothelial healing through PI3Kγ-dependent T cells response",
"author": "Lupieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/RCCM.201203-0508OC",
"article-title": "CXCL10-CXCR3 enhances the development of neutrophil-mediated fulminant lung injury of viral and nonviral origin",
"author": "Ichikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carpath.2020.107233",
"article-title": "The emerging spectrum of cardiopulmonary pathology of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 autopsies from Houston, Texas, and review of autopsy findings from other united states cities",
"author": "Buja",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Pathol Off J Soc Cardiovasc Pathol",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1134/S0006297920100065",
"article-title": "NETosis: Molecular mechanisms, role in physiology and pathology",
"author": "Vorobjeva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem (Mosc)",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.02063",
"article-title": "Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.138999",
"article-title": "Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/IJCP.14462",
"article-title": "Changes of serum IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, IP-10 and IL-4 in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S10020-020-00230-X",
"article-title": "IP-10 and MCP-1 as biomarkers associated with disease severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Mol Med",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0260623",
"article-title": "Serial measurement of cytokines strongly predict COVID-19 outcome",
"author": "Ozger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/3528312",
"article-title": "Prognostic markers in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: The role of IP-10 and c-reactive protein",
"author": "Rizzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Dis Markers",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.JACI.2020.04.027",
"article-title": "Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FIMMU.2021.681516",
"article-title": "Cytokine signature associated with disease severity in COVID-19",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41577-021-00553-8",
"article-title": "Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/S12879-021-05945-8",
"article-title": "Role of interleukin 6 as a predictive factor for a severe course of covid-19: Retrospective data analysis of patients from a long-term care facility during covid-19 outbreak",
"author": "Sabaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "308",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/FIMMU.2021.613422",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 is a biomarker for the development of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia",
"author": "Santa Cruz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7883/YOKEN.JJID.2020.463",
"article-title": "Association of interleukin-6 levels with morbidity and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jpn J Infect Dis",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0244628",
"article-title": "Interleukine-6 in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis",
"author": "Gorham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.JACI.2020.09.018",
"article-title": "IL-6 serum levels predict severity and response to tocilizumab in COVID-19: An observational study",
"author": "Galván-Román",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "72",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/IJMS20030649",
"article-title": "Interleukin-18 in health and disease",
"author": "Yasuda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/FMB-2022-0057",
"article-title": "Elevated IL-18 predicts poor prognosis in critically ill COVID-19 patients at a Brazilian hospital in 2020-21",
"author": "Coutinho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Future Microbiol",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/S41586-020-2588-Y",
"article-title": "Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/INFDIS/JIAB005",
"article-title": "Early differences in cytokine production by severity of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Tjan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CYTO.2020.155302",
"article-title": "Prognostic value of interleukin-18 and its association with other inflammatory markers and disease severity in COVID-19",
"author": "Satış",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155302",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "B74",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/JEM.20201707",
"article-title": "Inflammasomes are activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and are associated with COVID-19 severity in patients",
"author": "Rodrigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "B75",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/IJMS22157914",
"article-title": "Inflammatory response in COVID-19 patients resulting from the interaction of the inflammasome and SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Cheon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "B76",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.XINN.2022.100251",
"article-title": "Why is the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant milder",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Innov (Cambridge",
"key": "B77",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 77,
"references-count": 77,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123497/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Utility of laboratory and immune biomarkers in predicting disease progression and mortality among patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease at a Philippine tertiary hospital",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}