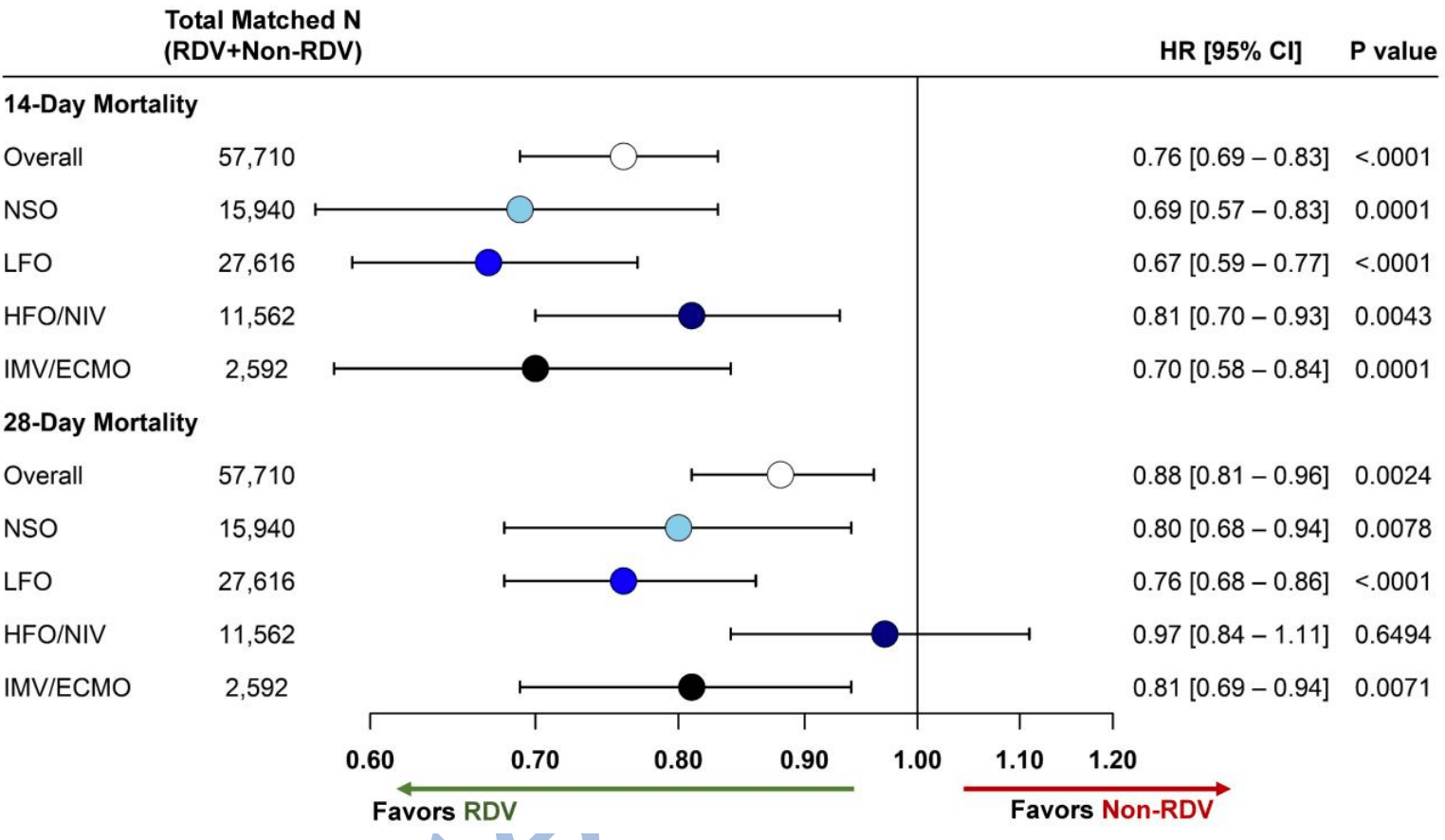
Remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a comparative analysis of in-hospital all-cause mortality in a large multi-center observational cohort
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab875, Oct 2021
Retrospective 28,855 remdesivir patients with PSM matched controls, showing lower mortality with treatment.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Remdesivir efficacy disappears with longer
followup. Mixed-effects meta-regression of efficacy as a function of
followup duration across all remdesivir studies shows decreasing efficacy with
longer followup15. This may reflect
antiviral efficacy being offset by serious adverse effects of treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments16.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 12.0% lower, HR 0.88, p = 0.003, treatment 4,441 of 28,855 (15.4%), control 5,499 of 28,855 (19.1%), NNT 27, adjusted per study, PSM, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 24.0% lower, HR 0.76, p < 0.001, treatment 3,057 of 28,855 (10.6%), control 4,437 of 28,855 (15.4%), NNT 21, adjusted per study, PSM, Cox proportional hazards, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Mozaffari et al., 1 Oct 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
doi:10.1093/cid/ciab875/6378778
Background: Remdesivir (RDV) improved clinical outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in randomized trials, but data from clinical practice are limited.
Methods: We examined survival outcomes for US patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between Aug-Nov 2020 and treated with RDV within two-days of hospitalization vs. those not receiving RDV during their hospitalization using the Premier Healthcare Database. Preferential within-hospital propensity score matching with replacement was used. Additionally, patients were also matched on baseline oxygenation level (no supplemental oxygen charges (NSO), low-flow oxygen (LFO), high-flow oxygen/non-invasive ventilation (HFO/NIV) and invasive mechanical ventilation/ECMO (IMV/ECMO) and two-month admission window and excluded if discharged within 3-days of admission (to exclude anticipated discharges/transfers within 72-hrs consistent with ACTT-1 study). Cox Proportional Hazards models were used to assess time to 14-/28-day mortality overall and for patients on NSO, LFO, HFO/NIV and IMV/ECMO. Results: 28,855 RDV patients were matched to 16,687 unique non-RDV patients. Overall, 10.6% and 15.4% RDV patients died within 14-and 28-days, respectively compared with 15.4% and 19.1% non-RDV patients. Overall, RDV was associated with a reduction in mortality at 14-days (HR[95% CI]: 0.76*0.70−0.83+) and 28-days (0.89*0.82−0.96+). This mortality benefit was also seen for NSO, LFO and IMV/ECMO at 14-days (NSO:0.69*0.57−0.83+, LFO:0.68*0.80−0.77+, IMV/ECMO:0.70*0.58−0.84+) and 28-days (NSO:0.80*0.68−0.94+, LFO:0.77*0.68−0.86+, IMV/ECMO:0.81*0.69−0.94+). Additionally, HFO/NIV RDV group had a lower risk of mortality at 14-days (0.81*0.70−0.93+) but no statistical significance at 28-days.
References
Acosta, Mathis, Budnitz, Geller, Chai et al., COVID-19
Al-Abdouh, Bizanti, Barbarawi, Jabri, Kumar et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Contemp Clin Trials
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med
Buckley, Wohlford, Ting, Alahmed, Van Tassell et al., Role for Anti-Cytokine Therapies in Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019, Crit Care Explor
Elsawah, Elsokary, Abdallah, Elshafie, Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in hospitalized Covid-19 patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis including network metaanalysis, Rev Med Virol
Falcão, Viegas, Carmo, Soares, Falcao et al., A prospective, observational study to evaluate adverse drug reactions in patients with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir or hydroxychloroquine: a preliminary report, Eur J Hosp Pharm
Garibaldi, Wang, Robinson, Zeger, Bandeen-Roche et al., Comparison of Time to Clinical Improvement With vs Without Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open
Garibaldi, Wang, Robinson, Zeger, Roche et al., Effectiveness of remdesivir with and without dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, medRxiv
Gilead, Remdesivir (Veklury) package insert
Goldman, Lye, Hui, Marks, Bruno et al., or 10, Remdesivir for
Gottlieb, A Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kadri, Gundrum, Warner, Cao, Babiker et al., Uptake and Accuracy of the Diagnosis Code for COVID-19 Among US Hospitalizations, JAMA
Kaka, Macdonald, Greer, Vela, Duan-Porter et al., Major Update: Remdesivir for Adults With COVID-19 : A Living Systematic Review and Meta-analysis for the American College of Physicians Practice Points, Ann Intern Med
Kalligeros, Tashima, Mylona, Rybak, Flanigan et al., Remdesivir Use Compared With Supportive Care in Hospitalized Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Single-Center Experience, Open Forum Infect Dis
Lai, Chen, Wang, Chen, Wang et al., Clinical efficacy and safety of remdesivir in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Antimicrob Chemother
Lapadula, Bernasconi, Bellani, Soria, Rona et al., Remdesivir Use in Patients Requiring Mechanical Ventilation due to COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis
Li, Zhang, Hu, Tong, Zheng et al., Effect of Convalescent Plasma Therapy on Time to Clinical Improvement in Patients With Severe and Life-threatening COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Ly-Cov555 Study, Group, Lundgren, Grund, Barkauskas et al., None
Morris, Jüni, Odutayo, Remdesivir for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Science Briefs of the Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table
Olender, Perez, Go, Balani, Eg et al., Remdesivir for Severe COVID-19 versus a Cohort Receiving Standard of Care, Clin Infect Dis
Olender, Walunas, Martinez, Perez, Castagna et al., Remdesivir versus Standard-of-Care for Severe Coronavirus Disease
Pasquini, Montalti, Temperoni, Canovari, Mancini et al., Effectiveness of remdesivir in patients with COVID-19 under mechanical ventilation in an Italian ICU, J Antimicrob Chemother
Rubin, Chan-Tack, Farley, Sherwat, FDA Approval of Remdesivir -A Step in the Right Direction, N Engl J Med
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Lopez, Cattelan et al., Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients With Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Stone, Frigault, Serling-Boyd, Fernandes, Harvey et al., Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Wise, Covid-19: Remdesivir is recommended for authorisation by European Medicines Agency, BMJ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab875",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab875",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Remdesivir (RDV) improved clinical outcomes among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in randomized trials, but data from clinical practice are limited.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We examined survival outcomes for US patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between August and November 2020 and treated with RDV within 2 days of hospitalization vs those not receiving RDV during their hospitalization using the Premier Healthcare Database. Preferential within-hospital propensity score matching with replacement was used. Additionally, patients were also matched on baseline oxygenation level (no supplemental oxygen charges [NSO], low-flow oxygen [LFO], high-flow oxygen/noninvasive ventilation [HFO/NIV], and invasive mechanical ventilation/extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [IMV/ECMO]) and 2-month admission window and excluded if discharged within 3 days of admission (to exclude anticipated discharges/transfers within 72 hours, consistent with the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial [ACTT-1] study). Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess time to 14-/28-day mortality overall and for patients on NSO, LFO, HFO/NIV, and IMV/ECMO.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 28855 RDV patients were matched to 16687 unique non-RDV patients. Overall, 10.6% and 15.4% RDV patients died within 14 and 28 days, respectively, compared with 15.4% and 19.1% non-RDV patients. Overall, RDV was associated with a reduction in mortality at 14 days (hazard ratio [95% confidence interval]: 0.76 [0.70–0.83]) and 28 days (0.89 [0.82–0.96]). This mortality benefit was also seen for NSO, LFO, and IMV/ECMO at 14 days (NSO: 0.69 [0.57–0.83], LFO: 0.68 [0.80–0.77], IMV/ECMO: 0.70 [0.58–0.84]) and 28 days (NSO: 0.80 [0.68–0.94], LFO: 0.77 [0.68–0.86], IMV/ECMO: 0.81 [0.69–0.94]). Additionally, HFO/NIV RDV group had a lower risk of mortality at 14 days (0.81 [0.70–0.93]) but no statistical significance at 28 days.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>RDV initiated upon hospital admission was associated with improved survival among patients with COVID-19. Our findings complement ACTT-1 and support RDV as a foundational treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences , Foster City, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mozaffari",
"given": "Essy",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5653-435X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara , New York, New York , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chandak",
"given": "Aastha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara , New York, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zhiji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences , Foster City, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Shuting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences , Foster City, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Thrun",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Baylor University Medical Center , Dallas, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott and White Heart and Vascular Hospital , Dallas, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott and White The Heart Hospital , Plano, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott and White Research Institute , Dallas, Texas , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gottlieb",
"given": "Robert L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School , Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kuritzkes",
"given": "Daniel R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Brigham and Women’s Hospital , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sax",
"given": "Paul E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of North Carolina , Chapel Hill, North Carolina , USA"
}
],
"family": "Wohl",
"given": "David A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7083-9536",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara , New York, New York , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Casciano",
"given": "Roman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences , Foster City, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hodgkins",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences , Foster City, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Haubrich",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T15:31:22Z",
"timestamp": 1633015882000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-25T03:09:44Z",
"timestamp": 1661396984000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100005564",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Gilead Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-26T23:18:07Z",
"timestamp": 1711495087917
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 76,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab875/40509854/ciab875.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e450/45514485/ciab875.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/75/1/e450/45514485/ciab875.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e450-e458",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"article-title": "Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2333",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0001",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033130",
"article-title": "A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Activ-Tico Ly- CoV555 Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0002",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Recovery Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0003",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000178",
"article-title": "Role for anti-cytokine therapies in severe Coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Buckley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0178",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Explor",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0004",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa528",
"article-title": "COVID-19 investigational treatments in use among hospitalized patients identified through the US Coronavirus disease 2019-associated hospitalization surveillance network, March 1-June 30, 2020",
"author": "Acosta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa528",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0005",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"article-title": "A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia",
"author": "Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0006",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"article-title": "Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0007",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0008",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2032369",
"article-title": "FDA approval of remdesivir - a step in the right direction",
"author": "Rubin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2598",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0009",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1048",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0010",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015301",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Goldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1827",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0011",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Gilead.",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0012",
"volume-title": "Remdesivir (Veklury) package insert",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m2610",
"article-title": "Covid-19: remdesivir is recommended for authorisation by European Medicines Agency",
"author": "Wise",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m2610",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0013",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19 - Interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Consortium WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0014",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkab093",
"article-title": "Clinical efficacy and safety of remdesivir in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1962",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0015",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cct.2021.106272",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Al-Abdouh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106272",
"journal-title": "Contemp Clin Trials",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0016",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-8148",
"article-title": "Major update: remdesivir for adults with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta-analysis for the American College of Physicians practice points",
"author": "Kaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "663",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0017",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Science briefs of the Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table",
"author": "Morris",
"first-page": "27",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0018",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for severe COVID-19 versus a cohort receiving standard of care",
"author": "Olender",
"first-page": "ciaa1041",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0019",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab278",
"article-title": "Remdesivir versus standard-of-care for severe Coronavirus disease 2019 infection: an analysis of 28-day mortality",
"author": "Olender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofab278",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0020",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-002613",
"article-title": "A prospective, observational study to evaluate adverse drug reactions in patients with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir or hydroxychloroquine: a preliminary report",
"author": "Falcão",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Eur J Hosp Pharm",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0021",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa319",
"article-title": "Remdesivir use compared with supportive care in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a single-center experience",
"author": "Kalligeros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa319",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0022",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa481",
"article-title": "Remdesivir use in patients requiring mechanical ventilation due to COVID-19",
"author": "Lapadula",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa481",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0023",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Comparison of time to clinical improvement with vs without remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Garibaldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e213071",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0024",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of remdesivir with and without dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Garibaldi",
"first-page": "2020.11.19.20234153",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0025",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa321",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of remdesivir in patients with COVID-19 under mechanical ventilation in an Italian ICU",
"author": "Pasquini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3359",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0026",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.20323",
"article-title": "Uptake and accuracy of the diagnosis code for COVID-19 among US hospitalizations",
"author": "Kadri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2553",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0027",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2187",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of remdesivir in hospitalized Covid-19 patients: systematic review and meta-analysis including network meta-analysis",
"author": "Elsawah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2187",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "2022082503063325800_CIT0028",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/75/1/e450/6378778"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Comparative Analysis of In-hospital All-cause Mortality in a Large Multicenter Observational Cohort",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "75"
}