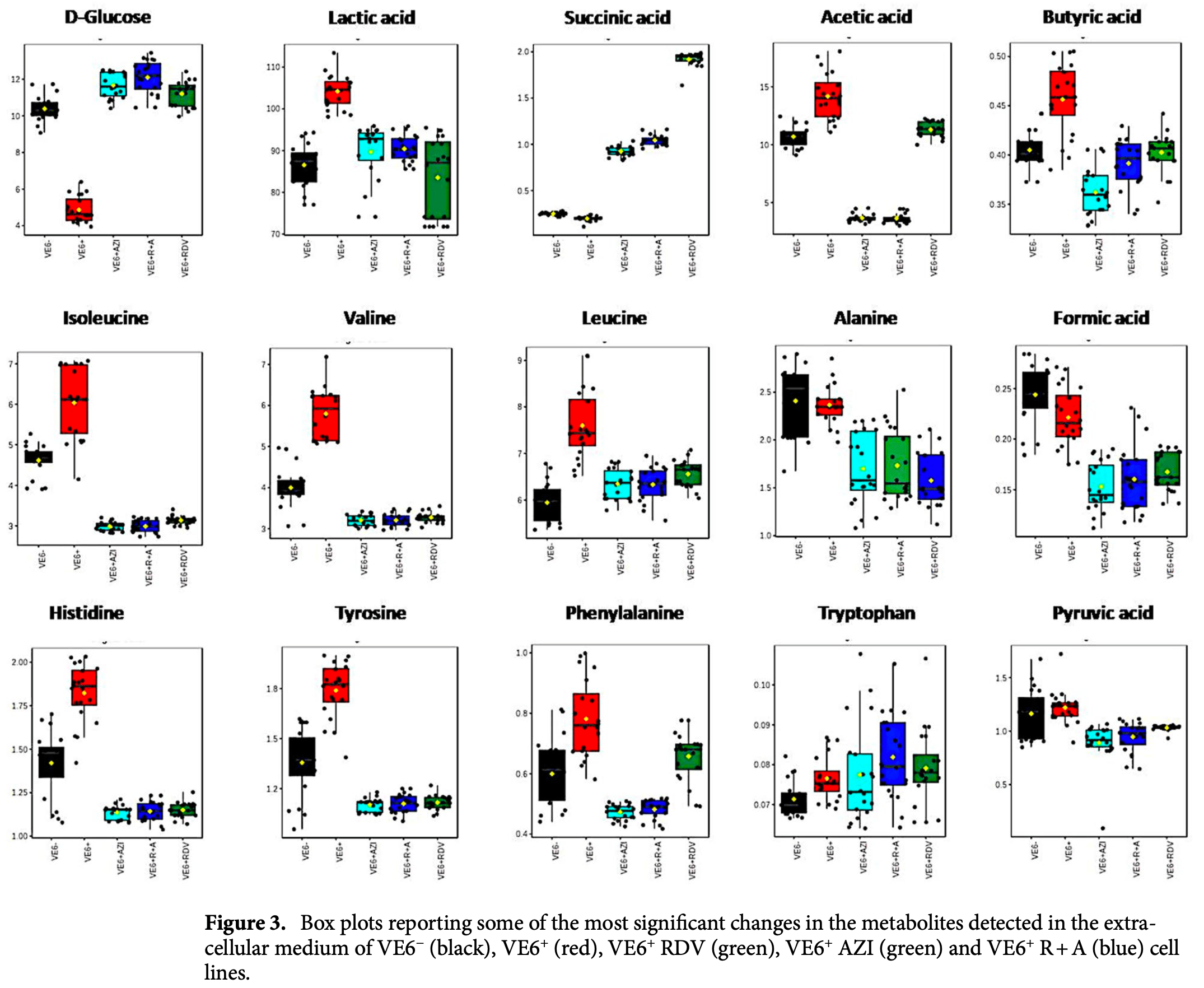
The metabolic footprint of Vero E6 cells highlights the key metabolic routes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and response to drug combinations
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57726-3, Apr 2024
In vitro study showing that remdesivir and azithromycin, either alone or in combination, can modify the glycolic-gluconeogenesis pathway in host cells, inhibiting the mitochondrial oxidative damage caused by SARS-CoV-2. Authors use Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-based metabolic footprinting to explore the metabolic impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on Vero E6 cells, showing that SARS-CoV-2 significantly alters the metabolic pathways, enhancing glucose uptake and modifying the glycolic-gluconeogenesis pathway, thereby leading to altered energy metabolism and oxidative stress.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Melis et al., 4 Apr 2024, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: anedda@portocontericerche.it.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
The metabolic footprint of Vero E6 cells highlights the key metabolic routes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and response to drug combinations
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57726-3
SARS-CoV -2 burdens healthcare systems worldwide, yet specific drug-based treatments are still unavailable. Understanding the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on host molecular pathways is critical for providing full descriptions and optimizing therapeutic targets. The present study used Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-based metabolic footprinting to characterize the secreted cellular metabolite levels (exometabolomes) of Vero E6 cells in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and to two candidate drugs (Remdesivir, RDV, and Azithromycin, AZI), either alone or in combination. SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to force VE6 cells to have increased glucose concentrations from extra-cellular medium and altered energetic metabolism. RDV and AZI, either alone or in combination, can modify the glycolicgluconeogenesis pathway in the host cell, thus impairing the mitochondrial oxidative damage caused by the SARS-CoV-2 in the primary phase. RDV treatment appears to be associated with a metabolic shift toward the TCA cycle. Our findings reveal a metabolic reprogramming produced by studied pharmacological treatments that protects host cells against virus-induced metabolic damage, with an emphasis on the glycolytic-gluconeogenetic pathway. These findings may help researchers better understand the relevant biological mechanisms involved in viral infection, as well as the creation of mechanistic hypotheses for such candidate drugs, thereby opening up new possibilities for SARS-CoV-2 pharmacological therapy. Keywords SARS-CoV-2
Statistical data analysis NMR data were imported into the Statistical Analysis module included in the web-based software Metabo-Analyst version 5.0 68 for multivariate and univariate data analysis 69 . For multivariate purposes, 1 H NMR data were preliminary constant sum normalized, logarithm-transformed and Pareto scaled. Unsupervised principal component analysis (PCA) was initially carried out to identify outlier samples and possibly observe group clustering. Additionally, the related PCA scores dendrogram was also generated, by using the PCA2Tree tool, to provide a quantitative measure of the significance of similarity/difference between the observed clusters. PCA2Tree computes the dendrograms using Mahalanobis distances and reports p-values for the null hypothesis at all internal branches, where p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference 70 . A more robust supervised multivariate approach, employing partial least square discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), was also carried out to better characterize sample grouping (1. infected vs. uninfected and 2. infected and treated vs. infected VE6 cells exometabolomes). For each PLS-DA model, cross-validation (CV) was also performed, by using the parameter Q2 as indicative of the predictive ability of the model. Good predictions will have high Q 2 computed values 71 . To get proper information on the metabolites responsible for observed sample clustering, the importance feature analysis based on univariate..
References
Adamson, Chapter 17 -Viral infections and glycolysis, doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-91704-9.00009-4
Ahmadian, A cost-effectiveness analysis of azithromycin for the prevention of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc
Ahn, Jung, Jang, Madsen, Park, Role of glyoxylate shunt in oxidative stress response, J. Biol. Chem
Albóniga, Differential abundance of lipids and metabolites related to SARS-CoV-2 infection and susceptibility, Sci. Rep
Aleem, Mahadevaiah, Shariff, Kothadia, Hepatic manifestations of COVID-19 and effect of remdesivir on liver function in patients with COVID-19 illness, Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent
Alvarado, Campos-Campos, Guerrero-Romero, Simental-Mendía, The triglycerides and glucose index is an independent risk factor for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19, Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord, doi:10.1089/met.2023.0247
Ambade, Ambade, Sharma, Sanas, Comparison between Amino Acid Profiling of Structural Proteins of earliest and recent omicron strain of SARS-CoV-2 and Nutritional Burden on COVID-19 patients, Hum. Nutr. Metab
Ansone, Longitudinal NMR-based metabolomics study reveals how hospitalized COVID-19 patients recover: Evidence of dyslipidemia and energy metabolism dysregulation, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Atieh, Systemic azithromycin versus amoxicillin/metronidazole as an adjunct in the treatment of periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Aust. Dent. J
Barcia, Polypharmacy and Drug Interactions in the COVID-19 Pandemic, Prague Med. Rep
Basit, COVID-19Base v3: Update of the knowledgebase for drugs and biomedical entities linked to COVID-19, Front. Public Health
Behrends, Williams, Bundy, Metabolic footprinting: extracellular metabolomic analysis, Methods Mol. Biol
Bhinderwala, Powers, NMR metabolomics protocols for drug discovery, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-9690-2_16
Bhowal, Ghosh, Ghatak, De, Pathophysiological involvement of host mitochondria in SARS-CoV-2 infection that causes COVID-19: A comprehensive evidential insight, Mol. Cell. Biochem
Blair, Remdesivir: a review in COVID-19, Drugs
Caceres-Cortes, Falk, Mueller, Dhar, Perspectives on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in drug discovery research, J. Med. Chem
Castro, Alterations in the cellular metabolic footprint induced by Mayaro virus, BioMed
Ceperuelo-Mallafré, Circulating pyruvate is a potent prognostic marker for critical COVID-19 outcomes, Front. Immunol
Corbin, The metabolomic signature of weight loss and remission in the Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT), Diabetologia
Cuevas, Systemic and functional effects of continuous azithromycin treatment in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and frequent exacerbations, Front. Med
De Forni, Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE
Di Cara, Savary, Kovacs, Kim, Rachubinski, The peroxisome: An up-and-coming organelle in immunometabolism, Trends Cell Biol
Dirajlal-Fargo, Altered mitochondrial respiration in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Mitochondrion
Du, Wang, Hu, Li, An, Integration analysis of pharmacokinetics and metabolomics to predict metabolic phenotype and drug exposure of remdesivir, Front. Pharmacol
Ermer, Oxalate homeostasis, Nat. Rev. Nephrol
Excler, Factors, enablers and challenges for COVID-19 vaccine development, BMJ Glob. Heal
Fišar, Ľupták, Hroudová, Little in vitro effect of remdesivir on mitochondrial respiration and monoamine oxidase activity in isolated mitochondria, Toxicol. Lett
Gassen, SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals, Nat. Commun
Georgieva, COVID-19 complications: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial and endothelial dysfunction, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Gudima, Kofiadi, Shilovskiy, Kudlay, Khaitov, Antiviral Therapy of COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Jacob, Deborde, Lefebvre, Maucourt, Moing, NMRProcFlow: a graphical and interactive tool dedicated to 1D spectra processing for NMR-based metabolomics, Metabolomics
Jadhav, Annapure, Triglycerides of medium-chain fatty acids: A concise review, J. Food Sci. Technol
Jiang, Baucom, Elliott, Mitochondrial toxicity of azithromycin results in aerobic glycolysis and DNA damage of human mammary epithelia and fibroblasts, Antibiotics
Kanehisa, Furumichi, Sato, Kawashima, Ishiguro-Watanabe, KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes, Nucleic Acids Res
Kanehisa, Goto, KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes, Nucleic Acids Res
Kanehisa, Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms, Protein Sci
Kell, Metabolic footprinting and systems biology: The medium is the message, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Kimura-Ohba, Blood levels of d-amino acids reflect the clinical course of COVID-19, Biochem. Biophys. reports
Kuretu, Drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity: Risks of developing glucose handling impairments, Front. Endocrinol
Lamb, Remdesivir, None, First Approval. Drugs
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, De Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov
Ling, Amino acid metabolism in health and disease, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Lodge, Integrative plasma metabolic and lipidomic modelling of SARS-CoV-2 infection in relation to clinical severity and early mortality prediction, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Luan, Glucose metabolism disorder: A potential accomplice of SARS-CoV-2, Int. J. Obes
Mahaling, Pandala, Wang, Lavik, Azithromycin protects retinal glia against oxidative stress-induced morphological changes, inflammation, and cell death, ACS Bio Med Chem Au
Maltais-Payette, Lajeunesse-Trempe, Pibarot, Biertho, Tchernof, Association between circulating amino acids and COVID-19 severity, Metabolites
Merches, The potential of remdesivir to affect function, metabolism and proliferation of cardiac and kidney cells in vitro, Arch. Toxicol
Mohammad, SARS-CoV-2-free residual proteins mediated phenotypic and metabolic changes in peripheral blood monocytic-derived macrophages in support of viral pathogenesis, PLoS ONE
Narayanan, A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Hum. Genet
Pagano, Blood lactate in mild and moderate ARDS secondary to SARS COV 2, Am. J. Emerg. Med
Panahi, An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19, Virol. J
Pang, MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights, Nucleic Acids Res
Rahman, Hossain, Eicosanoids signals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A foe or friend, Mol. Biotechnol, doi:10.1007/s12033-023-00919-4
Rochowski, Impact of Delta SARS-CoV-2 infection on glucose metabolism: Insights on host metabolism and virus crosstalk in a feline model, Viruses
Santos, Póvoa, Paixão, Mendonça, Taborda-Barata, Changes in glycolytic pathway in SARS-COV 2 infection and their importance in understanding the severity of COVID-19, Front. Chem
Scaini, Toxicity of octanoate and decanoate in rat peripheral tissues: evidence of bioenergetic dysfunction and oxidative damage induction in liver and skeletal muscle, Mol. Cell. Biochem
Sumner, Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI), Metabolomics
Szymańska, Saccenti, Smilde, Westerhuis, Double-check: validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies, Metabolomics
Ticinesi, Co-administration of remdesivir and azithromycin may protect against intensive care unit admission in COVID-19 pneumonia requiring hospitalization: A real-life observational study, Antibiot
Trevor, Lim, Urquhart, Pharmacometabolomics in drug disposition, toxicity and precision medicine, Drug Metab. Dispos, doi:10.1124/dmd.123.001074
Venditto, Immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin revisited: Potential applications to COVID-19, Front
Verleden, Verleden, Azithromycin for other lung diseases: Lung transplantation and sarcoidosis, doi:10.1007/978-3-031-42859-3_10
Vianey-Saban, Guffon, Fouilhoux, Acquaviva, Fifty years of research on mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation disorders: The remaining challenges, J. Inherit. Metab. Dis
Worley, Halouska, Powers, Utilities for quantifying separation in PCA/PLS-DA scores plots, Anal. Biochem
Xing, Liu, Azithromycin inhibited oxidative stress and apoptosis of high glucose-induced podocytes by inhibiting STAT1 pathway, Drug Dev. Res
Xu, Off-target in vitro profiling demonstrates that remdesivir is a highly selective antiviral agent, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Yadigaroğlu, Can lactate levels and lactate kinetics predict mortality in patients with COVID-19 with using qCSI scoring system?, Am. J. Emerg. Med
Yan, Wu, Li, Zhao, Xu, Immunomodulatory role of azithromycin: Potential applications to radiation-induced lung injury, Front. Oncol
Yousafzai, Clinical efficacy of Azithromycin for COVID-19 management: A systematic meta-analysis of metaanalyses, Heart Lung
Zhu, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-57726-3",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57726-3",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 burdens healthcare systems worldwide, yet specific drug-based treatments are still unavailable. Understanding the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on host molecular pathways is critical for providing full descriptions and optimizing therapeutic targets. The present study used Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-based metabolic footprinting to characterize the secreted cellular metabolite levels (exometabolomes) of Vero E6 cells in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and to two candidate drugs (Remdesivir, RDV, and Azithromycin, AZI), either alone or in combination. SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to force VE6 cells to have increased glucose concentrations from extra-cellular medium and altered energetic metabolism. RDV and AZI, either alone or in combination, can modify the glycolic-gluconeogenesis pathway in the host cell, thus impairing the mitochondrial oxidative damage caused by the SARS-CoV-2 in the primary phase. RDV treatment appears to be associated with a metabolic shift toward the TCA cycle. Our findings reveal a metabolic reprogramming produced by studied pharmacological treatments that protects host cells against virus-induced metabolic damage, with an emphasis on the glycolytic-gluconeogenetic pathway. These findings may help researchers better understand the relevant biological mechanisms involved in viral infection, as well as the creation of mechanistic hypotheses for such candidate drugs, thereby opening up new possibilities for SARS-CoV-2 pharmacological therapy.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"57726"
],
"article-number": "7950",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "22 November 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "21 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "4 April 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melis",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Braca",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pagnozzi",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anedda",
"given": "Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T15:02:53Z",
"timestamp": 1712242973000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T15:09:12Z",
"timestamp": 1712243352000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009873",
"award": [
"art. 9 L.R. 20/2015"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Regione Autonoma della Sardegna"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T00:52:56Z",
"timestamp": 1712278376048
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712188800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-57726-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-57726-3",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-57726-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "57726_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhu, N. et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2023-011879",
"author": "J-L Excler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e011879",
"journal-title": "BMJ Glob. Heal.",
"key": "57726_CR2",
"unstructured": "Excler, J.-L. et al. Factors, enablers and challenges for COVID-19 vaccine development. BMJ Glob. Heal. 8, e011879 (2023).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24108867",
"author": "G Gudima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8867",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "57726_CR3",
"unstructured": "Gudima, G., Kofiadi, I., Shilovskiy, I., Kudlay, D. & Khaitov, M. Antiviral Therapy of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 8867 (2023).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2023.1125917",
"author": "SA Basit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1125917",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "57726_CR4",
"unstructured": "Basit, S. A. et al. COVID-19Base v3: Update of the knowledgebase for drugs and biomedical entities linked to COVID-19. Front. Public Health 11, 1125917 (2023).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-023-01926-0",
"author": "HA Blair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1215",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "57726_CR5",
"unstructured": "Blair, H. A. Remdesivir: a review in COVID-19. Drugs 83, 1215–1237 (2023).",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-020-01378-w",
"author": "YN Lamb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1355",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "57726_CR6",
"unstructured": "Lamb, Y. N. Remdesivir: First Approval. Drugs 80, 1355–1363 (2020).",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-01973-9",
"author": "Y Panahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "57726_CR7",
"unstructured": "Panahi, Y. et al. An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19. Virol. J. 20, 23 (2023).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hrtlng.2023.03.004",
"author": "ADK Yousafzai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "Heart Lung",
"key": "57726_CR8",
"unstructured": "Yousafzai, A. D. K. et al. Clinical efficacy of Azithromycin for COVID-19 management: A systematic meta-analysis of meta-analyses. Heart Lung 60, 127–132 (2023).",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"author": "G Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "57726_CR9",
"unstructured": "Li, G., Hilgenfeld, R., Whitley, R. & De Clercq, E. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 22, 449–475 (2023).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.123.001074",
"author": "GR Trevor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "57726_CR10",
"unstructured": "Trevor, G. R., Lim, Y. J. & Urquhart, B. L. Pharmacometabolomics in drug disposition, toxicity and precision medicine. Drug Metab. Dispos. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.123.001074 (2024).",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02389",
"author": "J Caceres-Cortes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1701",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "57726_CR11",
"unstructured": "Caceres-Cortes, J., Falk, B., Mueller, L. & Dhar, T. G. M. Perspectives on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in drug discovery research. J. Med. Chem. 67, 1701–1733 (2024).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1177",
"author": "DB Kell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "557",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "57726_CR12",
"unstructured": "Kell, D. B. et al. Metabolic footprinting and systems biology: The medium is the message. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3, 557–565 (2005).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-0473-0_23",
"author": "V Behrends",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol. Biol.",
"key": "57726_CR13",
"unstructured": "Behrends, V., Williams, H. D. & Bundy, J. G. Metabolic footprinting: extracellular metabolomic analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 1149, 281–292 (2014).",
"volume": "1149",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomed3010013",
"author": "CMO Castro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "BioMed",
"key": "57726_CR14",
"unstructured": "Castro, C. M. O. et al. Alterations in the cellular metabolic footprint induced by Mayaro virus. BioMed 3, 152–165 (2023).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-023-06019-x",
"author": "LJ Corbin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "74",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "57726_CR15",
"unstructured": "Corbin, L. J. et al. The metabolomic signature of weight loss and remission in the Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT). Diabetologia 67, 74–87 (2024).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25031523",
"author": "L Ansone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1523",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "57726_CR16",
"unstructured": "Ansone, L. et al. Longitudinal NMR-based metabolomics study reveals how hospitalized COVID-19 patients recover: Evidence of dyslipidemia and energy metabolism dysregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 1523 (2024).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41366-023-01352-y",
"author": "Y Luan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "893",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Obes.",
"key": "57726_CR17",
"unstructured": "Luan, Y. et al. Glucose metabolism disorder: A potential accomplice of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Obes. 47, 893–902 (2023).",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-323-91704-9.00009-4",
"author": "AL Adamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "385",
"key": "57726_CR18",
"unstructured": "Adamson, A. L. Chapter 17 - Viral infections and glycolysis. In Glycolysis (eds Ferreira, R. et al.) 385–407 (Academic Press, 2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91704-9.00009-4.",
"volume-title": "Glycolysis",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41431-023-01462-1",
"author": "SA Narayanan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Hum. Genet.",
"key": "57726_CR19",
"unstructured": "Narayanan, S. A. et al. A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 32, 10–20 (2024).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16020295",
"author": "MT Rochowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "57726_CR20",
"unstructured": "Rochowski, M. T. et al. Impact of Delta SARS-CoV-2 infection on glucose metabolism: Insights on host metabolism and virus crosstalk in a feline model. Viruses 16, 295 (2024).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-022-04593-z",
"author": "C Bhowal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1325",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "57726_CR21",
"unstructured": "Bhowal, C., Ghosh, S., Ghatak, D. & De, R. Pathophysiological involvement of host mitochondria in SARS-CoV-2 infection that causes COVID-19: A comprehensive evidential insight. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 478, 1325–1343 (2023).",
"volume": "478",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2023.01.032",
"author": "A Pagano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "57726_CR22",
"unstructured": "Pagano, A. et al. Blood lactate in mild and moderate ARDS secondary to SARS COV 2. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 66, 73–75 (2023).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2023.01.019",
"author": "M Yadigaroğlu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Emerg. Med.",
"key": "57726_CR23",
"unstructured": "Yadigaroğlu, M. et al. Can lactate levels and lactate kinetics predict mortality in patients with COVID-19 with using qCSI scoring system?. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 66, 45–52 (2023).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.912579",
"author": "V Ceperuelo-Mallafré",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "912579",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "57726_CR24",
"unstructured": "Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V. et al. Circulating pyruvate is a potent prognostic marker for critical COVID-19 outcomes. Front. Immunol. 13, 912579 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241914876",
"author": "E Georgieva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14876",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "57726_CR25",
"unstructured": "Georgieva, E. et al. COVID-19 complications: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial and endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 14876 (2023).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mito.2024.101849",
"author": "S Dirajlal-Fargo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mitochondrion",
"key": "57726_CR26",
"unstructured": "Dirajlal-Fargo, S. et al. Altered mitochondrial respiration in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mitochondrion 75, 101849 (2024).",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101452",
"author": "S Kimura-Ohba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. reports",
"key": "57726_CR27",
"unstructured": "Kimura-Ohba, S. et al. Blood levels of d-amino acids reflect the clinical course of COVID-19. Biochem. Biophys. reports 34, 101452 (2023).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo13020201",
"author": "I Maltais-Payette",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Metabolites",
"key": "57726_CR28",
"unstructured": "Maltais-Payette, I., Lajeunesse-Trempe, F., Pibarot, P., Biertho, L. & Tchernof, A. Association between circulating amino acids and COVID-19 severity. Metabolites 13, 201 (2023).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hnm.2023.200220",
"author": "V Ambade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Hum. Nutr. Metab.",
"key": "57726_CR29",
"unstructured": "Ambade, V., Ambade, S., Sharma, V. & Sanas, P. Comparison between Amino Acid Profiling of Structural Proteins of earliest and recent omicron strain of SARS-CoV-2 and Nutritional Burden on COVID-19 patients. Hum. Nutr. Metab. 34, 200220 (2023).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-023-01569-3",
"author": "Z-N Ling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "57726_CR30",
"unstructured": "Ling, Z.-N. et al. Amino acid metabolism in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8, 345 (2023).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-40999-5",
"author": "OE Albóniga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15124",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "57726_CR31",
"unstructured": "Albóniga, O. E. et al. Differential abundance of lipids and metabolites related to SARS-CoV-2 infection and susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 13, 15124 (2023).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241411614",
"author": "S Lodge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11614",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "57726_CR32",
"unstructured": "Lodge, S. et al. Integrative plasma metabolic and lipidomic modelling of SARS-CoV-2 infection in relation to clinical severity and early mortality prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11614 (2023).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12033-023-00919-4",
"author": "MS Rahman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biotechnol.",
"key": "57726_CR33",
"unstructured": "Rahman, M. S. & Hossain, M. S. Eicosanoids signals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A foe or friend. Mol. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00919-4 (2023).",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/met.2023.0247",
"author": "M Alvarado",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord.",
"key": "57726_CR34",
"unstructured": "Alvarado, M., Campos-Campos, L., Guerrero-Romero, F. & Simental-Mendía, L. The triglycerides and glucose index is an independent risk factor for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2023.0247 (2024).",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.685196",
"author": "AF Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "685196",
"journal-title": "Front. Chem.",
"key": "57726_CR35",
"unstructured": "Santos, A. F., Póvoa, P., Paixão, P., Mendonça, A. & Taborda-Barata, L. Changes in glycolytic pathway in SARS-COV 2 infection and their importance in understanding the severity of COVID-19. Front. Chem. 9, 685196 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M115.708149",
"author": "S Ahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11928",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "57726_CR36",
"unstructured": "Ahn, S., Jung, J., Jang, I.-A., Madsen, E. L. & Park, W. Role of glyoxylate shunt in oxidative stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 11928–11938 (2016).",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-022-00643-3",
"author": "T Ermer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Nephrol.",
"key": "57726_CR37",
"unstructured": "Ermer, T. et al. Oxalate homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 19, 123–138 (2023).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24007-w",
"author": "NC Gassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3818",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "57726_CR38",
"unstructured": "Gassen, N. C. et al. SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals. Nat. Commun. 12, 3818 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00204-022-03306-1",
"author": "K Merches",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2341",
"journal-title": "Arch. Toxicol.",
"key": "57726_CR39",
"unstructured": "Merches, K. et al. The potential of remdesivir to affect function, metabolism and proliferation of cardiac and kidney cells in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 96, 2341–2360 (2022).",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.779135",
"author": "P Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779135",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "57726_CR40",
"unstructured": "Du, P., Wang, G., Hu, T., Li, H. & An, Z. Integration analysis of pharmacokinetics and metabolomics to predict metabolic phenotype and drug exposure of remdesivir. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 779135 (2022).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13197-022-05499-w",
"author": "HB Jadhav",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2143",
"journal-title": "J. Food Sci. Technol.",
"key": "57726_CR41",
"unstructured": "Jadhav, H. B. & Annapure, U. S. Triglycerides of medium-chain fatty acids: A concise review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 60, 2143–2152 (2023).",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tcb.2022.06.001",
"author": "F Di Cara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Trends Cell Biol.",
"key": "57726_CR42",
"unstructured": "Di Cara, F., Savary, S., Kovacs, W. J., Kim, P. & Rachubinski, R. A. The peroxisome: An up-and-coming organelle in immunometabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 33, 70–86 (2023).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jimd.12664",
"author": "C Vianey-Saban",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "848",
"journal-title": "J. Inherit. Metab. Dis.",
"key": "57726_CR43",
"unstructured": "Vianey-Saban, C., Guffon, N., Fouilhoux, A. & Acquaviva, C. Fifty years of research on mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation disorders: The remaining challenges. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 46, 848–873 (2023).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-011-1119-4",
"author": "G Scaini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "329",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "57726_CR44",
"unstructured": "Scaini, G. et al. Toxicity of octanoate and decanoate in rat peripheral tissues: evidence of bioenergetic dysfunction and oxidative damage induction in liver and skeletal muscle. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 361, 329–335 (2012).",
"volume": "361",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0280592",
"author": "MG Mohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "57726_CR45",
"unstructured": "Mohammad, M. G. et al. SARS-CoV-2-free residual proteins mediated phenotypic and metabolic changes in peripheral blood monocytic-derived macrophages in support of viral pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 18, 1–16 (2023).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.07.015",
"author": "Z Fišar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Toxicol. Lett.",
"key": "57726_CR46",
"unstructured": "Fišar, Z., Ľupták, M. & Hroudová, J. Little in vitro effect of remdesivir on mitochondrial respiration and monoamine oxidase activity in isolated mitochondria. Toxicol. Lett. 350, 143–151 (2021).",
"volume": "350",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08998280.2021.1885289",
"author": "A Aleem",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.",
"key": "57726_CR47",
"unstructured": "Aleem, A., Mahadevaiah, G., Shariff, N. & Kothadia, J. P. Hepatic manifestations of COVID-19 and effect of remdesivir on liver function in patients with COVID-19 illness. Proc. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. 34, 473–477 (2021).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02237-20",
"author": "Y Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "57726_CR48",
"unstructured": "Xu, Y. et al. Off-target in vitro profiling demonstrates that remdesivir is a highly selective antiviral agent. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65, 20 (2021).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0276751",
"author": "D De Forni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "57726_CR49",
"unstructured": "De Forni, D. et al. Synergistic drug combinations designed to fully suppress SARS-CoV-2 in the lung of COVID-19 patients. PLoS ONE 17, 1–14 (2022).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-031-42859-3_10",
"author": "GM Verleden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "195",
"key": "57726_CR50",
"unstructured": "Verleden, G. M. & Verleden, S. E. Azithromycin for other lung diseases: Lung transplantation and sarcoidosis. In Macrolides as Immunomodulatory Agents (eds Rubin, B. K. & Shinkai, M.) 195–205 (Springer, 2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42859-3_10.",
"volume-title": "Macrolides as Immunomodulatory Agents",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1229463",
"author": "E Cuevas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1229463",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "57726_CR51",
"unstructured": "Cuevas, E. et al. Systemic and functional effects of continuous azithromycin treatment in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and frequent exacerbations. Front. Med. 10, 1229463 (2023).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.202304-301OC",
"author": "S Ahmadian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1735",
"journal-title": "Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc.",
"key": "57726_CR52",
"unstructured": "Ahmadian, S. et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of azithromycin for the prevention of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 20, 1735–1742 (2023).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2023.966060",
"author": "Y Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Oncol.",
"key": "57726_CR53",
"unstructured": "Yan, Y., Wu, L., Li, X., Zhao, L. & Xu, Y. Immunomodulatory role of azithromycin: Potential applications to radiation-induced lung injury. Front. Oncol. 13, 966060 (2023).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.574425",
"author": "VJ Venditto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "57726_CR54",
"unstructured": "Venditto, V. J. et al. Immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin revisited: Potential applications to COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 12, 574425 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00013",
"author": "B Mahaling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "ACS Bio Med Chem Au",
"key": "57726_CR55",
"unstructured": "Mahaling, B., Pandala, N., Wang, H.-C. & Lavik, E. B. Azithromycin protects retinal glia against oxidative stress-induced morphological changes, inflammation, and cell death. ACS Bio Med Chem Au 2, 499–508 (2022).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/adj.12991",
"author": "MA Atieh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Aust. Dent. J.",
"key": "57726_CR56",
"unstructured": "Atieh, M. A. et al. Systemic azithromycin versus amoxicillin/metronidazole as an adjunct in the treatment of periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. Dent. J. 69, 4–17 (2024).",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21801",
"author": "YW Xing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "990",
"journal-title": "Drug Dev. Res.",
"key": "57726_CR57",
"unstructured": "Xing, Y. W. & Liu, K. Z. Azithromycin inhibited oxidative stress and apoptosis of high glucose-induced podocytes by inhibiting STAT1 pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 82, 990–998 (2021).",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics8030110",
"author": "X Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Antibiotics",
"key": "57726_CR58",
"unstructured": "Jiang, X., Baucom, C. & Elliott, R. L. Mitochondrial toxicity of azithromycin results in aerobic glycolysis and DNA damage of human mammary epithelia and fibroblasts. Antibiotics 8, 110 (2019).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2023.1123928",
"author": "A Kuretu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1123928",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol.",
"key": "57726_CR59",
"unstructured": "Kuretu, A. et al. Drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity: Risks of developing glucose handling impairments. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1123928 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14712/23362936.2023.30",
"author": "RE Barcia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "392",
"journal-title": "Prague Med. Rep.",
"key": "57726_CR60",
"unstructured": "Barcia, R. E. et al. Polypharmacy and Drug Interactions in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Prague Med. Rep. 124, 392–412 (2023).",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics11070941",
"author": "A Ticinesi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "941",
"journal-title": "Antibiot.",
"key": "57726_CR61",
"unstructured": "Ticinesi, A. et al. Co-administration of remdesivir and azithromycin may protect against intensive care unit admission in COVID-19 pneumonia requiring hospitalization: A real-life observational study. Antibiot. 11, 941 (2022).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-9690-2_16",
"author": "F Bhinderwala",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "265",
"key": "57726_CR62",
"unstructured": "Bhinderwala, F. & Powers, R. NMR metabolomics protocols for drug discovery. In NMR-Based Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols (eds Gowda, G. A. N. & Raftery, D.) 265–311 (Springer, 2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9690-2_16.",
"volume-title": "NMR-Based Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "57726_CR63",
"unstructured": "HMDB. https://hmdb.ca."
},
{
"key": "57726_CR64",
"unstructured": "BMRB. https://bmrb.io."
},
{
"key": "57726_CR65",
"unstructured": "NMRProcflow. https://www.nmrprocflow.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11306-017-1178-y",
"author": "D Jacob",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Metabolomics",
"key": "57726_CR66",
"unstructured": "Jacob, D., Deborde, C., Lefebvre, M., Maucourt, M. & Moing, A. NMRProcFlow: a graphical and interactive tool dedicated to 1D spectra processing for NMR-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 13, 36 (2017).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2",
"author": "LW Sumner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Metabolomics",
"key": "57726_CR67",
"unstructured": "Sumner, L. W. et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 3, 211–221 (2007).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"key": "57726_CR68",
"unstructured": "MetaboAnalyst. http://www.metaboanalyst.ca."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkab382",
"author": "Z Pang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "W388",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "57726_CR69",
"unstructured": "Pang, Z. et al. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, W388–W396 (2021).",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ab.2012.10.011",
"author": "B Worley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "Anal. Biochem.",
"key": "57726_CR70",
"unstructured": "Worley, B., Halouska, S. & Powers, R. Utilities for quantifying separation in PCA/PLS-DA scores plots. Anal. Biochem. 433, 102–104 (2013).",
"volume": "433",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11306-011-0330-3",
"author": "E Szymańska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Metabolomics",
"key": "57726_CR71",
"unstructured": "Szymańska, E., Saccenti, E., Smilde, A. K. & Westerhuis, J. A. Double-check: validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 8, 3–16 (2012).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "57726_CR72",
"unstructured": "Geneontology. http://geneontology.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pro.3715",
"author": "M Kanehisa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1947",
"journal-title": "Protein Sci.",
"key": "57726_CR73",
"unstructured": "Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 28, 1947–1951 (2019).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/28.1.27",
"author": "M Kanehisa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "57726_CR74",
"unstructured": "Kanehisa, M. & Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27–30 (2000).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac963",
"author": "M Kanehisa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "D587",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "57726_CR75",
"unstructured": "Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M. & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D587–D592 (2023).",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 75,
"references-count": 75,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-57726-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The metabolic footprint of Vero E6 cells highlights the key metabolic routes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and response to drug combinations",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}
melis