Results of Open-Label non-Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial: “BromhexIne and Spironolactone for CoronаvirUs Infection requiring hospiTalization (BISCUIT)
et al., Кардиология, doi:10.18087/cardio.2020.11.n1440, NCT04424134, Dec 2020
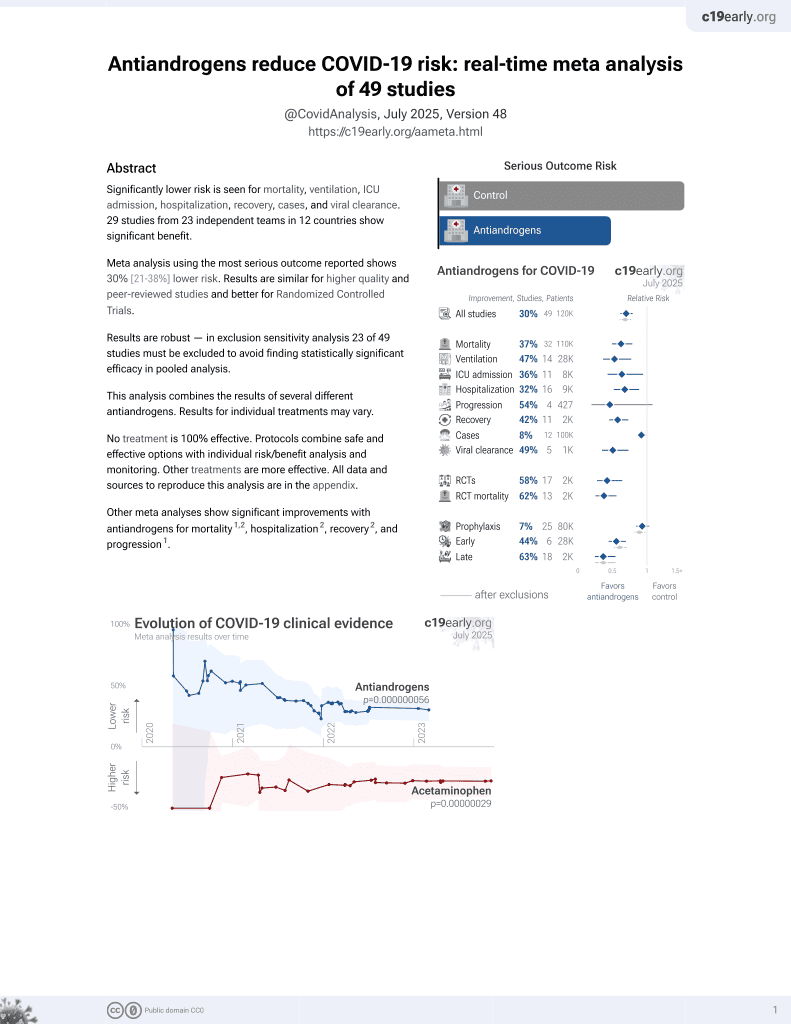
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
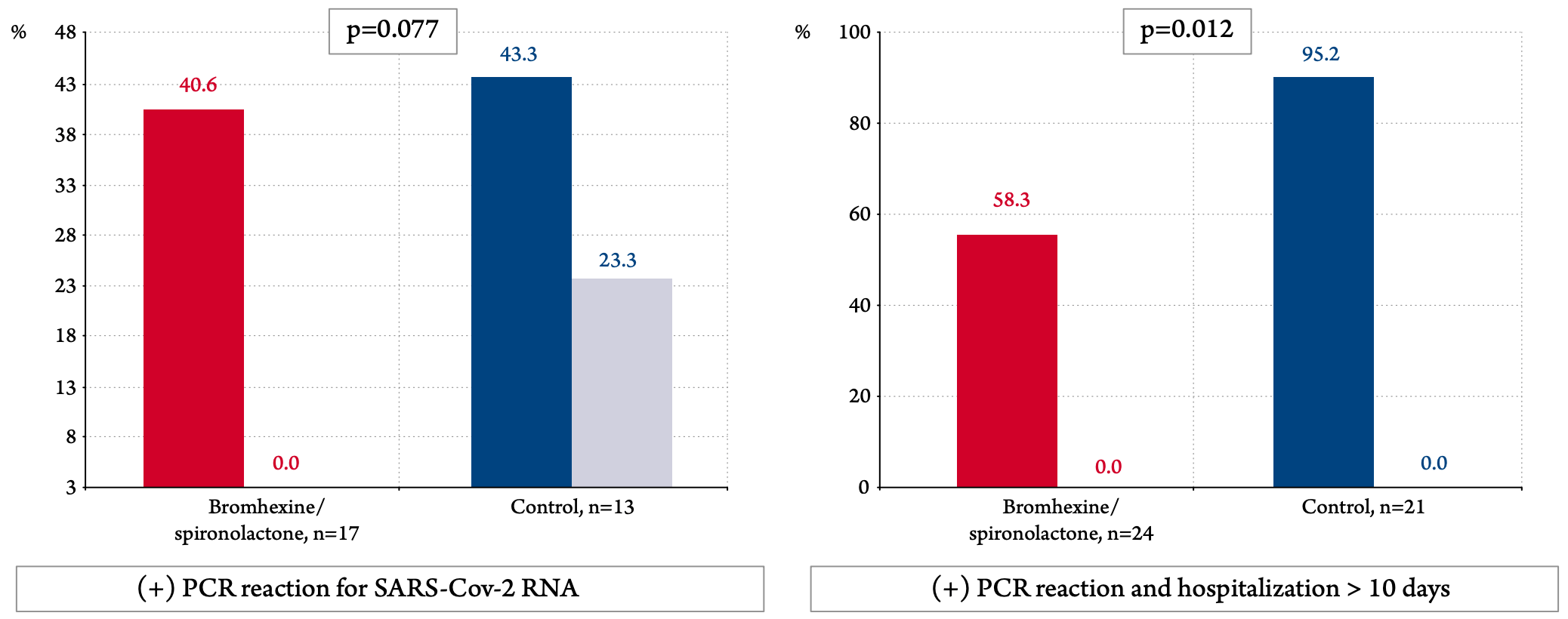
Prospective 103 PCR+ patients in Russia, 33 treated with bromexhine+spironolactone, showing lower PCR+ at day 10 or hospitalization >10 days with treatment. Bromhexine 8mg 4 times daily, spironolactone 25-50 mg/day for 10 days.
|
relative SHOKS-COVID score, 11.3% better, RR 0.89, p = 0.47, treatment mean 2.12 (±1.39) n=33, control mean 2.39 (±1.59) n=33.
|
|
risk of PCR+ on day 10 or hospitalization >10 days, 38.8% lower, RR 0.61, p = 0.02, treatment 14 of 24 (58.3%), control 20 of 21 (95.2%), NNT 2.7, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
hospitalization time, 8.2% lower, relative time 0.92, p = 0.35, treatment 33, control 33.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 87.4% lower, RR 0.13, p = 0.08, treatment 0 of 17 (0.0%), control 3 of 13 (23.1%), NNT 4.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mareev et al., 3 Dec 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Russia, peer-reviewed, 20 authors, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with bromhexine) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial NCT04424134 (history).
Abstract: §
EDITORIAL ARTICLES
Mareev V. Yu.1,2, Orlova Ya.A.1,2, Plisyk A.G.1,2, Pavlikova E.P.1,2, Matskeplishvili S.Т.1,
Akopyan Z.A.1,2, Seredenina E. M.1,2, Potapenko A. V.1,2, Agapov M.A.1,2, Asratyan D.A.1,
Dyachuk L.I.1,2, Samokhodskaya L. M.1,2, Mershina Е. А.1,2, Sinitsyn V. E.1,2, Pakhomov P. V.2,
Bulanova M.M.2, Fuks A.A.2, Mareev Yu.V.3,4, Begrambekova Yu. L.1,2, Kamalov А. А.1,2
Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
Faculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia
3
National Medical Research Centre for Therapy and Preventive Medicine Moscow, Russia
4
Robertson Centre for Biostatistics, Glasgow, Great Britain
1
2
Results of Open-Label non-Randomized Comparative
Clinical Trial: “BromhexIne and Spironolactone for
CoronаvirUs Infection requiring hospiTalization (BISCUIT)
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2020.11.n1440",
"ISSN": [
"2412-5660",
"0022-9040"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18087/cardio.2020.11.n1440",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:italic>Introduction</jats:italic> The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of a combination of bromhexine at a dose of 8 mg 4 times a day and spironolactone 50 mg per day in patients with mild and moderate COVID 19.<jats:italic>Material and methods</jats:italic> It was an open, prospective comparative non-randomized study. 103 patients were included (33 in the bromhexine and spironolactone group and 70 in the control group). All patients had a confirmed 2019 novel coronavirus infection (COVID 19) based on a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for SARS-CoV-2 virus RNA and/or a typical pattern of viral pneumonia on multispiral computed tomography. The severity of lung damage was limited to stage I-II, the level of CRP should not exceed 60 mg / dL and SO2 in the air within 92-98%. The duration of treatment is 10 days.<jats:italic>Results</jats:italic> The decrease in scores on the SHOKS-COVID scale, which, in addition to assessing the clinical status, the dynamics of CRP (a marker of inflammation), D-dimer (a marker of thrombus formation), and the degree of lung damage on CT (primary endpoint) was statistically significant in both groups and differences between them was not identified. Analysis for the group as a whole revealed a statistically significant reduction in hospitalization time from 10.4 to 9.0 days (by 1.5 days, p=0.033) and fever time from 6.5 to 3.9 days (by 2.5 days, p<0.001). Given the incomplete balance of the groups, the main analysis included 66 patients who were match with using propensity score matching. In matched patients, temperature normalization in the bromhexine/spironolactone group occurred 2 days faster than in the control group (p=0.008). Virus elimination by the 10th day was recorded in all patients in the bromhexine/spironolactone group; the control group viremia continued in 23.3% (p=0.077). The number of patients who had a positive PCR to the SARS-CoV-2 virus on the 10th day of hospitalization or longer (≥10 days) hospitalization in the control group was 20/21 (95.2%), and in the group with bromhexine /spironolactone -14/24 (58.3%), p=0.012. The odds ratio of having a positive PCR or more than ten days of hospitalization was 0.07 (95% CI: 0.008 - 0.61, p=0.0161) with bromhexine and spironolactone versus controls. No side effects were reported in the study group.<jats:italic>Conclusion</jats:italic> The combination of bromhexine with spironolactone appeared effective in treating a new coronavirus infection by achieving a faster normalization of the clinical condition, lowering the temperature one and a half times faster, and reducing explanatory combine endpoint the viral load or long duration of hospitalization (≥ 10 days).</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7285-2048",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mareev",
"given": "V. Yu.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8160-5612",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Orlova",
"given": "Ya. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Plisyk",
"given": "A. G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7693-5281",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Pavlikova",
"given": "E. P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5670-167X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Matskeplishvili",
"given": "S. T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Akopyan",
"given": "Z. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1490-2078",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Seredenina",
"given": "E. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9820-4276",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Potapenko",
"given": "A. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Agapov",
"given": "M. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1939-7189",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Asratyan",
"given": "D. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Dyachuk",
"given": "L. I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6734-3989",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Samokhodskaya",
"given": "L. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1266-4926",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mershina",
"given": "Е. А.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5649-2193",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Sinitsyn",
"given": "V. E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Pakhomov",
"given": "P. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Bulanova",
"given": "M. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Fuks",
"given": "A. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1939-7189",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Medical Research Centre for Therapy and Preventive Medicine, Moscow, Russia\r\nRobertson Centre for Biostatistics, Glasgow, Great Britain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mareev",
"given": "Yu. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7992-6081",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Begrambekova",
"given": "Yu. L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4251-7545",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research and Educational Center of the M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia\r\nFaculty of Fundamental Medicine, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Kamalov",
"given": "А. А.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Kardiologiia",
"container-title-short": "Kardiologiia",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-25T08:30:07Z",
"timestamp": 1611563407000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-11T11:30:52Z",
"timestamp": 1636630252000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T20:13:22Z",
"timestamp": 1704831202976
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 16,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://lib.ossn.ru/jour/about/editorialPolicies#openAccessPolicy",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1606953600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://lib.ossn.ru/jour/article/viewFile/1440/861",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "7442",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4-15",
"prefix": "10.18087",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "APO Society of Specialists in Heart Failure",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2008043",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G et al. A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382(19):1787–99. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Horby PW, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L, Staplin N, Emberson J et al. Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform tr al. The Lancet. 2020;396(10259):1345–52. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 — Preliminary Report. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;NEJMoa2007764. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Wang Y, Zhang D, Du G, Du R, Zhao J, Jin Y et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. The Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1569–78. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2020050589",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Adamsick ML, Gandhi RG, Bidell MR, Elshaboury RH, Bhattacharyya RP, Kim AY et al. Remdesivir in Patients with Acute or Chronic Kidney Disease and COVID-19. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2020;31(7):1384–6. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020050589"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110532",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Fan Q, Zhang B, Ma J, Zhang S. Safety profile of the antiviral drug remdesivir: An update. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2020;130:110532. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110532"
},
{
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Pharmaceutical technology. Fujifilm to seek approval for Avigan in Covid-19 after positive data. 23 September 2020. [Internet] Available at: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/news/fujifilm-avigan-covid-data/#:~:text=Japan’s%20Fujifilm%20Toyama%20Chemical%20plans,in%20Japan%20to%20treat%20influenza"
},
{
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Medvestnik. RDIF announced the first results of the Favipiravir study for COVID-19 in Russia. 14.05.2020. Available at: https://medvestnik.ru/content/news/Bolee-polovinyprinimavshih-Favipiravir-uchastnikov-issledovanii-izlechilis-ot-koronavirusa.html"
},
{
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health of Russian Federation. Temporary methodical recommendations. Prevention, diagnosis and treatment of new coronavirus infection (COVID-2019). Version 9 (26.10.2020)."
},
{
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Av. at: https://static-.minzdrav.gov.ru/system/attachments/attaches/000/052/548/original/%D0%9C%D0%A0_COVID19_%28v.9%29.pdf?1603730062."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2020.6.n1226",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Mareev V.Yu., Orlova Ya.A., Pavlikova E.P., Matskeplishvili S.T., Krasnova T.N., Malahov P.S. et al. Steroid pulse-therapy in patients With coronAvirus Pneumonia (COVID-19), sYstemic inFlammation And Risk of vEnous thRombosis and thromboembolism (WAYFARER Study). Kardiologiia. 2020;60(6):15–29. DOI: 10.18087/cardio.2020.6.n1226"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.12162360",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Sonawane K, Barale SS, Dhanavade MJ, Waghmare SR, Nadaf NH, Kamble SA et al. Homology Modeling and Docking Studies of TMPRSS2 with Experimentally Known Inhibitors Camostat Mesylate, Nafamostat and Bromhexine Hydrochloride to Control SARS-Coronavirus-2. 2020. [Av. at: https://chemrxiv.org/articles/Homology_Modeling_and_Docking_Studies_of_TMPRSS2_with_Experimentally_Known_Inhibitors_Camostat_Mesylate_Nafamostat_and_Bromhexine_Hydrochloride_to_Control_SARS-Coronavirus-2/12162360/1]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40248-017-0088-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Zanasi A, Mazzolini M, Kantar A. A reappraisal of the mucoactive activity and clinical efficacy of bromhexine. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine. 2017;12(1):7. DOI: 10.1186/s40248-017-0088-1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0081090",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Ji W-J, Ma Y-Q, Zhou X, Zhang Y-D, Lu R-Y, Guo Z-Z et al. Spironolactone Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Injury Partially via Modulating Mononuclear Phagocyte Phenotype Switching in Circulating and Alveolar Compartments. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(11):e81090. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081090"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3571863",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Wambier CG, Goren A, Ossimetha A, Nau G, Qureshi AA. Androgen-driven COVID-19 pandemic theory. ResearchGate. 2020; DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.21254.11848"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jocd.13443",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Goren A, Vaño‐Galván S, Wambier CG, McCoy J, Gomez‐Zubiaur A, Moreno‐Arrones OM et al. A preliminary observation: Male pattern hair loss among hospitalized COVID‐19 patients in Spain – A potential clue to the role of androgens in COVID‐19 severity. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 2020;19(7):1545–7. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.13443"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.30.20047878",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Asselta R, Paraboschi EM, Mantovani A, Duga S. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 variants and expression as candidates to sex and country differences in COVID-19 severity in Italy. 2020. [Av. at: http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.03.30.20047878]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2020.8.n1307",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Mareev V.Yu., Orlova Ya.A., Pavlikova E.P., Matskeplishvili S.T., Akopyan Zh.A., Plisyk A.G. et al. Combination therapy at an early stage of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19). Case series and design of the clinical trial “BromhexIne and Spironolactone for CoronаvirUs Infection requiring hospiTalization (BISCUIT)”. Kardiologiia. 2020;60(8):4–15. DOI: 10.18087/cardio.2020.8.n1307"
},
{
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Lomonosov Moscow State University Medical Research and Educational Center. Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial BromhexIne And Spironolactone For CoronаVirUs Infection Requiring HospiTalization. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04424134. 2020. [Av. at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04424134]."
},
{
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Royal College of Physicians. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2. [Av. at: https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/outputs/national-early-warning-score-news-2]. 2017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05954-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Liao X, Wang B, Kang Y. Novel coronavirus infection during the 2019–2020 epidemic: preparing intensive care units—the experience in Sichuan Province, China. Intensive Care Medicine. 2020;46(2):357–60. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-020-05954-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Spinner CD, Gottlieb RL, Criner GJ, Arribas López JR, Cattelan AM, Soriano Viladomiu A et al. Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients With Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020;324(11):1048. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.16349"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, Zucker J, Baldwin M, Hripcsak G et al. Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382(25):2411–8. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2012410"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.15.20151852",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Horby P, Mafham M, Linsell L, Bell JL, Staplin N, Emberson JR et al. Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary results from a multi-centre, randomized, controlled trial. 2020. [Av. at: http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.07.15.20151852]."
},
{
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "WHO Solidarity trial consortium, Pan H, Peto R, Karim QA, Alejandria M, Henao-Restrepo AM et al. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19 –interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. [Av. at: http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817]. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6019",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID- 19): A Review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824–36. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.6019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Cai Q, Yang M, Liu D, Chen J, Shu D, Xia J et al. Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: An Open-Label Control Study. Engineering. 2020; [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Hung IF-N, Lung K-C, Tso EY-K, Liu R, Chung TW-H, Chu M-Y et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. The Lancet. 2020;395(10238):1695–704. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Shen LW, Mao HJ, Wu YL, Tanaka Y, Zhang W. TMPRSS2: A potential target for treatment of influenza virus and coronavirus infections. Biochimie. 2017;142:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.07.016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.13.295691",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Olaleye OA, Kaur M, Onyenaka CC. Ambroxol Hydrochloride Inhibits the Interaction between Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Protein’s Receptor Binding Domain and Recombinant Human ACE2. [Av. at: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.09.13.295691]. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/bi.2020.27",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Ansarin K, Tolouian R, Ardalan M, Taghizadieh A, Varshochi M, Teimouri S et al. Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial. BioImpacts. 2020;10(4):209–15. DOI: 10.34172/bi.2020.27"
},
{
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "Yavas G, Yavas C, Celik E, Sen E, Ata O, Afsar RE. The impact of spironolactone on the lung injury induced by concomitant trastuzumab and thoracic radiotherapy. International Journal of Radiation Research. 2019;17(1):87–95. [Av. at: http://ijrr.com/article1-2461-en.html]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.11122",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Chen D, Li X, Song Q, Hu C, Su F, Dai J et al. Assessment of Hypokalemia and Clinical Characteristics in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wenzhou, China. JAMA Network Open. 2020;3(6):e2011122. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.11122"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa040135",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Lee DS, Kopp A, Austin PC, Laupacis A et al. Rates of Hyperkalemia after Publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study. New England Journal of Medicine. 2004;351(6):543–51. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa040135"
},
{
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "The Human Protein Atlas. Tissue expression of ADAM17. [Internet] Available at: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000151694-ADAM17/tissue"
},
{
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Lin B, Ferguson C, White JT, Wang S, Vessella R, True LD et al. Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2. Cancer Research. 1999;59(17):4180–4. PMID: 10485450"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Mikkonen L, Pihlajamaa P, Sahu B, Zhang F-P, Jänne OA. Androgen receptor and androgen-dependent gene expression in lung. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2010;317(1–2):14–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Montopoli M, Zumerle S, Vettor R, Rugge M, Zorzi M, Catapano V et al. Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532). Annals of Oncology. 2020;31(8):1040–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-85-5-630",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Loriaux DL. Spironolactone and Endocrine Dysfunction. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1976;85(5):630. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-5-630"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF03348960",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref40",
"unstructured": "McMullen GR, Van Herle AJ. Hirsutism and the effectiveness of spironolactone in its management. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 1993;16(11):925–32. DOI: 10.1007/BF03348960"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03055-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref41",
"unstructured": "Liaudet L, Szabo C. Blocking mineralocorticoid receptor with spironolactone may have a wide range of therapeutic actions in severe COVID-19 disease. Critical Care. 2020;24(1):318. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-03055-6"
},
{
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "Flávio C, Wambier C, Goren A. Spironolactone protection for SARSCoV-2: Targeting androgens and angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ResearchGate. 2020; [Av. at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341103985]"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://lib.ossn.ru/jour/article/view/1440"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Results of Open-Label non-Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial: “BromhexIne and Spironolactone for CoronаvirUs Infection requiring hospiTalization (BISCUIT)",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "60"
}
mareev