Effect of Nasal Irrigation in Children With Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Infection
et al., Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613231172337, Jun 2023
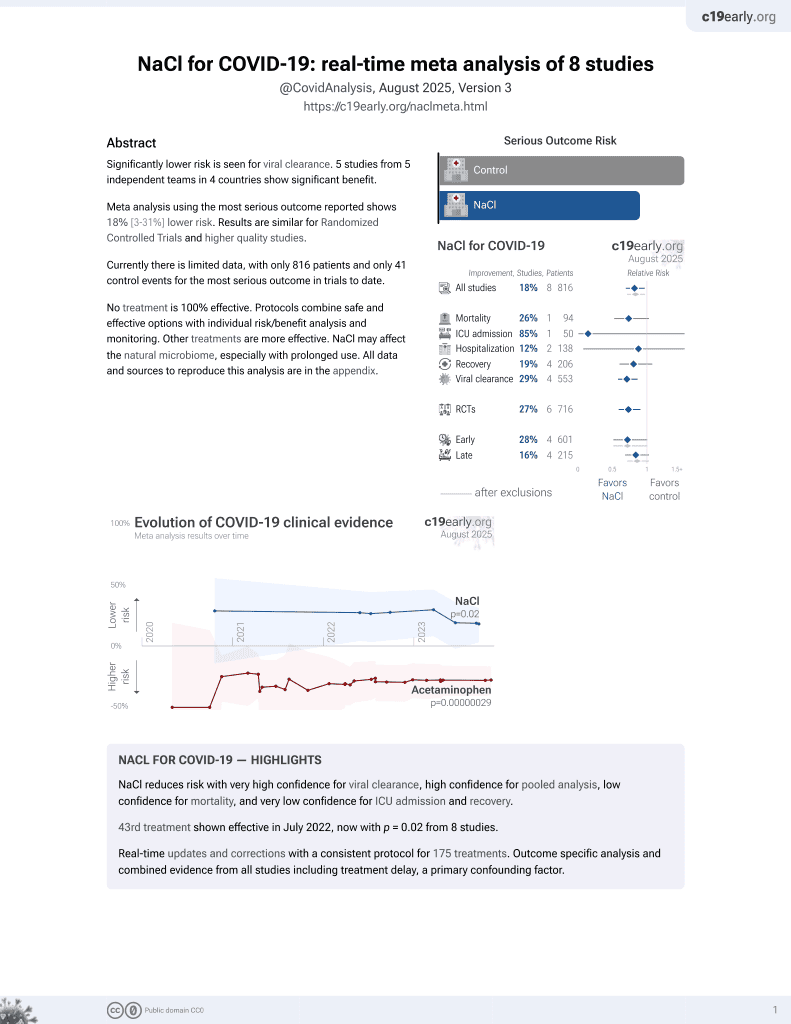
NaCl for COVID-19
44th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2022, now with p = 0.0028 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for progression and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
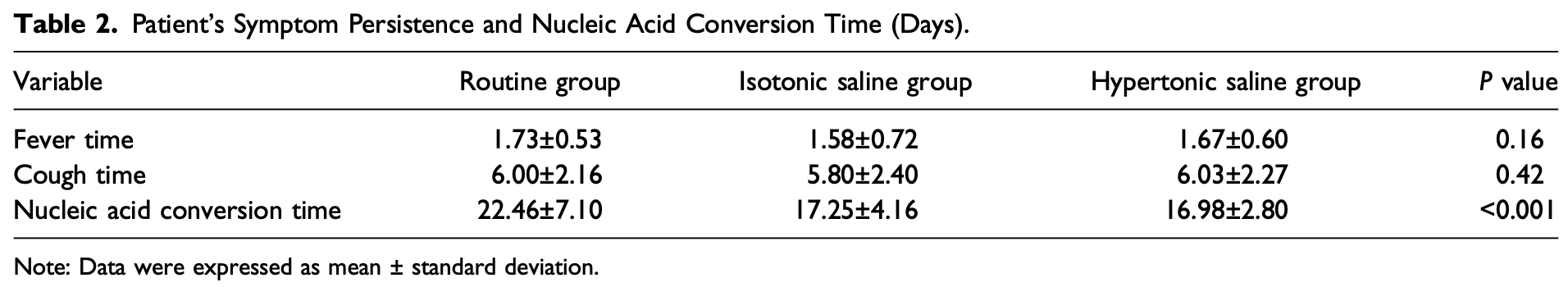
Quasi-experimental study of 60 pediatric patients with Omicron COVID-19 infection showing significant reduction in nucleic acid conversion time with nasal saline irrigation compared to routine treatment. Children aged 3-13 years were divided into three groups: routine treatment (Lianhua Qingwen granules), isotonic saline irrigation plus LhQw, and hypertonic saline irrigation plus LhQw. Both saline irrigation groups showed significantly shorter nucleic acid conversion time and increased lymphocyte counts, though no significant differences were observed in fever duration or cough symptoms. Isotonic saline had no adverse events while hypertonic saline caused mild nasal itching (15%) and pain (10%) in some children. Authors suggest that nasal irrigation may promote recovery in children with Omicron infection by physically removing virus particles from the nasal cavity.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
recovery time, 5.7% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.46, treatment 20, control 20, combined saline groups, fever.
|
|
recovery time, 8.7% lower, relative time 0.91, p = 0.46, treatment mean 1.58 (±0.72) n=20, control mean 1.73 (±0.53) n=20, isotonic, fever.
|
|
recovery time, 3.5% lower, relative time 0.97, p = 0.74, treatment mean 1.67 (±0.6) n=20, control mean 1.73 (±0.53) n=20, hypertonic, fever.
|
|
recovery time, 1.3% lower, relative time 0.99, p = 0.88, treatment 20, control 20, combined saline groups, cough.
|
|
recovery time, 3.3% lower, relative time 0.97, p = 0.78, treatment mean 5.8 (±2.4) n=20, control mean 6.0 (±2.16) n=20, isotonic, cough.
|
|
recovery time, 0.5% higher, relative time 1.01, p = 0.97, treatment mean 6.03 (±2.27) n=20, control mean 6.0 (±2.16) n=20, hypertonic, cough.
|
|
time to viral-, 23.8% lower, relative time 0.76, p < 0.001, treatment 20, control 20, combined saline groups.
|
|
time to viral-, 23.2% lower, relative time 0.77, p = 0.007, treatment mean 17.25 (±4.16) n=20, control mean 22.46 (±7.1) n=20, isotonic.
|
|
time to viral-, 24.4% lower, relative time 0.76, p = 0.003, treatment mean 16.98 (±2.8) n=20, control mean 22.46 (±7.1) n=20, hypertonic.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Liu et al., 17 Jun 2023, prospective, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 7.3, 5 authors, study period 1 April, 2022 - 1 May, 2022.
Contact: w.can@126.com.
Effect of Nasal Irrigation in Children With Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Infection
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/01455613231172337
Objective: To explore the effect of nasal irrigation on the disappearance of symptoms and nucleic acid conversion in children with Omicron variant. Methods: This quasi-experimental study included children diagnosed with asymptomatic, mild, and moderate Omicron variant infection during the isolation observation period in the Shandong Public Health Clinical Center between April 1, 2022 and May 1, 2022. The children were divided into a routine group (received Lianhua Qingwen (LhQw) Granules), isotonic saline group (received LhQw Granules combined with isotonic saline nasal irrigation), and hypertonic saline group (received LhQw Granules combined with 3% hypertonic saline nasal irrigation), respectively. The primary outcomes were the time of symptom disappearance and nucleic acid conversion time. The secondary outcomes were peripheral white blood cell count (WBC), lymphocyte count (LYM), neutrophil count (NEU), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Results: A total of 60 children (7.26 ± 3.15 years old) were included (20 per group). The average time of nucleic acid conversion in the 2 saline nasal irrigation groups was significantly reduced compared with the routine group (all P < 0.001), while the fever time and cough duration among the 3 groups were comparable (all P > 0.05). LYM count in the 2 saline nasal irrigation groups was significantly increased after treatment compared to before treatment and was significantly higher than in the routine group (all P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in LYM count between the isotonic and hypertonic saline groups (P = 0.76). Additionally, all children in the saline group well tolerated the treatment, and no adverse events occurred in the isotonic saline group. Conclusions: Timely use of saline nasal irrigation may promote nucleic acid conversion in children with Omicron virus infection.
Author Contributions Study concept and design: LS and LL, acquisition of data: CW, Analysis and interpretation of data: SX, Drafting of the manuscript: LL. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content and study supervision: CW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval This work has been carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2000) of the World Medical Association. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shandong Public Health Clinical Center (GWLCZXEC2022-65). None of the children had any known confirmed infection in the past, and informed consent was signed by their legal guardians.
References
Aktas, A comprehensive review on rational and effective treatment strategies against an invisible enemy; SARS Cov-2 infection, J-ebr, doi:10.30714/j-ebr.2020463629
Aktas, Balci, Yilmaz, Bardak, Duman, Characteristics of Covid-19 infection with the original SARS-Cov-2 virus and other variants: A comparative review, Jbm, doi:10.53545/jbm.2022.22
Brewster, Chrimes, Do, Consensus statement: Safe airway society principles of airway management and tracheal intubation specific to the COVID-19 adult patient group, Med J Aust, doi:10.5694/mja2.50598
Cameroni, Bowen, Rosen, Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2
De Gabory, Kérimian, Sagardoy, Verdaguer, Gauchez, Paediatric nasal irrigation: The "fencing" method, Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2020.08.004
Dimeglio, Loubes, Miedougé, Herin, Soulat et al., The real seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in France and its consequences for virus dynamics, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92131-0
Ding, Zeng, Li, The Chinese prescription lianhuaqingwen capsule exerts anti-influenza activity through the inhibition of viral propagation and impacts immune function, BMC Complement Altern Med, doi:10.1186/s12906-017-1585-7
Esakandari, Nabi-Afjadi, Fakkari-Afjadi, Farahmandian, Miresmaeili et al., A comprehensive review of COVID-19 characteristics, Biol Proced Online, doi:10.1186/s12575-020-00128-2
Espenhain, Funk, Overvad, Epidemiological characterisation of the first 785 SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant cases in Denmark, December 2021, Euro Surveill, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.50.2101146
Farrell, Klatt-Cromwell, Schneider, Benefits and safety of Nasal Saline irrigations in a pandemic-washing COVID-19 away, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1622
Garavello, Romagnoli, Sordo, Gaini, Berardino et al., Hypersaline nasal irrigation in children with symptomatic seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized study, Pediatr Allergy Immunol, doi:10.1034/j.1399-3038.2003.00021.x
Hoffmann, Krüger, Schulz, The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032
Hu, Guan, Bi, Efficacy and safety of Lianhua Qingwen capsules, a repurposed Chinese herb, in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153800
Hui, Zumla, Advances in the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, clinical management and prevention of coronavirus disease 2019, Curr Opin Pulm Med, doi:10.1097/mcp.0000000000000875
Huijghebaert, Hoste, Vanham, Essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00228-021-03102-3
Karanth, Karanth, Ward, Woodworth, Karanth, Medical interventions for chronic Rhinosinusitis in cystic fibrosis, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012979.pub3
Kuznetsov, Arukuusk, Hark, ACE2 peptide fragment interaction with different S1 protein sites, Int J Pept Res Ther, doi:10.1007/s10989-021-10324-7
Liu, Pan, Li, Tan, Yang, Efficacy of nasal irrigation with hypertonic saline on chronic rhinosinusitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.03.008
Liu, Xie, Li, Su, Zhu, Effect of nasal irrigation in adults infected with omicron variant of COVID-19: A quasiexperimental study, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.1046112
Rabago, Zgierska, Saline nasal irrigation for upper respiratory conditions, Am Fam Physician
Rahimi, Abadi, The omicron subvariant BA.2: Birth of a new challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic, Int J Surg, doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106261
Ramalingam, Graham, Dove, Morrice, Sheikh, Hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling should be considered as a treatment option for COVID-19, J Glob Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.10.010332
Shen, Yin, The mechanisms and clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine Lianhua-Qingwen capsule, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111998
Shuai, Chan, Hu, Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5
Suzuki, Yamasoba, Kimura, Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1
Tagarro, Coya, Pérez-Villena, Features of COVID-19 in children during the omicron wave compared with previous waves in Madrid, Spain, Pediatr Infect Dis J, doi:10.1097/inf.0000000000003482
Ural, Oktemer, Kizil, Ileri, Uslu, Impact of isotonic and hypertonic saline solutions on mucociliary activity in various nasal pathologies: Clinical study, J Laryngol Otol, doi:10.1017/s0022215108003964
Wang, Qi, Traditional Chinese medicine to treat COVID-19: The importance of evidence-based research, Drug Discov Ther, doi:10.5582/ddt.2020.03054
Wu, Chang, Hong, Wei, Development of an apparatus and procedure for evaluating the efficiency of nasal irrigation, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1007/s00405-021-07249-8
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Xia, Zhao, Shah, Wang, Baloch, Composition, clinical efficiency, and mechanism of NHC-approved "three Chinese medicines and three Chinese recipes" for COVID-19 treatment, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.781090
Yu, Yu, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-induced neurological complications, Front Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.605972
Zhang, Wu, Xu, Effectiveness of Lianhua Qingwen capsule in treatment of asymptomatic COVID-19 patients: A randomized, controlled multicenter trial, J Integr Complement Med, doi:10.1089/jicm.2021.0352
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/01455613231172337",
"ISSN": [
"0145-5613",
"1942-7522"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/01455613231172337",
"abstract": "<jats:p> Objective: To explore the effect of nasal irrigation on the disappearance of symptoms and nucleic acid conversion in children with Omicron variant. Methods: This quasi-experimental study included children diagnosed with asymptomatic, mild, and moderate Omicron variant infection during the isolation observation period in the Shandong Public Health Clinical Center between April 1, 2022 and May 1, 2022. The children were divided into a routine group (received Lianhua Qingwen (LhQw) Granules), isotonic saline group (received LhQw Granules combined with isotonic saline nasal irrigation), and hypertonic saline group (received LhQw Granules combined with 3% hypertonic saline nasal irrigation), respectively. The primary outcomes were the time of symptom disappearance and nucleic acid conversion time. The secondary outcomes were peripheral white blood cell count (WBC), lymphocyte count (LYM), neutrophil count (NEU), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Results: A total of 60 children (7.26 ± 3.15 years old) were included (20 per group). The average time of nucleic acid conversion in the 2 saline nasal irrigation groups was significantly reduced compared with the routine group (all P < 0.001), while the fever time and cough duration among the 3 groups were comparable (all P > 0.05). LYM count in the 2 saline nasal irrigation groups was significantly increased after treatment compared to before treatment and was significantly higher than in the routine group (all P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in LYM count between the isotonic and hypertonic saline groups ( P = 0.76). Additionally, all children in the saline group well tolerated the treatment, and no adverse events occurred in the isotonic saline group. Conclusions: Timely use of saline nasal irrigation may promote nucleic acid conversion in children with Omicron virus infection. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/01455613231172337"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7425-5127",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of liver Diseases, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center, Shandong University, Jinan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Service, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center, Shandong University, Jinan, China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Chen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of liver Diseases, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center, Shandong University, Jinan, China"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Shuangshuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1445-8392",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Service, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center, Shandong University, Jinan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Su",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of liver Diseases, Shandong Public Health Clinical Center, Shandong University, Jinan, China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Can",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Ear, Nose & Throat Journal",
"container-title-short": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-17T08:23:27Z",
"timestamp": 1686990207000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-01T11:48:30Z",
"timestamp": 1740829710000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100012905",
"award": [
"2021FGC0504"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100012905",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-02T05:41:01Z",
"timestamp": 1740894061241,
"version": "3.38.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "1_suppl",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1_suppl",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1686960000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/01455613231172337",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/01455613231172337",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/01455613231172337",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "54S-59S",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
17
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.605972",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-92131-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12575-020-00128-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10989-021-10324-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.30714/j-ebr.2020463629",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.53545/jbm.2022.22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-017-1585-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-01455613231172337"
},
{
"author": "General Office of the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China",
"first-page": "481",
"journal-title": "China Medicine",
"key": "bibr13-01455613231172337",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jicm.2021.0352",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.781090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111998",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153800",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.50.2101146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.anorl.2020.08.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.03.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD012979.pub3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-01455613231172337"
},
{
"author": "Rabago D",
"first-page": "1117",
"journal-title": "Am Fam Physician",
"key": "bibr22-01455613231172337",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0022215108003964",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-021-03102-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.50598",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.10.010332",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.1046112",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/ddt.2020.03054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/mcp.0000000000000875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106261",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/inf.0000000000003482",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1622",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-021-07249-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-01455613231172337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1399-3038.2003.00021.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-01455613231172337"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/01455613231172337"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Nasal Irrigation in Children With Omicron Variant of COVID-19 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "103"
}