Azelastine Nasal Spray for Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infections
et al., JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.4283, CONTAIN, 2022-003756-13, Sep 2025
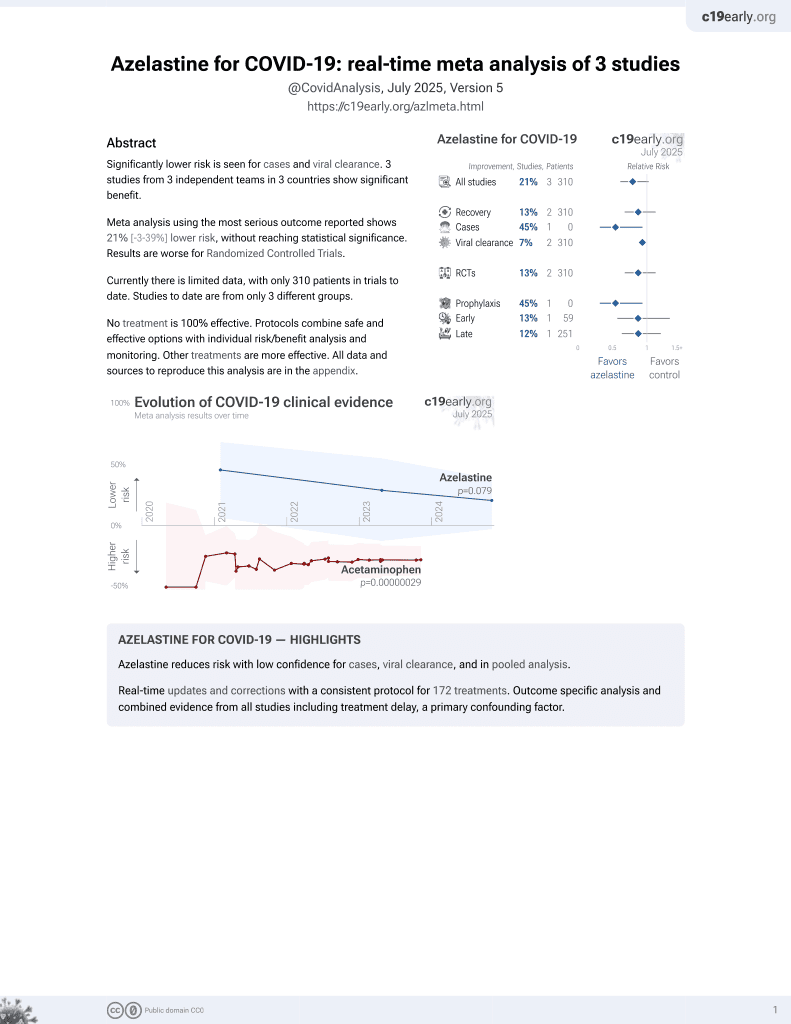
Azelastine for COVID-19
57th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2025, now with p = 0.048 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for cases.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
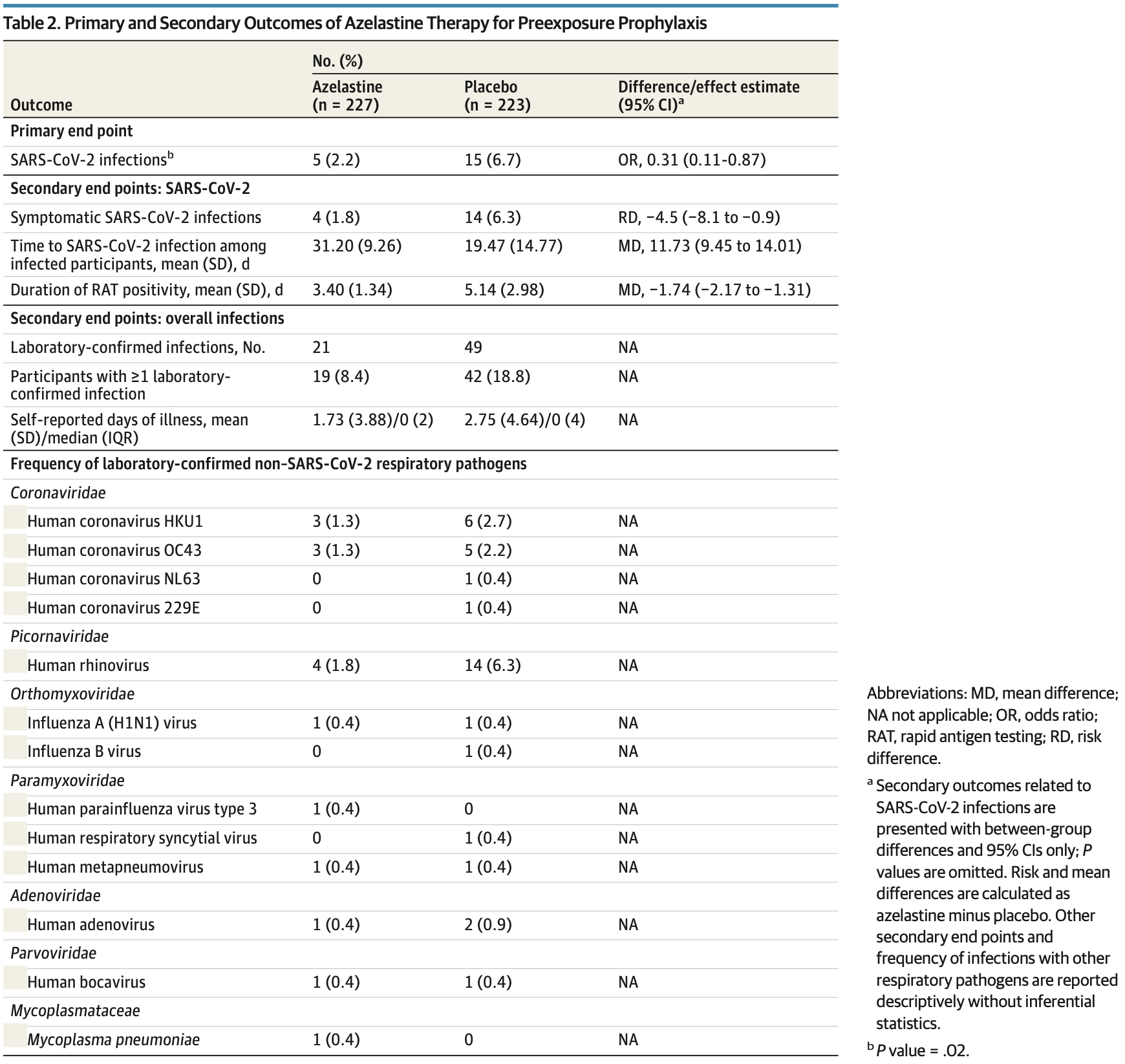
RCT 450 healthy adults showing lower PCR-confirmed and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections with azelastine 0.1% nasal spray (1 puff/nostril 3x/day for 56 days) versus placebo. The placebo formulation (hypromellose) may also have efficacy via barrier and mechanical effects, there is potential unblinding from azelastine’s bitter taste, and per-protocol exclusions were common due to visit schedule/adherence.
|
risk of symptomatic case, 71.9% lower, RR 0.28, p = 0.02, treatment 4 of 227 (1.8%), control 14 of 223 (6.3%), NNT 22.
|
|
risk of case, 69.0% lower, HR 0.31, p = 0.03, treatment 5 of 227 (2.2%), control 15 of 223 (6.7%), NNT 22, Cox proportional hazards, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
time to viral-, 33.9% lower, relative time 0.66, p < 0.001, treatment mean 3.4 (±1.34) n=227, control mean 5.14 (±2.98) n=223.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lehr et al., 2 Sep 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Germany, peer-reviewed, 25 authors, study period March 2023 - July 2024, trial 2022-003756-13 (CONTAIN).
Contact: robert.bals@uks.eu.
Azelastine Nasal Spray for Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infections
JAMA Internal Medicine, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.4283
IMPORTANCE Limited pharmaceutical options exist for preexposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 beyond vaccination. Azelastine, an antihistamine nasal spray used for decades to treat
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: URSAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH (Saarbruecken, Germany) is the sponsor of the clinical trial and designed the trial in cooperation with academic partners. Data were collected by investigators in collaboration with a contract research organization (ClinCompetence Cologne GmbH, Cologne, Germany) and analyzed by the academic partners.
Group Information: The CONTAIN Study Group appear listed in Supplement 4. Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 5.
Additional Contributions: We thank all the participants who volunteered for this clinical trial.
References
Basnet, Palmenberg, Gern, Rhinoviruses and their receptors, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2018.12.012
Berger, Hampel, Jr, Bernstein, Shah et al., Impact of azelastine nasal spray on symptoms and quality of life compared with cetirizine oral tablets in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis, Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60804-6
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009575
Bernstein, Azelastine hydrochloride: a review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and tolerability, Curr Med Res Opin, doi:10.1185/030079907X226302
Dings, Meiser, Holzer, Pharmacometric modeling of the impact of azelastine nasal spray on SARS-CoV-2 viral load and related symptoms in COVID-19 patients, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14102059
Drysdale, Mejias, Ramilo, Rhinovirusnot just the common cold, J Infect, doi:10.1016/S0163-4453(17)30190-1
Fischhuber, Bánki, Kimpel, Antiviral potential of azelastine against major respiratory viruses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15122300
Galmiche, Cortier, Charmet, SARS-CoV-2 incubation period across variants of concern, individual factors, and circumstances of infection in France: a case series analysis from the ComCor study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00005-8
Ge, Lu, Hou, Lv, Wang et al., Azelastine inhibits viropexis of SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudovirus by binding to SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2021.05.009
Ghahremanpour, Tirado-Rives, Deshmukh, Identification of 14 known drugs as inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2, ACS Med Chem Lett, doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00521
Ghahremanpour, Tirado-Rives, Deshmukh, Identification of 14 known drugs as inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.28.271957
Herman, Brien, Forleo-Neto, COVID-19 Phase 3 Prevention Trial Team. Efficacy and safety of a single dose of casirivimab and imdevimab for the prevention of COVID-19 over an 8-month period: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00416-9
Hou, Okuda, Edwards, SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042
Klussmann, Grosheva, Meiser, Early intervention with azelastine nasal spray may reduce viral load in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-32546-z
Konrat, Papp, Kimpel, The anti-histamine azelastine, identified by computational drug repurposing, inhibits infection by major variants of SARS-CoV-2 in cell cultures and reconstituted human nasal tissue, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.861295
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116620
Lohse, Sternjakob-Marthaler, Lagemann, German federal-state-wide seroprevalence study of 1st SARS-CoV-2 pandemic wave shows importance of long-term antibody test performance, Commun Med (Lond), doi:10.1038/s43856-022-00100-z
Meiser, Flegel, Holzer, Azelastine nasal spray in non-hospitalized subjects with mild COVID-19 infection: a randomized placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentric, phase II clinical trial, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16121914
Popov, Emberlin, Josling, Seifalian, In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the efficacy and safety of powder hydroxypropylmethylcellulose as nasal mucosal barrier, Med Devices (Auckl), doi:10.2147/MDER.S236104
Reznikov, Norris, Vashisht, Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095
Simon, The efficacy of azelastine in the prophylaxis of acute upper respiratory tract infections, Pediatric asthma, allergy, and immunology, doi:10.1089/08831870332275132
Wang, Guo, Ho, Ho, Activity of research-grade pemivibart against recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2410203
Xie, Choi, Al-Aly, Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the pre-Delta, Delta, and Omicron eras, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2403211
Zhou, Dael, Verweij, Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of European studies published up to 22 January 2024, Eur Respir Rev, doi:10.1183/16000617.0222-2024
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.4283",
"ISSN": [
"2168-6106"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.4283",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>Limited pharmaceutical options exist for preexposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 beyond vaccination. Azelastine, an antihistamine nasal spray used for decades to treat allergic rhinitis, has in vitro antiviral activity against respiratory viruses, including SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To determine the efficacy and safety of azelastine nasal spray for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infections in healthy adults.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>A phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center trial was conducted from March 2023 to July 2024. Healthy adults from the general population were enrolled at the Saarland University Hospital in Germany.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive azelastine, 0.1%, nasal spray or placebo 3 times daily for 56 days. SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen testing (RAT) was conducted twice weekly, with positive results confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Symptomatic participants with negative RAT results underwent multiplex PCR testing for respiratory viruses.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcome</jats:title><jats:p>The primary end point was the number of PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections during the study.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 450 participants were randomized, with 227 assigned to azelastine and 223 to placebo; 299 (66.4%) were female, 151 (33.6%) male, with a mean (SD) age of 33.0 (13.3) years. Most were White (417 [92.7%]), with 4 (0.9%) African, 22 (4.9%) Asian, and 7 (1.6%) of other ethnicity. In the intention-to-treat (ITT) population, the incidence of PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection was significantly lower in the azelastine group (n = 5 [2.2%]) compared with the placebo group (n = 15 [6.7%]) (OR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.11-0.87). As secondary end points, azelastine demonstrated an increase in mean (SD) time to SARS-CoV-2 infection among infected participants (31.2 [9.3] vs 19.5 [14.8] days), a reduction of the overall number of PCR-confirmed symptomatic infections (21 of 227 participants vs 49 of 223 participants), and a lower incidence of PCR-confirmed rhinovirus infections (1.8% vs 6.3%). Adverse events were comparable between the groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>In this single-center trial, azelastine nasal spray was associated with reduced risk of SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections. These findings support the potential of azelastine as a safe prophylactic approach warranting confirmation in larger, multicentric trials.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title><jats:p>EudraCT number: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://drks.de/search/de/trial/DRKS00031059\">2022-003756-13</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Saarland University, Saarbruecken, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Lehr",
"given": "Thorsten",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ursapharm Arzneimittel GmbH, Saarbruecken, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Meiser",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Saarland University, Saarbruecken, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Selzer",
"given": "Dominik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine V, Saarland University Medical Center, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Rixecker",
"given": "Torben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ursapharm Arzneimittel GmbH, Saarbruecken, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Holzer",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "ClinCompetence Cologne GmbH, Cologne, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Medical Statistics and Computational Biology, University of Cologne, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Mösges",
"given": "Ralph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Virology, Saarland University Medical Center, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Smola",
"given": "Sigrun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine V, Saarland University Medical Center, Germany"
},
{
"name": "Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Bals",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "CONTAIN Study Group",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Alberg",
"given": "Veronika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Bub",
"given": "Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Biwank",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Dette",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Dastgir",
"given": "Lale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kuntz",
"given": "Alina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Hale",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Kapp",
"given": "Johanna Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Litzenburger",
"given": "Kathrin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Morr",
"given": "Henning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Wagner",
"given": "Johanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Sahin",
"given": "Hacer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Schröder",
"given": "Nelli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Seibert",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Thieser",
"given": "Katrin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the CONTAIN Study Group"
}
],
"family": "Werthner",
"given": "Quirin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Internal Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Intern Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-02T15:00:31Z",
"timestamp": 1756825231000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-02T15:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1756825232000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-02T15:40:04Z",
"timestamp": 1756827604033,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/articlepdf/2838335/jamainternal_lehr_2025_oi_250054_1756319977.75536.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19.",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2451",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi250054r1",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2403211",
"article-title": "Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the pre-Delta, Delta, and Omicron eras.",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "515",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi250054r2",
"volume": "391",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1185/030079907X226302",
"article-title": "Azelastine hydrochloride: a review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and tolerability.",
"author": "Bernstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2441",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Curr Med Res Opin",
"key": "ioi250054r3",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2021.05.009",
"article-title": "Azelastine inhibits viropexis of SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudovirus by binding to SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2.",
"author": "Ge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ioi250054r4",
"volume": "560",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15122300",
"article-title": "Antiviral potential of azelastine against major respiratory viruses.",
"author": "Fischhuber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2300",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ioi250054r5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.861295",
"article-title": "The anti-histamine azelastine, identified by computational drug repurposing, inhibits infection by major variants of SARS-CoV-2 in cell cultures and reconstituted human nasal tissue.",
"author": "Konrat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ioi250054r6",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.095",
"article-title": "Identification of antiviral antihistamines for COVID-19 repurposing.",
"author": "Reznikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "ioi250054r7",
"volume": "538",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The efficacy of azelastine in the prophylaxis of acute upper respiratory tract infections.",
"author": "Simon",
"first-page": "275",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pediatric asthma, allergy, and immunology",
"key": "ioi250054r8",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00521",
"article-title": "Identification of 14 known drugs as inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Ghahremanpour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2526",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "ACS Med Chem Lett",
"key": "ioi250054r9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-32546-z",
"article-title": "Early intervention with azelastine nasal spray may reduce viral load in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients.",
"author": "Klussmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6839",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "ioi250054r10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16121914",
"article-title": "Azelastine nasal spray in non-hospitalized subjects with mild COVID-19 infection: a randomized placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentric, phase II clinical trial.",
"author": "Meiser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1914",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ioi250054r11",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics14102059",
"article-title": "Pharmacometric modeling of the impact of azelastine nasal spray on SARS-CoV-2 viral load and related symptoms in COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Dings",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2059",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"key": "ioi250054r12",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00005-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 incubation period across variants of concern, individual factors, and circumstances of infection in France: a case series analysis from the ComCor study.",
"author": "Galmiche",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e409",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ioi250054r13",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43856-022-00100-z",
"article-title": "German federal-state-wide seroprevalence study of 1st SARS-CoV-2 pandemic wave shows importance of long-term antibody test performance.",
"author": "Lohse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "52",
"journal-title": "Commun Med (Lond)",
"key": "ioi250054r14",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60804-6",
"article-title": "Impact of azelastine nasal spray on symptoms and quality of life compared with cetirizine oral tablets in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis.",
"author": "Berger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "375",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol",
"key": "ioi250054r15",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/16000617.0222-2024",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of European studies published up to 22 January 2024.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "175",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir Rev",
"key": "ioi250054r16",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00416-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of a single dose of casirivimab and imdevimab for the prevention of COVID-19 over an 8-month period: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Herman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1444",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "ioi250054r17",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"article-title": "Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19.",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2188",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi250054r18",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2410203",
"article-title": "Activity of research-grade pemivibart against recent SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 sublineages.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1863",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ioi250054r19",
"volume": "391",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2018.12.012",
"article-title": "Rhinoviruses and their receptors.",
"author": "Basnet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1018",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ioi250054r20",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0163-4453(17)30190-1",
"article-title": "Rhinovirus - not just the common cold.",
"author": "Drysdale",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S41",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "ioi250054r21",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract.",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "429",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ioi250054r23",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/MDER.S236104",
"article-title": "In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the efficacy and safety of powder hydroxypropylmethylcellulose as nasal mucosal barrier.",
"author": "Popov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Med Devices (Auckl)",
"key": "ioi250054r24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.28.271957",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ioi250054r22",
"unstructured": "Ghahremanpour? MM, Tirado-Rives? J, Deshmukh? M, . Identification of 14 known drugs as inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2.? bioRxiv. 2020;doi:10.1101/2020.08.28.271957"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2838335"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [
"A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Azelastine Nasal Spray for Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infections",
"type": "journal-article"
}