No Statistically Apparent Difference in Antiviral Effectiveness Observed Among Ribavirin Plus Interferon-Alpha, Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha, and Ribavirin Plus Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha in Patients With Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results of a Randomized, Open-Labeled Prospective Study
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01071, ChiCTR2000029387, Jul 2020
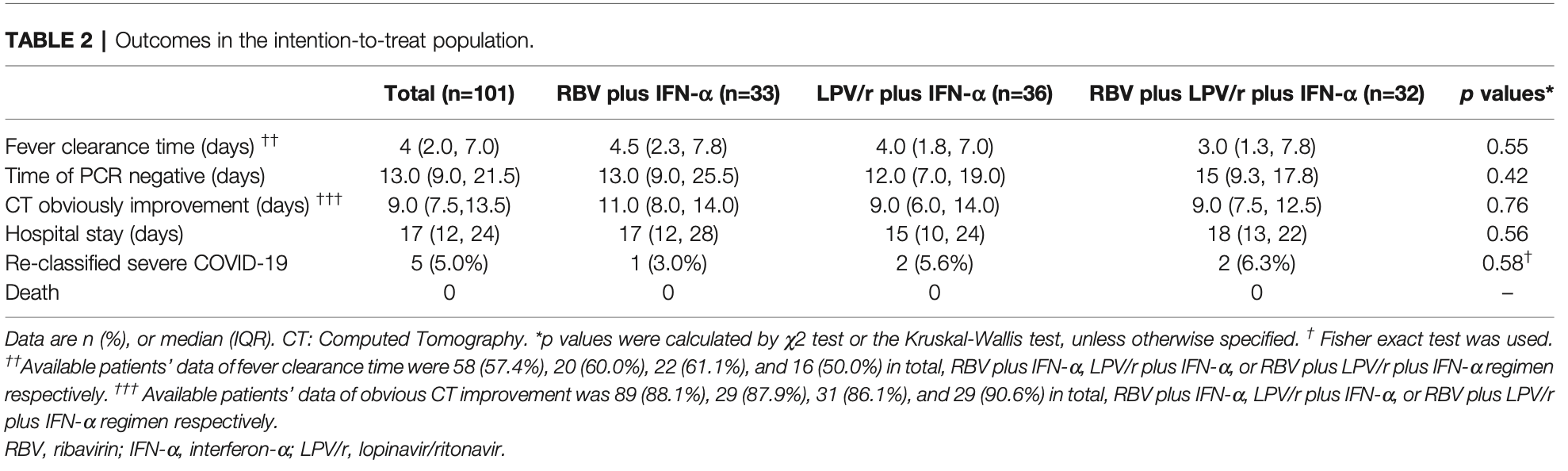
RCT 101 mild to moderate COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in antiviral effectiveness among three treatment regimens: ribavirin plus interferon-alpha, lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha, and ribavirin plus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of severe case, 106.2% higher, RR 2.06, p = 0.61, treatment 2 of 32 (6.2%), control 1 of 33 (3.0%), RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a vs. RBV plus IFN-a.
|
|
hospitalization time, 5.9% higher, relative time 1.06, p = 0.68, treatment median 18.0 IQR 9.0 n=32, control median 17.0 IQR 16.0 n=33, RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a vs. RBV plus IFN-a.
|
|
recovery time, 33.3% lower, relative time 0.67, p = 0.32, treatment median 3.0 IQR 6.5 n=16, control median 4.5 IQR 5.5 n=20, RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a vs. RBV plus IFN-a, fever.
|
|
time to improvement, 18.2% lower, relative time 0.82, p = 0.07, treatment median 9.0 IQR 5.0 n=29, control median 11.0 IQR 6.0 n=29, RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a vs. RBV plus IFN-a.
|
|
time to viral-, 15.4% higher, relative time 1.15, p = 0.41, treatment median 15.0 IQR 8.5 n=32, control median 13.0 IQR 16.5 n=33, RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a vs. RBV plus IFN-a.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Huang et al., 14 Jul 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 42.5, 15 authors, study period 29 January, 2020 - 25 February, 2020, trial ChiCTR2000029387.
Contact: yaokaichen@hotmail.com, 1046580277@qq.com.
No Statistically Apparent Difference in Antiviral Effectiveness Observed Among Ribavirin Plus Interferon-Alpha, Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha, and Ribavirin Plus Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha in Patients With Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results of a Randomized, Open-Labeled Prospective Study
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01071
Background: Currently, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has spread globally, causing an unprecedented pandemic. However, there is no specific antiviral therapy for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a clinical trial to compare the effectiveness of three antiviral treatment regimens in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. Methods: This was a single-center, randomized, open-labeled, prospective clinical trial. Eligible patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 were randomized into three groups: ribavirin (RBV) plus interferon-a (IFN-a), lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) plus IFN-a, and RBV plus LPV/r plus IFN-a at a 1:1:1 ratio. Each patient was invited to participate in a 28-d follow-up after initiation of an antiviral regimen. The outcomes include the difference in median interval to SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid negativity, the proportion of patients with SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid negativity at day 14, the mortality at day 28, the proportion of patients re-classified as severe cases, and adverse events during the study period. Results: In total, we enrolled 101 patients in this study. Baseline clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients were comparable among the three groups. In the analysis of
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of Chongqing Public Health Medical Center (2020-002-01-KY). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Y-KC and Z-PY conceived the study. LZ, Y-MZ, Q-ZS, N-NS, and YW collected data. S-QT, YL, G-XW, and X-LX analyzed data. Y-QH, S-QT, and Y-KC interpreted the results. Y-QH and S-QT wrote the manuscript. VH, X-QH, and Y-QL edited and revised the article.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
Booth, Matukas, Tomlinson, Rachlis, Rose et al., Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.289.21.JOC30885
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, New Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Chan, Yao, Man-Lung, Deng, Bao et al., Treatment With Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Interferon-b1b Improves Outcome of MERS-CoV Infection in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Common Marmoset, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiv392
Chen, Chan, Jiang, Kao, Lu et al., In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds, J. Clin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.003
De Wilde, Jochmans, Posthuma, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Van Nieuwkoop et al., Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture, Antimicrobial. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.03011-14
Falzarano, De Wit, Martellaro, Callison, Munster et al., Inhibition of novel b coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-a2b and ribavirin, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep01686
Falzarano, De Wit, Rasmussen, Feldmann, Okumura et al., Treatment with interferon-a2b and ribavirin improves outcome in MERS-CoV-infected rhesus macaques, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm.3362
Hung, Lung, Tso, Liu, Chung et al., Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/6S0140-6736(20)31042-4
Knowles, Phillips, Dresser, Matukas, Common Adverse Events Associated with the Use of Ribavirin for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in Canada, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1086/378304
Ling, Xu, Lin, Tian, Zhu et al., Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients, Chin. Med. J, doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000774
Liu, Liu, Chu, Wang, Yu et al., Biodistribution and Metabolic Pathway of Interferon-a1b Administered by Aerosol Inhalation in Rabbits, Med. Herald, doi:10.3870/yydb.2013.01.001
Lu, Dong, Pocket handbook of anti-infective agents (The Third Edition)
Momattin, Al-Ali, Al-Tawfiq, A Systematic Review of therapeutic agents for the treatment of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Travel Med. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2019.06.012
Morgenstern, Michaelis, Baer, Doerr, Cinatl, Ribavirin and interferon-b synergistically inhibit SARS-associated coronavirus replication in animal and human cell lines, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.128
Omrani, Saad, Baig, Bahloul, Abdul-Matin et al., Ribavirin and interferon alfa-2a for severe Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70920-X
Tong, Medical immunology and microbiology (The third version)
Wang, Chen, Yang, Liao, Xu et al., Inhalation properties of the nebulized recombinant human interferon-a1b injection, Int. J. Pharm. Res, doi:10.13220/j.cnki.jipr.2019.06.008
Wang, Cheng, Lu, Zhou, Ni et al., The Effects of Atomization Inhalation on Biological Activity and Molecular Structure of Human Recombinant Interferon Alpha 2b, J. Pediatr. Pharm, doi:10.13407/j.cnki.jpp.1672-108X.2017.03.001
Who, Guideline on the Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected
Yang, Liu, Chu, Gao, Zheng et al., Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of interferon a2b(Pseudomonas putida)administered via atomization inhalation and intramuscular injection by 125I labeling, Int. J. Radiol. Nuclear Med, doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4114.2015.03.001
Zeng, Xu, He, Tang, Li et al., Comparative effectiveness and safety of ribavirin plus interferon-alpha, lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha and ribavirin plus lopinavir/ ritonavir plus interferon-alphain in patients with mild to moderate novel coronavirus pneumonia, Chin. Med. J. (Engl.), doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000790
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China 2019, New Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01071",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01071",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2020.01071"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yin-Qiu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Sheng-Quan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Xiao-Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Yan-Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Xiao-Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harypursat",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Yan-Qiu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Qiang-Zhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Nan-Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Gui-Xue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Zhong-Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yao-Kai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-14T06:42:01Z",
"timestamp": 1594708921000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-16T07:37:07Z",
"timestamp": 1594885027000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-25T07:34:58Z",
"timestamp": 1750836898468
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 39,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
14
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1594684800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fphar.2020.01071/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.289.21.JOC30885",
"article-title": "Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area",
"author": "Booth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2801",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "New Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiv392",
"article-title": "Treatment With Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Interferon-β1b Improves Outcome of MERS-CoV Infection in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Common Marmoset",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1904",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.003",
"article-title": "In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03011-14",
"article-title": "Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture",
"author": "de Wilde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4875",
"journal-title": "Antimicrobial. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep01686",
"article-title": "Inhibition of novel β coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-α2b and ribavirin",
"author": "Falzarano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1686",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3362",
"article-title": "Treatment with interferon-α2b and ribavirin improves outcome in MERS-CoV–infected rhesus macaques",
"author": "Falzarano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1313",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/6S0140-6736(20)31042-4",
"article-title": "Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1695",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/378304",
"article-title": "Common Adverse Events Associated with the Use of Ribavirin for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in Canada",
"author": "Knowles",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1139",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000774",
"article-title": "Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients",
"author": "Ling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1039",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3870/yydb.2013.01.001",
"article-title": "Biodistribution and Metabolic Pathway of Interferon-α1b Administered by Aerosol Inhalation in Rabbits",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Med. Herald",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"author": "Lu",
"first-page": "326",
"key": "B12",
"volume-title": "Pocket handbook of anti-infective agents (The Third Edition)",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2019.06.012",
"article-title": "A Systematic Review of therapeutic agents for the treatment of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)",
"author": "Momattin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Travel Med. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.128",
"article-title": "Ribavirin and interferon-β synergistically inhibit SARS-associated coronavirus replication in animal and human cell lines",
"author": "Morgenstern",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70920-X",
"article-title": "Ribavirin and interferon alfa-2a for severe Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Omrani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1090",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "Tong",
"first-page": "178",
"key": "B16",
"volume-title": "Medical immunology and microbiology (The third version)",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13407/j.cnki.jpp.1672-108X.2017.03.001",
"article-title": "The Effects of Atomization Inhalation on Biological Activity and Molecular Structure of Human Recombinant Interferon Alpha 2b",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Pediatr. Pharm.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13220/j.cnki.jipr.2019.06.008",
"article-title": "Inhalation properties of the nebulized recombinant human interferon-α1b injection",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "456",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pharm. Res.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "B19",
"volume-title": "Guideline on the Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4114.2015.03.001",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of interferon α2b(Pseudomonas putida)administered via atomization inhalation and intramuscular injection by 125I labeling",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Radiol. Nuclear Med.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000790",
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness and safety of ribavirin plus interferon-alpha, lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alpha and ribavirin plus lopinavir/ritonavir plus interferon-alphain in patients with mild to moderate novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1132",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J. (Engl.)",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "New Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fphar.2020.01071/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "No Statistically Apparent Difference in Antiviral Effectiveness Observed Among Ribavirin Plus Interferon-Alpha, Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha, and Ribavirin Plus Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha in Patients With Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results of a Randomized, Open-Labeled Prospective Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "11"
}