Clinical and treatment factors associated with the mortality of COVID-19 patients admitted to a referral hospital in Indonesia
et al., The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167, Feb 2023
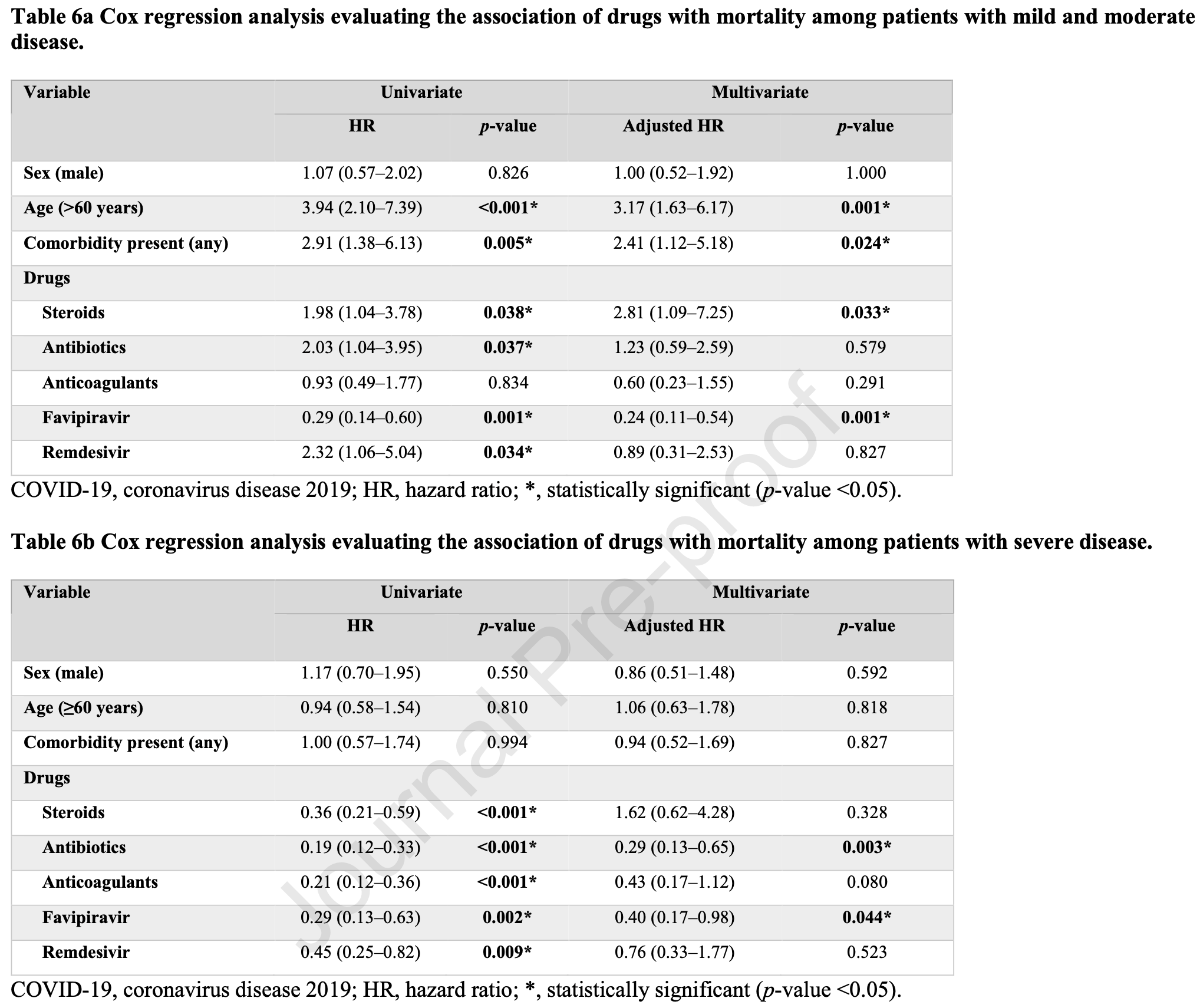
Retrospective 689 hospitalized patients in Indonesia, showing no significant difference in mortality with remdesivir treatment.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Remdesivir efficacy disappears with longer
followup. Mixed-effects meta-regression of efficacy as a function of
followup duration across all remdesivir studies shows decreasing efficacy with
longer followup15. This may reflect
antiviral efficacy being offset by serious adverse effects of treatment.
Study covers remdesivir and favipiravir.
|
risk of death, 11.0% lower, HR 0.89, p = 0.84, adjusted per study, mild/moderate, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 24.0% lower, HR 0.76, p = 0.53, adjusted per study, severe, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Hartantri et al., 9 Feb 2023, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 December, 2020.
Contact: b.alisjahbana@unpad.ac.id.
Clinical and treatment factors associated with the mortality of COVID-19 patients admitted to a referral hospital in Indonesia
The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Research in context Evidence before this study Before this study, we searched PubMed for articles that assessed factors associated with mortality in COVID-19 inpatients, using search terms ("COVID-19" OR "coronavirus") AND ("mortality" OR "death"), from March until April 2022. We found the mortality studies were mainly from China, America, and Europe that associated mortality with older age, male, and pre-existing comorbidities besides the severity of the disease itself. Indonesia had the second-highest total number of cases and deaths in South-East Asia. However, there were still limited studies and inadequate reliable data about COVID-19 mortality in Indonesia. Previously published studies in Indonesia reported a CFR of around 9.4% to 18%, associated with older age, male, pre-existing comorbidity, immediate ICU admission, and intubation. Laboratory parameters such as NLR, D-dimer, and lymphocyte count were also associated with a greater risk of overall mortality.
Added value of this study This study is a retrospective cohort study of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a top referral hospital in Bandung of West Java, the largest province in Indonesia, during the first ten months of the epidemic. Our report is the most comprehensive mortality study in our region that analyzed the clinical characteristics, laboratory parameters, and treatments associated with survival outcomes. The case fatality rate of 14.9% was similar to previous..
References
Alene, Yismaw, Assemie, Magnitude of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases throughout the course of infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PloS one
Altonen, Arreglado, Leroux, Murray-Ramcharan, Engdahl, Characteristics, comorbidities and survival analysis of young adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in New York City, PloS one
Azwar, Setiati, Rizka, Fitriana, Saldi et al., Clinical Profile of Elderly Patients with COVID-19 hospitalised in Indonesia's National General Hospital, Acta Medica Indonesiana
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19-Final Report, N Engl J Med
Benfield, Bodilsen, Brieghel, Improved Survival Among Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treated With Remdesivir and Dexamethasone. A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Biswas, Rahaman, Biswas, Haque, Association of sex, age, and comorbidities with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Intervirology
Chedid, Waked, Haddad, Chetata, Saliba et al., Antibiotics in treatment of COVID-19 complications: a review of frequency, indications, and efficacy, Journal of infection and public health
Cox, Loman, Bogaert, Grady, Co-infections: potentially lethal and unexplored in COVID-19, The Lancet Microbe
Diabetes, Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus, Diabetes care
Fan, Lu, Li, Ding, Wang, ACE2 expression in kidney and testis may cause kidney and testis infection in COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in medicine
Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Hariyanto, Japar, Kwenandar, Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and metaanalysis, The American journal of emergency medicine
Hu, Han, Pei, Yin, Chen, Procalcitonin levels in COVID-19 patients, International journal of antimicrobial agents
Jalili, Payandemehr, Saghaei, Sari, Safikhani et al., Characteristics and mortality of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Iran: a National Retrospective Cohort Study, Annals of internal medicine
Levey, Eckardt, Tsukamoto, Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO), Kidney international
Lippi, Plebani, Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry
Lu, Yu, Liu, Survival analysis and risk factors in COVID-19 patients, Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness
Opal, Girard, Ely, The immunopathogenesis of sepsis in elderly patients, Clinical infectious diseases
Pinte, Ceasovschih, Niculae, Antibiotic Prescription and In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19: A Prospective Multicentre Cohort Study, Journal of Personalized Medicine
Rozaliyani, Savitri, Setianingrum, Factors Associated with Death in COVID-19 Patients in Jakarta, Indonesia: An Epidemiological Study, Acta Med Indones
Sahu, Cerny, Managing patients with hematological malignancies during COVID-19 pandemic
Salinas-Escudero, Carrillo-Vega, Granados-García, Martínez-Valverde, Toledano-Toledano et al., A survival analysis of COVID-19 in the Mexican population, BMC Public Health
Santoso, Sung, Hartantri, MDR Pathogens Organisms as Risk Factor of Mortality in Secondary Pulmonary Bacterial Infections Among COVID-19 Patients: Observational Studies in Two Referral Hospitals in West Java, Indonesia, International Journal of General Medicine
Shang, Wang, Zhang, The relationship between diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 prognosis: a retrospective cohort study in Wuhan, China, The American journal of medicine
Shinkai, Tsushima, Tanaka, Efficacy and safety of favipiravir in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia patients without oxygen therapy: a randomized, phase III clinical trial. Infectious diseases and therapy
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome, Clinical Research & Reviews
Surendra, Elyazar, Djaafara, Clinical characteristics and mortality associated with COVID-19 in Jakarta, Indonesia: a hospital-based retrospective cohort study, The Lancet Regional Health-Western Pacific
Whelton, Williams, The 2018 European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension and 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guidelines: More Similar Than Different, Jama
Wu, Wang, Kuo, An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19, Current pharmacology reports
Yang, Liu, -P, Tao, -Q et al., The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients, International immunopharmacology
Zhang, Wang, Jia, Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China, Clinical microbiology and infection
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167",
"ISSN": [
"2772-3682"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167",
"alternative-id": [
"S2772368223000276"
],
"article-number": "100167",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Clinical and treatment factors associated with the mortality of COVID-19 patients admitted to a referral hospital in Indonesia"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartantri",
"given": "Yovita",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Debora",
"given": "Josephine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Widyatmoko",
"given": "Leonardus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giwangkancana",
"given": "Gezy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suryadinata",
"given": "Hendarsyah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Susandi",
"given": "Evan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutajulu",
"given": "Elisabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amalya Hakiman",
"given": "Assica Permata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pusparini",
"given": "Yesy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alisjahbana",
"given": "Bachti",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-09T16:13:21Z",
"timestamp": 1675959201000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-09T16:13:53Z",
"timestamp": 1675959233000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-10T05:40:35Z",
"timestamp": 1676007635724
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675209600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 1,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675296000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772368223000276?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772368223000276?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100167",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data. Accessed 22 October 2022, https://COVID19.who.int/region/searo/country/id"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0249090",
"article-title": "Magnitude of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases throughout the course of infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Alene",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib2",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.012",
"article-title": "Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "767",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clinical microbiology and infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib3",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "The lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib4",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0243343",
"article-title": "Characteristics, comorbidities and survival analysis of young adults hospitalized with COVID-19 in New York City",
"author": "Altonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.033",
"article-title": "The relationship between diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 prognosis: a retrospective cohort study in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e6",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The American journal of medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib6",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17474086.2020.1787147",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib7",
"unstructured": "Sahu KK, Cerny J. Managing patients with hematological malignancies during COVID-19 pandemic. Taylor & Francis; 2020. p. 787-793."
},
{
"article-title": "Survival analysis and risk factors in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Lu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "A survival analysis of COVID-19 in the Mexican population",
"author": "Salinas-Escudero",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib9",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100108",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and mortality associated with COVID-19 in Jakarta, Indonesia: a hospital-based retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Surendra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Regional Health-Western Pacific",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib10",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors Associated with Death in COVID-19 Patients in Jakarta, Indonesia: An Epidemiological Study",
"author": "Rozaliyani",
"first-page": "246",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Acta Med Indones",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib11",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2018.16755",
"article-title": "The 2018 European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension and 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guidelines: More Similar Than Different",
"author": "Whelton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1749",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib12",
"volume": "320",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc09-S062",
"article-title": "Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S62",
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"journal-title": "Diabetes care",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib13",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x",
"article-title": "Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)",
"author": "Levey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2089",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Kidney international",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib14",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib15",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. COVID-19 clinical management: living guidance, 25 January 2021. 2021."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib16",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Haemoglobin concentrations for the diagnosis of anaemia and assessment of severity. 2011."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504",
"article-title": "The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "International immunopharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib17",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical Profile of Elderly Patients with COVID-19 hospitalised in Indonesia’s National General Hospital",
"author": "Azwar",
"first-page": "199",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Acta Medica Indonesiana",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib18",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-2911",
"article-title": "Characteristics and mortality of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Iran: a National Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Jalili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Annals of internal medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib19",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/432007",
"article-title": "The immunopathogenesis of sepsis in elderly patients",
"author": "Opal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S504",
"issue": "Supplement_7",
"journal-title": "Clinical infectious diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib20",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000512592",
"article-title": "Association of sex, age, and comorbidities with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Biswas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Intervirology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib21",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "ACE2 expression in kidney and testis may cause kidney and testis infection in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Fan",
"first-page": "1045",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40495-020-00216-7",
"article-title": "An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Current pharmacology reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib23",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib24",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.076",
"article-title": "Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "The American journal of emergency medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib25",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.004",
"article-title": "Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Lippi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib26",
"volume": "505",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106051",
"article-title": "Procalcitonin levels in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "International journal of antimicrobial agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib27",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib28",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib29",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab536",
"article-title": "Improved Survival Among Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treated With Remdesivir and Dexamethasone. A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study",
"author": "Benfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2031",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib30",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00517-4",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of favipiravir in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia patients without oxygen therapy: a randomized, phase III clinical trial",
"author": "Shinkai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2489",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Infectious diseases and therapy",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib31",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm12060877",
"article-title": "Antibiotic Prescription and In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19: A Prospective Multicentre Cohort Study",
"author": "Pinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "877",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of Personalized Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30009-4",
"article-title": "Co-infections: potentially lethal and unexplored in COVID-19",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e11",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib33",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.02.001",
"article-title": "Antibiotics in treatment of COVID-19 complications: a review of frequency, indications, and efficacy",
"author": "Chedid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "570",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Journal of infection and public health",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib34",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S359959",
"article-title": "MDR Pathogens Organisms as Risk Factor of Mortality in Secondary Pulmonary Bacterial Infections Among COVID-19 Patients: Observational Studies in Two Referral Hospitals in West Java, Indonesia",
"author": "Santoso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4741",
"journal-title": "International Journal of General Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100167_bib35",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2772368223000276"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical and treatment factors associated with the mortality of COVID-19 patients admitted to a referral hospital in Indonesia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
hartantri