A real-life setting evaluation of the effect of remdesivir on viral load in COVID-19 patients admitted to a large tertiary center in Israel
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029, Mar 2021
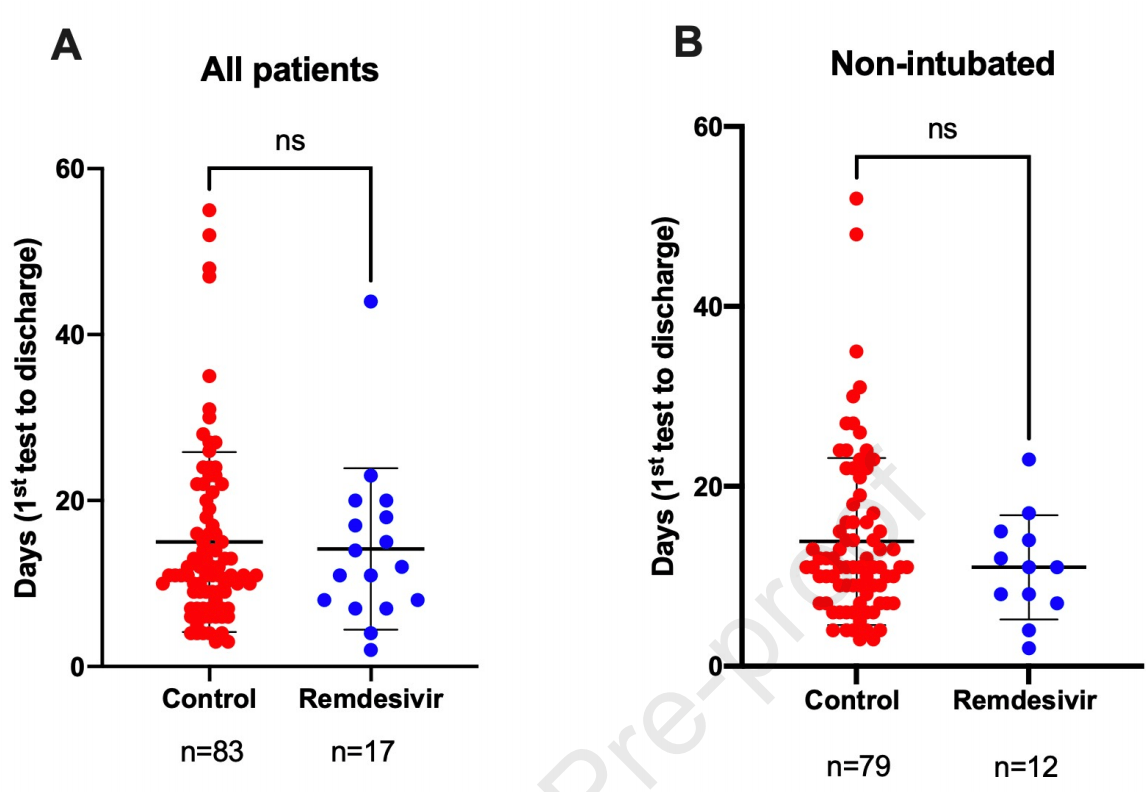
Retrospective 29 remdesivir patients and 113 controls, not finding a significant difference in nasopharyngeal viral load or hospitalization time. Hospitalization time was lower with treatment, with a larger reduction for non-intubated patients, although not statistically significant in both cases.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
hospitalization time, 9.2% lower, relative time 0.91, p = 0.77, treatment 29, control 113.
|
|
hospitalization time, 21.8% lower, relative time 0.78, p = 0.30, non-intubated patients only.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 0.1% lower, RR 1.00, p = 0.98, treatment 29, control 113, relative change in Ct values.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Goldberg et al., 9 Mar 2021, retrospective, Israel, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
A real-life setting evaluation of the effect of remdesivir on viral load in COVID-19 patients admitted to a large tertiary centre in Israel
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029
Objectives: The effectiveness of remdesivir, a Food and Drug Administration-approved drug for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), has been repeatedly questioned during the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Most of the recently reported studies were randomized controlled multicentre clinical trials. Our goal was to test the efficiency of remdesivir in reducing nasopharyngeal viral load and hospitalization length in a real-life setting in patients admitted to a large tertiary centre in Israel. Methods: A total of 142 COVID-19 patients found to have at least three reported SARS-CoV-2 quantitative RT-PCR tests during hospitalization were selected for this study. Of these, 29 patients received remdesivir, while the remaining non-treated 113 patients served as controls. Results: Among the tested parameters, the control and remdesivir groups differed significantly only in the intubation rates. Remdesivir treatment did not significantly affect nasopharyngeal viral load, as determined by comparing the differences between the first and last cycle threshold values of the SARS-CoV-2 quantitative RT-PCR tests performed during hospitalization (cycle threshold 7.07 ± 6.85 vs. 7.08 ± 7.27, p 0.977 in the control and treated groups, respectively). Remdesivir treatment shortened hospitalization length by less than a day compared with non-treated controls and by 3.1 days when nonintubated patients from both groups were compared. These differences, however, were not statistically significant, possibly because of the small size of the remdesivir group. Discussion: Remdesivir was not associated with nasopharyngeal viral load changes, but our study had a significant disease severity baseline imbalance and was not powered to detect viral load or clinical differences.
Transparency declaration The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Author contributions E.G. and E.H.S. conceptualized the study and its methodology. H.B.Z., L.S. and S.S. collected and analysed the data. I.K., A.S., E.G., and E.H.S. wrote the first draft. All authors reviewed and edited the final manuscript.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Members, remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 e final report, N Engl J Med
Eastman, Roth, Brimacombe, Simeonov, Shen et al., Remdesivir: a review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19, ACS Cent Sci
Ko, Rolain, Lee, Chen, Huang et al., Arguments in favour of remdesivir for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Magleby, Westblade, Trzebucki, Simon, Rajan et al., Impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 viral load on risk of intubation and mortality among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa851
Malin, Suarez, Priesner, Fatkenheuer, Rybniker, Remdesivir against COVID-19 and other viral diseases, Clin Microbiol Rev
Maltezou, Raftopoulos, Vorou, Papadima, Mellou et al., Association between upper respiratory tract viral load, comorbidities, disease severity, and outcome of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa804
Mckee, Sternberg, Stange, Laufer, Naujokat, Candidate drugs against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Pharmacol Res
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi, Sathiyamoorthy et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19 e interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Pruijssers, George, Schafer, Leist, Gralinksi et al., Remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice, Cell Rep
Shlomai, Ben-Zvi, Bendersky, Shafran, Goldberg et al., Nasopharyngeal viral load predicts hypoxemia and disease outcome in admitted COVID-19 patients, Crit Care
Singanayagam, Patel, Charlett, Bernal, Saliba et al., Duration of infectiousness and correlation with RT-PCR cycle threshold values in cases of COVID-19, England, January to, Euro Surveill
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Meade-White, Porter et al., Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Young, Tan, Leo, The place for remdesivir in COVID-19 treatment, Lancet Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029",
"ISSN": [
"1198-743X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029",
"alternative-id": [
"S1198743X21001130"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldberg",
"given": "Elad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ben Zvi",
"given": "Haim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheena",
"given": "Liron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sofer",
"given": "Summer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krause",
"given": "Ilan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sklan",
"given": "Ella H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shlomai",
"given": "Amir",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-10T00:36:33Z",
"timestamp": 1615336593000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-30T10:47:56Z",
"timestamp": 1627642076000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-19T07:18:43Z",
"timestamp": 1710832723582
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1622505600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1614988800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21001130?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21001130?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "917.e1-917.e4",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104859",
"article-title": "Candidate drugs against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "McKee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104859",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib1",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.0c00489",
"article-title": "Remdesivir: a review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Eastman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "ACS Cent Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib2",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105933",
"article-title": "Arguments in favour of remdesivir for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections",
"author": "Ko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105933",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib3",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940",
"article-title": "Remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice",
"author": "Pruijssers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107940",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib4",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00162-20",
"article-title": "Remdesivir against COVID-19 and other viral diseases",
"author": "Malin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib5",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19 – interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib6",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Members, remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 – final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib7",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30911-7",
"article-title": "The place for remdesivir in COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Young",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib8",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa851",
"article-title": "Impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 viral load on risk of intubation and mortality among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Magleby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ciaa851",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa804",
"article-title": "Association between upper respiratory tract viral load, comorbidities, disease severity, and outcome of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Maltezou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib10",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03244-3",
"article-title": "Nasopharyngeal viral load predicts hypoxemia and disease outcome in admitted COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Shlomai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "539",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib11",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.32.2001483",
"article-title": "Duration of infectiousness and correlation with RT-PCR cycle threshold values in cases of COVID-19, England, January to May 2020",
"author": "Singanayagam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2001483",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib12",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5",
"article-title": "Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib13",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.029_bib14",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1198743X21001130"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A real-life setting evaluation of the effect of remdesivir on viral load in COVID-19 patients admitted to a large tertiary centre in Israel",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "27"
}