Bamlanivimab as monotherapy for high-risk COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms
et al., International Journal of Scientific Research, 11:7, Jul 2022
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
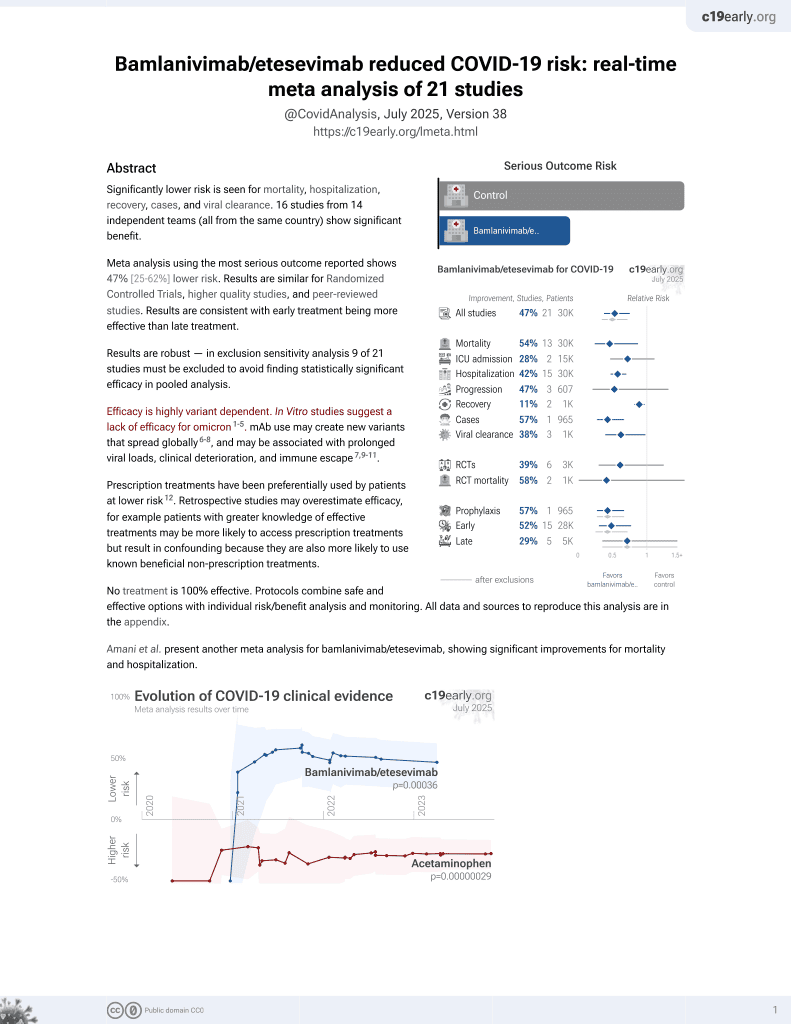
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 335 outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 and at least one high-risk comorbidity, showing significantly lower hospitalization with bamlanivimab treatment compared to the control group.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 144.2% higher, RR 2.44, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 335 (0.3%), control 0 of 148 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 62.9% lower, RR 0.37, p < 0.001, treatment 21 of 335 (6.3%), control 25 of 148 (16.9%), NNT 9.4.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Fivelstad et al., 31 Jul 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Abstract: ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER
Volume - 11 | Issue - 07 | July - 2022 | PRINT ISSN No. 2277 - 8179 | DOI : 10.36106/ijsr
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
BAMLANIVIMAB AS MONOTHERAPY FOR HIGH-RISK COVID-19 PATIENTS
WITH MILD TO MODERATE SYMPTOMS
Emergency Medicine
MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Valley Health System, 500 N Rainbow Blvd,
Kathryn Fivelstad STE 203 Las Vegas, NV 89107 USA.
Tuong Pham
Kristen Meacham
Alberto Hazan
Patrick Olivieri
Michael Doctor *
MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Valley Health System, 500 N Rainbow Blvd,
STE 203 Las Vegas, NV 89107 USA
MS, Touro University Nevada. 874 American Pacic Drive #8801, Henderson, NV
89014. USA
MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Valley Health System, 500 N Rainbow Blvd,
STE 203 Las Vegas, NV 89107 USA
MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Valley Health System, 500 N Rainbow Blvd,
STE 203 Las Vegas, NV 89107 USA
MD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Valley Health System, 500 N Rainbow Blvd,
STE 203 Las Vegas, NV 89107 USA *Corresponding Author
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is known to progress from mild to severe disease, especially in patients with high-risk
comorbidities. Monoclonal antibody treatment of COVID-19 with bamlanivimab has been proposed to decrease illness severity. Non-industry
sponsored data is lacking. This study will investigate the effects of bamlanivimab on hospitalization and mortality when administered to patients
with COVID-19. METHODS: This was a retrospective analysis of bamlanivimab use within eight emergency departments in Las Vegas, NV.
Patients who tested positive for COVID-19 and met inclusion criteria for bamlanivimab but were not administered this treatment were used as a
control group. Patients were tracked for hospital admissions and mortality for the 28 days following their treatment. RESULTS: 335 patients
diagnosed with COVID-19 were treated with bamlanivimab infusion and tracked for hospitalization within 28 days. Of these patients, 21 (6.3%)
required admission, including one who expired on day 46 after a prolonged ICU stay. Of the 148 control patients, 25 required admission (16.9%)
and there were no deaths. Relative risk of hospitalization with administration of bamlanivimab was 0.37 (CI 95% 0.22 to 0.61, p<0.01). The
absolute risk reduction is 10.6% making the number needed to treat for potential benet 9.4 (95% CI 6.0 to 19.9). CONCLUSION: The results of
our study are in alignment with those of the clinical trials funded by Eli Lilly supporting bamlanivimab to reduce 28-day hospitalization for
COVID-19 positive patients with mild to moderate symptoms and signicant comorbidities.
KEYWORDS
COVID-19; Bamlanivimab; Coronavirus; Monoclonal Antibody