REGEN-COV antibody cocktail (casirivimab/imdevimab) for the treatment of inpatients with early hospital-acquired COVID-19: a single center experience
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1170976/v1, May 2022
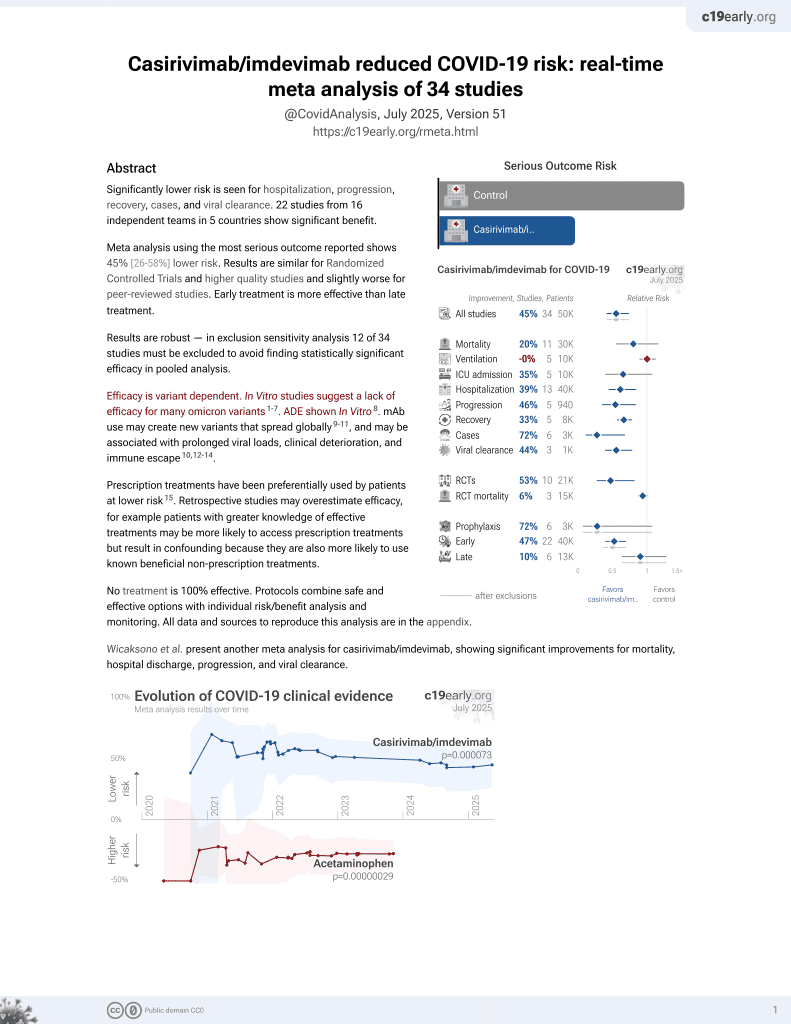
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 34 patients with hospital-acquired COVID-19, showing lower mortality and oxygen requirements with early casirivimab/imdevimab treatment.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
|
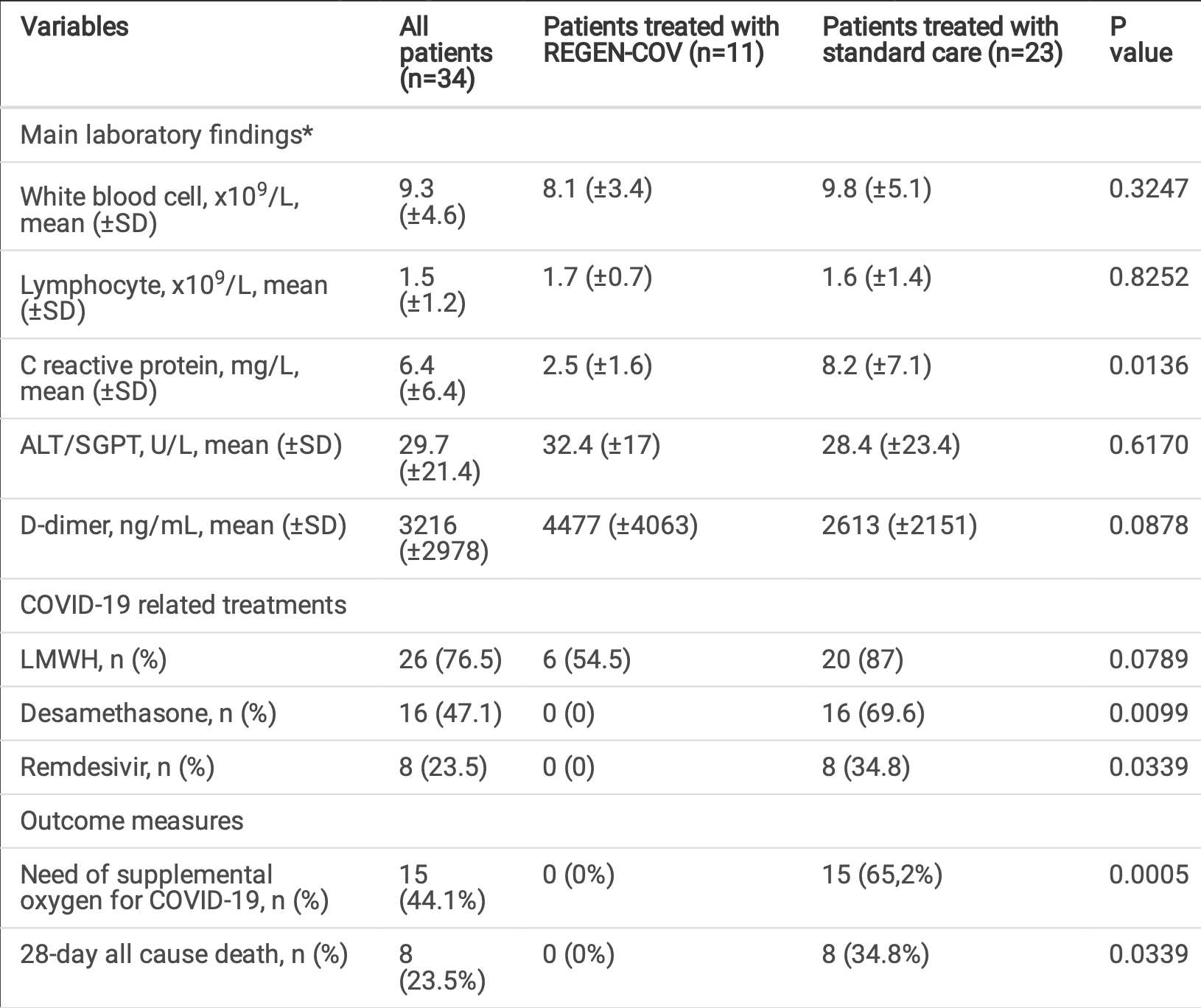
risk of death, 92.2% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 11 (0.0%), control 8 of 23 (34.8%), NNT 2.9, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 94.5% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.02, treatment 0 of 11 (0.0%), control 15 of 23 (65.2%), NNT 1.5, odds ratio converted to relative risk, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Faraone et al., 5 May 2022, retrospective, Italy, preprint, 12 authors, study period 25 October, 2020 - 30 April, 2021, average treatment delay 2.3 days.
Contact: antfaraone@gmail.com.
REGEN-COV antibody cocktail (casirivimab/imdevimab) for the treatment of inpatients with early hospital-acquired COVID-19: a single center experience
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1170976/v1
Inpatients with hospital-acquired (HA) COVID-19 have mortality rates above 30%. Subjects with early diagnosis of COVID-19 and risk factors for disease progression are suitable for treatment with anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We retrospectively assessed the outcome of a cohort of hospitalized patients with laboratory con rmed SARS-CoV-2 nosocomial infection who were admitted to the COVID-19 general ward of an acute-care Italian hospital between October 25, 2020 and April 30, 2021. Patients receiving the REGEN-COV mAb cocktail (casirivimab/imdevimab) were compared with those receiving standard care. Of 34 patients, 11 (mean age, 73.1; 9 males) underwent treatment with REGEN-COV and 23 received standard care. The 2 study groups were well balanced regarding age, sex, comorbidities, acute illness severity at diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all participants had at least 2 risk factors for disease progression. Five of 11 patients in the REGEN-COV group and 16 of 23 in the standard care group were asymptomatic at diagnosis; the remaining had symptoms of mild COVID-19. All patients received REGEN-COV within 3 days of infection con rmation. Treatment with REGEN-COV was inversely associated with oxygen requirement for COVID-19 during hospital stay (OR 0.02, CI 0-0.52, p=0.0174). No 28-day deaths were registered in the REGEN-COV group, compared to 8 (34.8%) in the standard care group (p=0.0339). Kaplan-Meier analysis con rmed the survival advantage of REGEN-COV group (log-rank p=0.00324). No serious adverse events related to REGEN-COV administration were recorded. Based on these ndings, REGEN-COV appears safe and might prevent disease progression in high-risk inpatients with early diagnosis of HA-COVID-19.
Author contributions All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by T Picchioni, E Lovicu, G Scocchera, A Lo Forte, A Crociani, P Carrai, S Sbaragli, M Bettucchi. Data analysis was conducted by A Faraone and L Tofani. The rst draft of the manuscript was written by A Faraone, F Fabbrizzi and A Fortini and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the nal manuscript. Ethical standards The study was approved by the institutional review board of the Department of Medicine of the "Azienda USL Toscana Centro", Florence, Italy. All procedures were performed in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, informed consent was weaved according to the applicable local law. Data were de-identi ed to preserve the anonymity of participants.
References
Abbas, Nunes, Martischang, Nosocomial transmission and outbreaks of coronavirus disease 2019: the need to protect both patients and healthcare workers, Antimicrob Resist Infect Control, doi:10.1186/s13756-020-00875-7
Aifa, Determina, De nizione delle modalita' e delle condizioni di impiego dell'anticorpo monoclonale casirivimab-imdevimab ai sensi del decreto 6
Arnold, Bishop, Oppy, Scott, Stevenson, Surveillance testing reveals a signi cant proportion of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 are asymptomatic, Am J Infect Control, doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2021.01.005
Barranco, Bernucci, Tremoul, Ventura, Hospital-Acquired SARS-Cov-2 Infections in Patients: Inevitable Conditions or Medical Malpractice?, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18020489
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bierle, Ganesh, Tulledge-Scheitel, Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of Breakthrough COVID-19 in Fully Vaccinated Individuals with High-Risk Comorbidities, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab570
Chen, Nirula, Heller, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
Copin, Baum, Wloga, The monoclonal antibody combination REGEN-COV protects against SARS-CoV-2 mutational escape in preclinical and human studies, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.002
Curry, Salgado, When Hospitals Harm: Multimodal Entry of SARS-CoV-2 into Inpatient Healthcare, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa957
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Blaze-, 1 Investigators et al (2021) Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in Mild or Moderate COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102685
Fda, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Monoclonal Antibody Bamlanivimab
Fda, Letter of Authorization for Emergency Use of REGEN-COV (casirivimab with imdevimab
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0827
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Khan, Reed-Embleton, Lewis, Saldanha, Does nosocomial COVID-19 result in increased 30-day mortality? A multi-centre observational study to identify risk factors for worse outcomes in patients with COVID-19, J Hosp Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.09.017
Khonyongwa, Taori, Soares, Incidence and outcomes of healthcare-associated COVID-19 infections: signi cance of delayed diagnosis and correlation with staff absence, J Hosp Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.10.006
Kim, Read, Fauci, Therapy for Early COVID-19: A Critical Need, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22813
Koehler, Ritzer, Weidlich, Use of monoclonal antibody therapy for nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients at high risk for severe COVID-19: experience from a tertiary-care hospital in Germany, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-021-01657-y
Ly-Cov555 Study, Group, Lundgren, Grund, A Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033130
Planas, Veyer, Baidaliuk, Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9
Rhee, Baker, Vaidya, CDC Prevention Epicenters Program. Incidence of Nosocomial COVID-19 in Patients Hospitalized at a Large US Academic Medical Center, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.20498
Rickman, Rampling, Shaw, Nosocomial Transmission of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 66 Hospital-acquired Cases in a London Teaching Hospital, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa816
Shiwani, Bilal, Shahzad, A comparison of characteristics and outcomes of patients with community-acquired and hospital-acquired COVID-19 in the United Kingdom: An observational study, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106314
Tani, Sawano, Kawamoto, Ozaki, Tanimoto, Nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Japan: A Cross-sectional Newspaper Database Survey, Int J Health Policy Manag, doi:10.34172/ijhpm.2020.75
Taylor, Adams, Hufford, De La Torre, Winthrop et al., Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00542-x
Wake, Morgan, Choi, Winn, Reducing nosocomial transmission of COVID-19: implementation of a COVID-19 triage system, Clin Med (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0411
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1170976/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1170976/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Inpatients with hospital-acquired (HA) COVID-19 have mortality rates above 30%. Subjects with early diagnosis of COVID-19 and risk factors for disease progression are suitable for treatment with anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We retrospectively assessed the outcome of a cohort of hospitalized patients with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 nosocomial infection who were admitted to the COVID-19 general ward of an acute-care Italian hospital between October 25, 2020 and April 30, 2021. Patients receiving the REGEN-COV mAb cocktail (casirivimab/imdevimab) were compared with those receiving standard care. Of 34 patients, 11 (mean age, 73.1; 9 males) underwent treatment with REGEN-COV and 23 received standard care. The 2 study groups were well balanced regarding age, sex, comorbidities, acute illness severity at diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all participants had at least 2 risk factors for disease progression. Five of 11 patients in the REGEN-COV group and 16 of 23 in the standard care group were asymptomatic at diagnosis; the remaining had symptoms of mild COVID-19. All patients received REGEN-COV within 3 days of infection confirmation. Treatment with REGEN-COV was inversely associated with oxygen requirement for COVID-19 during hospital stay (OR 0.02, CI 0–0.52, p=0.0174). No 28-day deaths were registered in the REGEN-COV group, compared to 8 (34.8%) in the standard care group (p=0.0339). Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed the survival advantage of REGEN-COV group (log-rank p=0.00324). No serious adverse events related to REGEN-COV administration were recorded. Based on these findings, REGEN-COV appears safe and might prevent disease progression in high-risk inpatients with early diagnosis of HA-COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
14
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6095-8403",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Faraone",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Fabbrizzi",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Picchioni",
"given": "Tommaso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Lovicu",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Statistics, Computer Science, Applications, University of Florence, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Tofani",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Scocchera",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Forte",
"given": "Aldo Lo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Crociani",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Carrai",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Sbaragli",
"given": "Serena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Bettucchi",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, San Giovanni di Dio Hospital, Florence"
}
],
"family": "Fortini",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-05T16:08:51Z",
"timestamp": 1651766931000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-05T16:08:53Z",
"timestamp": 1651766933000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-06T11:11:21Z",
"timestamp": 1651835481347
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1651708800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1170976/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1170976/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1170976/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "REGEN-COV antibody cocktail (casirivimab/imdevimab) for the treatment of inpatients with early hospital-acquired COVID-19: a single center experience",
"type": "posted-content"
}