Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of Breakthrough COVID-19 in Fully Vaccinated Individuals with High-Risk Comorbidities
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab570, Oct 2021 (preprint)
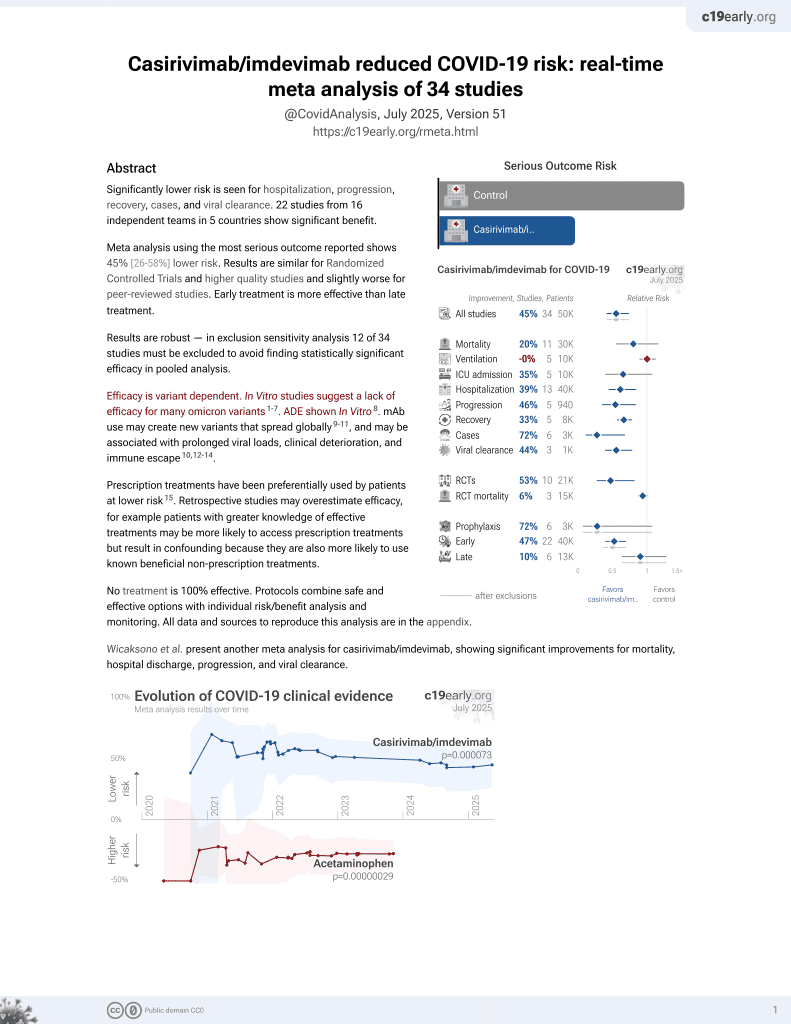
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
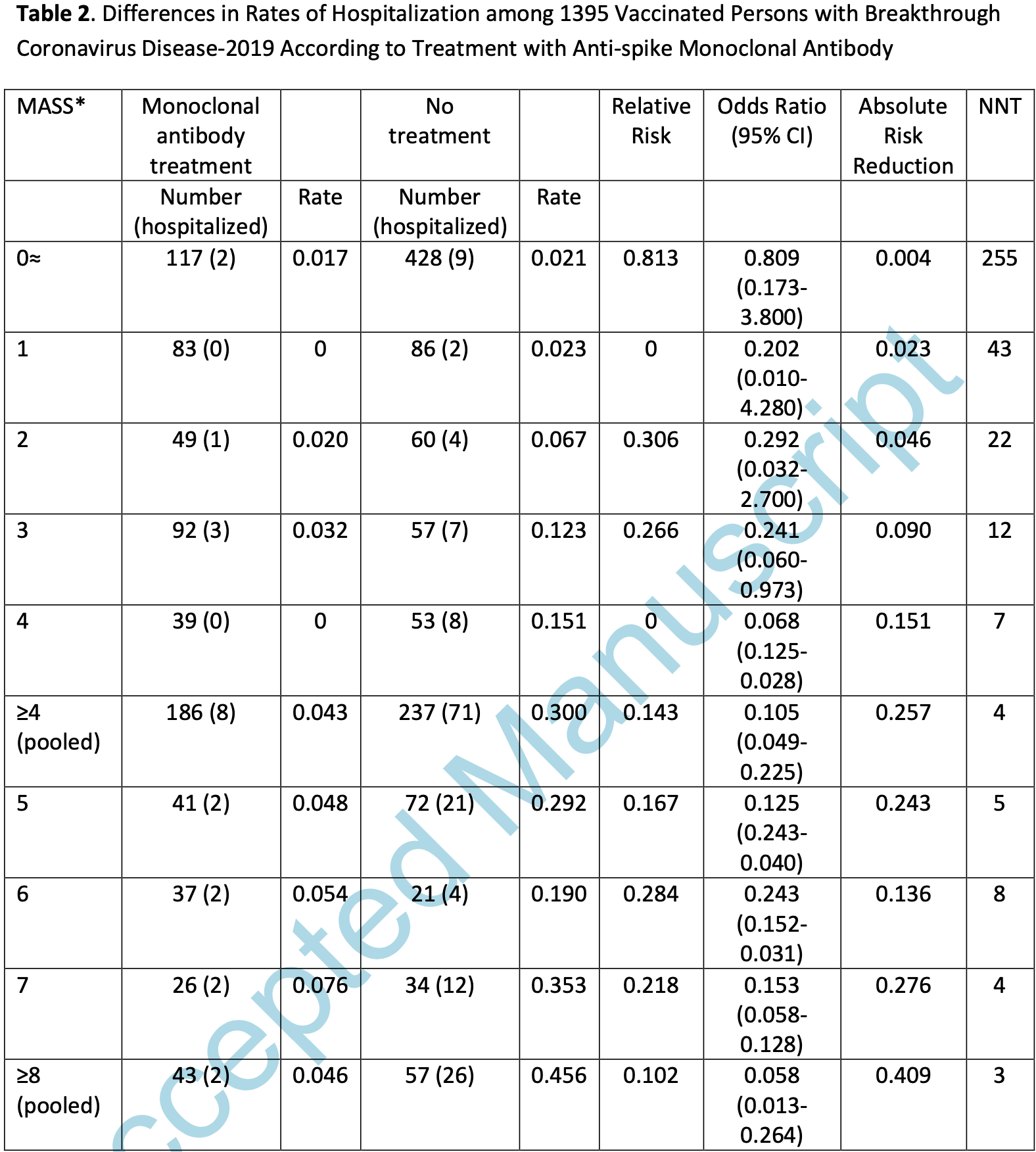
Retrospective 1,395 vaccinated COVID-19 cases, showing significantly lower hospitalization and oxygen supplementation with monoclonal antibody treatment, primarily casirivimab-imdevimab. Hospitalization was significantly associated with comorbidities.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments8.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
patients were treated with different medications, results specific to each medication were not reported.
|
risk of ICU admission, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.16, treatment 0 of 527 (0.0%), control 5 of 868 (0.6%), NNT 174, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 85.3% lower, RR 0.15, p < 0.001, treatment 5 of 527 (0.9%), control 56 of 868 (6.5%), NNT 18, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 75.3% lower, RR 0.25, p < 0.001, treatment 14 of 527 (2.7%), control 93 of 868 (10.7%), NNT 12, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Conflicts of interest:
research funding from the drug patent holder.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
6.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Bierle et al., 20 Oct 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, average treatment delay 5.0 days.
Contact: razonable.raymund@mayo.edu.
doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab570/6429422
Breakthrough COVID-19 may occur among vaccinated individuals with a high number of medical comorbidities, especially during the SARS-CoV-2 Delta surge. Anti-spike monoclonal antibody treatment was associated with significantly lower rates of hospitalization, particularly among highrisk persons.
Conflict of Interest Statement: Dr. Razonable is principal investigator of research funded by Regeneron, Roche, Gilead (all funds provided to his institution), and is a member of Data Safety Monitoring Board of Novartis, on projects not directly related to this submission. Dr. Razonable received research funds from the Mayo Clinic for studies on monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19. All other no conflict to report.
Results The total population consisted of 1395 fully vaccinated patients (mean age, 54.3 years; 39.6% male) with breakthrough COVID-19 and were screened for monoclonal antibody therapy, under US FDA EUA guidance. The majority of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections (n=1002; 71.8%) occurred during a 6-week period from July 1 to August 16, 2021, when the Delta variant was predominant in our region (Supplemental Figure). The most common medical comorbidities were hypertension (34.5%), cardiovascular disease (13.8%), chronic pulmonary disease (13.6%), and chronic kidney disease (10.2%) (Table 1 ). A total of 170 (12.2%) patients were immunocompromised, including 149 patients (10.7%) with solid cancer and hematologic malignancies and 35 (2.5%) transplant recipients. Most patients (69.8%) received the Pfizer-BioNTech SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. Breakthrough COVID-19 occurred at median of 124 days (mean, 120 days) after full completion of the vaccination series. At 28 days after breakthrough COVID-19 diagnosis, 107 patients (7.7%) had progressed to require hospitalization...
References
Baden, Sahly, Essink, Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2
Bergwerk, Gonen, Lustig, Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Andrews, Gower, Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant, N Engl J Med
Bierle, Ganesh, Wilker, Influence of Social and Cultural Factors on the Decision to Consent for Monoclonal Antibody Treatment among High-Risk Patients with Mild-Moderate COVID-19, J Prim Care Community Health
Ganesh, Pawlowski, Horo, Intravenous bamlanivimab use associates with reduced hospitalization in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, J Clin Invest
Ganesh, Philpot, Bierle, Real-World Clinical Outcomes of Bamlanivimab and Casirivimab-Imdevimab among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019, J Infect Dis
Razonable, Aloia, Anderson, A Framework for Outpatient Infusion of Antispike Monoclonal Antibodies to High-Risk Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease-19: The Mayo Clinic Model, Mayo Clin Proc
Razonable, Pawlowski, Horo, Bierle, Arndt et al., Casirivimab-Imdevimab Treatment is Associated with Reduced Rates of Hospitalization among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease-19, EClinicalMedicine
Swift, Breeher, Tande, Effectiveness of Messenger RNA Coronavirus Disease
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Lancet
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Wilhelm, Toptan, Pallas, Antibody-Mediated Neutralization of Authentic SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 Variants Harboring L452R and T478K/E484Q, Viruses
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab570",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab570",
"container-title": [
"The Journal of Infectious Diseases"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-12T20:10:14Z",
"timestamp": 1636747814000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-16T20:11:17Z",
"timestamp": 1637093477000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-16T20:44:41Z",
"timestamp": 1637095481009
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0022-1899"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1537-6613"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"The Journal of Infectious Diseases"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"OUP accepted manuscript"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}