Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100, BLAZE-4, NCT04634409, Mar 2022
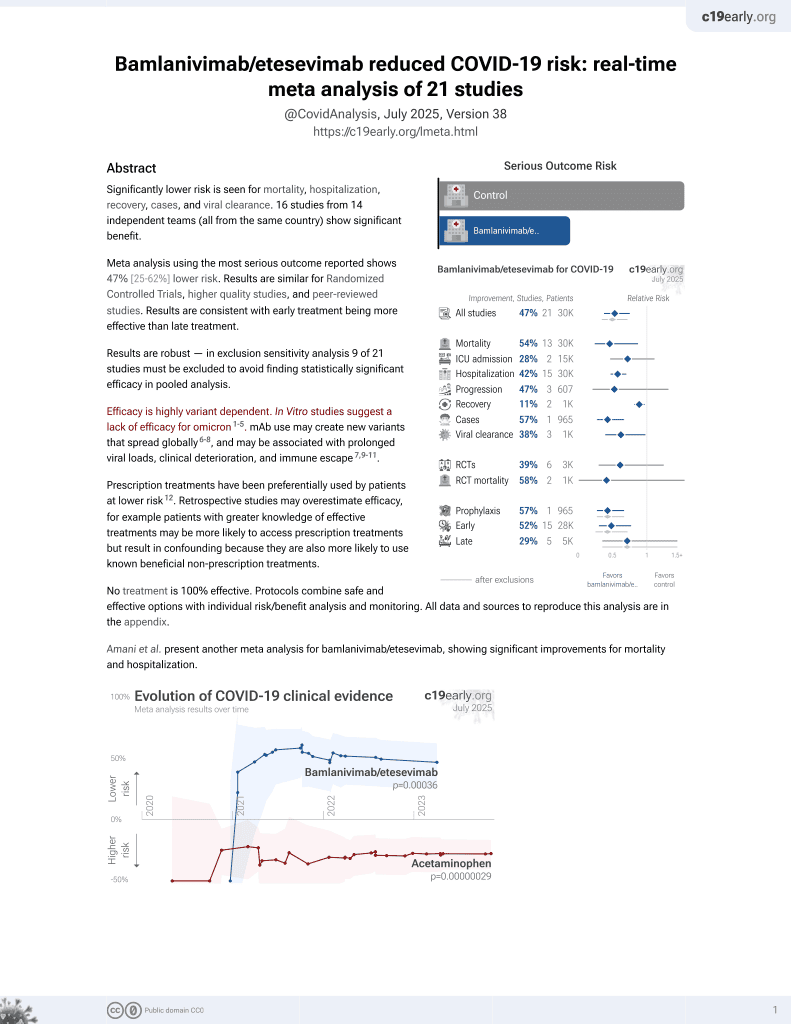
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
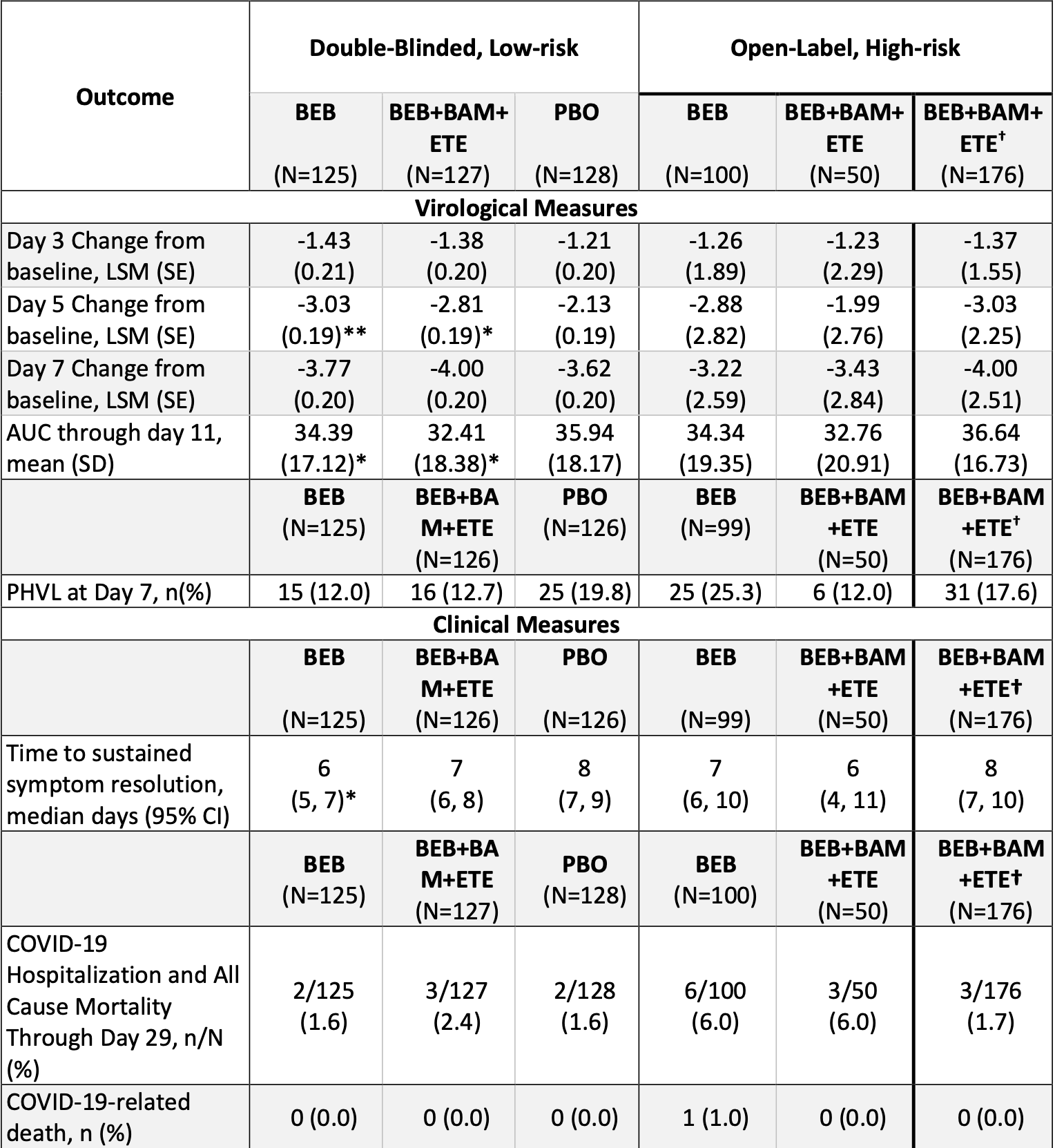
RCT showing improved viral clearance with bamlanivimab/etesevimab combined with bebtelovimab. Results refer to the placebo controlled portion of the trial.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers bamlanivimab/etesevimab and bebtelovimab.
|
risk of hospitalization, 51.2% higher, RR 1.51, p = 0.68, treatment 3 of 127 (2.4%), control 2 of 128 (1.6%).
|
|
recovery time, 12.5% lower, relative time 0.88, treatment 127, control 128.
|
|
relative viral load reduction, 9.5% better, RR 0.91, p < 0.001, treatment mean 4.0 (±0.2) n=125, control mean 3.62 (±0.2) n=128, day 7.
|
|
relative viral load reduction, 24.2% better, RR 0.76, p < 0.001, treatment mean 2.81 (±0.19) n=125, control mean 2.13 (±0.19) n=128, day 5.
|
|
relative viral load reduction, 12.3% better, RR 0.88, p < 0.001, treatment mean 1.38 (±0.2) n=125, control mean 1.21 (±0.2) n=128, day 3.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 35.5% lower, RR 0.65, p = 0.17, treatment 16 of 127 (12.6%), control 25 of 128 (19.5%), NNT 14, persistently high viral load, day 7, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Dougan et al., 12 Mar 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, preprint, 22 authors, study period 19 April, 2021 - 19 July, 2021, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with bebtelovimab) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial NCT04634409 (history) (BLAZE-4).
Contact: robert.gottlieb@bswhealth.org.
Abstract: medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100; this version posted March 12, 2022. The copyright holder for this
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in
perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license .
Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly
neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19.
Authors: Michael Dougan, MD, PhD1; Masoud Azizad, MD2, Peter Chen, MD3; Barry Feldman,
MD4; Matthew Frieman, PhD5; Awawu Igbinadolor, MD6; Princy Kumar, MD7; Jason Morris,
MD8; Jeffrey Potts, MD9; Lauren Baracco, BS5; Lisa Macpherson, MSPHc10; Nicole L.
Kallewaard, PhD10; Dipak R. Patel, MD, PhD10; Matthew M. Hufford, PhD10; Linda Wietecha,
MSc10; Emmanuel Chigutsa, PhD10; Sarah L. Demmon, MS10; Bryan E. Jones, PhD10; Ajay Nirula,
MD, PhD10; Daniel M. Skovronsky, MD, PhD10; Mark Williams, MD, FCCM, FCCP10; Robert L.
Gottlieb, MD, PhD11.
Affiliations: 1Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA;
2Valley Clinical Trials, Northridge, CA, USA; 3Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA,
USA; 4Millennium Medical Group, Farmington Hills, MI, USA; 5University of Maryland School
of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 6Monroe Biomedical Research, Monroe, NC, USA; 7Georgetown
University, Washington, DC, USA; 8Clinical Trials of Southwest Louisiana, Lake Charles, LA,
USA; 9Great Lakes Research Group, Inc., Bay City, MI, USA; 10Eli Lilly and Company,
Indianapolis, IN, USA. 11Baylor University Medical Center and Baylor Scott & White Research
Institute, Dallas, TX, USA;
Corresponding author: Robert L. Gottlieb, MD, PhD, Baylor University Medical Center and
Baylor Scott & White Research Institute, Dallas, TX, USA. E-mail:
Robert.Gottlieb@BSWHealth.org. Phone: +1-214-820-6856 (Office).
NOTE: This preprint reports new research that has not been certified by peer review and should not be used to guide clinical practice.
1
medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100; this version posted March 12, 2022. The copyright holder for this
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in
perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license .
BACKGROUND: Bebtelovimab is a potent, fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb)
targeting the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2, with broad neutralizing activity to all currently known
SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, including omicron variant lineages. Specialized
developmental approaches accelerated the initiation of a clinical trial designed to evaluate
the efficacy and safety of bebtelovimab alone (BEB) or together with bamlanivimab (BAM)
and etesevimab (ETE) delivered via slow intravenous push for the treatment of mild-tomoderate COVID-19.
METHODS: This portion of the phase 2, BLAZE-4 trial (J2X-MC-PYAH; NCT04634409) enrolled
714 patients (between May and July 2021) with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 within 3 days (≤3
days) of laboratory diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients at low risk for severe COVID19 were randomized 1:1:1 (double-blinded) to placebo, BEB 175 mg, or BEB 175 mg+BAM 700
mg+ETE 1400 mg (BEB+BAM+ETE). Patients at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19
were randomized 2:1 (open-label) to BEB or BEB+BAM+ETE, and a subsequent treatment arm
enrolled..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>BACKGROUND</jats:title><jats:p>Bebtelovimab is a potent, fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2, with broad neutralizing activity to all currently known SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, including omicron variant lineages. Specialized developmental approaches accelerated the initiation of a clinical trial designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of bebtelovimab alone (BEB) or together with bamlanivimab (BAM) and etesevimab (ETE) delivered via slow intravenous push for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>METHODS</jats:title><jats:p>This portion of the phase 2, BLAZE-4 trial (J2X-MC-PYAH; <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04634409\">NCT04634409</jats:ext-link>) enrolled 714 patients (between May and July 2021) with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 within 3 days (≤3 days) of laboratory diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients at low risk for severe COVID-19 were randomized 1:1:1 (double-blinded) to placebo, BEB 175 mg, or BEB 175 mg+BAM 700 mg+ETE 1400 mg (BEB+BAM+ETE). Patients at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 were randomized 2:1 (open-label) to BEB or BEB+BAM+ETE, and a subsequent treatment arm enrolled patients to BEB+BAM+ETE using Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) updated criteria for High-risk. All treatments were administered intravenously over ≥30 seconds (open-label BEB) or ≥6.5 minutes (all other treatment arms). For the placebo-controlled patients (termed Low-risk), the primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with persistently high viral load (PHVL) (log viral load >5.27) on Day 7. For the open-label patients (termed High-risk), the primary endpoint was safety. In nonclinical studies, SARS-CoV-2 isolates were tested using an endpoint neutralization assay to measure BEB’s inhibitory concentration greater than 99% (IC<jats:sub>99</jats:sub>).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>RESULTS</jats:title><jats:p>Baseline viral sequencing data were available from 611 patients; 90.2% (n=551) aligned with a variant of interest or concern (WHO designation), with the majority infected with delta (49.8%) or alpha (28.6%) variants. Among the Low-risk patients, PHVL occurred in 19.8% of patients treated with placebo, as compared to 12.7% (p=0.132) of patients treated with BEB+BAM+ETE and 12.0% (p=0.097) of patients treated with BEB, a 36% and 40% relative risk reduction, respectively. Viral load-area under the curve analysis from baseline to Day 11 showed statistically signficant reductions for patients treated with BEB (p=0.006) and BEB+BAM+ETE (p=0.043) compared to patients who received placebo. Time to sustained symptom resolution was reduced by a median of 2 days for patients treated with BEB (6 days; p=0.003) and 1 day for patients treated with BEB+BAM+ETE (7 days; p=0.289) compared to placebo (8 days). The incidence of COVID-19-related hospitalization or all-cause deaths by day 29 were similar across treatment arms, as expected given the patients’ risk status (the Low risk cohorts had a Low risk of hospitalization, and High risk cohorts received only active therapy without placebo). Overall, safety results were consistent with previous studies investigating mAbs targeting SARS-CoV-2. The proportion of patients with treatment emergent adverse events (AEs) were 9.7% in Low-risk (n=37/380) and 14.7% in High-risk (n=48/326) patients treated with BEB or BEB+BAM+ETE; majority of AEs were considered mild or moderate in severity. Serious AEs were reported in 2.1% of High-risk patients (n=7/326), including one death (a cerebrovascular accident); 1 serious AE was reported among Low-risk patients. In an in vitro neutralization assay, BEB neutralized the omicron isolate (BA.1) with <2.44ng/ml estimated IC<jats:sub>99</jats:sub>.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>CONCLUSIONS</jats:title><jats:p>In patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, treatment with BEB or BEB+BAM+ETE was associated with greater viral clearance, a reduction in time to sustained symptom resolution, and safety results consistent with mAbs that target SARS-CoV-2. Integration of clinical findings with in vitro neutralization of emerging viral variants offered a pragmatic framework for investigating the efficacy of a new antiviral mAb agent, as demonstrated by bebtelovimab.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
12
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dougan",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azizad",
"given": "Masoud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feldman",
"given": "Barry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0107-0775",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Frieman",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igbinadolor",
"given": "Awawu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5994-2727",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Princy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potts",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6984-5832",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baracco",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3224-9233",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Macpherson",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kallewaard",
"given": "Nicole L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Dipak R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hufford",
"given": "Matthew M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wietecha",
"given": "Linda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chigutsa",
"given": "Emmanuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Demmon",
"given": "Sarah L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4764-6290",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Bryan E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nirula",
"given": "Ajay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skovronsky",
"given": "Daniel M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8376-8709",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gottlieb",
"given": "Robert L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-13T06:50:11Z",
"timestamp": 1647154211000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-15T04:50:31Z",
"timestamp": 1647319831000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-20T06:19:57Z",
"timestamp": 1681971597955
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
12
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
12
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.1",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. [WHO] World Health Organization, 2022. (Accessed January 11, 2022., at https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-1911-january-2022.)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2020.07.004",
"article-title": "Fruitful Neutralizing Antibody Pipeline Brings Hope To Defeat SARS-Cov-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "815",
"journal-title": "Trends in pharmacological sciences",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.2",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Perspectives on monoclonal antibody therapy as potential therapeutic intervention for Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19)",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Asian Pacific journal of allergy and immunology",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.3",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00542-x",
"article-title": "Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.4",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2772-0",
"article-title": "Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.8",
"volume": "588",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in Mild or Moderate Covid-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.9",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab912",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.10",
"unstructured": "Dougan M , Azizad M , Mocherla B , et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of bamlanivimab and etesevimab together in high-risk ambulatory patients with COVID-19 and validation of the prognostic value of persistently high viral load. Clin Infect Dis 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab305",
"article-title": "Real-World Experience of Bamlanivimab for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Case-Control Study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.11",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.032",
"article-title": "The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "447",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.12",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"article-title": "Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination With Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.14",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2035002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"article-title": "Early Treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.16",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2459",
"article-title": "A Quantitative Modeling and Simulation Framework to Support Candidate and Dose Selection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies to Advance Bamlanivimab Into a First-in-Human Clinical Trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "595",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.17",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0262-4079(21)02140-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.18"
},
{
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.19",
"unstructured": "FACT SHEET FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS EMERGENCY USE AUTHORIZATION (EUA) OF SOTROVIMAB. Food and Drug Administration 2022. (Accessed February 22, 2022, at https://www.fda.gov/media/149534/download.)"
},
{
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.20",
"unstructured": "Westendorf K , Wang L , Zentelis S , et al. LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants. bioRxiv 2022."
},
{
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.21",
"unstructured": "People at increased risk and other people who need to take extra precautions. [CDC] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (Accessed March 16, 2021, at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/index.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https://%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fcoronavirus%25.)"
},
{
"article-title": "Assignment of epidemiological lineages in an emerging pandemic using the pangolin tool",
"first-page": "veab064",
"journal-title": "Virus Evol",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.22",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"first-page": "1302",
"journal-title": "Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Neutralizing Antibodies Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Infection",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.23",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2420",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2026920",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.8828",
"article-title": "Effect of Bamlanivimab vs Placebo on Incidence of COVID-19 Among Residents and Staff of Skilled Nursing and Assisted Living Facilities: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.26",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.02.07.479306",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.27",
"unstructured": "Iketani S , Liu L , Guo Y , et al. Antibody Evasion Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages. bioRxiv 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/archdischild-2020-320338",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022031421501172000_2022.03.10.22272100v1.29",
"unstructured": "Zimmermann P , Curtis N. Why is COVID-19 less severe in children? A review of the proposed mechanisms underlying the age-related difference in severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Arch Dis Child 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2022.03.10.22272100"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Bebtelovimab, alone or together with bamlanivimab and etesevimab, as a broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment for mild to moderate, ambulatory COVID-19",
"type": "posted-content"
}
dougan2