Retrospective Clinical Investigation into the Association Between Abnormal Blood Clotting, Oral Anticoagulant Therapy, and Medium-Term Mortality in a Cohort of COVID-19 Patients
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13030535, Feb 2025 (preprint)
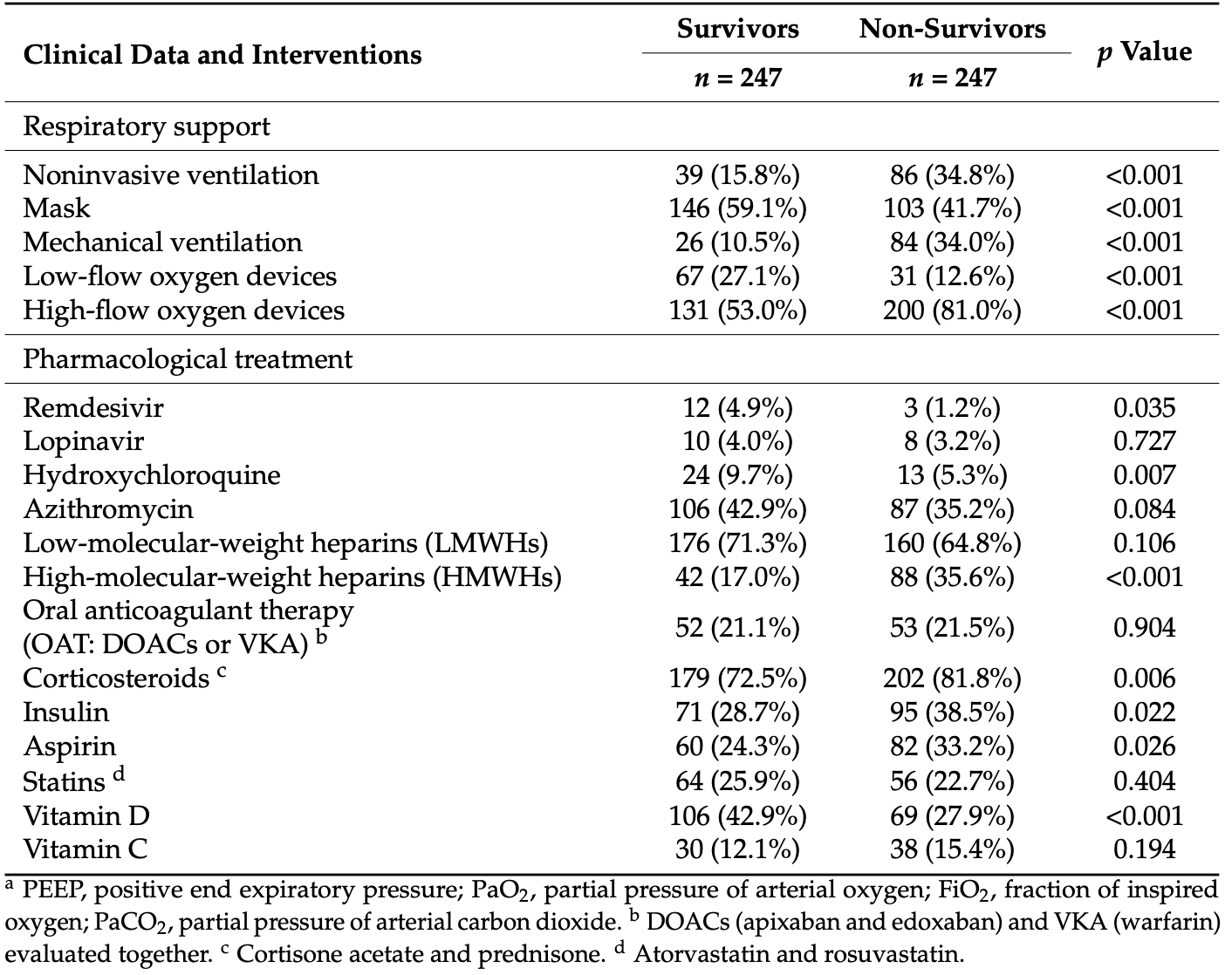
Retrospective 247 non-survivors and 247 matched survivors in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Italy showing results for several treatments.
|
risk of death, 54.9% higher, OR 1.55, p = 0.03, treatment 82 of 247 (33.2%) cases,
60 of 247 (24.3%) controls, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Dinoi et al., 20 Feb 2025, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 17 March, 2020 - 15 June, 2021.
Contact: antonella.liantonio@uniba.it (corresponding author), giorgia.dinoi@uniba.it, maria.togo@uniba.it, caterina.deruvo@uniba.it, francesco.samarelli@uniba.it, paola.imbrici@uniba.it, orazio.nicolotti@uniba.it, annamaria.deluca@uniba.it, p.guida@miulli.it, f.mastroianni@miulli.it, cosimodamiano.altomare@uniba.it.
Retrospective Clinical Investigation into the Association Between Abnormal Blood Clotting, Oral Anticoagulant Therapy, and Medium-Term Mortality in a Cohort of COVID-19 Patients
Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13030535
Background/Objectives: People affected by COVID-19 are exposed to abnormal clotting and endothelial dysfunction, which may trigger thromboembolic events. This study aimed at retrospectively investigating whether oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT), encompassing either direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), mainly apixaban, or the vitamin K antagonist (VKA) warfarin, could have impacted medium-term mortality in a cohort of SARS-CoV-2 patients. Methods: Among 1238 COVID-19 patients, hospitalized from 17 March 2020 to 15 June 2021, 247 survivors and 247 deceased within 90 days from hospitalization were matched 1:1 based on age, sex, and intensive care unit (ICU) admission within three days. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate associations by means of odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: A univariate regression analysis suggested that OAT, no differently from subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) during hospitalization, has no significant impact (p value > 0.05) on medium-term mortality. A multivariate analysis, limited to baseline variables (i.e., comorbidities and pharmacotherapies at hospital admission) showing significant association (p < 0.05) to mortality in a univariate analysis, revealed that, compared to patients living at 90 days from hospitalization, deceased patients had cancer histories (OR 1.75, CI 1.06-2.90, p = 0.029) or suffered from asthma (OR 2.25, CI 1.13-4.47, p = 0.021). In contrast, heart failure (HF), atrial fibrillation (AF), arteriopathy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and kidney failure (KF), which, in a univariate analysis, were found to be associated with the endpoint (p < 0.05), lost significance in a multivariate analysis. Therapy at admission with aldosterone antagonists also appeared to be associated with medium-term mortality (OR 2.49, CI 1.52-4.08, p < 0.001); whereas, vitamin D supplementation during hospitalization appeared to be beneficial. Although not conclusive, a search into the Eudravigilance database, combined with consulting a digital predictive platform (PLATO, polypharmacology platform prediction), suggested potential off-target activities, which might contribute to increasing the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Conclusions: This retrospective clinical study furnished evidences of the impact of OAT, comorbidities and other pharmacological treatments on COVID-19 clinical course.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13030535/s1 , Figure S1 : Analysis of Odds Ratios for subgroups encompassing laboratory parameters and pharmacological therapies at admission for investigating the association between oral anticoagulant therapy and mortality; Figure S2 : Analysis of Odds Ratios for subgroups encompassing clinical and respiratory parameters at admission for the association between oral anticoagulant therapy and mortality; Figure S3 : Output report from target fishing analysis of potassium canrenoate by PLATO-Polypharmacology pLATform prediction ( https://prometheus.farmacia.uniba.it/plato/ , accessed on 18 December 2024); Table S1 : Multivariate analysis of clinical variables (comorbidities, pharmacotherapies) of COVID-19 patients at hospital admission according to 90-day mortality endpoint; Table S2 : Laboratory data of blood count and serum proteins of patients at hospital admission according to 90-day mortality. Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Ageno, De Candia, Iacoviello, Di Castelnuovo, Protective Effect of Oral Anticoagulant Drugs in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Admitted for COVID-19: Results from the CORIST Study, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2021.05.006
Al-Aly, Topol, Solving the Puzzle of Long COVID, Science, doi:10.1126/science.adl0867
Bader, Manla, Atallah, Starling, Heart Failure and COVID-19, Heart Fail. Rev, doi:10.1007/s10741-020-10008-2
Baumann Kreuziger, Sholzberg, Cushman, Anticoagulation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2021014527
Beladiya, Kumar, Vasava, Parmar, Patel et al., Safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled and randomized clinical trials, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2507
Chen, Klein, Garibaldi, Li, Wu et al., Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, Immunity and Intervention, Ageing Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101205
Ciriaco, Gambacorta, Alberga, Nicolotti, Quantitative Polypharmacology Profiling Based on a Multifingerprint Similarity Predictive Approach, J. Chem. Inf. Model, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00498
Ciriaco, Gambacorta, Trisciuzzi, Nicolotti, PLATO: A Predictive Drug Discovery Web Platform for Efficient Target Fishing and Bioactivity Profiling of Small Molecules, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23095245
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and Its Implications for Thrombosis and Anticoagulation, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020006000
Conway, Mackman, Warren, Wolberg, Mosnier et al., Understanding COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathy, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00762-9
Covino, De Matteis, Della Polla, Burzo, Pascale et al., Does Chronic Oral Anticoagulation Reduce In-Hospital Mortality among COVID-19 Older Patients?, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-021-01924-w
De Maio, Rullo, De Candia, Purgatorio, Lopopolo et al., Evaluation of Novel Guanidino-Containing Isonipecotamide Inhibitors of Blood Coagulation Factors against SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14081730
Denas, Gennaro, Ferroni, Fedeli, Lorenzoni et al., Reduction in All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients on Chronic Oral Anticoagulation: A Population-Based Propensity Score Matched Study, Int. J. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.12.024
Deplanque, Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19: The endgame!, Therapie, doi:10.1016/j.therap.2023.06.003
Di Micco, Russo, Carannante, Imparato, Rodolfi et al., Clotting Factors in COVID-19: Epidemiological Association and Prognostic Values in Different Clinical Presentations in an Italian Cohort, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9051371
Dos Anjos, Simões, Assmann, Carvalho, Bagatini, Potential Therapeutic Role of Purinergic Receptors in Cardiovascular Disease Mediated by SARS-CoV-2, J. Immunol. Res
Duangrat, Parichatikanond, Chanmahasathien, Mangmool, Adenosine A3 Receptor: From Molecular Signaling to Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25115763
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and Comorbidities: Deleterious Impact on Infected Patients, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Fels, Acharya, Vahldieck, Graf, Käding et al., Mineralocorticoid Receptor-Antagonism Prevents COVID-19-Dependent Glycocalyx Damage, Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol, doi:10.1007/s00424-022-02726-3
Fumagalli, Trevisan, Signore, Pelagalli, Volpato et al., COVID-19 and Atrial Fibrillation in Older Patients: Does Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Provide a Survival Benefit?-An Insight from the GeroCOVID Registry, Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1055/a-1503-3875
Getachew, Tizabi, Vitamin D and COVID-19: Role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27075
Gotelli, Soldano, Hysa, Paolino, Campitiello et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19: Narrative Review after 3 Years of Pandemic, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14224907
Gupta, Extrapulmonary Manifestations of COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3
Hadid, Kafri, Al-Katib, Coagulation and Anticoagulation in COVID-19, Blood Rev, doi:10.1016/j.blre.2020.100761
Harrison, Forte, Buscher, Chess, Patel et al., The Association of Preinfection Daily Oral Anticoagulation Use and All-Cause in Hospital Mortality from Novel Coronavirus 2019 at 21 Days: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Crit. Care Explor, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000324
Heestermans, Poenou, Hamzeh-Cognasse, Cognasse, Bertoletti, Anticoagulants: A Short History, Their Mechanism of Action, Pharmacology, and Indications, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11203214
Hempel, Elez, Krüger, Raich, Shrimp et al., Synergistic Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry by Otamixaban and Covalent Protease Inhibitors: Pre-Clinical Assessment of Pharmacological and Molecular Properties, Chem. Sci, doi:10.1039/D1SC01494C
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Jacobson, Merighi, Varani, Borea, Baraldi et al., A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy, Med. Res. Rev, doi:10.1002/med.21456
Jolliffe, Holt, Greenig, Talaei, Perdek et al., Effect of a test-and-treat approach to vitamin D supplementation on risk of all cause acute respiratory tract infection and COVID-19: Phase 3 randomised controlled trial (CORONAVIT), BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071230
Jose, Manuel, COVID-19 Cytokine Storm: The Interplay between Inflammation and Coagulation, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2
Kabir, Uddin, Hossain, Abdulhakim, Alam et al., nCOVID-19 Pandemic: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Potential Investigational Therapeutics, Front. Cell Dev. Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00616
Kim, Miyazaki, Shah, Kozai, Kewcharoen, Association between Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Healthcare, doi:10.3390/healthcare10040645
Kumar, Zuo, Yalavarthi, Hunker, Knight et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1-Mediated Endothelial Injury and Pro-Inflammatory State Is Amplified by Dihydrotestosterone and Prevented by Mineralocorticoid Antagonism, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13112209
Magrini, Garlanda, COVID-19 Thromboinflammation: Adding Inflammatory Fibrin to the Puzzle, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2024.09.003
Mele, Mele, Imbrici, Samarelli, Purgatorio et al., Pleiotropic Effects of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Chronic Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: Machine Learning Analysis, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules29112651
Müller-Wieland, Marx, Dreher, Fritzen, Schnell, COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Comorbidities, Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes, doi:10.1055/a-1269-1405
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Khoury, Amar et al., Effectiveness of Paxlovid in Reducing Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Mortality in High-Risk Patients, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac443
Russo, Cardillo, Viggiano, Mangiacapra, Cavalli et al., Fondaparinux Use in Patients with COVID-19: A Preliminary Multicenter Real-World Experience, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol, doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000000893
Russo, Chronic Oral Anticoagulation and Clinical Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther, doi:10.1007/s10557-021-07194-y
Russo, Di Maio, Attena, Silverio, Scudiero et al., Clinical Impact of Pre-Admission Antithrombotic Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Observational Study, Pharmacol. Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104965
Ryu, Yan, Montano, Sozmen, Dixit et al., Fibrin Drives Thromboinflammation and Neuropathology in COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07873-4
Samarelli, Graziano, Gambacorta, Graps, Leonetti et al., Small Molecules for the Treatment of Long-COVID-Related Vascular Damage and Abnormal Blood Clotting: A Patent-Based Appraisal, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16030450
Schiavone, Gasperetti, Mancone, Curnis, Mascioli et al., Oral Anticoagulation and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19: An Italian Multicenter Experience, Int. J. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.001
Schwartz, Boulware, Lee, Hydroxychloroquine for COVID19: The curtains close on a comedy of errors, Lancet Reg. Health Am, doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100268
Scudiero, Silverio, Di Maio, Russo, Citro et al., Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence, Predictors and Clinical Outcome, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.11.017
Smilowitz, Kunichoff, Garshick, Shah, Pillinger et al., C-Reactive Protein and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1103
Spiegelenberg, Prior Use of Therapeutic Anticoagulation Does Not Protect against COVID-19 Related Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients: A Propensity Score-matched Cohort Study, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.14877
Spyropoulos, Good Practice Statements for Antithrombotic Therapy in the Management of COVID-19: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.15809
Tang, Li, Wang, Sun, Abnormal Coagulation Parameters Are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14768
Thachil, Tang, Gando, Falanga, Cattaneo et al., ISTH Interim Guidance on Recognition and Management of Coagulopathy in COVID-19, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14810
Tremblay, Van Gerwen, Alsen, Thibaud, Kessler et al., Impact of Anticoagulation Prior to COVID-19 Infection: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020006941
Valdés, Moreno, Rello, Orduña, Bernardo et al., Metabolomics Study of COVID-19 Patients in Four Different Clinical Stages, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-05667-0
Vicenzi, Ruscica, Iodice, Rota, Ratti et al., The Efficacy of the Mineralcorticoid Receptor Antagonist Canrenone in COVID-19 Patients, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9092943
Vincenzi, Pasquini, Contri, Cappello, Nigro et al., Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: Recent Advancements, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom13091387
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Wong, Tomlinson, Brown, Elson, Walker et al., Association between Oral Anticoagulants and COVID 19-Related Outcomes: A population-based cohort study, Br. J. Gen. Pract, doi:10.3399/BJGP.2021.0689
Zarei, Vaighan, Ziai, Purinergic Receptor Ligands: The Cytokine Storm Attenuators, Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of COVID-19, Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol, doi:10.1080/08923973.2021.1988102
Zhou, Guo, He, Zuo, Liu et al., COVID-19 Is Distinct from SARS-CoV-2-Negative Community-Acquired Pneumonia, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00322
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines13030535",
"ISSN": [
"2227-9059"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030535",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background/Objectives: People affected by COVID-19 are exposed to abnormal clotting and endothelial dysfunction, which may trigger thromboembolic events. This study aimed at retrospectively investigating whether oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT), encompassing either direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), mainly apixaban, or the vitamin K antagonist (VKA) warfarin, could have impacted medium-term mortality in a cohort of SARS-CoV-2 patients. Methods: Among 1238 COVID-19 patients, hospitalized from 17 March 2020 to 15 June 2021, 247 survivors and 247 deceased within 90 days from hospitalization were matched 1:1 based on age, sex, and intensive care unit (ICU) admission within three days. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate associations by means of odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: A univariate regression analysis suggested that OAT, no differently from subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) during hospitalization, has no significant impact (p value > 0.05) on medium-term mortality. A multivariate analysis, limited to baseline variables (i.e., comorbidities and pharmacotherapies at hospital admission) showing significant association (p < 0.05) to mortality in a univariate analysis, revealed that, compared to patients living at 90 days from hospitalization, deceased patients had cancer histories (OR 1.75, CI 1.06–2.90, p = 0.029) or suffered from asthma (OR 2.25, CI 1.13–4.47, p = 0.021). In contrast, heart failure (HF), atrial fibrillation (AF), arteriopathy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and kidney failure (KF), which, in a univariate analysis, were found to be associated with the endpoint (p < 0.05), lost significance in a multivariate analysis. Therapy at admission with aldosterone antagonists also appeared to be associated with medium-term mortality (OR 2.49, CI 1.52–4.08, p < 0.001); whereas, vitamin D supplementation during hospitalization appeared to be beneficial. Although not conclusive, a search into the Eudravigilance database, combined with consulting a digital predictive platform (PLATO, polypharmacology platform prediction), suggested potential off-target activities, which might contribute to increasing the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Conclusions: This retrospective clinical study furnished evidences of the impact of OAT, comorbidities and other pharmacological treatments on COVID-19 clinical course.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biomedicines13030535"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0007-9250-5610",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dinoi",
"given": "Giorgia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Togo",
"given": "Maria Vittoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, F. Miulli General Hospital, 70021 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Guida",
"given": "Pietro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Deruvo",
"given": "Caterina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6753-3528",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Samarelli",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9140-5350",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Imbrici",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6533-5539",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nicolotti",
"given": "Orazio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5652-7341",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Luca",
"given": "Annamaria De",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0506-8031",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, F. Miulli General Hospital, 70021 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mastroianni",
"given": "Franco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4103-7577",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liantonio",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5016-5805",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy—Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Bari Aldo Moro, 70125 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Altomare",
"given": "Cosimo Damiano",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedicines",
"container-title-short": "Biomedicines",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-20T16:03:37Z",
"timestamp": 1740067417000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-20T17:17:11Z",
"timestamp": 1740071831000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T05:28:54Z",
"timestamp": 1740115734403,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740009600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/13/3/535/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "535",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00322",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Zhou, Y., Guo, S., He, Y., Zuo, Q., Liu, D., Xiao, M., Fan, J., and Li, X. (2020). COVID-19 Is Distinct from SARS-CoV-2-Negative Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2507",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled and randomized clinical trials",
"author": "Beladiya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2507",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in Reducing Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Mortality in High-Risk Patients",
"author": "Gronich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00616",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Kabir, M.T., Uddin, M.S., Hossain, M.F., Abdulhakim, J.A., Alam, M.A., Ashraf, G.M., Bungau, S.G., Bin-Jumah, M.N., Abdel-Daim, M.M., and Aleya, L. (2020). nCOVID-19 Pandemic: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Potential Investigational Therapeutics. Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary Manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D1SC01494C",
"article-title": "Synergistic Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry by Otamixaban and Covalent Protease Inhibitors: Pre-Clinical Assessment of Pharmacological and Molecular Properties",
"author": "Hempel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12600",
"journal-title": "Chem. Sci.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14081730",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "De Maio, F., Rullo, M., de Candia, M., Purgatorio, R., Lopopolo, G., Santarelli, G., Palmieri, V., Papi, M., Elia, G., and De Candia, E. (2022). Evaluation of Novel Guanidino-Containing Isonipecotamide Inhibitors of Blood Coagulation Factors against SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection. Viruses, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16030450",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Samarelli, F., Graziano, G., Gambacorta, N., Graps, E.A., Leonetti, F., Nicolotti, O., and Altomare, C.D. (2024). Small Molecules for the Treatment of Long-COVID-Related Vascular Damage and Abnormal Blood Clotting: A Patent-Based Appraisal. Viruses, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10557-021-07194-y",
"article-title": "Chronic Oral Anticoagulation and Clinical Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "705",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.adl0867",
"article-title": "Solving the Puzzle of Long COVID",
"author": "Topol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "830",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00762-9",
"article-title": "Understanding COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathy",
"author": "Conway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11203214",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Heestermans, M., Poenou, G., Hamzeh-Cognasse, H., Cognasse, F., and Bertoletti, L. (2022). Anticoagulants: A Short History, Their Mechanism of Action, Pharmacology, and Indications. Cells, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules29112651",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Mele, M., Mele, A., Imbrici, P., Samarelli, F., Purgatorio, R., Dinoi, G., Correale, M., Nicolotti, O., Luca, A.D., and Brunetti, N.D. (2024). Pleiotropic Effects of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Chronic Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation: Machine Learning Analysis. Molecules, 29."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15809",
"article-title": "Good Practice Statements for Antithrombotic Therapy in the Management of COVID-19: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH",
"author": "Spyropoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2226",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2021014527",
"article-title": "Anticoagulation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Sholzberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "809",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.14877",
"article-title": "Prior Use of Therapeutic Anticoagulation Does Not Protect against COVID-19 Related Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients: A Propensity Score-matched Cohort Study",
"author": "Spiegelenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4842",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-021-01924-w",
"article-title": "Does Chronic Oral Anticoagulation Reduce In-Hospital Mortality among COVID-19 Older Patients?",
"author": "Covino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2335",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000324",
"article-title": "The Association of Preinfection Daily Oral Anticoagulation Use and All-Cause in Hospital Mortality from Novel Coronavirus 2019 at 21 Days: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0324",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Explor.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.12.024",
"article-title": "Reduction in All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients on Chronic Oral Anticoagulation: A Population-Based Propensity Score Matched Study",
"author": "Denas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1503-3875",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Atrial Fibrillation in Older Patients: Does Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Provide a Survival Benefit?—An Insight from the GeroCOVID Registry",
"author": "Fumagalli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2021.05.006",
"article-title": "Protective Effect of Oral Anticoagulant Drugs in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Admitted for COVID-19: Results from the CORIST Study",
"author": "Ageno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3399/BJGP.2021.0689",
"article-title": "Association between Oral Anticoagulants and COVID 19-Related Outcomes: A population-based cohort study",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e456",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Gen. Pract.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "(2025, February 07). Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/."
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine for COVID19: The curtains close on a comedy of errors",
"author": "Schwartz",
"first-page": "100268",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg. Health Am.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.therap.2023.06.003",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19: The endgame!",
"author": "Deplanque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Therapie",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1269-1405",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Comorbidities",
"author": "Marx",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "178",
"journal-title": "Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Comorbidities: Deleterious Impact on Infected Patients",
"author": "Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1833",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2020.101205",
"article-title": "Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, Immunity and Intervention",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101205",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10741-020-10008-2",
"article-title": "Heart Failure and COVID-19",
"author": "Bader",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Heart Fail. Rev.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1103",
"article-title": "C-Reactive Protein and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Smilowitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2270",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9051371",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Di Micco, P., Russo, V., Carannante, N., Imparato, M., Rodolfi, S., Cardillo, G., and Lodigiani, C. (2020). Clotting Factors in COVID-19: Epidemiological Association and Prognostic Values in Different Clinical Presentations in an Italian Cohort. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Cytokine Storm: The Interplay between Inflammation and Coagulation",
"author": "Jose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e46",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14768",
"article-title": "Abnormal Coagulation Parameters Are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "844",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14810",
"article-title": "ISTH Interim Guidance on Recognition and Management of Coagulopathy in COVID-19",
"author": "Thachil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1023",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/FJC.0000000000000893",
"article-title": "Fondaparinux Use in Patients with COVID-19: A Preliminary Multicenter Real-World Experience",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.001",
"article-title": "Oral Anticoagulation and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19: An Italian Multicenter Experience",
"author": "Schiavone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006941",
"article-title": "Impact of Anticoagulation Prior to COVID-19 Infection: A Propensity Score–Matched Cohort Study",
"author": "Tremblay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "144",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104965",
"article-title": "Clinical Impact of Pre-Admission Antithrombotic Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Observational Study",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104965",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006000",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Its Implications for Thrombosis and Anticoagulation",
"author": "Connors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2033",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.blre.2020.100761",
"article-title": "Coagulation and Anticoagulation in COVID-19",
"author": "Hadid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100761",
"journal-title": "Blood Rev.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.11.017",
"article-title": "Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence, Predictors and Clinical Outcome",
"author": "Scudiero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2024.09.003",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Thromboinflammation: Adding Inflammatory Fibrin to the Puzzle",
"author": "Magrini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "721",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-024-07873-4",
"article-title": "Fibrin Drives Thromboinflammation and Neuropathology in COVID-19",
"author": "Ryu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "633",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-45837/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Vicenzi, M., Ruscica, M., Iodice, S., Rota, I., Ratti, A., Cosola, R.D., Corsini, A., Bollati, V., Aliberti, S., and Blasi, F. (2020). The Efficacy of the Mineralcorticoid Receptor Antagonist Canrenone in COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13112209",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_48",
"unstructured": "Kumar, N., Zuo, Y., Yalavarthi, S., Hunker, K.L., Knight, J.S., Kanthi, Y., Obi, A.T., and Ganesh, S.K. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1-Mediated Endothelial Injury and Pro-Inflammatory State Is Amplified by Dihydrotestosterone and Prevented by Mineralocorticoid Antagonism. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00424-022-02726-3",
"article-title": "Mineralocorticoid Receptor-Antagonism Prevents COVID-19-Dependent Glycocalyx Damage",
"author": "Fels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1069",
"journal-title": "Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "474",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/healthcare10040645",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Kim, J., Miyazaki, K., Shah, P., Kozai, L., and Kewcharoen, J. (2022). Association between Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23095245",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_51",
"unstructured": "Ciriaco, F., Gambacorta, N., Trisciuzzi, D., and Nicolotti, O. (2022). PLATO: A Predictive Drug Discovery Web Platform for Efficient Target Fishing and Bioactivity Profiling of Small Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00498",
"article-title": "Quantitative Polypharmacology Profiling Based on a Multifingerprint Similarity Predictive Approach",
"author": "Ciriaco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4868",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21456",
"article-title": "A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy",
"author": "Jacobson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1031",
"journal-title": "Med. Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.1030895",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Vincenzi, F., Pasquini, S., Contri, C., Cappello, M., Nigro, M., Travagli, A., Merighi, S., Gessi, S., Borea, P.A., and Varani, K. (2023). Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: Recent Advancements. Biomolecules, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25115763",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Duangrat, R., Parichatikanond, W., Chanmahasathien, W., and Mangmool, S. (2024). Adenosine A3 Receptor: From Molecular Signaling to Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25."
},
{
"article-title": "Potential Therapeutic Role of Purinergic Receptors in Cardiovascular Disease Mediated by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Assmann",
"first-page": "8632048",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Res.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-05667-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Valdés, A., Moreno, L.O., Rello, S.R., Orduña, A., Bernardo, D., and Cifuentes, A. (2022). Metabolomics Study of COVID-19 Patients in Four Different Clinical Stages. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08923973.2021.1988102",
"article-title": "Purinergic Receptor Ligands: The Cytokine Storm Attenuators, Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Zarei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "633",
"journal-title": "Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_59",
"unstructured": "(2024, December 01). Piclidenoson for Treatment of COVID-19—A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04333472."
},
{
"key": "ref_60",
"unstructured": "(2024, December 01). The European Database of Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents. Available online: https://dap.ema.europa.eu/analytics/saw.dll?PortalPages."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14224907",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_61",
"unstructured": "Gotelli, E., Soldano, S., Hysa, E., Paolino, S., Campitiello, R., Pizzorni, C., Sulli, A., Smith, V., and Cutolo, M. (2022). Vitamin D and COVID-19: Narrative Review after 3 Years of Pandemic. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27075",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19: Role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity",
"author": "Getachew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5285",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2022-071230",
"article-title": "Effect of a test-and-treat approach to vitamin D supplementation on risk of all cause acute respiratory tract infection and COVID-19: Phase 3 randomised controlled trial (CORONAVIT)",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e071230",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 63,
"references-count": 63,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/13/3/535"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Retrospective Clinical Investigation into the Association Between Abnormal Blood Clotting, Oral Anticoagulant Therapy, and Medium-Term Mortality in a Cohort of COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}
dinoi