Is vitamin D level important in pregnant women with COVID-19?
et al., Journal of Controversies in Obstetrics & Gynecology and Pediatrics, doi:10.51271/JCOGP-0035, Jul 2024
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
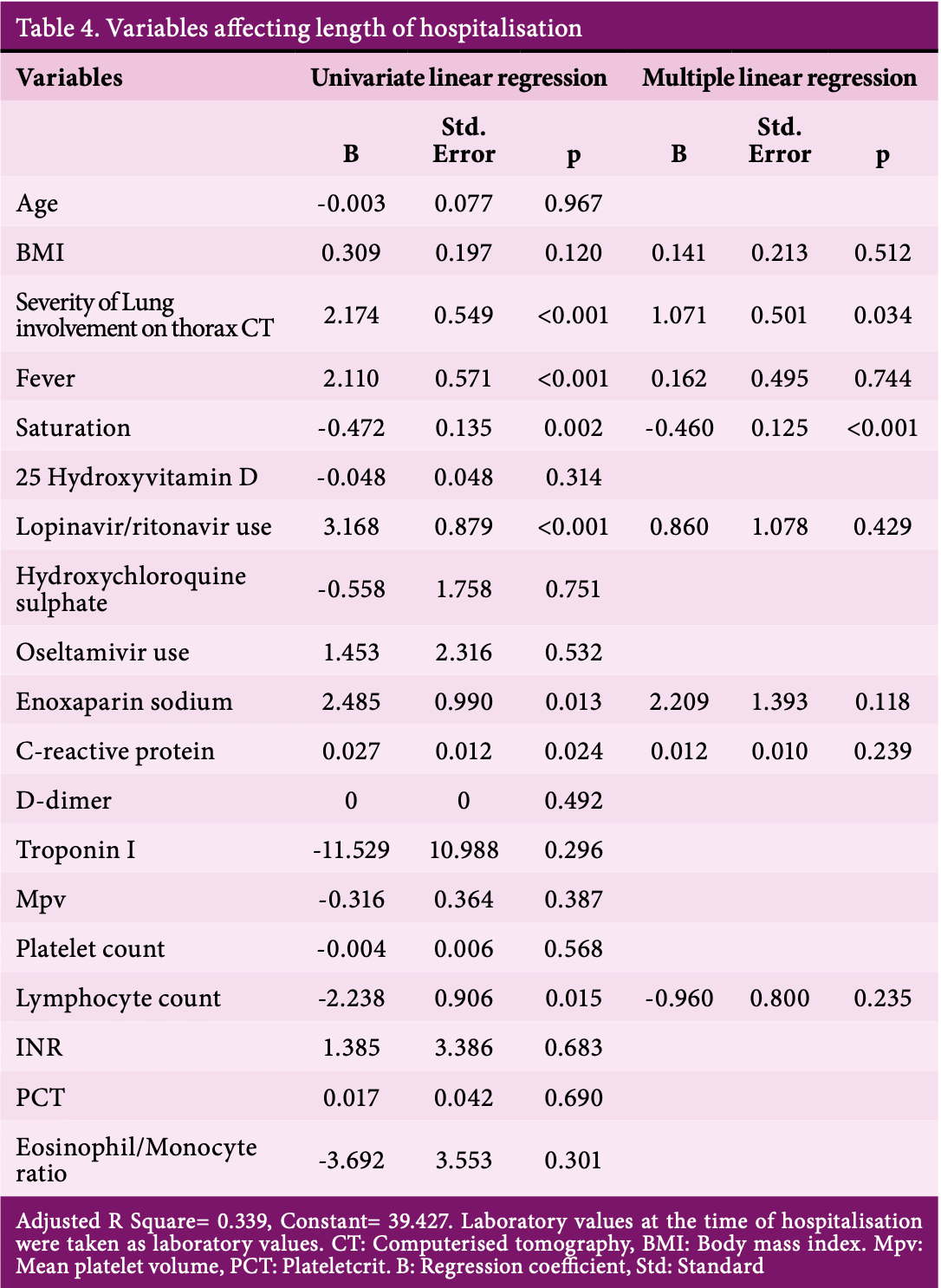
Retrospective 125 pregnant women hospitalized with COVID-19 in Turkey, showing no significant difference in hospitalization length with HCQ, and longer hospitalization with lopinavir/ritonavir use.
Study covers HCQ, lopinavir/ritonavir, and vitamin D.
|
risk of hospitalization, 42.8% lower, OR 0.57, p = 0.76, treatment 10, control 115, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Değirmenci et al., 30 Jul 2024, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, mean age 29.3, 7 authors, study period March 2020 - January 2021.
Contact: mulayimsizer@hotmail.com.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.51271/jcogp-0035",
"ISSN": [
"2980-0579"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.51271/JCOGP-0035",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Aims: The Covid-19 pandemic started in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China in late December 2019. In our study, we aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of vitamin D levels on the clinic of the disease, laboratory findings, severity of the disease and, length of hospital stay by grouping pregnant patients with a diagnosis of Covid-19 according to their vitamin D levels.\nMethods: A total of 125 patients were included. According to the vitamin D levels of the patients at the time of hospitalization, two groups were determined as below and above 20ng/ml, which is the limit of vitamin D deficiency. The patients in these two groups were compared in terms of demographic features, clinical findings, laboratory findings, imaging findings, hospitalization times and need for intensive care.\nResults: When evaluated according to serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D level, patients’ fever, pulse, oxygen saturation, the severity of lung involvement in computed tomography, hospitalization there was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of duration and need for intensive care. When the laboratory parameters of the patients at hospitalization were compared according to serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D levels, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of any laboratory parameter. As a result of the analysis, only lymphocyte count was determined as the independent variable affecting the severity of lung involvement in thorax CT (Computed tomography). As the lymphocyte count decreased, the severity of involvement in thorax CT increased.\nConclusion: Our study showed that vitamin D level did not have a significant relationship with any of the parameters related to Covid-19 such as clinical and laboratory findings, severity of the disease and duration of hospitalisation. It is also supported by our study that the decrease in lymphocyte counts is associated with severe Covid-19 disease.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4685-3335",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Değirmenci",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9306-6281",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ayçiçek",
"given": "Sertaç",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9142-6127",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fındık",
"given": "Fatih Mehmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4864-7287",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sizer",
"given": "Mulaim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0006-1602-4009",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Değirmenci",
"given": "Azize Pervin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0108-2856",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Değirmenci Ayçiçek",
"given": "Pelin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1836-6281",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mermutluoğlu",
"given": "Çiğdem",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Controversies in Obstetrics & Gynecology and Pediatrics",
"container-title-short": "JCOGP",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-08T06:06:54Z",
"timestamp": 1723097214000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-08T06:06:57Z",
"timestamp": 1723097217000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-09T00:10:17Z",
"timestamp": 1723162217242
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
30
]
]
}
},
"member": "28304",
"original-title": [],
"page": "51-57",
"prefix": "10.51271",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "MediHealth Academy",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journal-jcogp.com/Publication/DisplayArticle/27358"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Is vitamin D level important in pregnant women with COVID-19?",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2"
}
