Comparative Efficacy of Combination Treatment with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Remdesivir Versus Remdesivir Monotherapy in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients: A Target Trial Emulation Study
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.4683854, Jan 2024
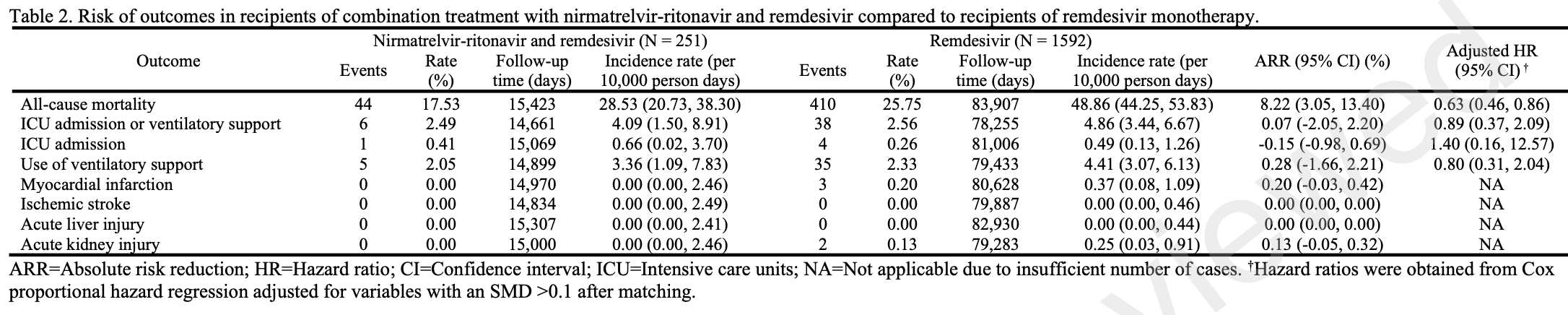
Retrospective 1,843 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Hong Kong showing lower mortality with paxlovid. All patients received remdesivir. No significant difference was found for ICU admission or ventilatory support.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
|
risk of death, 37.0% lower, HR 0.63, p = 0.004, treatment 251, control 1,592, day 90.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 40.0% higher, HR 1.40, p = 0.78, treatment 251, control 1,592, day 90.
|
|
ventilatory support, 20.0% lower, HR 0.80, p = 0.66, treatment 251, control 1,592, day 90.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Choi et al., 8 Jan 2024, retrospective, China, preprint, 7 authors, study period 31 December, 2021 - 29 January, 2023.
Contact: ivanhung@hku.hk.
Comparative Efficacy of Combination Treatment with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Remdesivir versus Remdesivir Monotherapy in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients: A Target Trial Emulation Study
Background Remdesivir (Veklury®) and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid®) are the two commonly used antiviral agents for hospitalised patients suffering from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Hong Kong. Although current therapeutic studies demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of remdesivir in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients by shortening the time to clinical recovery and hospital stay, there is a significant proportion of high-risk individuals in Hong Kong who fail to achieve optimal clinical response after a course of standard antiviral monotherapy regimen. Preclinical data has shown the in vitro synergy between remdesivir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, which can potentially hasten the virologic and clinical recovery in hospitalised patients with COVID-19.
Methods We conducted a target trial emulation study to critically analyse the current evidence of a combination of remdesivir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus remdesivir alone in the management of COVID-19 in Hong Kong and dissect the aspects of their safety and efficacy. This study utilised the territory-wide electronic health records databases. Patients aged ≥ 18 years with an initial diagnosis of COVID-19 who received either combination treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and remdesivir or remdesivir between 16 March 2022 and 31 December
Supplementary Table 1 . Target trial specification and emulation using observational data Protocol component Specification Emulation using observational data
Eligible criteria Age ≥ 18, hospitalized with COVID-19 during the inclusion period 1 Exclude patients who: had a history of COVID-19 infection before baseline; had contraindications to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or remdesivir 2 The index date was the prescription date of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or remdesivir. Same as for specification. The date of COVID-19 infection was determined based on the date of the first positive polymerase chain reaction or rapid antigen test result during the study inclusion period. Individuals who initiated nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or remdesivir more than 5 days after the date of COVID-19 infection were excluded from the analysis. Treatment strategy Combination treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and remdesivir versus Remdesivir monotherapy Patients were expected to complete one full course of combination treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and remdesivir or remdesivir monotherapy according to the regimen approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, unless clinical conditions prevented them from completing the treatment (e.g. oral intake no longer possible, severe adverse effects). Patients are allowed to receive additional concurrent treatments, such as steroids, based on clinical judgment in both treatment groups. Same as for specification. It was assumed that upon the..
References
Adams Hp, Bendixen, Kappelle, Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment, Stroke
Baldi, Dentone, Mikulska, Fenoglio, Mirabella et al., Case report: Sotrovimab, remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir combination as salvage treatment option in two immunocompromised patients hospitalised for COVID-19, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.1062450
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Baden, Cheng et al., Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac724
Chan, Lui, Wong, Yip, Li et al., Safety Profile and Clinical and Virological Outcomes of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment in Patients With Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad371
Cheung, Leung, Seto, Application of Big Data analysis in gastrointestinal research, World J Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i24.2990
Dai, Liu, Liu, Zhou, Li et al., Patients with Cancer Appear More Vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: A Multicenter Study during the COVID-19 Outbreak, Cancer Discov, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422
Ford, Simmons, Karmarkar, Yoke, Braimah et al., Successful Treatment of Prolonged, Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Lower Respiratory Tract Disease in a B cell Acute Lymphoblastic 21, Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab989
Gidari, Sabbatini, Schiaroli, Bastianelli, Pierucci et al., Synergistic Activity of Remdesivir-Nirmatrelvir Combination on a SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro Model and a Case Report, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15071577
Grundeis, Ansems, Dahms, Thieme, Metzendorf et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00519-0
Haidar, Agha, Bilderback, Lukanski, Linstrum et al., Prospective Evaluation of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Vaccine Responses Across a Broad Spectrum of Immunocompromising Conditions: the COVID-19 Vaccination in the Immunocompromised Study (COVICS), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac103
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Wisemandle et al., Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalised Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hernán, Logan, Observational studies analyzed like randomized experiments: an application to postmenopausal hormone therapy and coronary heart disease, Epidemiology
Hernán, Methods of public health research-strengthening causal inference from observational data, New England Journal of Medicine
Hernán, Robins, Using big data to emulate a target trial when a randomized trial is not available, American journal of epidemiology
Lai, Huang, Chui, Multimorbidity and adverse events of special interest associated with Covid-19 vaccines in Hong Kong, Nature Communications
Lai, Huang, Peng, Post-Covid-19-vaccination adverse events and healthcare utilisation among individuals with or without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13453
Lai, Li, Peng, Carditis After COVID-19 Vaccination With a Messenger RNA Vaccine and an Inactivated Virus Vaccine: A Case-Control Study, Annals of Internal Medicine
Lamontagne, Agarwal, Rochwerg, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Li, Tong, Wong, Lack of inflammatory bowel disease flare-up following two-dose BNT162b2 vaccine: a population-based cohort study, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326860
Li, Tong, Yeung, Two-dose COVID-19 vaccination and possible arthritis flare among patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Hong Kong, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221571
Liu, Pan, Zhang, Li, Ma et al., Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Boyle, Gibbons et al., Recommendations for the Management of Drug-Drug Interactions Between the COVID-19 Antiviral Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) and Comedications, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.2646
Ning, Liu, Li, Liu, Wang et al., Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection in a renal transplant recipient: Case report, Am J Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.15897
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, Aschenbrenner, Avery et al., An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Schultz, Johnson, Ayyanathan, Miller, Whig et al., Pyrimidine inhibitors synergise with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x
Stravitz, Lee, Acute liver failure, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31894-X
Thygesen, Alpert, Jaffe, Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018), J Am Coll Cardiol
Vanderweele, Ding, Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-value, Annals of internal medicine
Wan, Chui, Wang, Herpes zoster related hospitalisation after inactivated (CoronaVac) and mRNA (BNT162b2) SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: A self-controlled case series and nested case-control study, The Lancet Regional Health -Western Pacific, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100393
Wang, Sacramento, Jockusch, Chaves, Tao et al., Combination of antiviral drugs inhibits SARS-CoV-2 polymerase and exonuclease and demonstrates COVID-19 therapeutic potential in viral cell culture, Commun Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03101-9
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Xiong, Wong, Au, Safety of Inactivated and mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination Among Patients Treated for Hypothyroidism: A Population-Based Cohort Study, Thyroid, doi:10.1089/thy.2021.0684
Yang, Xie, Xue, Yang, Ma et al., Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030324
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.4683854",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4683854",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Ming Hong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Eric Yuk Fai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Ian Chi Kei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Esther W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tam",
"given": "Anthony Raymond",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chu",
"given": "Wing-Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hung",
"given": "Ivan Fan Ngai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-08T19:37:06Z",
"timestamp": 1704742626000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-08T19:37:06Z",
"timestamp": 1704742626000
},
"group-title": "SSRN",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T00:24:20Z",
"timestamp": 1704759860658
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.2139",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=4683854"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Comparative Efficacy of Combination Treatment with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Remdesivir Versus Remdesivir Monotherapy in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients: A Target Trial Emulation Study",
"type": "posted-content"
}