Safety Monitoring of Oral Antiviral COVID-19 Treatment Using Korea Adverse Event Reporting System (KAERS) Database
et al., Pharmacoepidemiology and Risk Management, doi:10.56142/perm.24.0006, Mar 2024
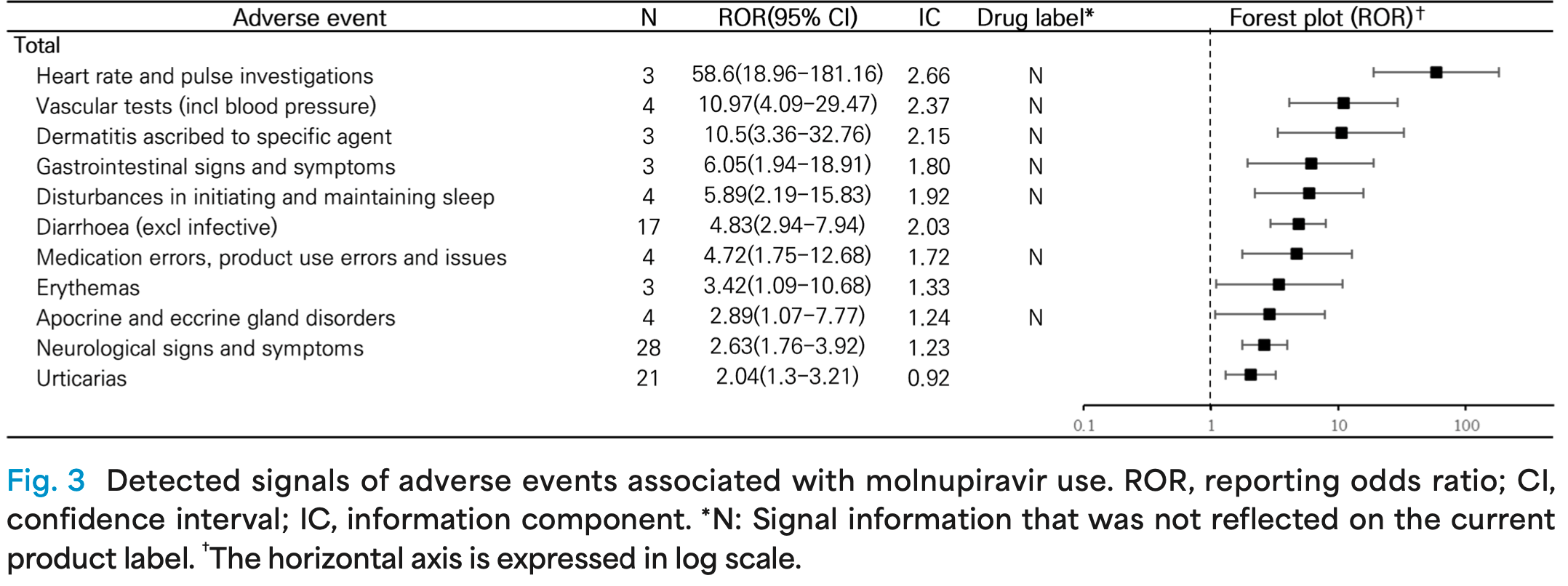
Safety analysis of paxlovid and molnupiravir. Disproportionality analysis found significant signals for paxlovid with sensory abnormalities, interactions, fecal abnormalities, and signals not on the label including olfactory nerve disorders, appetite disorders, hallucinations and urinary adverse events. For molnupiravir, significant signals were found for cardiovascular adverse events not on the label like heart rate and vascular tests.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Study covers paxlovid and molnupiravir.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Choe et al., 31 Mar 2024, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Safety Monitoring of Oral Antiviral COVID-19 Treatment Using Korea Adverse Event Reporting System (KAERS) Database
doi:10.56142/perm.24.0006
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the association between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, molnupiravir and adverse events and identify safety signals not previously known. Methods: To identify major adverse events and safety signals associated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir, we conducted pharmacovigilance study using drug-related adverse events reported to KIDS KAERS DB (2305A0011). Disproportionality analysis were performed using reporting odds ratio (ROR) and information component (IC) method to detected new safety signals not listed in drug label. Results: Adverse events related to nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir were frequently reported in women and person aged ≥ 65, and mostly reported as not serious. Following nirmatrelvir/ritonavir administration, 'sensory abnormalities' (20.18%), 'diarrhoea' (13.76%), and 'nausea and vomiting symptoms' (9.87%) were most commonly reported, while for molnupiravir, 'nausea and vomiting symptoms' (15.92%), 'neurological signs and symptoms' (15.92%), 'urticarias' (10.45%) were predominantly reported. Disproportionality analysis revealed a significant association of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir with 'sensory abnormalities' (ROR [95% CI] = 223.74 [207.24-241.55]), 'interactions' (ROR [95% CI] = 37. 35 [15.10-92.35]), 'faecal abnormalities' (ROR [95% CI] = 32. 33 [18.68-56.36]). Adverse events not listed on drug label included 'olfactory nerve disorders', 'appitite disorder', 'hallucinations' and urinary adverse events. For molnupiravir, strong association were observed with cardiovascular adverse events such as 'heart rate and pulse investigations' (ROR [95% CI] = 58. 60 [18.96-181.16]) and 'vascular tests' (ROR [95% CI] = 10.97 [4.09-29.47]), which were not included in drug label. Conclusion: Adverse events following the use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir were generally not serious, but some safety signals not listed on drug label were newly detected and warranted attention. We expected this study to provide basic data of safety for oral antivirals of COVID-19 and may contribute to the development of future drug safety guidelines. (PeRM 2024;16:65-78)
References
Agarwal, Hunt, Stegemann, A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Butler, Hobbs, Gbinigie, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an openlabel, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet
Bálint, Vörös-Horváth, Széchenyi, Omicron: increased transmissibility and decreased pathogenicity, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Carabelli, Peacock, Thorne, SARS-COV-2 variant biology: immune escape, transmission and fitness, Nat Rev Microbiol
Cvancara, Baertsch, Lehmann, Postmarketing reporting of Paxlovid-related dysgeusia: a real-world pharmacovigilance study, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Gerhart, Cox, Singh, A comprehensive review of the clinical pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and drug interactions of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, Clin Pharmacokinet
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kim, Yoo, Bae, Effectiveness of Paxlovid, an oral antiviral drug, against the Omicron BA.5 variant in Korea: severe progression and death between July and November 2022, J Korean Med Sci
Li, Zhang, Liu, Adverse events associated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: A pharmacovigilance analysis based on FAERS, Pharmaceuticals
Liang, Ma, Wang, Adverse events associated with molnupiravir: a real-world disproportionality analysis in food and drug administration adverse event reporting system, Front Pharmacol
Long, Carius, Chavez, Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency clinician: presentation and evaluation, Am J Emerg Med
Mazzitelli, Mengato, Sasset, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: tolerability, safety, and adherence in a retrospective cohort study, Viruses
Moore, Berdaï, Blin, Pharmacovigilance -The next chapter, Therapie
Oran, Topol, The proportion of SARS-COV-2 infections that are asymptomatic: A systematic review, Ann Intern Med
Pannu, Udongwo, Imburgio, Adverse events of SARS-CoV-2 therapy: A pharmacovigilance study of the FAERS database, Ann Pharmacother
Park, Kim, Kim, Effectiveness and adverse events of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir versus molnupiravir for COVID-19 in outpatient setting: multicenter prospective observational study, J Korean Med Sci
Park, Yoo, Kim, Effectiveness of molnupiravir treatment in patients with COVID-19 in Korea: A propensity score matched study, Infect Chemother
Santi Laurini, Montanaro, Motola, Safety profile of molnupiravir in the treatment of COVID-19: a descriptive study based on FAERS data, J Clin Med
Singh, Toussi, Hackman, Innovative randomized phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Van Puijenbroek, Bate, Leufkens, A comparison of measures of disproportionality for signal detection in spontaneous reporting systems for adverse drug reactions, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf
Vito, Colpani, Bitti, Safety and efficacy of molnupiravir in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients: A real-life experience, J Med Virol
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wong, Au, Lau, Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet
Xie, Choi, Al-Aly, Association of treatment with nirmatrelvir and the risk of post-COVID-19 condition, JAMA Intern Med
Zhuang, Xu, Wu, Post-marketing safety concerns with nirmatrelvir: A disproportionality analysis of spontaneous reports submitted to the FDA adverse event reporting system, Br J Clin Pharmacol
choe