A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients with common coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19)
et al., J. Zhejiang University (Med Sci), doi:10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.03, NCT04261517, Mar 2020
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
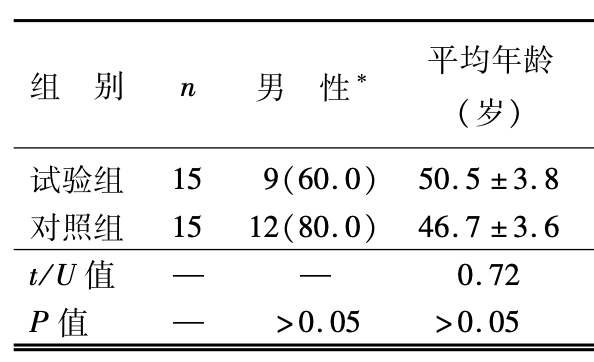
30 moderate hospitalized cases, all recovered. Time to RNA negative comparable. Less frequent radiological progression with HCQ but not statistically significant. One HCQ patient developed to a severe case. Treatment group 4 years older and with higher incidence of hypertension.
Viral load measured by PCR may not accurately reflect infectious virus measured by viral culture. Porter et al. show that viral load early in infection was correlated with infectious virus, but viral load late in infection could be high even with low or undetectable infectious virus. Assessing viral load later in infection may underestimate reductions in infectious virus with treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments2.
|
risk of radiological progression, 29.0% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.57, treatment 5 of 15 (33.3%), control 7 of 15 (46.7%), NNT 7.5.
|
|
risk of viral+ at day 7, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 15 (13.3%), control 1 of 15 (6.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Chen et al., 6 Mar 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period 6 February, 2020 - 25 February, 2020, trial NCT04261517 (history).
Abstract: 浙 江 大 学 学 报 ( 医 学 版 )
2020 年 4 月
April 2020
http:∥www. zjujournals. com / med
DOI:10. 3785 / j. issn. 1008 ̄9292. 2020. 03. 03
JOURNAL OF ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY ( MEDICAL SCIENCES)
原
著
硫酸羟氯喹治疗 2019 冠状病毒病( COVID ̄19)
普通型患者的初步研究
陈 军ꎬ刘丹萍ꎬ刘
张丹丹ꎬ钱志平ꎬ李
莉ꎬ刘 萍ꎬ徐庆年ꎬ夏
涛ꎬ沈银忠ꎬ卢洪洲
露ꎬ凌
云ꎬ黄
丹ꎬ宋树丽ꎬ
上海市公共卫生临床中心感染与免疫科ꎬ 上海 201508
[摘 要] 目的:初步评价硫酸羟氯喹治疗 2019 冠状病毒病( COVID ̄19) 普通型
患者的疗效和安全性ꎮ 方法:收集 2020 年 2 月 6 至 25 日在上海市公共卫生临床
中心住院治疗的 30 例 COVID ̄19 普通型患者ꎮ 患者 1∶ 1随机分配到试验组和对照
组ꎮ 对照组接受常规治疗ꎬ试验组在常规治疗的基础上口服硫酸羟氯喹(400 mgꎬ
1 次 / d) 治疗ꎬ疗程为 5 dꎮ 比较两组治疗第 7 天时咽拭子病毒核酸转阴率等指标ꎮ
研究获上海市公共卫生临床中心伦理委员会批准ꎬ并登记注册( NCT04261517) ꎮ
结果:在治疗过程中ꎬ试验组 1 例患者发展为重型ꎮ 入组后第 7 天ꎬ试验组中 13 例
(86. 7% ) 和对照组中 14 例(93. 3% ) 患者咽拭子病毒核酸检测为阴性( P > 0. 05) ꎮ
在2 周的访视期内ꎬ所有受试者的咽拭子核酸检测均转为阴性ꎬ其中试验组咽拭子
核酸转阴时间为入院后第 4 (1ꎬ9) 天ꎬ对照组为第 2 (1ꎬ4) 天ꎬ差异无统计学意义
(Z = 1. 27ꎬP > 0. 05) ꎮ 试验组在入院后第 1(0ꎬ2)天体温恢复正常ꎬ对照组在入院后
第1(0ꎬ3)天体温恢复正常ꎮ 影像学检查结果显示ꎬ试验组 5 例(33. 3% ) 和对照组 7
例(46. 7% ) 患者均在入院 3 d 后的复查中出现了进展ꎬ所有患者在随后的复查中
均提示病灶好转ꎮ 试验组和对照组分别有 4 例(26. 7% ) 和 3 例(20. 0% ) 患者出现
一过性的腹泻和肝功能异常等不良反应ꎬ两组不良反应发生率差异无统计学意义
( P > 0. 05) ꎮ 结论:目前 COVID ̄19 普通型患者预后较好ꎬ以病毒转阴率、重症化率
为主要终点的研究难以对药物的疗效进行判断ꎮ 开展后续的研究需要确定更合适
的人群和终点事件ꎬ并充分考虑样本量等试验的可行性问题ꎮ
[关键词] 2019 冠状病毒病ꎻ 严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒 2ꎻ 新型冠状病毒肺
炎ꎻ 羟氯喹ꎻ 治疗结果ꎻ 安全性ꎻ 随机对照试验
[ 中图分类号] R512. 99
[ 文献标志码] A
收稿日期:2020 ̄02 ̄29
接受日期:2020 ̄03 ̄03
在线优先出版日期:2020 ̄03 ̄06
基金项目: 上 海 市 科 学 技 术 委 员 会 应 急 科 技 攻 关 专 项 ( 20431900103 ) ꎻ 复 旦 大 学 一 流 大 学 和 一 流 学 科 建 设 项 目
( IDF162005) ꎻ浙江大学新型冠状病毒(2019 ̄nCoV) 肺炎应急科研专项(2020XGZX030) ꎻ上海市公共卫生临床中心新型
冠状病毒“2019 ̄nCoV” 科研攻关院内专项(2020YJKY01) ꎻ上海市重点专科传染病项目( shslczdzk01102) ꎻ上海市“ 医苑新
星” 医学人才项目(2019 ̄72)
第一作者:陈
军(1984—) ꎬ男ꎬ博士ꎬ副主任医师ꎬ主要从事感染性疾病的诊治和发病机制研究ꎻE ̄mail: qtchenjun@
163. comꎻ https: / / orcid. org / 0000 ̄0002 ̄3850 ̄4875
通信作者:卢洪洲( 1966—) ꎬ 男ꎬ 博 士ꎬ 教 授ꎬ 主 任 医 师ꎬ 博 士 生 导 师ꎬ 主 要 从 事 感 染 性 疾 病 的 诊 治 和 发 病 机 制 研 究ꎻ
E ̄mail: luhongzhou@ fudan. edu. cnꎻ https: / / orcid. org / 0000 ̄0002 ̄8308 ̄5534
浙江大学学报( 医学版) Journal of Zhejiang University ( Medical Sciences)
216
A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients
with moderate COVID ̄19
CHEN Junꎬ LIU Danpingꎬ LIU Liꎬ LIU Pingꎬ XU Qingnianꎬ XIA Luꎬ LING Yunꎬ
HUANG Danꎬ SONG Shuliꎬ ZHANG Dandanꎬ QIAN Zhipingꎬ LI Taoꎬ SHEN
Yinzhongꎬ LU Hongzhou ( Department of Infection and Immunityꎬ Shanghai Public
Health Clinical Centerꎬ Fudan Universityꎬ Shanghai 201508ꎬ China)
Corresponding author: LU Hongzhouꎬ E ̄mail: luhongzhou @ fudan. edu. cnꎬ https: / /
orcid. org / 0000 ̄0002 ̄8308 ̄5534
[ Abstract] Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine
( HCQ) in the treatment of patients with moderate coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID ̄
19) . Methods: We prospectively enrolled 30 treatment ̄naïve patients with confirmed
COVID ̄19 after informed consent at Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center. The
patients were randomized 1 ∶ 1 to HCQ group and the control group. Patients in HCQ
group were given HCQ 400 mg per day for 5 days plus conventional treatmentsꎬ while
those in the control group were given conventional treatment only. The primary endpoint
was negative conversion rate of SARS ̄CoV ̄2 nucleic acid in respiratory pharyngeal swab
on days 7 after randomization. This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of
Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center and registered online ( NCT04261517 ) .
Results: One patient in HCQ group developed to severe during the treatment. On day
7ꎬ nucleic acid of throat swabs was negative in 13 (86. 7% ) cases in the HCQ group
and 14 (93. 3% ) cases in the control group ( P > 0. 05) . The median duration..
