Antiviral Activity and Safety of Darunavir/Cobicistat for the Treatment of COVID-19
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa241, NCT04252274, Jun 2020
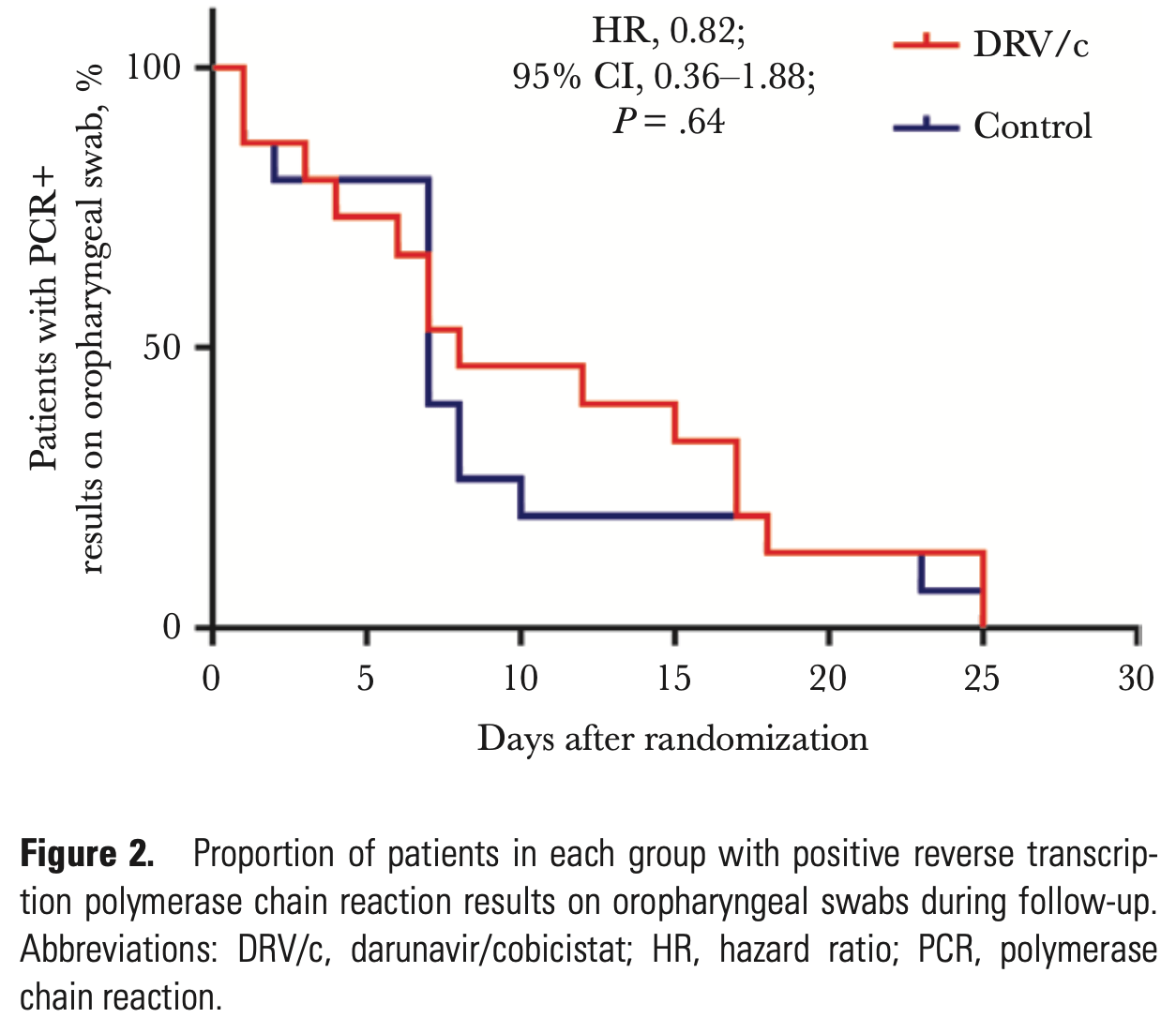
RCT 30 mild COVID-19 patients showing no benefit of darunavir/cobicistat compared to standard care for viral clearance.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of no viral clearance, 22.0% higher, HR 1.22, p = 0.64, treatment 15, control 15, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Chen et al., 21 Jun 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 47.2, 11 authors, study period 30 January, 2020 - 6 February, 2020, trial NCT04252274 (history).
Contact: luhongzhou@fudan.edu.cn.
Antiviral Activity and Safety of Darunavir/Cobicistat for the Treatment of COVID-19
Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa241
Background. We aimed to evaluate the antiviral activity and safety of darunavir/cobicistat (DRV/c) in treating COVID-19 patients. Methods. In this single-center, randomized, and open-label trial, mild patients with polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-confirmed COVID-19 were enrolled in Shanghai, China. Participants were randomized to receive DRV/c for 5 days on the top of interferon alpha 2b inhaling or interferon alpha 2b inhaling alone. The primary end point was the virological clearance rate of oropharyngeal swabs at day 7 after randomization in the intention-to-treat population (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04252274). Results. From January 30, 2020, to February 6, 2020, a total of 30 patients were enrolled, of whom 18 (60%) were male, aged 47.2 ± 2.8 years; 63.3% (19/30) of the participants had fever, and 46.7% (14/30) had cough at enrollment. The participants were randomized (range) at 4 (2-5) days after onset of symptoms. The proportion of negative PCR results at day 7 was 46.7% (7/15) and 60.0% (9/15) in the DRV/c and control groups (P = .72), respectively. The viral clearance rate at day 3 was 20% (3/15) in both study groups, while the number increased to 26.7% (4/15) in the DRV/c group and remained 20% (3/15) in the control group at day 5. Fourteen days after randomization, 1 participant in the DRV/c group progressed to critical illness and discontinued DRV/c, while all the patients in the control group were stable (P = 1.0). The frequencies of adverse events in the 2 groups were comparable. Conclusions. Five days of DRV/c did not increase the proportion of negative conversion vs standard of care alone, although it was well tolerated.
References
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Chan, Lai, Chu, Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with lopinavir/ritonavir: a multicentre retrospective matched cohort study, Hong Kong Med J
Chen, Qi, Liu, Clinical progression of patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China, J Infect
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kim, Won, Kee, Combination therapy with lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin and interferon-α for Middle East respiratory syndrome, Antivir Ther
Lu, Zhao, Li, Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Meyer, Bojkova, Cinati, Lack of antiviral activity of darunavir against SARS-CoV-2, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.03.20052548
Min, Cheon, Ha, Comparative and kinetic analysis of viral shedding and immunological responses in MERS patients representing a broad spectrum of disease severity, Sci Rep
Orkin, Dejesus, Khanlou, Final 192-week efficacy and safety of oncedaily darunavir/ritonavir compared with lopinavir/ritonavir in HIV-1-infected treatment-naïve patients in the ARTEMIS trial, HIV Med
Spanakis, Tsiodras, Haagmans, Virological and serological analysis of a recent Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection case on a triple combination antiviral regimen, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Wu, Liu, Yang, Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Wu, Zhao, Yu, A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature
Yao, Qian, Zhu, Wang, Wang, A systematic review of lopinavir therapy for SARS coronavirus and MERS coronavirus-a possible reference for coronavirus disease-19 treatment option, J Med Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa241",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaa241",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We aimed to evaluate the antiviral activity and safety of darunavir/cobicistat (DRV/c) in treating COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this single-center, randomized, and open-label trial, mild patients with polymerase chain reaction (PCR)–confirmed COVID-19 were enrolled in Shanghai, China. Participants were randomized to receive DRV/c for 5 days on the top of interferon alpha 2b inhaling or interferon alpha 2b inhaling alone. The primary end point was the virological clearance rate of oropharyngeal swabs at day 7 after randomization in the intention-to-treat population (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04252274).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>From January 30, 2020, to February 6, 2020, a total of 30 patients were enrolled, of whom 18 (60%) were male, aged 47.2 ± 2.8 years; 63.3% (19/30) of the participants had fever, and 46.7% (14/30) had cough at enrollment. The participants were randomized (range) at 4 (2–5) days after onset of symptoms. The proportion of negative PCR results at day 7 was 46.7% (7/15) and 60.0% (9/15) in the DRV/c and control groups (P = .72), respectively. The viral clearance rate at day 3 was 20% (3/15) in both study groups, while the number increased to 26.7% (4/15) in the DRV/c group and remained 20% (3/15) in the control group at day 5. Fourteen days after randomization, 1 participant in the DRV/c group progressed to critical illness and discontinued DRV/c, while all the patients in the control group were stable (P = 1.0). The frequencies of adverse events in the 2 groups were comparable.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Five days of DRV/c did not increase the proportion of negative conversion vs standard of care alone, although it was well tolerated.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3850-4875",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Tuberculosis, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Qingnian",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "Yun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hepatology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Tuberculosis, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiovascular Diseases, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Shuli",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Shuibao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Shen",
"given": "Yingzhong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, China"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Hongzhou",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-21T01:23:35Z",
"timestamp": 1592702615000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-10T18:14:33Z",
"timestamp": 1594404873000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2017ZX09304027"
],
"name": "Ministry of Science and Technology of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003399",
"award": [
"20411950200"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100003399",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality"
},
{
"award": [
"shslczdzk01102"
],
"name": "Shanghai Major Projects on Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"award": [
"2019–72"
],
"name": "Shanghai “Rising Stars of Medical Talent” Youth Development Program"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-08T05:03:47Z",
"timestamp": 1744088627896,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 91,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1592697600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofaa241/33412058/ofaa241.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/7/7/ofaa241/33482543/ofaa241.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/7/7/ofaa241/33482543/ofaa241.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0003",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0004",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with lopinavir/ritonavir: a multicentre retrospective matched cohort study",
"author": "Chan",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Hong Kong Med J",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0005",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25729",
"article-title": "A systematic review of lopinavir therapy for SARS coronavirus and MERS coronavirus—a possible reference for coronavirus disease-19 treatment option",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "556",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0006",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3851/IMP3002",
"article-title": "Combination therapy with lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin and interferon-α for Middle East respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "455",
"journal-title": "Antivir Ther",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0007",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.07.026",
"article-title": "Virological and serological analysis of a recent Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection case on a triple combination antiviral regimen",
"author": "Spanakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "528",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0008",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep25359",
"article-title": "Comparative and kinetic analysis of viral shedding and immunological responses in MERS patients representing a broad spectrum of disease severity",
"author": "Min",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25359",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0009",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1468-1293.2012.01060.x",
"article-title": "Final 192-week efficacy and safety of once-daily darunavir/ritonavir compared with lopinavir/ritonavir in HIV-1-infected treatment-naïve patients in the ARTEMIS trial",
"author": "Orkin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "49",
"journal-title": "HIV Med",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0010",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"author": "National Health Commission of China",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0012",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods",
"author": "Wu",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0013",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0014",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical progression of patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0015"
},
{
"article-title": "Lack of antiviral activity of darunavir against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "De Meyer",
"journal-title": "medRxiv 2020.04.03.20052548 [Preprint]",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0016",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0017",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0018",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2020071014141840300_CIT0019",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofaa241/5860459"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral Activity and Safety of Darunavir/Cobicistat for the Treatment of COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "7"
}