Mass spectrometry‐based metabolomics reveals metabolism of molnupiravir may lead to metabolic disorders and hepatotoxicity
et al., Biomedical Chromatography, doi:10.1002/bmc.5996, Aug 2024
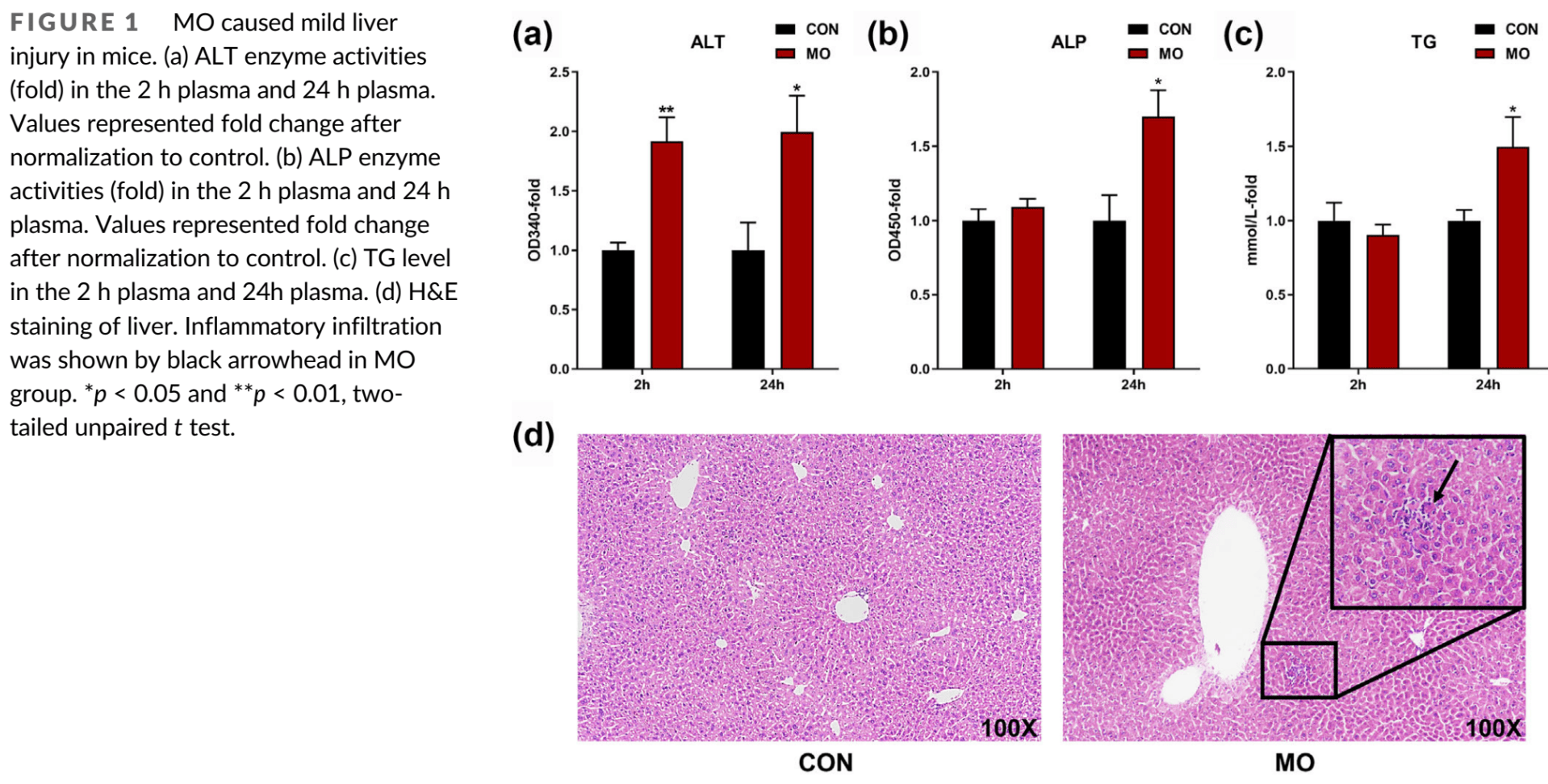
Analysis of molnupiravir induced liver injury. Molnupiravir treatment may disrupt metabolic homeostasis and cause liver injury by increasing levels of certain metabolites and activating inflammatory pathways.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Chen et al., 23 Aug 2024, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bmc.5996",
"ISSN": [
"0269-3879",
"1099-0801"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bmc.5996",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Molnupiravir (MO) is a pyrimidine nucleoside anti‐SARS‐CoV‐2 drug. MO treatment could cause mild liver injury. However, the underlying mechanism of MO‐induced liver injury and the metabolic pathway of MO in vivo are unclear. In this study, metabolomics analysis and molecular biology methods were used to explore these issues. Through metabolomics analysis, it was found that the homeostasis of pyrimidine, purine, lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and amino acids in mice was destroyed after MO treatment. A total of 80 changed metabolites were detected. Among these changed metabolites, 4‐ethylphenyl sulfate, dihydrouracil, and LPC 20:0 was related to the elevation of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), interleukin‐6 (IL6), and nuclear factor kappa‐B (NF‐κB). The levels of 4‐ethylphenyl sulfate, dihydrouracil, and LPC 20:0 in plasma were positively correlated with their levels in the liver, suggesting that these metabolites were associated with MO‐induced liver injury. MO treatment could increase NHC and cytidine levels, activate cytidine deaminase (CDA), and increase LPC levels. CDA and LPC could increase the mRNA expression level of toll‐like receptor (TLR). The current study indicated that the elevation of hepatic TLR may be an important reason for MO leading to the liver injury.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/bmc.5996"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-06-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-08-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2024-08-23"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Laboratory of Hepato‐intestinal Diseases and Metabolism, Frontiers Science Center for Disease‐Related Molecular Network, and State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Health and Multimorbidity, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jiahui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Laboratory of Hepato‐intestinal Diseases and Metabolism, Frontiers Science Center for Disease‐Related Molecular Network, and State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Health and Multimorbidity, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Liqiong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Laboratory of Hepato‐intestinal Diseases and Metabolism, Frontiers Science Center for Disease‐Related Molecular Network, and State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Health and Multimorbidity, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Laboratory of Hepato‐intestinal Diseases and Metabolism, Frontiers Science Center for Disease‐Related Molecular Network, and State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Health and Multimorbidity, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Dongmei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academician Workstation Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Nanchang China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Hongning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Laboratory of Hepato‐intestinal Diseases and Metabolism, Frontiers Science Center for Disease‐Related Molecular Network, and State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Health and Multimorbidity, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Fei",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedical Chromatography",
"container-title-short": "Biomedical Chromatography",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T09:34:21Z",
"timestamp": 1724405661000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T09:34:28Z",
"timestamp": 1724405668000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012166",
"award": [
"2021YFF0702003"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100012166",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Key Research and Development Program of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013365",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100013365",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "West China Hospital, Sichuan University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-24T00:31:18Z",
"timestamp": 1724459478158
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1724371200000
}
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2022.2102878",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/en.2007-1747",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00280-003-0695-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-73966-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(86)90625-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.04.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2011.04.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep46658",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1462-2920.15025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0950-3552(05)80289-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abb5813",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.779135",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.12.21.22283811",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1",
"unstructured": "Fountain‐Jones N. M. Vanhaeften R. Williamson J. Maskell J. Chua I. L. J. Charleston M. &Cooley L.(2022).Antiviral treatments lead to the rapid accrual of hundreds of SARS‐CoV‐2 mutations in immunocompromised patients. medRxivhttps://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.21.22283811"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxy075",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.M700184-JLR200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2015.4312",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4254/wjh.v8.i1.1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104752",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac477",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/tx300298m",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1574888X12666171012141908",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1253799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11233791",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117443",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.355",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24098065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12263-019-0653-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04396-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06073-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1517/17425255.2015.985648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.122.000918",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00915-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.855496",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8121899",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.20774",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-37459-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_43_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bmc.5996"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Mass spectrometry‐based metabolomics reveals metabolism of molnupiravir may lead to metabolic disorders and hepatotoxicity",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}