Early oral nutritional supplement improves COVID-19 outcomes among hospitalized older patients during the omicron wave
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2023.112087, May 2023
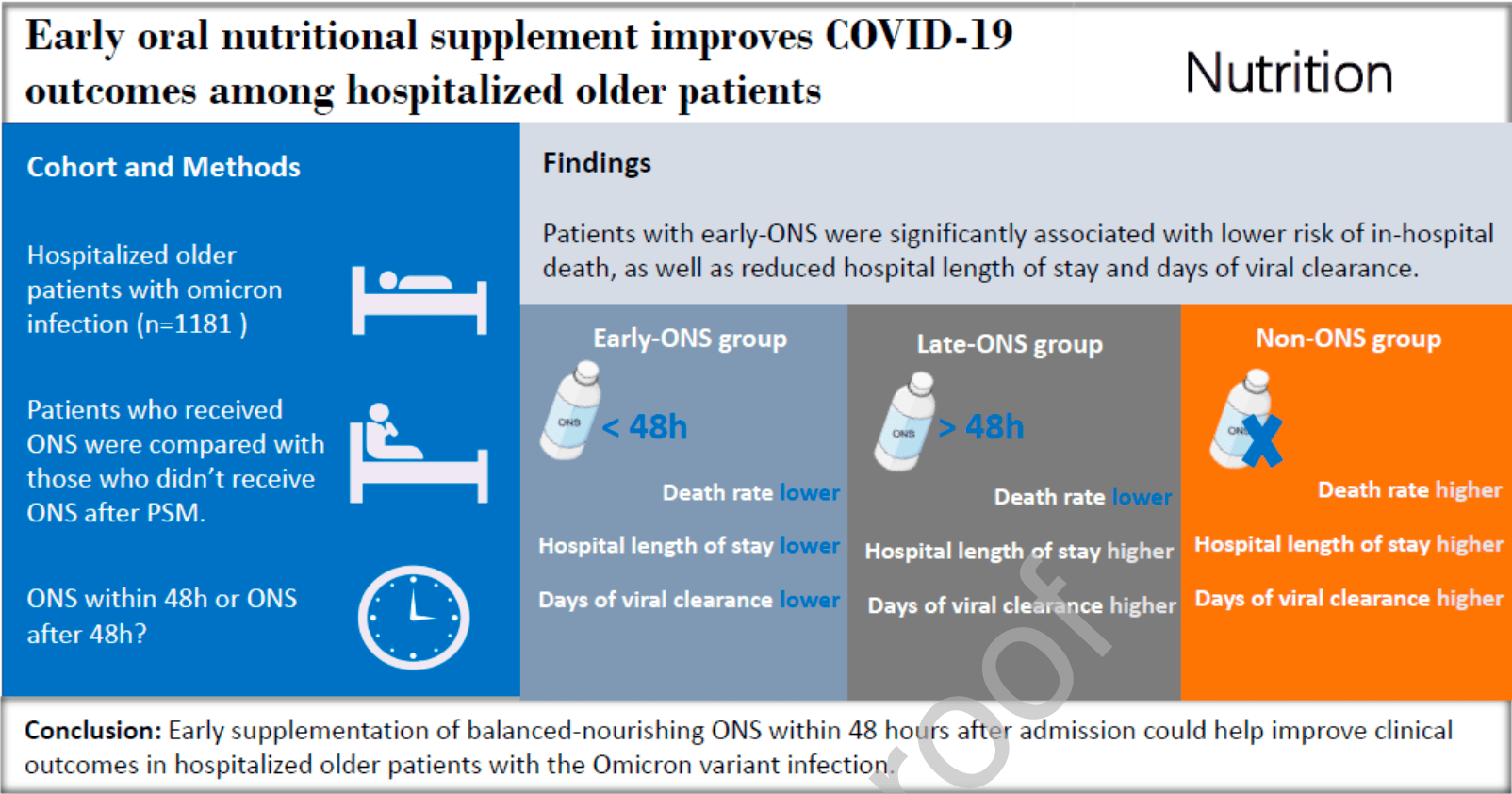
PSM retrospective 1,181 COVID-19 patients ≥60 years old in China, showing significantly lower mortality with a nutritional supplement. Hospitalization time and viral clearance time was improved with earlier initiation of treatment. The supplement contained 28 vitamins and minerals including vitamins A, C, D, B9, and zinc.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
nutritional supplement containing 28 vitamins and minerals.
|
risk of death, 72.7% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.03, treatment 3 of 258 (1.2%), control 11 of 258 (4.3%), NNT 32, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 93.0% lower, OR 0.07, p = 0.003, adjusted per study, <48hrs, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death, 91.0% lower, OR 0.09, p = 0.005, adjusted per study, >48hrs, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Chen et al., 21 May 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, mean age 78.0, 7 authors, study period April 2022 - June 2022, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with 27 vitamins and minerals) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Contact: chenshunjie77csj@163.com, 18916484569@163.com.
Early oral nutritional supplement improves COVID-19 outcomes among hospitalized older patients during the omicron wave
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2023.112087
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Abu-Raya, Predictors of Refractory Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pneumonia, Clin Infect Dis
Barazzoni, Bischoff, Breda, Wickramasinghe, Krznaric et al., ESPEN expert statements and practical guidance for nutritional management of individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin Nutr
Bourbour, Mirzaei, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus, Arch Physiol Biochem
Caccialanza, Laviano, Lobascio, Montagna, Bruno et al., Early nutritional supplementation in non-critically ill patients hospitalized for the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Rationale and feasibility of a shared pragmatic protocol, Nutrition
Cederholm, Barazzoni, Austin, Ballmer, Biolo et al., ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition, Clin Nutr
Chow, Yin, Yamane, Davison, Keneally et al., Association of prehospital antiplatelet therapy with survival in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A propensity score-matched analysis, J Thromb Haemost
Doig, Sutherland, Sandham, Fick, Verhoef et al., Increased intestinal permeability is associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in critically ill 25 ICU patients, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Fan, Li, Zhang, Wan, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: recent progress and future perspectives, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Feng, Hong, Fan, Shi, Ma et al., Age and Sex Differences Among Mildly Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Patients with Omicron Infection in 2022 in Shanghai, China. J Multidiscip Healthc
Filippo, Lorenzo, 'amico, Sofia, Roveri et al., COVID-19 is associated with clinically significant weight loss and risk of malnutrition, independent of hospitalisation: A post-hoc analysis of a prospective cohort study, Clin Nutr
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, García-Unzueta, Hernández-Hernández et al., Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Holder, Malnutrition in the elderly: a public health concern, Br J Nurs
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Fernandez, Samouda et al., Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis, Nutrients
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Cheng, Deng et al., A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Mil Med Res
Keller, Nutritional Laboratory Markers in Malnutrition, J Clin Med
Laviano, Koverech, Zanetti, Nutrition support in the time of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), Nutrition
Leisman, Ten Pearls and Pitfalls of Propensity Scores in Critical Care Research: A Guide for Clinicians and Researchers, Crit Care Med
Li, Zhang, Gong, Wang, Liu et al., Prevalence of malnutrition and analysis of related factors in elderly patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Eur J Clin Nutr
Lu, Zhang, Zhang, He, Yuan, Geriatric risk and protective factors for serious COVID-19 outcomes among older adults in Shanghai Omicron wave, Emerg Microbes Infect
Majidi, Rabbani, Gholami, Gholamalizadeh, Bourbour et al., The Effect of Vitamin C on Pathological Parameters and Survival Duration of Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Front Immunol
Mcclave, Taylor, Martindale, Warren, Johnson et al., Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Adult Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr
Mcmenamin, Lin, Wong, Cheung, Lau, Vaccine effectiveness of one, two, and three doses of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac against COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a population-based observational study, Lancet Infect Dis
Meizlish, Goshua, Liu, Fine, Amin et al., Intermediate-dose anticoagulation, aspirin, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A propensity score-matched analysis, Am J Hematol
Mentella, Scaldaferri, Gasbarrini, Miggiano, The Role of Nutrition in the COVID-19 Pandemic, Nutrients
Ortiz-Reyes, Patel, Jiang, Coz, Day et al., Early versus delayed enteral nutrition in mechanically ventilated patients with circulatory shock: a nested cohort analysis of an international multicenter, pragmatic clinical trial, Crit Care
Qi, Wang, Guo, Peng, Zhang et al., Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with rheumatic diseases: a retrospective cohort study and synthesis analysis in Wuhan, Clin Rheumatol
Sakai, Kamada, Takano, Ichikawa, Kurimoto et al., Continuous partially hydrolyzed guar gum intake reduces cold-like symptoms: a randomized, placebo-controlled, doubleblinded trial in healthy adults, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Schuetz, Fehr, Baechli, Geiser, Deiss et al., Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: a randomised clinical trial, Lancet
Singer, Blaser, Berger, Alhazzani, Calder et al., ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit, Clin Nutr
Srinivasan, Hasbani, Mehta, Irving, Kandil et al., Early Enteral Nutrition Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Children: A Secondary Analysis of Nutrition Support in the Heart and Lung Failure-Pediatric Insulin Titration Trial, Pediatr Crit Care Med
Volkert, Beck, Cederholm, Cruz-Jentoft, Goisser et al., ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics, Clin Nutr
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among communitydwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet
Zhang, He, Yu, Peng, Feng et al., The modified NUTRIC score can be used for nutritional risk assessment as well as prognosis prediction in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Nutr
Zhang, Kim, Lonjon, Zhu, Balance diagnostics after propensity score matching, Ann Transl Med
Zhang, Zhang, Chen, Shanghai's life-saving efforts against the current omicron wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2023.112087",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2023.112087",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900723001168"
],
"article-number": "112087",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Early oral nutritional supplement improves COVID-19 outcomes among hospitalized older patients during the omicron wave"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2023.112087"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1742-4411",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Yinfan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ran",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Jingjue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Zhangwei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Shunjie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-21T21:33:46Z",
"timestamp": 1684704826000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-21T21:33:47Z",
"timestamp": 1684704827000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-22T04:04:54Z",
"timestamp": 1684728294090
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900723001168?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900723001168?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "112087",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900723001168"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early oral nutritional supplement improves COVID-19 outcomes among hospitalized older patients during the omicron wave",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
chen10