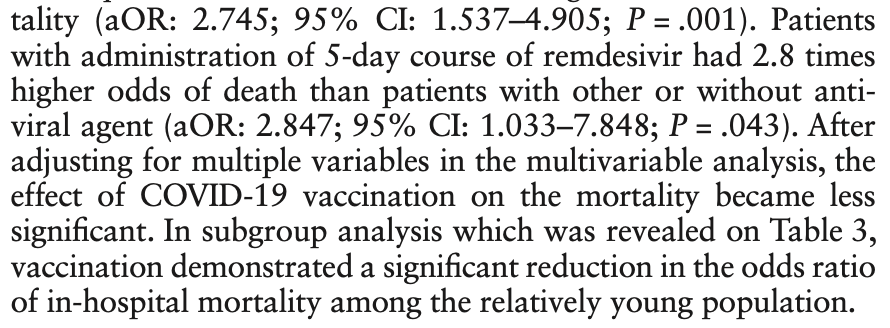
The association between COVID-19 vaccination and confirmed patients with hospitalization in Omicron era: A retrospective study
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036777, Dec 2023
Retrospective 209 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Taiwan showing higher mortality with a 5-day course of remdesivir compared to other antivirals or no antiviral treatment in multivariable analysis. Adjustments include qSOFA and CCI, with the adjusted result decreasing risk by 3x, however adjustment may not fully account for confounding by severity.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 184.7% higher, OR 2.85, p = 0.04, treatment 81, control 81, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Chang et al., 29 Dec 2023, retrospective, Taiwan, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
The association between COVID-19 vaccination and confirmed patients with hospitalization in Omicron era A retrospective study
doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036777
With the emergence of Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Taiwan has encountered the greatest coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic since 2022 spring. We analyzed the characteristics, vaccinations, and outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients quarantined in a dedicated ward. This retrospective study enrolled hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the dedicated wards of a district hospital in southern Taiwan from May 2022 to July 2022. We assessed in-hospital mortality, hospital length of stay (LOS), and dedicated ward LOS. Among 209 COVID-19 patients, the in-hospital mortality rates were 20.7% and 29.7% (P = .145) in patients with and without vaccination. A shorter dedicated ward LOS was noted in the vaccination group, with marginal statistical significance. Age, Charlson Comorbidity Index, and quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score were recognized as strong prognostic indicators for mortality in multivariable analysis. Vaccination demonstrated significant lower odds of death among relatively young populations in subgroup analysis. COVID-19 vaccination had significant efficacy in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the relatively young group, and the effect may decline among individuals with advanced age and multiple comorbidities.
Author contributions
Conceptualization
References
Abu-Raddad, Chemaitelly, Ayoub, Effect of mRNA vaccine boosters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection in Qatar, N Engl J Med
Agrawal, Bedston, Mccowan, Severe COVID-19 outcomes after full vaccination of primary schedule and initial boosters: pooled analysis of national prospective cohort studies of 30 million individuals in England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales, Lancet
Agrawal, Katikireddi, Mccowan, COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths after BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccinations in 2•57 million people in Scotland (EAVE II): a prospective cohort study, Lancet Respir Med
Andrews, Stowe, Kirsebom, Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron (B11529) variant, N Engl J Med
Baden, Sahly, Essink, Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Andrews, Gower, Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on covid-19 related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: test negative case-control study, BMJ
Butt, Talisa, Shaikh, Relative vaccine effectiveness of a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 messenger RNA vaccine booster dose against the omicron variant, Clin Infect Dis
Chalkias, Harper, Vrbicky, A bivalent omicron-containing booster vaccine against Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chronic Dis
Chemaitelly, Ayoub, Almukdad, Duration of mRNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA1 and BA2 subvariants in Qatar, Nat Commun
Citu, Citu, Motoc, Predictive value of SOFA and qSOFA for in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: a single-center study in Romania, J Pers Med
Dagan, Barda, Kepten, BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass vaccination setting, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kuswardhani, Henrina, Pranata, Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Mohammed, Nauman, Paul, The efficacy and effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccines in reducing infection, severity, hospitalization, and mortality: a systematic review, Hum Vaccin Immunother
Naik, Avula, Palleti, From emergence to endemicity: a comprehensive review of COVID-19, Cureus
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med 2020 Apr 6, Intensive Care Med
Shao, Zhang, Fang, Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and appropriate countermeasures, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Singer, Deutschman, Seymour, The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3), JAMA
Tenforde, Self, Adams, Association between mRNA vaccination and COVID-19 hospitalization and disease severity, JAMA
Tsai, Hervey, Hoffman, COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and acceptance among individuals with cancer, autoimmune diseases, or other serious comorbid conditions: cross-sectional, internet-based survey, JMIR Public Health Surveill
Vasileiou, Simpson, Shi, Interim findings from firstdose mass COVID-19 vaccination roll-out and COVID-19 hospital admissions in Scotland: a national prospective cohort study, Lancet
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China [published correction appears, JAMA
Willett, Grove, Maclean, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron is an immune escape variant with an altered cell entry pathway [published correction appears in, Nat Microbiol
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA
Zhang, Li, Liang, The significant immune escape of pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron, Emerg Microbes Infect
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, correction appears in Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000036777",
"ISSN": [
"0025-7974",
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000036777",
"abstract": "<jats:p>With the emergence of Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Taiwan has encountered the greatest coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic since 2022 spring. We analyzed the characteristics, vaccinations, and outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients quarantined in a dedicated ward. This retrospective study enrolled hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the dedicated wards of a district hospital in southern Taiwan from May 2022 to July 2022. We assessed in-hospital mortality, hospital length of stay (LOS), and dedicated ward LOS. Among 209 COVID-19 patients, the in-hospital mortality rates were 20.7% and 29.7% (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .145) in patients with and without vaccination. A shorter dedicated ward LOS was noted in the vaccination group, with marginal statistical significance. Age, Charlson Comorbidity Index, and quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score were recognized as strong prognostic indicators for mortality in multivariable analysis. Vaccination demonstrated significant lower odds of death among relatively young populations in subgroup analysis. COVID-19 vaccination had significant efficacy in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the relatively young group, and the effect may decline among individuals with advanced age and multiple comorbidities.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0003-8319-3927",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Chest Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Chiali, Tainan, Taiwan."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Ming-Hung",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Chest Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center, Chiali, Tainan, Taiwan."
}
],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Kuang-Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T16:03:27Z",
"timestamp": 1704816207000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T16:03:37Z",
"timestamp": 1704816217000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T00:35:50Z",
"timestamp": 1712622950751
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "52",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "52",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1703808000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000036777",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e36777",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21645515.2022.2027160",
"article-title": "The efficacy and effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccines in reducing infection, severity, hospitalization, and mortality: a systematic review.",
"author": "Mohammed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2027160",
"journal-title": "Hum Vaccin Immunother",
"key": "R3-20240109",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.19499",
"article-title": "Association between mRNA vaccination and COVID-19 hospitalization and disease severity.",
"author": "Tenforde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2043",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R4-20240109",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00677-2",
"article-title": "Interim findings from first-dose mass COVID-19 vaccination roll-out and COVID-19 hospital admissions in Scotland: a national prospective cohort study.",
"author": "Vasileiou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1646",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R5-20240109",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00380-5",
"article-title": "COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths after BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccinations in 2·57 million people in Scotland (EAVE II): a prospective cohort study.",
"author": "Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1439",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "R6-20240109",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2022.03.007",
"article-title": "Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and appropriate countermeasures.",
"author": "Shao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "R7-20240109",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation.",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis",
"key": "R8-20240109",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2016.0287",
"article-title": "The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3).",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "801",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R9-20240109",
"volume": "315",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.2017757",
"article-title": "The significant immune escape of pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "R11-20240109",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01143-7",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron is an immune escape variant with an altered cell entry pathway [published correction appears in Nat Microbiol 2022 Oct;7(10):1709].",
"author": "Willett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1161",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "R12-20240109",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119451",
"article-title": "Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron (B11529) variant.",
"author": "Andrews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1532",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R13-20240109",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2200797",
"article-title": "Effect of mRNA vaccine boosters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection in Qatar.",
"author": "Abu-Raddad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1804",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R14-20240109",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac328",
"article-title": "Relative vaccine effectiveness of a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 messenger RNA vaccine booster dose against the omicron variant.",
"author": "Butt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2161",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R15-20240109",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-30895-3",
"article-title": "Duration of mRNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA1 and BA2 subvariants in Qatar.",
"author": "Chemaitelly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3082",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "R16-20240109",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01656-7",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 outcomes after full vaccination of primary schedule and initial boosters: pooled analysis of national prospective cohort studies of 30 million individuals in England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales.",
"author": "Agrawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1305",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R17-20240109",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "From emergence to endemicity: a comprehensive review of COVID-19.",
"author": "Naik",
"first-page": "e48046",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "R18-20240109",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/29872",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and acceptance among individuals with cancer, autoimmune diseases, or other serious comorbid conditions: cross-sectional, internet-based survey.",
"author": "Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29872",
"journal-title": "JMIR Public Health Surveill",
"key": "R19-20240109",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.022",
"article-title": "Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Tuty Kuswardhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2103",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "R20-20240109",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm12060878",
"article-title": "Predictive value of SOFA and qSOFA for in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: a single-center study in Romania.",
"author": "Citu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "878",
"journal-title": "J Pers Med",
"key": "R21-20240109",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China.",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R22-20240109",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China [published correction appears in Lancet 2020 Jan 30].",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R23-20240109",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study [published correction appears in Lancet 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1038].",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R24-20240109",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China [published correction appears in JAMA 2021 Mar 16;325(11):1113].",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R25-20240109",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention.",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R26-20240109",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med 2020 Apr 6].",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "R27-20240109",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2208343",
"article-title": "A bivalent omicron-containing booster vaccine against Covid-19.",
"author": "Chalkias",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1279",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R28-20240109",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n1088",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on covid-19 related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: test negative case-control study.",
"author": "Lopez Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n1088",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "R29-20240109",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2101765",
"article-title": "BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass vaccination setting.",
"author": "Dagan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1412",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R30-20240109",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035389",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.",
"author": "Baden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R31-20240109",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2800430/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000036777"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The association between COVID-19 vaccination and confirmed patients with hospitalization in Omicron era: A retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "102"
}