Use of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection
et al., Kidney International, doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001, Oct 2022
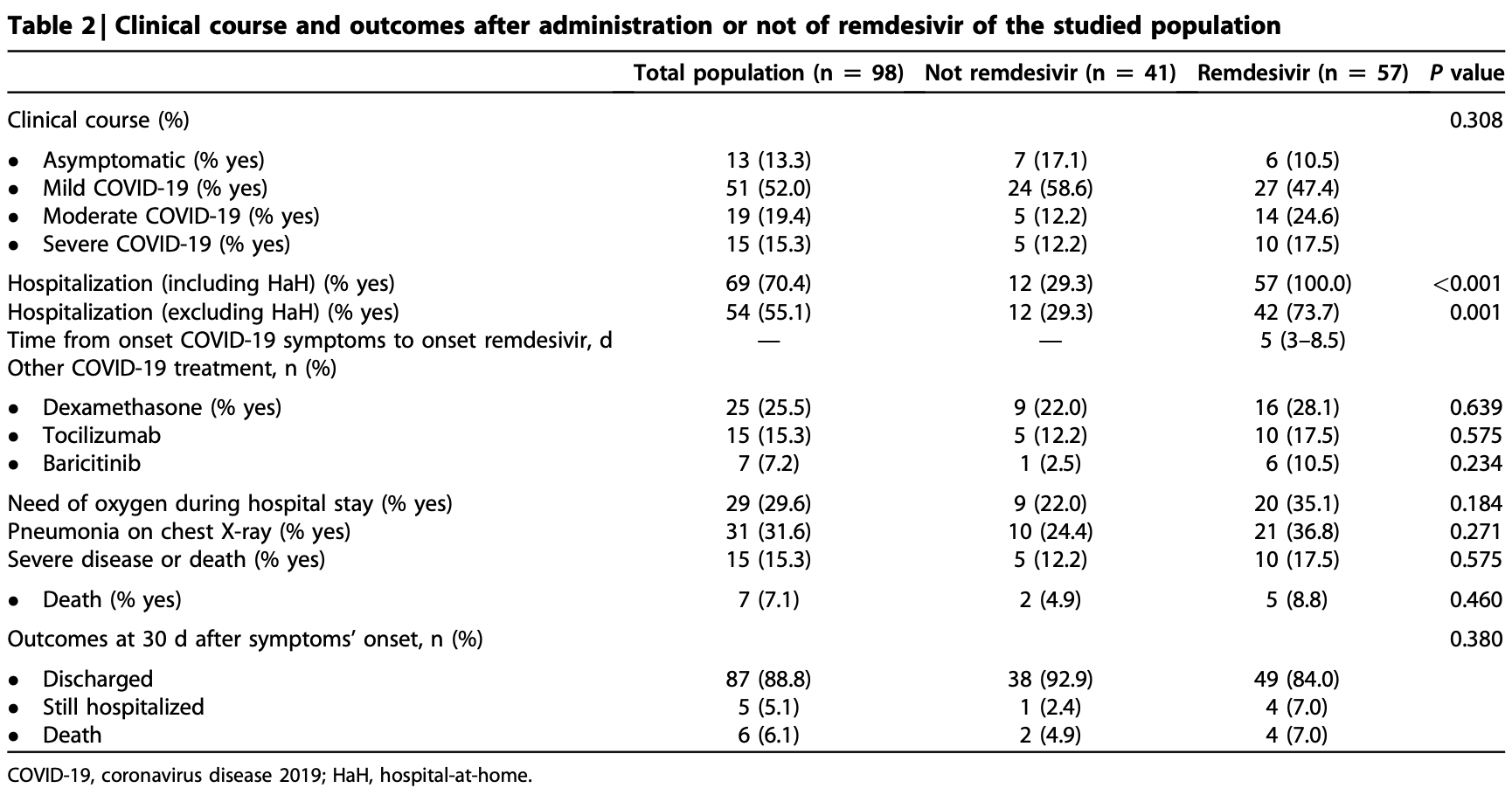
Retrospective 98 kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection in Spain, showing no significant difference in mortality with remdesivir treatment. Earlier administration was associated with improved results, although this analysis is subject to survivorship/selection bias.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 79.8% higher, RR 1.80, p = 0.70, treatment 5 of 57 (8.8%), control 2 of 41 (4.9%).
|
|
risk of severe case, 43.9% higher, RR 1.44, p = 0.58, treatment 10 of 57 (17.5%), control 5 of 41 (12.2%).
|
|
risk of moderate/severe case, 72.6% higher, RR 1.73, p = 0.09, treatment 24 of 57 (42.1%), control 10 of 41 (24.4%).
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 91.8% higher, RR 1.92, p = 0.35, treatment 8 of 57 (14.0%), control 3 of 41 (7.3%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Cacho et al., 31 Oct 2022, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, 15 authors, study period 1 November, 2021 - 28 February, 2022, average treatment delay 5.0 days.
Contact: cucchiari@clinic.cat, fdiekman@clinic.cat.
Abstract: Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with
free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the
company's public news and information website.
Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related
research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre - including this
research content - immediately available in PubMed Central and other
publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights
for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means
with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are
granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre
remains active.
research letter
www.kidney-international.org
Use of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients
with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection
Judit Cacho1, David Nicolás2, Marta Bodro3, Elena Cuadrado-Payán1, Verónica Torres-Jaramillo1,
Ángela Gonzalez-Rojas1, Pedro Ventura-Aguiar1,2, Enrique Montagud-Marrahi1, Sabina Herrera3,
Veronica Rico2, Frederic Cofàn1, Frederic Oppenheimer1, Ignacio Revuelta1,4,5, Fritz Diekmann1,4,5,6 and
David Cucchiari1,4,6
1
Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation, Hospital Clínic, Barcelona, Spain; 2Hospital-at-Home Unit, Department of
Internal Medicine, Hospital Clínic, Barcelona, Spain; 3Department of Infectious Diseases Service, Hospital Clínic-IDIBAPS, University of
Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain; 4Laboratori Experimental de Nefrologia i Trasplantament (LENIT), Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques
August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain; and 5Red de Investigación Renal (REDINREN), Madrid, Spain
Kidney International (2022) 102, 917–921; https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.kint.2022.08.001
Copyright ª 2022, International Society of Nephrology. Published by
Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Correspondence: David Cucchiari or Fritz Diekmann, Department of
Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation, Hospital Clínic, Carrer Villarroel 170
(Escala 12–Planta 5), 08036 Barcelona, Spain. E-mail: cucchiari@clinic.cat
(D. Cucchiari) or fdiekman@clinic.cat (F. Diekmann)
6
FD and DC are contributed equally to this work.
Received 20 April 2022; revised 27 July 2022; accepted 4 August 2022;
published online 11 August 2022
Kidney International (2022) 102, 917–921
I
nfection from the Omicron variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) seems to be
less severe in general population in comparison with the
previous variants of concern.1 However, in kidney transplant
recipients (KTRs), Omicron continues to be a considerable
threat2 due to immunosuppression status and blunt response
to vaccination.3
Clinical trials with remdesivir have demonstrated
improved time to recovery in patients on oxygen with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).4 In Spain, it was approved
in September 2020 for the treatment of COVID-19 in patients
with pneumonia, respiratory failure, and less than 8 days
since symptoms’ onset. Then, in consideration of the Phase 3
Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial to
Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Remdesivir (GS-5734)
Treatment of COVID-19 in an Outpatient Setting (PINETREE), patients with mild symptomatology and comorbidities were also considered to receive treatment with remdesivir
because of its safety profile and the lower risk of hospitalization or death than placebo.5
Taking into consideration these..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001",
"ISSN": [
"0085-2538"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001",
"alternative-id": [
"S0085253822006135"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Use of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Kidney International"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cacho",
"given": "Judit",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicolás",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bodro",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cuadrado-Payán",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torres-Jaramillo",
"given": "Verónica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonzalez-Rojas",
"given": "Ángela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ventura-Aguiar",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montagud-Marrahi",
"given": "Enrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herrera",
"given": "Sabina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rico",
"given": "Veronica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cofàn",
"given": "Frederic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oppenheimer",
"given": "Frederic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Revuelta",
"given": "Ignacio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diekmann",
"given": "Fritz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cucchiari",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Kidney International",
"container-title-short": "Kidney International",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"kidney-international.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-11T15:14:30Z",
"timestamp": 1660230870000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-11T08:20:45Z",
"timestamp": 1704961245000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-03T22:45:46Z",
"timestamp": 1722725146973
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1664582400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0085253822006135?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0085253822006135?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "917-921",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0000000000004126",
"article-title": "Trends in COVID-19 outcomes in kidney transplant recipients during the period of omicron variant predominance",
"author": "Villanego",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e304",
"journal-title": "Transplantation",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib1",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ekir.2022.03.020",
"article-title": "Early administration of anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies prevents severe COVID-19 in kidney transplant patients",
"author": "Gueguen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1241",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib2",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.16701",
"article-title": "Cellular and humoral response after mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients",
"author": "Cucchiari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2727",
"journal-title": "Am J Transplant",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib3",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib4",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib5",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ekir.2021.06.023",
"article-title": "Use and safety of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19",
"author": "Buxeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2305",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib6",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1851",
"article-title": "Remdesivir use in the setting of severe renal impairment: a theoretical concern or real risk?",
"author": "Pettit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3990",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.08.001_bib7",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 7,
"references-count": 7,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0085253822006135"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Use of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "102"
}