Does the Consumption of Metformin Correlate With a Reduction in Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19 in Morocco?
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.77288, Jan 2025
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 115 hospitalized type 2 diabetes patients in Morocco showing significantly lower mortality with metformin use.
|
risk of death, 53.6% lower, RR 0.46, p = 0.04, treatment 8 of 41 (19.5%), control 30 of 74 (40.5%), NNT 4.8, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Benfathallah et al., 11 Jan 2025, retrospective, Morocco, peer-reviewed, mean age 65.5, 5 authors, study period 1 August, 2020 - 1 August, 2021.
Contact: bouchra_benfathallah@um5.ac.ma.
Does the Consumption of Metformin Correlate With a Reduction in Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19 in Morocco?
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.77288
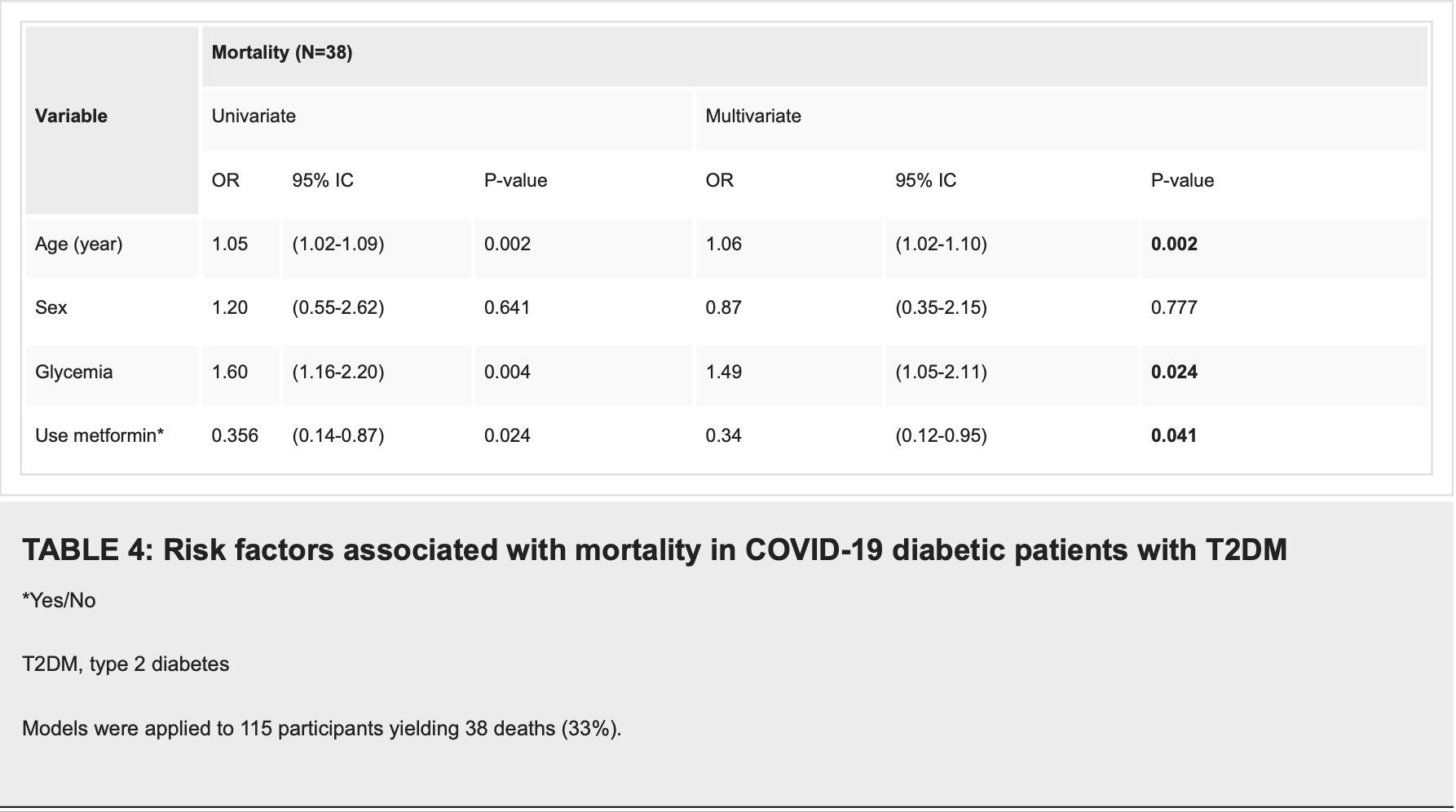
Objectives: To assess whether metformin therapy for type 2 diabetes (T2DM) was associated with a reduced mortality rate in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 compared to other antihyperglycemic drugs. Methods: This retrospective study included patients with T2DM who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 between 1 August 2020 and 1 August 2021. The patients were required to be aged over 18 years old and to be undergoing treatment for hyperglycemia, whether with metformin, other oral antidiabetic drugs, or insulin. A data exploitation sheet was completed for each patient. The Jamovi ( https://www.jamovi.org/ ) software was applied to conduct the statistical analyses. Multivariate logistic regression was used to determine whether metformin use was associated with reduced mortality among patients with T2DM and COVID-19. Results: We identified 115 COVID-19 patients with T2DM, of whom 41 were on metformin, 35 patients were on insulin, and 39 patients were on other oral antihyperglycemic agents; the average age of patients was 65.5±13.2 years, and 52.2% were male. The mortality rate was lower in the metformin user group (21.1%) compared to the non-user group (78.9%). The multivariate logistic regression model indicated that age (OR=1.06; 95% CI (1.02-1.10); p=0.002) and glycemia (OR=1.49; 95% CI (1.05-2.11); p=0.024) were significantly associated with mortality in patients with T2DM and COVID-19. Whereas, the use of metformin was identified as a protective factor (OR=0.34 95% CI (0.12-0.95); p=0.041). Conclusion: This study highlighted that metformin seems to be associated with significantly decreased mortality in adults with T2DM and COVID-19.
Additional Information Author Contributions All authors have reviewed the final version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. Concept and design: Bouchra Benfathallah, Abha Cherkani Hassani , Redouane Abouqal, Laïla Benchekroun Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Bouchra Benfathallah, Abha Cherkani Hassani , Samia El Hilali, Redouane Abouqal, Laïla Benchekroun Drafting of the manuscript: Bouchra Benfathallah, Laïla Benchekroun Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Bouchra Benfathallah, Abha Cherkani Hassani , Samia El Hilali, Redouane Abouqal, Laïla Benchekroun Supervision: Bouchra Benfathallah, Abha Cherkani Hassani , Samia El Hilali, Redouane Abouqal, Laïla Benchekroun
Disclosures Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. The Ethics Committee of Biomedical Research (CERB) issued approval N/R: Dossier n°L/21. Data access and patient anonymity were respected according to national and international guidelines. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they..
References
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev, doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7
Cao, Baranova, Wei, Wang, Zhang, Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28100
Cao, Li, Tao, Metformin inhibits vascular calcification in female rat aortic smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway, Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/en.2013-1002
Cheng, Xin, Chen, Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: a multicentral retrospective study, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371
Erickson, Fenno, Barzilai, Metformin for treatment of acute COVID-19: systematic review of clinical trial data against SARS-CoV-2, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc22-2539
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8
Gallo Marin, Aghagoli, Lavine, Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a literature review, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2146
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12897
Ghany, Palacio, Dawkins, Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Obes Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290
Holman, Knighton, Kar, Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0
Kaneto, Kimura, Obata, Shimoda, Kaku, Multifaceted mechanisms of action of metformin which have been unraveled one after another in the long history, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22052596
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216
Li, Yang, Yan, Sun, Zeng et al., Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.704666
Lukito, Pranata, Henrina, Lim, Lawrensia et al., The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006
Luo, Qiu, Liu, Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375
Ma, Krishnamurthy, Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282210
Malhotra, Hepokoski, Mccowen, Shyy, ACE2, metformin, and COVID-19, Iscience
Samuel, Varghese, Büsselberg, Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183
Silverii, Fumagalli, Rozzini, Milani, Mannucci et al., Is metformin use associated with a more favorable Covid-19 course in people with diabetes?, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm13071874
Singh, Singh, Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268
Song, Zhang, Meng, Mechanism and application of metformin in kidney diseases: an update, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111454
Tong, Grant, Gras, The role of T-cell immunity in COVID-19 severity amongst people living with type II diabetes, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.16105
Wang, Cooper, Gokhale, Association of metformin with susceptibility to COVID-19 in people with type 2 diabetes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab067
Wang, Lin, Sy, Renal protective effect of metformin in type 2 diabetes patients, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgae477
Watson, Dhaliwal, Robertshaw, Consensus recommendations for sick day medication guidance for people with diabetes, kidney, or cardiovascular disease: a modified Delphi process, Am J Kidney Dis, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.10.012
Wiernsperger, Al-Salameh, Cariou, Lalau, Protection by metformin against severe COVID-19: an in-depth mechanistic analysis, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101359
Zumla, Hui, Azhar, Memish, Maeurer, Reducing mortality from 2019-nCoV: host-directed therapies should be an option, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30305-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.77288",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.77288",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benfathallah",
"given": "Bouchra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherkani Hassani",
"given": "Abha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El Hilali",
"given": "Samia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abouqal",
"given": "Redouane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benchekroun",
"given": "Laïla",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-11T17:55:46Z",
"timestamp": 1736618146000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-11T17:55:48Z",
"timestamp": 1736618148000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-12T05:21:46Z",
"timestamp": 1736659306657,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/325967-does-the-consumption-of-metformin-correlate-with-a-reduction-in-mortality-among-patients-with-type-2-diabetes-and-covid-19-in-morocco",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.16105",
"article-title": "The role of T-cell immunity in COVID-19 severity amongst people living with type II diabetes",
"author": "Tong ZW",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Tong ZW, Grant E, Gras S, et al.. The role of T-cell immunity in COVID-19 severity amongst people living with type II diabetes. FEBS J. 2021, 288:5042-54. 10.1111/febs.16105",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Holman N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Holman N, Knighton P, Kar P, et al.. Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8:823-33. 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"article-title": "Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?",
"author": "Fang L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8:e21. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28100",
"article-title": "Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19",
"author": "Cao H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Cao H, Baranova A, Wei X, Wang C, Zhang F. Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2023, 95:e28100. 10.1002/jmv.28100",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab067",
"article-title": "Association of metformin with susceptibility to COVID-19 in people with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Wang J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Wang J, Cooper JM, Gokhale K, et al.. Association of metformin with susceptibility to COVID-19 in people with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021, 106:1255-68. 10.1210/clinem/dgab067",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm13071874",
"article-title": "Is metformin use associated with a more favorable Covid-19 course in people with diabetes?",
"author": "Silverii GA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Silverii GA, Fumagalli C, Rozzini R, Milani M, Mannucci E, Marchionni N. Is metformin use associated with a more favorable Covid-19 course in people with diabetes?. J Clin Med. 2024, 13:1874. 10.3390/jcm13071874",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-2539",
"article-title": "Metformin for treatment of acute COVID-19: systematic review of clinical trial data against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Erickson SM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Erickson SM, Fenno SL, Barzilai N, et al.. Metformin for treatment of acute COVID-19: systematic review of clinical trial data against SARS-CoV-2. Diabetes Care. 2023, 46:1432-42. 10.2337/dc22-2539",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"article-title": "Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis",
"author": "Bramante CT",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Healthy Longev",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Ingraham NE, Murray TA, et al.. Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2:e34-41. 10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30033-7",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0282210",
"article-title": "Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis",
"author": "Ma Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Ma Z, Krishnamurthy M. Is metformin use associated with low mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized for COVID-19? a multivariable and propensity score-adjusted meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023, 18:e0282210. 10.1371/journal.pone.0282210",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.704666",
"article-title": "Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Yang X, Yan P, Sun T, Zeng Z, Li S. Metformin in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021, 8:704666. 10.3389/fmed.2021.704666",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19",
"author": "Lalau JD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Lalau JD, Al-Salameh A, Hadjadj S, et al.. Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 47:101216. 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101216",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"article-title": "Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Luo P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Luo P, Qiu L, Liu Y, et al.. Metformin treatment was associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in a retrospective analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020, 103:69-72. 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0375",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371",
"article-title": "Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: a multicentral retrospective study",
"author": "Cheng X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Cheng X, Xin S, Chen Y, et al.. Effects of metformin, insulin on COVID-19 patients with pre-existed type 2 diabetes: a multicentral retrospective study. Life Sci. 2021, 275:119371. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119371",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2",
"article-title": "Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Bornstein SR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Bornstein SR, Rubino F, Khunti K, et al.. Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8:546-50. 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268",
"article-title": "Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?",
"author": "Singh AK",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Singh R. Is metformin ahead in the race as a repurposed host-directed therapy for patients with diabetes and COVID-19?. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020, 165:108268. 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108268",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"article-title": "Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes",
"author": "Sharma S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Sharma S, Ray A, Sadasivam B. Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020, 164:108183. 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108183",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2146",
"article-title": "Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a literature review",
"author": "Gallo Marin B",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Gallo Marin B, Aghagoli G, Lavine K, et al.. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: a literature review. Rev Med Virol. 2021, 31:1-10. 10.1002/rmv.2146",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role",
"author": "Samuel SM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Samuel SM, Varghese E, Büsselberg D. Therapeutic potential of metformin in COVID-19: reasoning for its protective role. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29:894-907. 10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.004",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgae477",
"article-title": "Renal protective effect of metformin in type 2 diabetes patients",
"author": "Wang HH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Wang HH, Lin SH, Hung SY, et al.. Renal protective effect of metformin in type 2 diabetes patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024, 477. 10.1210/clinem/dgae477",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111454",
"article-title": "Mechanism and application of metformin in kidney diseases: an update",
"author": "Song A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Song A, Zhang C, Meng X. Mechanism and application of metformin in kidney diseases: an update. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021, 138:111454. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111454",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"article-title": "The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lukito AA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Lukito AA, Pranata R, Henrina J, Lim MA, Lawrensia S, Suastika K. The effect of metformin consumption on mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020, 14:2177-83. 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.11.006",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"article-title": "Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA",
"author": "Ghany R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Ghany R, Palacio A, Dawkins E, et al.. Metformin is associated with lower hospitalizations, mortality and severe coronavirus infection among elderly medicare minority patients in 8 states in USA. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021, 15:513-8. 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.02.022",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12897",
"article-title": "Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report",
"author": "Gao Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Gao Y, Liu T, Zhong W, Liu R, Zhou H, Huang W, Zhang W. Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report. Clin Transl Sci. 2020, 13:1055-9. 10.1111/cts.12897",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19",
"author": "Bramante CT",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Bramante CT, Huling JD, Tignanelli CJ, et al.. Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2022, 387:599-610. 10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.10.012",
"article-title": "Consensus recommendations for sick day medication guidance for people with diabetes, kidney, or cardiovascular disease: a modified Delphi process",
"author": "Watson KE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Kidney Dis",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Watson KE, Dhaliwal K, Robertshaw S, et al.. Consensus recommendations for sick day medication guidance for people with diabetes, kidney, or cardiovascular disease: a modified Delphi process. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023, 81:564-74. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.10.012",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.101425",
"article-title": "ACE2, metformin, and COVID-19",
"author": "Malhotra A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Iscience",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Malhotra A, Hepokoski M, McCowen KC, Shyy JY. ACE2, metformin, and COVID-19. Iscience. 2020, 23:",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22052596",
"article-title": "Multifaceted mechanisms of action of metformin which have been unraveled one after another in the long history",
"author": "Kaneto H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Kaneto H, Kimura T, Obata A, Shimoda M, Kaku K. Multifaceted mechanisms of action of metformin which have been unraveled one after another in the long history. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22:2596. 10.3390/ijms22052596",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto TI",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Obes Med",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Hariyanto TI, Kurniawan A. Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality rate from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Obes Med. 2020, 19:100290. 10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100290",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101359",
"article-title": "Protection by metformin against severe COVID-19: an in-depth mechanistic analysis",
"author": "Wiernsperger N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Wiernsperger N, Al-Salameh A, Cariou B, Lalau JD. Protection by metformin against severe COVID-19: an in-depth mechanistic analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 48:101359. 10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101359",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/en.2013-1002",
"article-title": "Metformin inhibits vascular calcification in female rat aortic smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway",
"author": "Cao X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Cao X, Li H, Tao H, et al.. Metformin inhibits vascular calcification in female rat aortic smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway. Endocrinol. 2013, 154:3680-9. 10.1210/en.2013-1002",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30305-6",
"article-title": "Reducing mortality from 2019-nCoV: host-directed therapies should be an option",
"author": "Zumla A",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Zumla A, Hui DS, Azhar EI, Memish ZA, Maeurer M. Reducing mortality from 2019-nCoV: host-directed therapies should be an option. Lancet. 2020, 395:e35-6. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30305-6",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/325967-does-the-consumption-of-metformin-correlate-with-a-reduction-in-mortality-among-patients-with-type-2-diabetes-and-covid-19-in-morocco"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Does the Consumption of Metformin Correlate With a Reduction in Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19 in Morocco?",
"type": "journal-article"
}
