Significance of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Overall Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients with COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092050, Apr 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
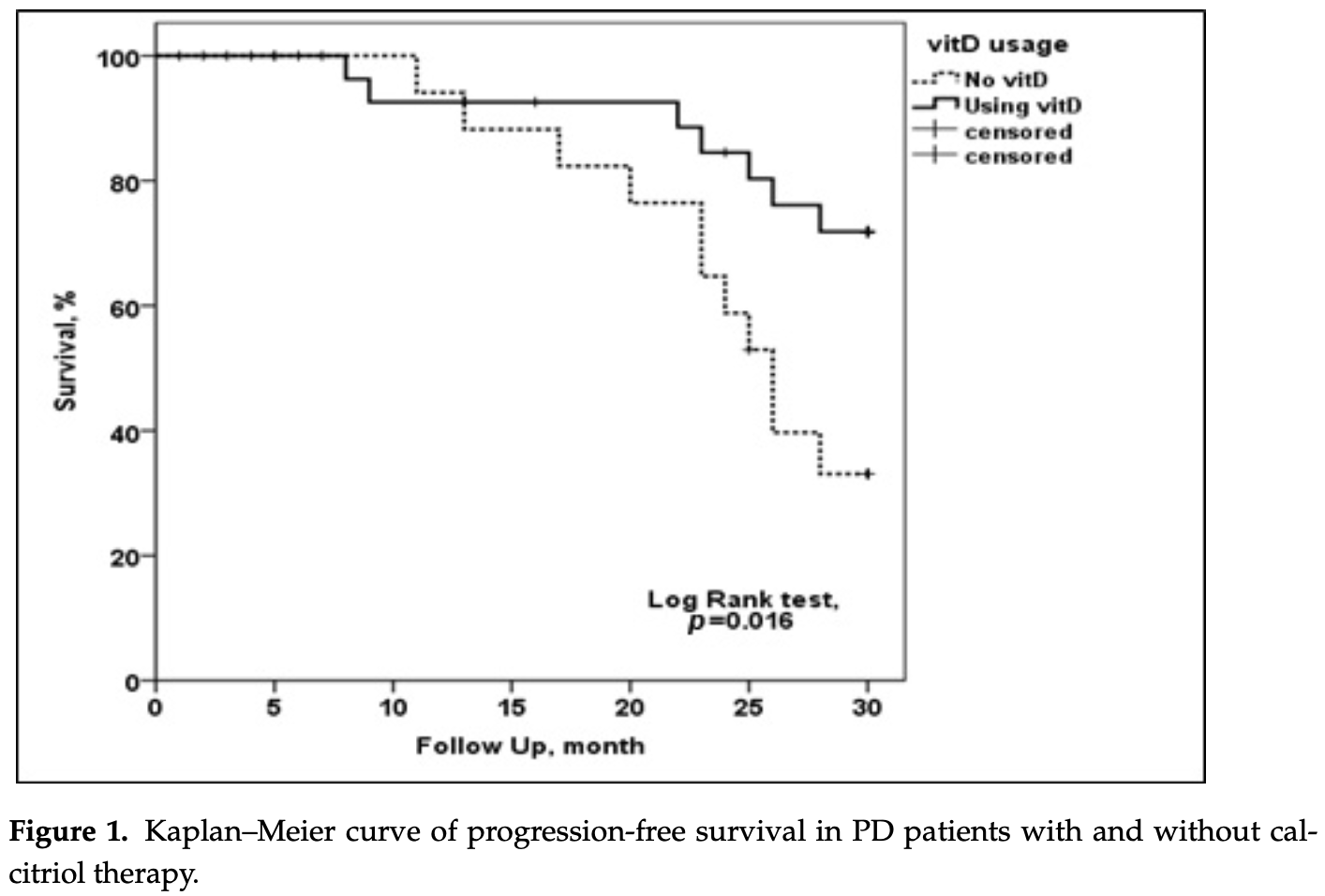
Prospective analysis of 52 peritoneal dialysis patients, 31 on calcitriol (vitamin D) therapy. All patients tested positive for COVID-19 during followup (median 26 months). Mortality was significantly lower for patients on calcitriol therapy in univariate Cox regression analysis and in Kaplan-Meier analysis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed only diabetes mellitus with statistical significance.
This is the 115th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of death, 66.8% lower, HR 0.33, p = 0.02, treatment 7 of 31 (22.6%), control 11 of 21 (52.4%), NNT 3.4, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Baralić et al., 24 Apr 2023, prospective, France, peer-reviewed, 15 authors, study period March 2020 - September 2022, dosage not specified.
Contact: baralicmarko@yahoo.com (corresponding author).
Significance of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Overall Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients with COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092050
In previous publications, we pointed out the importance of mannosylation of fibrinogen for the development of cardiovascular complications and fucosylation as a predictor of peritoneal membrane dysfunction in patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD). After a follow-up period of 30 months from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, we evaluated the significance of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 (calcitriol) therapy, primary disease, biochemical and hematologic analyzes, and previously performed glycan analysis by lectin-based microarray as predictors of mortality in this patient group. After univariate Cox regression analysis, diabetes mellitus (DM) and calcitriol therapy were found to be potential predictors of mortality. Additional multivariate Cox regression analysis confirmed that only DM was a predictor of mortality. Nevertheless, the use of calcitriol in therapy significantly reduced mortality in this patient group, as shown by the Kaplan-Meier survival curve. The presence of DM as a concomitant disease proved to be a strong predictor of fatal outcome in PD patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. This is the first study to indicate the importance and beneficial effect of calcitriol therapy on survival in PD patients with COVID-19 infection. In addition, this study points to the possibility that adverse thrombogenic events observed in PD patients during the pandemic may be caused by aberrant fibrinogen glycosylation.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
References
Akácsos-Szász, Pál, Nyulas, Nemes-Nagy, Fárr et al., Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24054319
Alfano, Fontana, Ferrari, Guaraldi, Mussini et al., -19 Working Group (MoCo19). Peritoneal dialysis in the time of coronavirus disease 2019, Clin. Kidney J, doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa093
Arenas-Jimenez, González-Parra, Riera, Bello, López-Herradón et al., Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients with COVID-19, the Effect of Paricalcitol or Calcimimetics, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082559
Baralić, Gligorijević, Brković, Katrlík, Pažitná et al., Fibrinogen Fucosylation as a Prognostic Marker of End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom10081165
Baralić, Pažitna, Brković, Laušević, Gligorijević et al., Prediction of mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis based on the fibrinogen mannosylation, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12030351
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, El-Zein, Rahme et al., The link between COVID-19 and Vitamin D (VIVID): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Cnossen, Smith, Konings, Kooman, Leunissen et al., Quantification of free water transport during the peritoneal equilibration test, Perit. Dial. Int, doi:10.1177/089686080902900509
D'ecclesiis, Gavioli, Martinoli, Raimondi, Chiocca et al., Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268396
Dror, Morozov, Daoud, Namir, Yakir et al., Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0263069
El Ghoul, Daaboul, Korjian, El Alam, Mansour et al., Etiology of End-Stage Renal Disease and Arterial Stiffness among Hemodialysis Patients, Biomed Res. Int
Hanff, Mohareb, Giri, Cohen, Chirinos, Thrombosis in COVID-19, Am. J. Hematol
Hemmelder, Noordzij, Vart, Hilbrands, Jager et al., Recovery of dialysis patients with COVID-19: Health outcomes 3 months after diagnosis in ERACODA, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfac008
Huang, Li, Fan, Zhou, Fu et al., Serum Phosphorus and Albumin in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: Interaction and Association with Mortality, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.760394
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Jager, Kovesdy, Langham, Rosenberg, Jha et al., A single number for advocacy and communicationworldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant, doi:10.1093/ndt/gfz174
Jaiswal, Ishak, Ang, Pokhrel, Shama et al., Hypovitaminosis D and cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc, doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101019
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Aglipay et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6
Kadkhoda, COVID-19: An Immunopathological View, mSphere, doi:10.1128/mSphere.00344-20
Kiebalo, Holotka, Habura, Pawlaczyk, Nutritional Status in Peritoneal Dialysis: Nutritional Guidelines, Adequacy and the Management of Malnutrition, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061715
Krötz, Sohn, Gloe, Zahler, Riexinger et al., NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.V100.3.917
Li, Chow, Van De Luijtgaarden, Johnson, Jager et al., Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis, Nat. Rev. Nephrol
Mazziotti, Lavezzi, Brunetti, Mirani, Favacchio et al., Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force. Vitamin D deficiency, secondary hyperparathyroidism and respiratory insufficiency in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01535-2
Mehrotra, Devuyst, Davies, Johnson, The Current State of Peritoneal Dialysis, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol, doi:10.1681/ASN.2016010112
Mehrotra, Duong, Jiwakanon, Kovesdy, Moran et al., Serum albumin as a predictor of mortality in peritoneal dialysis: Comparisons with hemodialysis, Am. J. Kidney Dis, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.03.018
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Messa, Alfieri, Secondary and Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism, Front. Horm. Res, doi:10.1159/000491041
Miedziaszczyk, Idasiak-Piechocka, Wiśniewski, Lacka, A systematic review of the pharmacotherapy of secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) in grades 3-5 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Moiseiwitsch, Zwennes, Szlam, Sniecinski, Brown, COVID-19 patient fibrinogen produces dense clots with altered polymerization kinetics, partially explained by increased sialic acid, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.15882
Paces, Strizova, Smrz, Cerny, COVID-19 and the immune system, Physiol. Res, doi:10.33549/physiolres.934492
Parapiboon, Ponce, Cullis, Acute peritoneal dialysis in COVID-19, Perit. Dial. Int, doi:10.1177/0896860820931235
Park, Cook, Lim, Sun, Dickens, A Systematic Review of COVID-19 Epidemiology Based on Current Evidence, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9040967
Patel, Mishra, Barot, Naik, Browne et al., Prophylactic and Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19: A Review, Eur. J. Med. Health Sci
Rossi, Muollo, Dalla-Valle, Urbani, Pellegrini et al., The Role of Obesity, Body Composition, and Nutrition in COVID-19 Pandemia: A Narrative Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14173493
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004
Surma, Banach, Fibrinogen and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases-Review of the Literature and Clinical Studies, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23010193
Vallianou, Mitesh, Gkogkou, Geladari, Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Is there Any Relationship?, Curr. Cardiol. Rev, doi:10.2174/1573403X14666180711124825
Wang, Yu, Cai, Ma, Zhao et al., Dialysate glucose response phenotypes during peritoneal equilibration test and their association with cardiovascular death: A cohort study, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020447
Whyte, Rastogi, Ferguson, Donnarumma, Mutch, The Efficacy of Fibrinogen Concentrates in Relation to Cryoprecipitate in Restoring Clot Integrity and Stability against Lysis, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23062944
Yang, Xiao, Chen, Chen, Luo et al., COVID-19 and chronic renal disease: Clinical characteristics and prognosis, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcaa258
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Żmijewski, Nongenomic Activities of Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235104
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15092050",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15092050",
"abstract": "<jats:p>In previous publications, we pointed out the importance of mannosylation of fibrinogen for the development of cardiovascular complications and fucosylation as a predictor of peritoneal membrane dysfunction in patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD). After a follow-up period of 30 months from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, we evaluated the significance of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) therapy, primary disease, biochemical and hematologic analyzes, and previously performed glycan analysis by lectin-based microarray as predictors of mortality in this patient group. After univariate Cox regression analysis, diabetes mellitus (DM) and calcitriol therapy were found to be potential predictors of mortality. Additional multivariate Cox regression analysis confirmed that only DM was a predictor of mortality. Nevertheless, the use of calcitriol in therapy significantly reduced mortality in this patient group, as shown by the Kaplan–Meier survival curve. The presence of DM as a concomitant disease proved to be a strong predictor of fatal outcome in PD patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. This is the first study to indicate the importance and beneficial effect of calcitriol therapy on survival in PD patients with COVID-19 infection. In addition, this study points to the possibility that adverse thrombogenic events observed in PD patients during the pandemic may be caused by aberrant fibrinogen glycosylation.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15092050"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5585-9793",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baralić",
"given": "Marko",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Robajac",
"given": "Dragana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2539-4507",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Penezić",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5077-2779",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brković",
"given": "Voin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8691-2486",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Chemistry, Technology and Metallurgy National, Institute of the Republic of Serbia, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gligorijević",
"given": "Nikola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8209-8552",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bontić",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Pavlović",
"given": "Jelena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Nikolić",
"given": "Jelena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Miljuš",
"given": "Goran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4652-7719",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dobrijević",
"given": "Zorana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0940-9481",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Šunderić",
"given": "Miloš",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2144-2476",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Chemistry, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 84538 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pažitná",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2876-9298",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Chemistry, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 84538 Bratislava, Slovakia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Katrlík",
"given": "Jaroslav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2042-0056",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for the Application of Nuclear Energy (INEP), University of Belgrade, 11080 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nedić",
"given": "Olgica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
},
{
"name": "Clinic of Nephrology, University Clinical Centre of Serbia, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia"
}
],
"family": "Laušević",
"given": "Mirjana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-24T07:38:07Z",
"timestamp": 1682321887000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-24T09:30:41Z",
"timestamp": 1682328641000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"451-03-47/2023-01/200019"
],
"name": "Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia"
},
{
"award": [
"337-00-107/2019-09/12",
"APVV SK-SRB-21-0046",
"VEGA 2/0120/22",
"APVV-20-0243"
],
"name": "Bilateral Cooperation project with the Republic of Slovakia"
},
{
"award": [
"313011V358"
],
"name": "European Regional Development Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-25T04:32:51Z",
"timestamp": 1682397171361
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682294400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/9/2050/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2050",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneph.2016.181",
"article-title": "Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Nephrol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000491041",
"article-title": "Secondary and Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism",
"author": "Messa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Front. Horm. Res.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Modena COVID-19 Working Group (MoCo19). Peritoneal dialysis in the time of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Alfano",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Clin. Kidney J.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01535-2",
"article-title": "Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force. Vitamin D deficiency, secondary hyperparathyroidism and respiratory insufficiency in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Mazziotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2285",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33549/physiolres.934492",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the immune system",
"author": "Paces",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Res.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.V100.3.917",
"article-title": "NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment",
"author": "Sohn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "917",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25982",
"article-title": "Thrombosis in COVID-19",
"author": "Hanff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1578",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hematol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom10081165",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Baralić, M., Gligorijević, N., Brković, V., Katrlík, J., Pažitná, L., Šunderić, M., Miljuš, G., Penezić, A., Dobrijević, Z., and Laušević, M. (2020). Fibrinogen Fucosylation as a Prognostic Marker of End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Biomolecules, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15882",
"article-title": "COVID-19 patient fibrinogen produces dense clots with altered polymerization kinetics, partially explained by increased sialic acid",
"author": "Moiseiwitsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2909",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000020447",
"article-title": "Dialysate glucose response phenotypes during peritoneal equilibration test and their association with cardiovascular death: A cohort study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20447",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/089686080902900509",
"article-title": "Quantification of free water transport during the peritoneal equilibration test",
"author": "Cnossen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "523",
"journal-title": "Perit. Dial. Int.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells12030351",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Baralić, M., Pažitna, L., Brković, V., Laušević, M., Gligorijević, N., Katrlik, J., Nedić, O., and Robajac, D. (2023). Prediction of mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis based on the fibrinogen mannosylation. Cells, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ndt/gfz174",
"article-title": "A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases",
"author": "Jager",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1803",
"journal-title": "Nephrol. Dial. Transplant.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Etiology of End-Stage Renal Disease and Arterial Stiffness among Hemodialysis Patients",
"author": "Daaboul",
"first-page": "2543262",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res. Int.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ndt/gfac008",
"article-title": "ERACODA Collaborators. Recovery of dialysis patients with COVID-19: Health outcomes 3 months after diagnosis in ERACODA",
"author": "Hemmelder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1140",
"journal-title": "Nephrol. Dial. Transplant.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00344-20",
"article-title": "COVID-19: An Immunopathological View",
"author": "Kadkhoda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00344-20",
"journal-title": "mSphere",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2016010112",
"article-title": "The Current State of Peritoneal Dialysis",
"author": "Mehrotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3238",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Soc. Nephrol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0896860820931235",
"article-title": "Acute peritoneal dialysis in COVID-19",
"author": "Parapiboon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Perit. Dial. Int.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcaa258",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and chronic renal disease: Clinical characteristics and prognosis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573403X14666180711124825",
"article-title": "Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Is there Any Relationship?",
"author": "Vallianou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Curr. Cardiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14173493",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Rossi, A.P., Muollo, V., Dalla-Valle, Z., Urbani, S., Pellegrini, M., El Ghoch, M., and Mazzali, G. (2022). The Role of Obesity, Body Composition, and Nutrition in COVID-19 Pandemia: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A systematic review of the pharmacotherapy of secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) in grades 3–5 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)",
"author": "Miedziaszczyk",
"first-page": "232",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268396",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "D’Ecclesiis, O., Gavioli, C., Martinoli, C., Raimondi, S., Chiocca, S., Miccolo, C., Bossi, P., Cortinovis, D., Chiaradonna, F., and Palorini, R. (2022). Vitamin D and SARS-CoV2 infection, severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"article-title": "Hypovitaminosis D and cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Jaiswal",
"first-page": "101019",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14235104",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Żmijewski, M.-A. (2022). Nongenomic Activities of Vitamin D. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9040967",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Park, M., Cook, A.-R., Lim, J.-T., Sun, Y., and Dickens, B.-L. (2020). A Systematic Review of COVID-19 Epidemiology Based on Current Evidence. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0263069",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Dror, A.-A., Morozov, N., Daoud, A., Namir, Y., Yakir, O., Shachar, Y., Lifshitz, M., Segal, E., Fisher, L., and Mizrachi, M. (2022). Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness. PLoS ONE, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.24018/ejmed.2021.3.4.943",
"article-title": "Prophylactic and Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D Supplementation in COVID-19: A Review",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Health Sci.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"article-title": "The link between COVID-19 and Vitamin D (VIVID): A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154753",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.760394",
"article-title": "Serum Phosphorus and Albumin in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: Interaction and Association with Mortality",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "760394",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23010193",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Surma, S., and Banach, M. (2021). Fibrinogen and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases-Review of the Literature and Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23062944",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Whyte, C.-S., Rastogi, A., Ferguson, E., Donnarumma, M., and Mutch, N.-J. (2022). The Efficacy of Fibrinogen Concentrates in Relation to Cryoprecipitate in Restoring Clot Integrity and Stability against Lysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13082559",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "Arenas-Jimenez, M.-D., González-Parra, E., Riera, M., Bello, A.R., López-Herradón, A., Cao, H., Hurtado, S., Collado, S., Ribera, L., and Barbosa, F. (2021). Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients with COVID-19, the Effect of Paricalcitol or Calcimimetics. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24054319",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "Akácsos-Szász, O.Z., Pál, S., Nyulas, K.I., Nemes-Nagy, E., Fárr, A.M., Dénes, L., Szilveszter, M., Bán, E.G., Tilinca, M.C., and Simon-Szabó, Z. (2023). Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061715",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Kiebalo, T., Holotka, J., Habura, I., and Pawlaczyk, K. (2020). Nutritional Status in Peritoneal Dialysis: Nutritional Guidelines, Adequacy and the Management of Malnutrition. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.03.018",
"article-title": "Serum albumin as a predictor of mortality in peritoneal dialysis: Comparisons with hemodialysis",
"author": "Mehrotra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Kidney Dis.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2011"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/9/2050"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Significance of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Overall Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
