Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity
et al., BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-021-00355-48, Jan 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
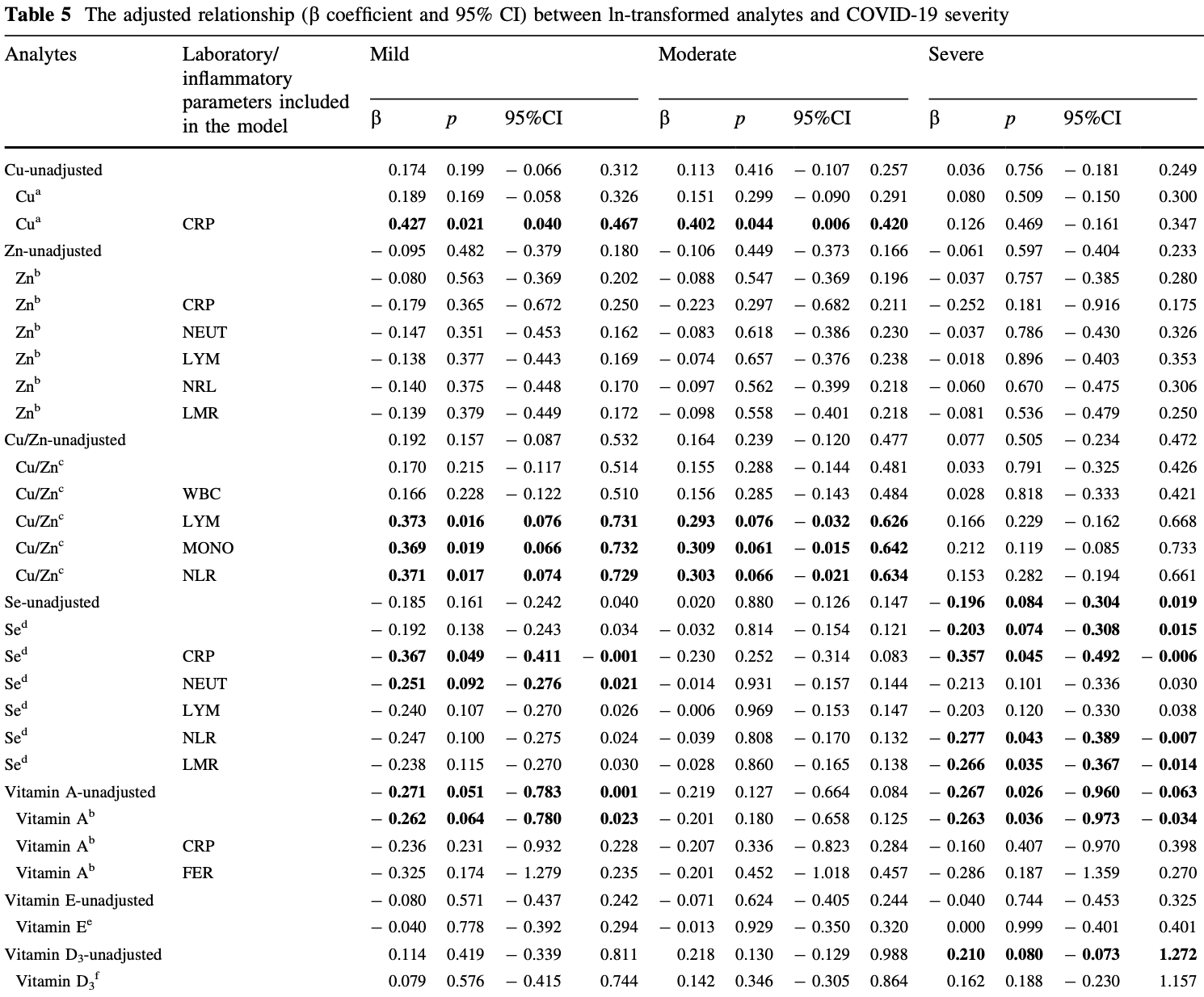
Prospective study of 155 COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia, showing that 25% of patients were zinc deficient (<0.693 μg/mL). There were no significant differences in zinc levels between the asymptomatic, mild, moderate and severe COVID-19 groups. Low zinc levels were not associated with COVID-19 severity even after adjusting for inflammatory markers. Only 7 patients had very low zinc levels (<0.5 μg/mL) so the study may have been underpowered to detect an association. Zinc deficiency was common among the COVID-19 patients, but the study did not find evidence of an association between zinc status and disease severity. In summary, 25% of patients were zinc deficient but zinc levels were not associated with COVID-19 severity in this study of 155 patients. The lack of association may be due to few patients with very low zinc levels. Authors provide results only for zinc levels as a continuous variable.
Al-Saleh et al., 7 Jan 2022, prospective, Saudi Arabia, peer-reviewed, median age 50.0, 8 authors, study period 3 June, 2020 - 11 July, 2020.
Contact: iman@kfshrc.edu.sa.
Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity
doi:10.1007/s10534-021-00355-4(
The role of micronutrient deficiency in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 has been reviewed in the literature; however, the data are limited and conflicting. This study investigated the association between the status of essential metals, vitamins, and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and disease severity. We recruited 155 patients, who were grouped into four classes based on the Adults guideline for the Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 at King Faisal Specialist & Research Centre (KFSH&RC): asymptomatic (N = 16), mild (N = 49), moderate (N = 68), and severe (N = 22). We measured serum levels of copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), selenium (Se), vitamin D 3 , vitamin A, vitamin E, total antioxidant capacity, and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Among the patients, 30%, 25%, 37%, and 68% were deficient in Se (\ 70.08 lg/L), Zn (\ 0.693 lg/mL), vitamin A (\ 0.343 lg/mL), and vitamin D 3 (\ 20.05 lg/L), respectively, and SOD activity was low. Among the patients, 28% had elevated Cu levels ([ 1.401 lg/mL, KFSH&RC upper reference limit). Multiple regression analysis revealed an 18% decrease in Se levels in patients with severe symptoms, which increased to 30% after adjusting the model for inflammatory markers. Regardless of inflammation, Se was independently associated with COVID-19 severity. In contrast, a 50% increase in Cu levels was associated with disease severity only after adjusting for C-reactive protein, reflecting its possible inflammatory and pro-oxidant role in COVID-19 pathogenesis. We noted an imbalance in the ratio between Cu and Zn, with * 83% of
Author contributions IAS-study design, data analysis, results interpretation and writing the manuscript. NA-collection of clinical data. HA-methodology/validation. REmethodology/validation. MS-sampling design. FA-samples provision. RB-methodology. MA-resources.
Conflict of interest The authors reported no potential conflict of interest.
References
Al-Alyani, Ha, On, Alani, Sadat-Ali, Vitamin D deficiency in Saudi Arabians: a reality or simply hype: a meta-analysis (2008-2015), J Family Community Med, doi:10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_73_17
Alsafar, Grant, Hijazi, Uddin, Alkaabi et al., COVID-19 disease severity and death in relation to vitamin D status among SARS-CoV-2-positive UAE residents, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13051714
Anurag, Jha, Kumar, Differential white blood cell count in the COVID-19: a cross-sectional study of 148 patients, Diabet Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.029
Asl, Nikfarjam, Zolbanin, Nassiri, Jafari, Immunopharmacological perspective on zinc in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107630
Bae, Kim, Mini-review on the roles of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in the immune system against COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25225346
Bahi, Boyvin, Me ´ite ´s, Boh, Yeo et al., Assessments of serum copper and zinc concentration, and the Cu/Zn ratio determination in patients with multidrug resistant pulmonary tuberculosis (MDR-TB) in Co ˆte d'Ivoire, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2343-7
Banerjee, Mondal, Das, Ray, Neutrophilic inflammatory response and oxidative stress in premenopausal women chronically exposed to indoor air pollution from biomass burning, Inflammation, doi:10.1007/s10753-011-9360-2
Barciszewska, Elucidating of oxidative distress in COVID-19 and methods of its prevention, Chem Biol Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109501
Barffour, Schulze, Kalungwana, Moss, West et al., Relative contributions of malaria, inflammation, and deficiencies of iron and vitamin A to the burden of anemia during low and high malaria seasons in rural zambian children, J Pediatr, doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.06.039
Barocas, So-Armah, Cheng, Lioznov, Baum et al., Zinc deficiency and advanced liver fibrosis among HIV and hepatitis C co-infected antiretroviral naı ¨ve persons with alcohol use in Russia, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0218852
Beck, Nelson, Shi, Van Dael, Schiffrin et al., Selenium deficiency increases the pathology of an influenza virus infection, FASEB J
Beltra ´n-Garcı ´a, Osca-Verdegal, Pallardo, Ferreres, Rodrı ´guez et al., Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: the potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9100936
Bermano, Me ´plan, Mercer, Hesketh, Selenium and viral infection: are there lessons for COVID-19?, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/s0007114520003128
Bo, Durazzo, Gambino, Berutti, Milanesio et al., Associations of dietary and serum copper with inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolic variables in adults, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/138.2.305
Booth, Golly, Sacheck, Roubenoff, Dallal et al., Effect of vitamin E supplementation on vitamin K status in adults with normal coagulation status, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.1.143
Bourbour, Dahka, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on coronavirus, Arch Physiol Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188
Branda ˜o, Chiamolera, Biscolla, Lima, De et al., No association between vitamin D status and COVID-19 infection in Sa ˜o Paulo, Brazil, Arch Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.20945/2359-3997000000343
Brenner, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent COVID-19 infections and deaths-accumulating evidence from epidemiological and intervention studies calls for immediate action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020411
Burk, Selenium, an antioxidant nutrient, Nutr Clin Care, doi:10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00006.x
Campi, Gennari, Merlotti, Mingiano, Frosali et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: a prospective study in Italy, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7
Chan, Kok, Zhu, Chu, To et al., Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902
Chan, Yuan, Kok, To, Chu et al., A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30154-9
Charoenngam, Shirvani, Holick, Vitamin D and its potential benefit for the COVID-19 pandemic, Endocr Pract, doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2021.03.006
Danwang, Endomba, Nkeck, Wouna, Robert et al., A meta-analysis of potential biomarkers associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Biomark Res, doi:10.1186/s40364-020-00217-0
Davoudi, Najafi, Aarabi, Tayebi, Nikaeen et al., Lack of association between vitamin D insufficiency and clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19 infection, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06168-7
De Roman ˜a, Olivares, Uauy, Araya, Risks and benefits of copper in light of new insights of copper homeostasis, J Trace Elem Med Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.11.004
Djoko, Ong, Walker, Mcewan, The role of copper and zinc toxicity in innate immune defense against bacterial pathogens, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.R115.647099
Domingo, Marque, The effects of some essential and toxic metals/metalloids in COVID-19: a review, Food Chem Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112161
Fedele, Francesco, Riso, Collo, Obesity, malnutrition, and trace element deficiency in the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: an overview, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111016
Fernandes, De Brito, Reis, Sato, Pereira, SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses: what does oxidative stress have to do with it?, Oxid Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2020/8844280
Forcados, Muhammad, Oladipo, Makama, Meseko, Metabolic implications of oxidative stress and inflammatory process in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: therapeutic potential of natural antioxidants, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.654813
Gadotti, Lipinski, Vasconcellos, Marqueze, Cunha et al., Susceptibility of the patients infected with Sars-Cov2 to oxidative stress and possible interplay with severity of the disease, Free Radic Biol Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.044
Gaziano, Pistoia, Campione, Fontana, Marino et al., Immunomodulatory agents as potential therapeutic or preventive strategies for COVID-19, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202106_26061
Ghiselli, Serafini, Natella, Scaccini, Total antioxidant capacity as a tool to assess redox status: critical view and experimental data, Free Radic Biol Med, doi:10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00394-4
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A review of micronutrients and the immune system-working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Gonc ¸alves, Gonc ¸alves, Guarnieri, Risegato, Guimara ˜es et al., Association between low zinc levels and severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome by new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Nutr Clin Pract, doi:10.1002/ncp.10612
Goud, Bai, Hm, A multiple-hit hypothesis involving reactive oxygen species and myeloperoxidase explains clinical deterioration and fatality in COVID-19, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.51811
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7064240
Grove, Osokogu, Al-Khudairy, Mehrabian, Zanganeh et al., Association between vitamin D supplementation or serum vitamin D level and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 including clinical course, morbidity and mortality outcomes? A systematic review, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043737
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in china, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092101
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabet Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Hawkins, Charles, Mehaffey, Socio-economic status and COVID-19-related cases and fatalities, Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2020.09.016
Henry, De Oliveira, Benoit, Plebani, Lippi, Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, Clin Chem Lab Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0369
Herta, Berg, COVID-19 and the liver-lessons learned, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/liv.14854
Hoffmann, Berry, The influence of selenium on immune responses, Mol Nutr Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.200700330
Hordyjewska, Popiołek, Kocot, The many ''faces'' of copper in medicine and treatment, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-014-9736-5
Huang, Liu, Qi, Brand, Zheng, Role of vitamin A in the immune system, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm7090258
Huang, Rose, Hoffmann, The role of selenium in inflammation and immunity: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2011.4145
Ivanov, Bartosch, Isaguliants, Oxidative stress in infection and consequent disease, Oxid Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2017/3496043
Jolliffe, Camargo, Jr, Sluyter, Aglipay et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabet Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00051-6
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Karkhanei, Ghane, Mehri, Evaluation of oxidative stress level: total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897
Khatiwada, Subedi, A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Curr Nutr Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4
Larson, Guo, Williams, Young, Ismaily et al., Approaches to assess vitamin a status in settings of inflammation: biomarkers reflecting inflammation and nutritional determinants of anemia (BRINDA) project, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10081100
Le, Kesayan, Chang, Rose, Cryptogenic intracranial hemorrhagic strokes associated with hypervitaminosis E and acutely elevated a-tocopherol levels, J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104747
Li, Fan, Lai, Han, Li et al., Coronavirus infections and immune responses, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25685
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Majeed, Nagabhushanam, Gowda, Mundkur, An exploratory study of selenium status in healthy individuals and in patients with COVID-19 in a south Indian population: the case for adequate selenium status, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111053
Malavolta, Piacenza, Basso, Giacconi, Costarelli et al., Serum copper to zinc ratio: relationship with aging and health status, Mech Ageing Dev, doi:10.1016/j.mad.2015.01.004
Man, Rajnoveanu, Motoc, Bondor, Chis et al., Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelets-to-lymphocyte ratio, and eosinophils correlation with high-resolution computer tomography severity score in COVID-19 patients, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252599
Maqsood, Dancheck, Gamble, Palafox, Ricks et al., Vitamin A deficiency and inflammatory markers among preschool children in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, Nutr J, doi:10.1186/1475-2891-3-21
Marcinowska-Suchowierska, Kupisz-Urban ´ska, Łukaszkiewicz, Płudowski, Jones, Vitamin D toxicity-A clinical perspective, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2018.00550
Mawson, Croft, Gonzalez-Fernandez, Liver damage and exposure to toxic concentrations of endogenous retinoids in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 disease: hypothesis, Viral Immunol, doi:10.1089/vim.2020.0330
Mawson, Role of fat-soluble vitamins A and D in the pathogenesis of influenza: a new perspective, ISRN Infect Dis, doi:10.5402/2013/246737
Mitra, Alvarez, Wahed, Fuchs, Stephensen, Predictors of serum retinol in children with shigellosis, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/68.5.1088
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med, doi:10.1177/2050312121991246
Nelson, Shi, Van Dael, Schiffrin, Blum et al., Host nutritional selenium status as a driving force for influenza virus mutations, FASEB J
Oh, Shin, Choi, Kim, Park et al., Assessment of 7 trace elements in serum of patients with nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease, J Trace Elem Med Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.02.004
Oscanoa, Amado, Vidal, Laird, Ghashut et al., The relationship between the severity and mortality of SARS-CoV-2 infection and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration-a metaanalysis, Adv Respir Med, doi:10.5603/ARM.a2021.0037
Owen, Dewald, Vitamin E toxicity
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12103198
Peng, Liu, Zheng, Lu, Hou et al., Immunological aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the putative beneficial role of vitamin-D, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22105251
Raha, Mallick, Basak, Duttaroy, Is copper beneficial for COVID-19 patients?, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109814
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Adv Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmz013
Rubin, Ross, Stephensen, Bohn, Tanumihardjo, Metabolic effects of inflammation on vitamin A and carotenoids in humans and animal models, Adv Nutr, doi:10.3945/an.116.014167
Rubio, Herna ´ndez-Ruiz, Martinez-Subiela, Tvarijonaviciute, Ceron, Spectrophotometric assays for total antioxidant capacity (TAC) in dog serum: an update, BMC Vet Res, doi:10.1186/s12917-016-0792-7
Sarohan, COVID-19: endogenous retinoic acid theory and retinoic acid depletion syndrome, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110250
Sattler, The role of the immune system beyond the fight against infection, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-57613-8_1
Sepehri, Mirzaei, Sargazi, Sargazi, Mishkar et al., Essential and toxic metals in serum of individuals with active pulmonary tuberculosis in an endemic region, J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis, doi:10.1016/j.jctube.2017.01.001
Shah, Saxena, Mavalankar, Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: a meta-analysis, QJM: Int J Med, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab009
Shi, Wang, Shao, Huang, Gan et al., COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-020-0530-3
Skalny, Timashev, Aschner, Aaseth, Chernova et al., Serum zinc, copper, and other biometals are associated with COVID-19 severity markers, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11040244
Skrobot, Demkow, Wachowska, Immunomodulatory role of vitamin D: a review, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/5584_2018_246
Tang, Smit, Selected vitamins in HIV infection: a review, AIDS Patient Care STDS, doi:10.1089/apc.1998.12.263
Trasino, A role for retinoids in the treatment of COVID-19?, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13354
Ukleja, Scolapio, Mcconnell, Spivey, Dickson et al., Nutritional assessment of serum and hepatic vitamin A levels in patients with cirrhosis, J Parenter Enter Nutr, doi:10.1177/0148607102026003184
Vogel-Gonza ´lez, Tallo, -Parra, Herrera-Ferna ´ndez, ´rez-Vilaro et al., Low zinc levels at admission associates with poor clinical outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020562
Watkins, Lemonovich, Salata, An update on the association of vitamin D deficiency with common infectious diseases, Can J Physiol Pharmacol, doi:10.1139/cjpp-2014-0352
Weiss, Carver, Role of divalent metals in infectious disease susceptibility and outcome, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2017.01.018
Weitkunat, Wildner, Exploratory causal modeling in epidemiology: are all factors created equal?, J Clin Epidemiol
Wenzhong, Hualan, COVID-19: captures iron and generates reactive oxygen species to damage the human immune system, Autoimmunity, doi:10.1080/08916934.2021.1913581
Wessels, Maywald, Rink, Zinc as a gatekeeper of immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9121286
Wilhelm, Benjamin, Rainer, Interpretation of statistical significance-exploratory versus confirmative testing in clinical trials, epidemiological studies, metaanalyses and toxicological screening (using Ginkgo biloba as an example), J Clin Exp Pharmacol
Winbauer, Pingree, Nuttall, Evaluating serum alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) in terms of a lipid ratio, Ann Clin Lab Sci
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Wu, Meydani, Vitamin E, immune function, and protection against infection
Wu, Wang, Li, Meng, Jie et al., Circulating white blood cells and lung function impairment: the observational studies and Mendelian randomization analysis, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1948603
Younesian, Khodabakhshi, Abdolahi, Norouzi, Behnampour et al., Decreased serum selenium levels of COVID-19 patients in comparison with healthy individuals, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w
Yu, Du, Ojcius, Pan, Jiang, Measures for diagnosing and treating infections by a novel coronavirus responsible for a pneumonia outbreak originating in Wuhan, China, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.01.003
Zeng, Yang, Yuan, Wang, Cheng, Associations of essential and toxic metals/metalloids in whole blood with both disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202002346RR
Zeng, Zhang, Wang, Yang, Cheng, Urinary trace elements in association with disease severity and outcome in patients with COVID-19, Environ Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110670
Zhang, Liu, Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: a systematic review, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25707
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095
˜a, Lee, Thiele, A delicate balance: homeostatic control of copper uptake and distribution, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/129.7.1251
alsaleh
