Serum Zinc, Copper, and Other Biometals Are Associated with COVID-19 Severity Markers
et al., Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11040244, Apr 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
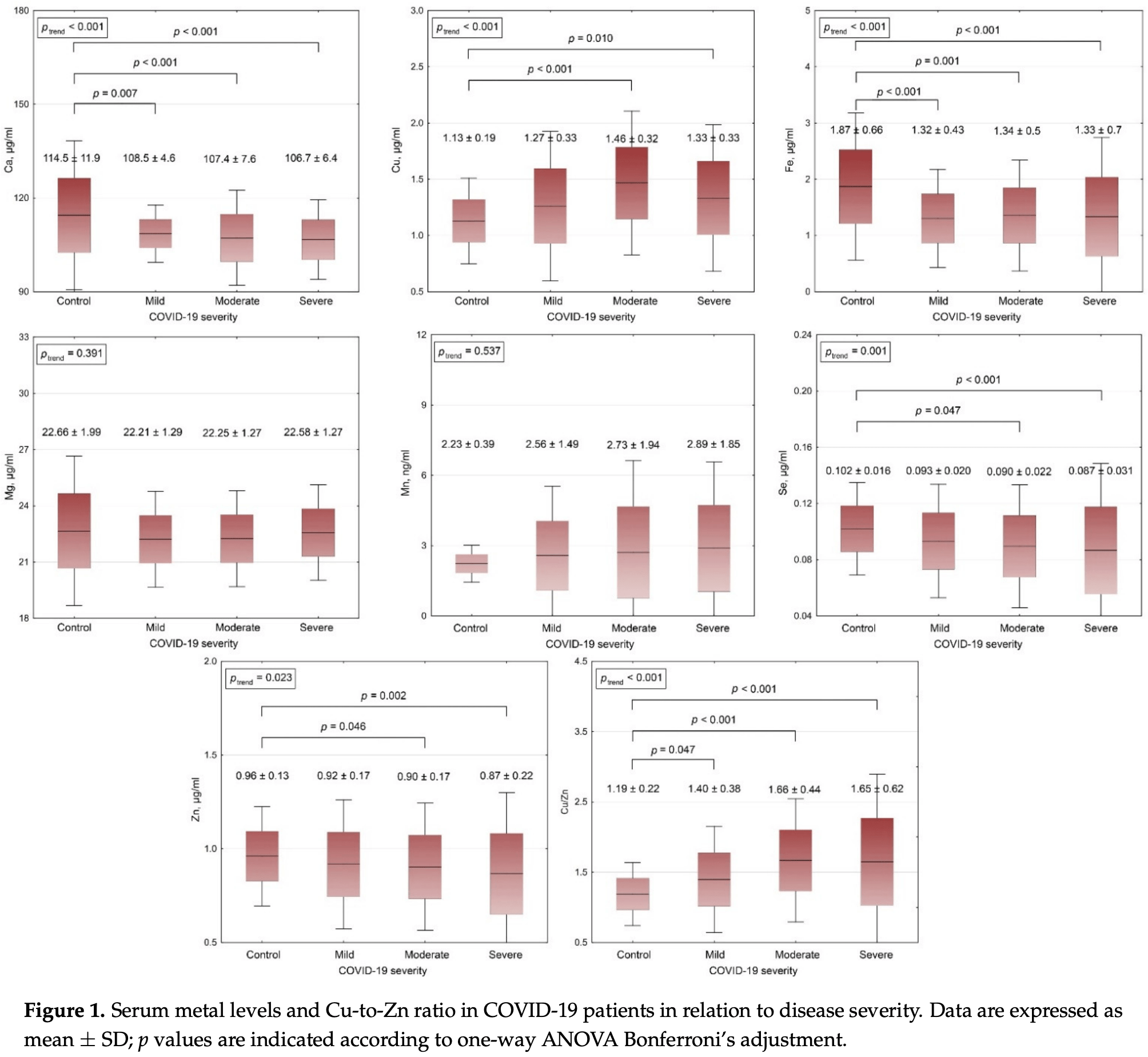
Analysis of serum metal levels in 150 COVID-19 patients and 44 controls, finding that COVID-19 severity was associated with lower serum Ca, Fe, Se, Zn levels when compared to controls.
Study covers selenium and zinc.
Skalny et al., 15 Apr 2021, prospective, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Serum Zinc, Copper, and Other Biometals Are Associated with COVID-19 Severity Markers
Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11040244
The objective of the present study was to evaluate of serum metal levels in COVID-19 patients with different disease severity, and to investigate the independent association between serum metal profile and markers of lung damage. The cohort of COVID-19 patients consisted of groups of subjects with mild, moderate, and severe illness, 50 examinees each. Forty-four healthy subjects of the respective age were involved in the current study as the control group. Serum metal levels were evaluated using inductively-coupled plasma mass-spectrometry. Examination of COVID-19 patients demonstrated that heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, C-reactive protein levels, as well as lung damage increased significantly with COVID-19 severity, whereas SpO 2 decreased gradually. Increasing COVID-19 severity was also associated with a significant gradual decrease in serum Ca, Fe, Se, Zn levels as compared to controls, whereas serum Cu and especially Cu/Zn ratio were elevated. No significant group differences in serum Mg and Mn levels were observed. Serum Ca, Fe, Se, Zn correlated positively with SpO 2 , being inversely associated with fever, lung damage, and C-reactive protein concentrations. Opposite correlations were observed for Cu and Cu/Zn ratio. In regression models, serum Se levels were inversely associated with lung damage independently of other markers of disease severity, anthropometric, biochemical, and hemostatic parameters. Cu/Zn ratio was also considered as a significant predictor of lower SpO 2 in adjusted regression models. Taken together, these findings demonstrated that metal metabolism significantly interferes with COVID-19 pathogenesis, although the causal relations as well as precise mechanisms are yet to be characterized.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization: A.V.S., P.S.T., A.A.T.; methodology: A.V.S., R.L.; validation: J.A., M.A., R.L., A.T.; formal analysis: L.N.C., J.A., A.R.G., S.V.N.; investigation: L.N.C., V.E.B., S.V.N.; resources: A.A.S., V.V.F., P.V.G.; data curation: A.T., A.A.T.; writing-original draft preparation: P.S.T., L.N.C., V.E.B., A.R.G., S.V.N., A.A.S., V.V.F., A.A.T.; writing-review & editing: A.V.S., P.V.G., M.A., J.A., R.L., A.T.; visualization: A.A.T.; supervision: A.V.S., P.S.T.; project administration: A.V.S., P.S.T., A.A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082358
Anuk, Polat, Akdas, Erol, Tanacan et al., The Relation Between Trace Element Status (Zinc, Copper, Magnesium) and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Infection during Pregnancy, Biol. Trace Element Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02496-y
Bermano, Méplan, Mercer, Hesketh, Selenium and viral infection: Are there lessons for COVID-19?, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114520003128
Bolondi, Russo, Gamberini, Circelli, Meca et al., Iron metabolism and lymphocyte characterisation during Covid-19 infection in ICU patients: An observational cohort study, World J. Emerg. Surg, doi:10.1186/s13017-020-00323-2
Cappellini, Brivio, Casati, Cavallero, Contro et al., Low levels of total and ionized calcium in blood of COVID-19 patients, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0611
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001250
Di Filippo, Formenti, Giustina, Hypocalcemia: The quest for the cause of a major biochemical feature of COVID-19, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02525-9
Di Filippo, Formenti, Rovere-Querini, Carlucci, Conte et al., Hypocalcemia is highly prevalent and predicts hospitalization in patients with COVID-19, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02383-5
Fooladi, Matin, Mahmoodpoor, Copper as a potential adjunct therapy for critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin. Nutr. ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.022
Gonçalves, Gonçalves, Guarnieri, Risegato, Guimarães et al., Association Between Low Zinc Levels and Severity of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by New Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Nutr. Clin. Pr, doi:10.1002/ncp.10612
Heller, Sun, Hackler, Seelig, Seibert et al., Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker, Redox Biol
Henderson, Canna, Schulert, Volpi, Lee et al., On the Alert for Cytokine Storm: Immunopathology in COVID-19, Arthritis Rheumatol, doi:10.1002/art.41285
Hiffler, Rakotoambinina, Selenium and RNA Virus Interactions: Potential Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19), Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.00164
Im, Je, Baek, Chung, Kwon et al., Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Laine, Tuomainen, Salonen, Virtanen, Serum copper-to-zinc-ratio and risk of incident infection in men: The Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study, Eur. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-020-00644-1
Liu, Han, Wu, Gong, Tian, Prevalence and predictive value of hypocalcemia in severe COVID-19 patients, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.05.029
Majeed, Nagabhushanam, Gowda, Mundkur, An Exploratory Study of Selenium Status in Normal Subjects and COVID-19 Patients in South Indian population: Case for Adequate Selenium Status: Selenium Status in COVID-19 Patients, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111053
Malavoltarobertina, Giacconi, Piacenza, Santarelli, Cipriano et al., Plasma copper/zinc ratio: An inflammatory/nutritional biomarker as predictor of all-cause mortality in elderly population, Biogerontology, doi:10.1007/s10522-009-9251-1
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Munblit, Nekliudov, Bugaeva, Blyuss, Kislova et al., StopCOVID cohort: An observational study of 3,480 patients admitted to the Sechenov University hospital network in Moscow city for suspected COVID-19 infection, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1535
Osredkar, Sustar, Copper and Zinc, Biological Role and Significance of Copper/Zinc Imbalance, J. Clin. Toxicol, doi:10.4172/2161-0495.S3-001
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Pawar, Rongioletti et al., Zinc and COVID-19: Basis of Current Clinical Trials, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9
Pereira, Campos, Bogo, Copper toxicology, oxidative stress and inflammation using zebrafish as experimental model, J. Appl. Toxicol, doi:10.1002/jat.3303
Petrakis, Margină, Tsarouhas, Tekos, Stan et al., Obesity-A risk factor for increased COVID-19 prevalence, severity and lethality (Review), Mol. Med. Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11127
Richardson, Lovegrove, Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: A UK perspective, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711452000330X
Shah, Frost, Aaron, Donovan, Drakesmith et al., Systemic hypoferremia and severity of hypoxemic respiratory failure in COVID-19, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03051-w
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19 (Review), Int. J. Mol. Med
Sonnweber, Boehm, Sahanic, Pizzini, Aichner et al., Persisting alterations of iron homeostasis in COVID-19 are associated with non-resolving lung pathologies and poor patients' performance: A prospective observational cohort study, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-020-01546-2
Torres, Alcubilla, González-Cordón, Inciarte, Chumbita et al., COVID19 Hospital Clínic Infectious Diseases research group. Impact of low serum calcium at hospital admission on SARS-CoV-2 infection outcome, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.207
Tsatsakis, Calina, Falzone, Petrakis, Mitrut et al., SARS-CoV-2 pathophysiology and its clinical implications: An integrative overview of the pharmacotherapeutic management of COVID-19, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111769
Velthuis, Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn2+ Inhibits Coronavirus and Arterivirus RNA Polymerase Activity In Vitro and Zinc Ionophores Block the Replication of These Viruses in Cell Culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The Potential Impact of Zinc Supplementation on COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839
Yang, Ma, Wu, Han, Zheng et al., Low serum calcium and phosphorus and their clinical performance in detecting COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26515
Yao, Paguio, Dee, Tan, Moulick et al., The Minimal Effect of Zinc on the Survival of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Observational Study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082
Yasui, Yasui, Suzuki, Saitou, Yamamoto et al., Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment-relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095
Zhao, Huang, Dai, Feng, Liu et al., Serum Iron Level as a Potential Predictor of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Severity and Mortality: A Retrospective Study, Open Forum Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa250
Zhou, Chen, Ji, He, Xue, Increased Serum Levels of Hepcidin and Ferritin Are Associated with Severity of COVID-19, Med. Sci. Monit, doi:10.12659/MSM.926178
Zhou, Chen, Wang, Zhao, Wei et al., Low serum calcium: A new, important indicator of COVID-19 patients from mild/moderate to severe/critical, Biosci. Rep, doi:10.1042/BSR20202690
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo11040244",
"ISSN": [
"2218-1989"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040244",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The objective of the present study was to evaluate of serum metal levels in COVID-19 patients with different disease severity, and to investigate the independent association between serum metal profile and markers of lung damage. The cohort of COVID-19 patients consisted of groups of subjects with mild, moderate, and severe illness, 50 examinees each. Forty-four healthy subjects of the respective age were involved in the current study as the control group. Serum metal levels were evaluated using inductively-coupled plasma mass-spectrometry. Examination of COVID-19 patients demonstrated that heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, C-reactive protein levels, as well as lung damage increased significantly with COVID-19 severity, whereas SpO2 decreased gradually. Increasing COVID-19 severity was also associated with a significant gradual decrease in serum Ca, Fe, Se, Zn levels as compared to controls, whereas serum Cu and especially Cu/Zn ratio were elevated. No significant group differences in serum Mg and Mn levels were observed. Serum Ca, Fe, Se, Zn correlated positively with SpO2, being inversely associated with fever, lung damage, and C-reactive protein concentrations. Opposite correlations were observed for Cu and Cu/Zn ratio. In regression models, serum Se levels were inversely associated with lung damage independently of other markers of disease severity, anthropometric, biochemical, and hemostatic parameters. Cu/Zn ratio was also considered as a significant predictor of lower SpO2 in adjusted regression models. Taken together, these findings demonstrated that metal metabolism significantly interferes with COVID-19 pathogenesis, although the causal relations as well as precise mechanisms are yet to be characterized.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"metabo11040244"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skalny",
"given": "Anatoly V.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timashev",
"given": "Peter S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2619-1656",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aschner",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7518-5703",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aaseth",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chernova",
"given": "Lyubov N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belyaev",
"given": "Vladimir E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grabeklis",
"given": "Andrey R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Notova",
"given": "Svetlana V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lobinski",
"given": "Ryszard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3824-2462",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsatsakis",
"given": "Aristides",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Svistunov",
"given": "Andrey A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fomin",
"given": "Victor V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinkov",
"given": "Alexey A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glybochko",
"given": "Peter V.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Metabolites",
"container-title-short": "Metabolites",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-15T16:11:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618503060000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-15T17:43:04Z",
"timestamp": 1618508584000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012190",
"award": [
"075-15-2020-926"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T07:46:37Z",
"timestamp": 1715586397521
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 63,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618444800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/11/4/244/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "244",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.41285",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2020.111769",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1535",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2020.11127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711452000330X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082358",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa250",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-020-01546-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ncp.10612",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072098",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20202690",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114520003128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.00164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13017-020-00323-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.926178",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03051-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02496-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0611",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.05.029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02525-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.207",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26515",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02383-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jat.3303",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/2161-0495.S3-001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10522-009-9251-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00644-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "Temporary Methodologic Guidelines “Prophylaxis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19), v. 7 (03.06. 2020)\nhttp://edu.rosminzdrav.ru/fileadmin/user_upload/specialists/COVID-19/MR_COVID-19_v7.pdf"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/11/4/244"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Serum Zinc, Copper, and Other Biometals Are Associated with COVID-19 Severity Markers",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
