Early treatment with fluvoxamine, bromhexine, cyproheptadine, and niclosamide to prevent clinical deterioration in patients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
et al., eClinicalMedicine, 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102517, NCT05087381, Mar 2024
56th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2025, now with p = 0.0069 from 7 studies.
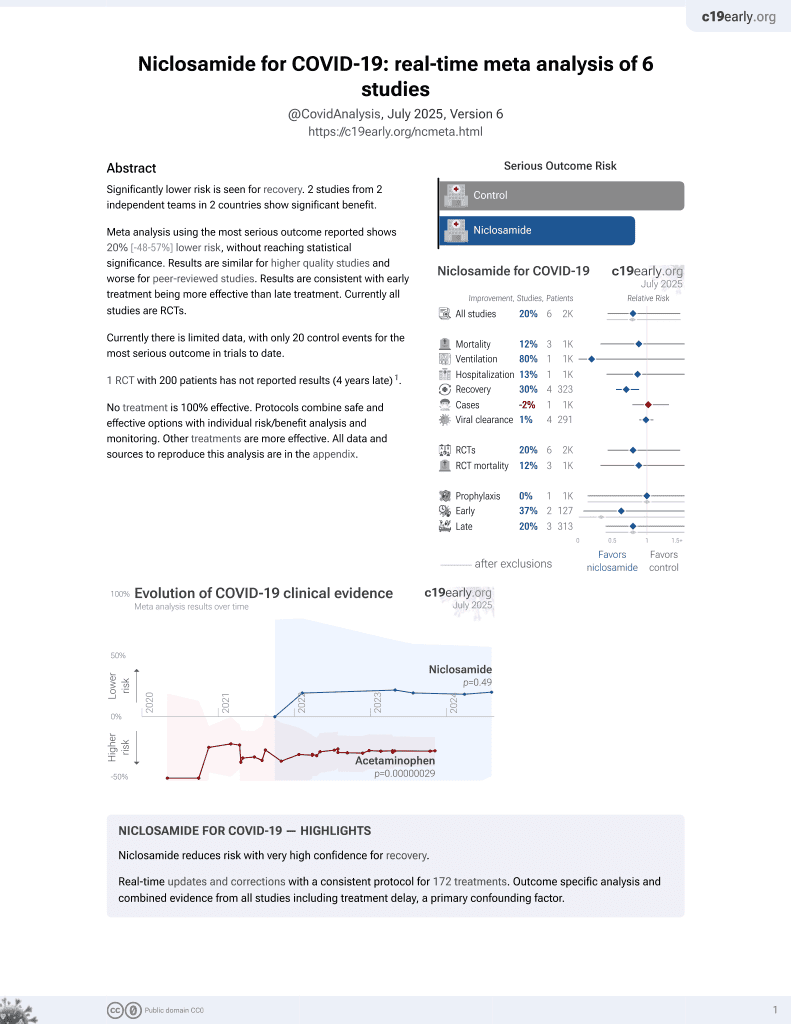
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 995 outpatients showing significantly lower progression with early treatment within 48 hours using fluvoxamine, fluvoxamine+bromhexine, fluvoxamine+cyproheptadine, and niclosamide+bromhexine.
70% of patients received treatment within 12 hours of symptom onset.
Treatments groups showed significantly lower long COVID (PASC). The combined treatment groups showed significantly lower viral load as early as day 3. The 3 combination arms were superior to fluvoxamine alone.
The study was open-label. 593 out of 1,900 randomized participants did not receive the treatment, mostly due to inability to confirm eligibility, however baseline characteristics were similar for these patients.
There was a very high hospitalization rate in the control arm. Authors note that the majority of cases were mild - the threshold for hospitalization may have been very low (in some places/times all cases were hospitalized). Authors also note that the patients requiring high flow oxygen all had the delta/alpha variants, and that the population has many health disparities.
Publication was over 500 days after the 90 day followup.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 98.0% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 32 of 336 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 97.6% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 27 of 336 (8.0%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 96.6% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 19 of 336 (5.7%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 9.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.6% lower, RR 0.004, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 171 of 336 (50.9%), NNT 2.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.6% lower, RR 0.004, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 150 of 336 (44.6%), NNT 2.2, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.4% lower, RR 0.006, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 117 of 336 (34.8%), NNT 2.9, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 9.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 98.0% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 32 of 336 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 97.6% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 27 of 336 (8.0%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 14.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 96.6% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 172 (0.0%), control 19 of 336 (5.7%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 9.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 59.3% lower, RR 0.41, p < 0.001, treatment 70 of 172 (40.7%), control 336 of 336 (100.0%), NNT 1.7, day 90.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wannigama et al., 14 Mar 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Thailand, peer-reviewed, 29 authors, study period 1 October, 2021 - 21 June, 2022, average treatment delay 0.5 days, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with bromhexineDOSE:B8MG:BID:D1-10) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial NCT05087381 (history).
Contact: Dhammika.L@chula.ac.th, Phatthranit.pha@mahidol.edu, gochi.akk@gmail.com.
Early treatment with fluvoxamine, bromhexine, cyproheptadine, and niclosamide to prevent clinical deterioration in patients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102517
Background Repurposed drugs with host-directed antiviral and immunomodulatory properties have shown promise in the treatment of COVID-19, but few trials have studied combinations of these agents. The aim of this trial was to assess the effectiveness of affordable, widely available, repurposed drugs used in combination for treatment of COVID-19, which may be particularly relevant to low-resource countries.
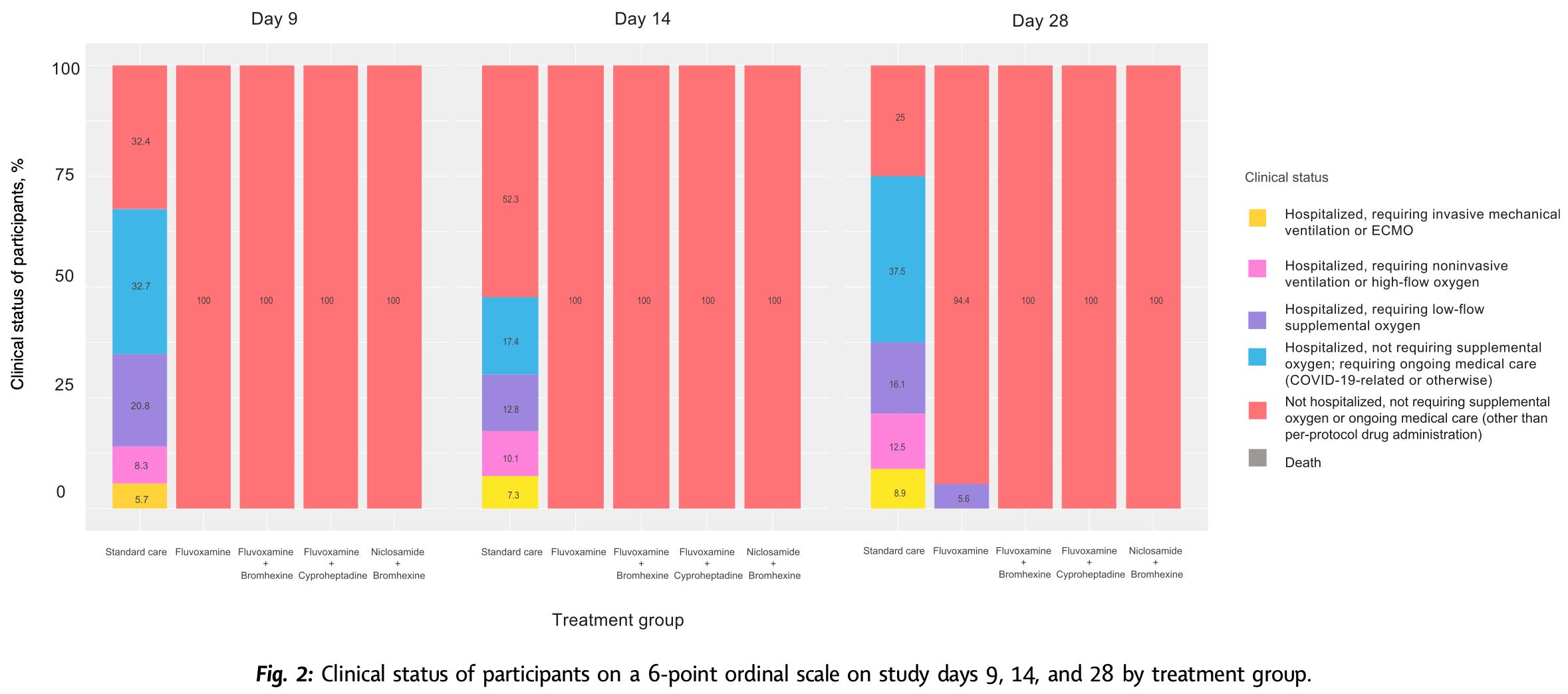
Methods We conducted an open-label, randomized, outpatient, controlled trial in Thailand from October 1, 2021, to June 21, 2022, to assess whether early treatment within 48-h of symptoms onset with combinations of fluvoxamine, bromhexine, cyproheptadine, and niclosamide, given to adults with confirmed mild SARS-CoV-2 infection, can prevent 28-day clinical deterioration compared to standard care. Participants were randomly assigned to receive treatment with fluvoxamine alone, fluvoxamine + bromhexine, fluvoxamine + cyproheptadine, niclosamide + bromhexine, or standard care. The primary outcome measured was clinical deterioration within 9, 14, or 28 days using a 6-point ordinal scale. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05087381). Findings Among 1900 recruited, a total of 995 participants completed the trial. No participants had clinical deterioration by day 9, 14, or 28 days among those treated with fluvoxamine plus bromhexine (0%), fluvoxamine plus cyproheptadine (0%), or niclosamide plus bromhexine (0%). Nine participants (5.6%) in the fluvoxamine arm had clinical deterioration by day 28, requiring low-flow oxygen. In contrast, most standard care arm participants had clinical deterioration by 9, 14, and 28 days. By day 9, 32.7% (110) of patients in the standard care arm had been hospitalized without requiring supplemental oxygen but needing ongoing medical care. By day 28, this percentage increased to 37.5% (21). Additionally, 20.8% (70) of patients in the standard care arm required low-flow oxygen by day 9, and 12.5% ( 16 ) needed non-invasive or mechanical ventilation by day 28. All treated groups significantly differed from the standard care group by days 9, 14, and 28 (p < 0.0001). Also, by day 28, the three 2-drug treatments were significantly better than the fluvoxamine arm (p < 0.0001). No deaths occurred in any study group. Compared to standard care, participants treated with the combination agents had significantly decreased
Cameron Hurst data curation, statistical analysis, supervision, critical review, and editing of the manuscript. Phatthranit Phattharapornjaroen supervision, conception, investigation, funding acquisition, data curation, critical review, and editing of the manuscript. Parichart Hongsing supervision, conception, investigation, data curation, critical review, and editing of the manuscript. Natchalaikorn Sirichumroonwit supervision, conception, investigation, funding acquisition, data curation, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Kanokpoj Chanpiwat supervision, conception, investigation, funding acquisition, data curation, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Ali Hosseini Rad S. M. supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Robin James Storer supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Puey Ounjai supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Phitsanuruk Kanthawee supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Natharin Ngamwongsatit supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Rosalyn Kupwiwat clinical data collection, supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Chaisit Kupwiwat clinical data collection, supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. James Michael Brimson clinical data collection, supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Naveen Kumar Devanga Ragupathi supervision, critical review and editing of the manuscript. Sirirat..
References
Abdulamir, Gorial, Saadi, A randomised controlled trial of effectiveness and safety of Niclosamide as add on therapy to the standard of care measures in COVID-19 management, Ann Med Surg
Andrews, Stowe, Kirsebom, Effectiveness of COVID-19 booster vaccines against COVID-19-related symptoms, hospitalization and death in England, Nat Med
Ansarin, Tolouian, Ardalan, Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a randomized clinical trial, Bioimpacts
Anupong, Chadsuthi, Hongsing, Exploring indoor and outdoor dust as a potential tool for detection and monitoring of COVID-19 transmission, iScience
Anupong, Chantanasaro, Wilasang, Modeling vaccination strategies with limited early COVID-19 vaccine access in low-and middle-income countries: a case study of Thailand, Infect Dis Model
Bai, Shen, Zhang, Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir for COVID-19 treatment, Viruses
Cai, Yang, Liu, Experimental treatment with favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study, Engineering
Cairns, Dulko, Griffiths, Efficacy of niclosamide vs placebo in SARS-CoV-2 respiratory viral clearance, viral shedding, and duration of symptoms among patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Canas, Molteni, Deng, Profiling post-COVID syndrome across different variants of SARS-CoV-2, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.7.28.22278159
Chasco, Dukes, Jones, Comellas, Hoffman et al., Brain fog and fatigue following COVID-19 infection: an exploratory study of patient experiences of long COVID, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Clarkson, Fan, Joe, A remark on algorithm 643: fexact: an algorithm for performing Fisher's exact test in r x c contingency tables, ACM Trans Math Softw
Cloutier, Allaeys, Marcoux, Platelets release pathogenic serotonin and return to circulation after immune complexmediated sequestration, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Conway, Mackman, Warren, Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy, Nat Rev Immunol
Cramer, Haller, Dobos, Lauche, A systematic review and meta-analysis estimating the expected dropout rates in randomized controlled trials on yoga interventions, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Cuerdo, Ogbac, Tamayo, Effect of bromhexine among COVID-19 patients -a meta-anaylsis, ERJ Open Res
Davis, Assaf, Mccorkell, Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact, eClinicalMedicine
Davis, Mccorkell, Vogel, Topol, Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations, Nat Rev Microbiol
Deng, Rayner, Ramaraju, Efficacy and safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in COVID-19 management: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect
Dodds, Doyle, Reiersen, Brown, Rayner, Fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19, Lancet Global Health
El Mdawar, Maître, Magnenat, Platelet FcγRIIAinduced serotonin release exacerbates the severity of transfusionrelated acute lung injury in mice, Blood Adv
Gordon, Hiatt, Bouhaddou, Comparative hostcoronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms, Science
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med
Hashimoto, Detrimental effects of COVID-19 in the brain and therapeutic options for long COVID: the role of Epstein-Barr virus and the gut-brain axis, Mol Psychiatry
Hashimoto, Overview of the potential use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 and long COVID, Discov Ment Health
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Cougoule, Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms, Mol Psychiatry
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Kornhuber, Antidepressant use and its association with 28-day mortality in inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: support for the FIASMA model against COVID-19, J Clin Med
Holm, A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure, Scand J Stat
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol
Imsuwansri, Jongthitinon, Pojdoung, Assessment of safety and intranasal neutralizing antibodies of HPMC-based human anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG1 nasal spray in healthy volunteers, Sci Rep
Jalali, Rezaie, Rola, Kyle-Sidell, COVID-19 pathophysiology: are platelets and serotonin hiding in plain sight?, SSRN Electron J, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3800402
Kunzelmann, Getting hands on a drug for Covid-19: inhaled and intranasal niclosamide, Lancet Reg Health Eur
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Liu, Zhao, Ma, Nie, Wu et al., Return to normal pre-COVID-19 life is delayed by inequitable vaccine allocation and SARS-CoV-2 variants, Epidemiol Infect
Maggio, Corsini, Repurposing the mucolytic cough suppressant and TMPRSS2 protease inhibitor bromhexine for the prevention and management of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Pharmacol Res
Manabe, Sharfstein, Armstrong, The need for more and better testing for COVID-19, JAMA
Marcec, Likic, Could fluvoxamine dose de-escalation increase treatment compliance without sacrificing efficacy in COVID-19 patients?, Clin Pharmacokinet
Martins, Ferreira, Jorge, In vitro inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by bromhexine hydrochloride, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.23.521817
Mehta, Patel, Algorithm 643: fexact: a FORTRAN subroutine for Fisher's exact test on unordered r×c contingency tables, ACM Trans Math Softw
Mikhaylov, Lyubimtseva, Vakhrushev, Bromhexine hydrochloride prophylaxis of COVID-19 for medical personnel: a randomized open-label study, Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis
Mills, Reis, Evaluating COVID-19 vaccines in the real world, Lancet
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin Infect Dis
Nakhaee, Zangiabadian, Bayati, Rahmanian, Jolfayi et al., The effect of antidepressants on the severity of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One
Nicol, Karp, Reiersen, Zorumski, Lenze, What were you before the war?" Repurposing psychiatry during the COVID-19 pandemic, J Clin Psychiatry
Pinheiro, Bates, Team, Nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models, R package version
Rad, Wannigama, Hirankarn, Mclellan, The impact of non-synonymous mutations on miRNA binding sites within the SARS-CoV-2 NSP3 and NSP4 genes, Sci Rep
Reiersen, Mattar, Ignacio, The STOP COVID 2 study: fluvoxamine vs placebo for outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19, a fully remote randomized controlled trial, Open Forum Infect Dis
Reis, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health
Retamal, Grace, Dill, Serotonin-induced vascular permeability is mediated by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 in the airways and upper gastrointestinal tract of mice, Lab Invest
Schultheiß, Willscher, Paschold, The IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, Cell Rep Med
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis
Shah, Joyce, Plumb, Paxlovid associated with decreased hospitalization rate among adults with COVID-19 -United States, April-September 2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Sherif, Gomez, Connors, Henrich, Reeves, Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), Elife
Sidky, Sahner, Girvin, Hotaling, Michael et al., Assessing the effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the prevention of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, medRxiv
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 Days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Stewart, Rebolledo, Mourad, Higher-dose fluvoxamine and time to sustained recovery in outpatients with COVID-19: the ACTIV-6 randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Stowe, Andrews, Kirsebom, Ramsay, Bernal, Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron and Delta hospitalisation, a test negative case-control study, Nat Commun
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol
Sánchez-Rico, Rezaei, Lenze, Limosin, Hoertel, Efficacy of fluvoxamine in outpatients with COVID-19: understanding conflicting conclusions from 2 recent meta-analyses of the same clinical trials, Ann Pharmacother
Team, R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Vardanyan, Hruby, 16 -Antihistamine drugs
Vegivinti, Evanson, Lyons, Efficacy of antiviral therapies for COVID-19: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials, BMC Infect Dis
Wannigama, Amarasiri, Hongsing, COVID-19 monitoring with sparse sampling of sewered and non-sewered wastewater in urban and rural communities, iScience
Wannigama, Amarasiri, Hongsing, Multiple traces of monkeypox detected in non-sewered wastewater with sparse sampling from a densely populated metropolitan area in Asia, Sci Total Environ
Wannigama, Amarasiri, Hurst, Tracking COVID-19 with wastewater to understand asymptomatic transmission, Int J Infect Dis
Wannigama, Amarasiri, Phattharapornjaroen, Tracing the new SARS-CoV-2 variant BA.2.86 in the community through wastewater surveillance in Bangkok, Thailand, Lancet Infect Dis
Wannigama, Amarasiri, Phattharapornjaroen, Tracing the transmission of mpox through wastewater surveillance in Southeast Asia, J Trav Med
Wannigama, Jacquet, NOD2-dependent BCG-induced trained immunity: a way to regulate innate responses to SARS-CoV2?, Int J Infect Dis
Weinstock, Reiersen, Jain, Konstantinoff, James et al., Cyproheptadine treatment of COVID-19-induced enteritis: implications for hyperinflammatory phase management, ACG Case Rep J
Weiss, Touret, Baronti, Niclosamide shows strong antiviral activity in a human airway model of SARS-CoV-2 infection and a conserved potency against the Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351) and Delta variant (B.1.617.2), PLoS One
Wen, Chen, Tang, Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19:a meta-analysis, Ann Med
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvirritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Wong, Devason, Umana, Serotonin reduction in postacute sequelae of viral infection, Cell
Woodrum, Brown, Management of SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction, Ann Pharmacother
Wroe, Seung, Baker, Farmer, Test and treat: a missing link in the global fight against COVID-19, Lancet Global Health
Xie, Bowe, Al-Aly, Burdens of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 by severity of acute infection, demographics and health status, Nat Commun
Yin, Agbana, Sun, Increased interleukin-6 is associated with long COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Infect Dis Poverty
Zaid, Guessous, Puhm, Platelet reactivity to thrombin differs between patients with COVID-19 and those with ARDS unrelated to COVID-19, Blood Adv
Zaid, Khalki, Jalali, Low α-thrombin/GPIbα interaction is a potential contributor to platelet hyper-reactivity in COVID-19 patients, Thromb Haemost
wannigama