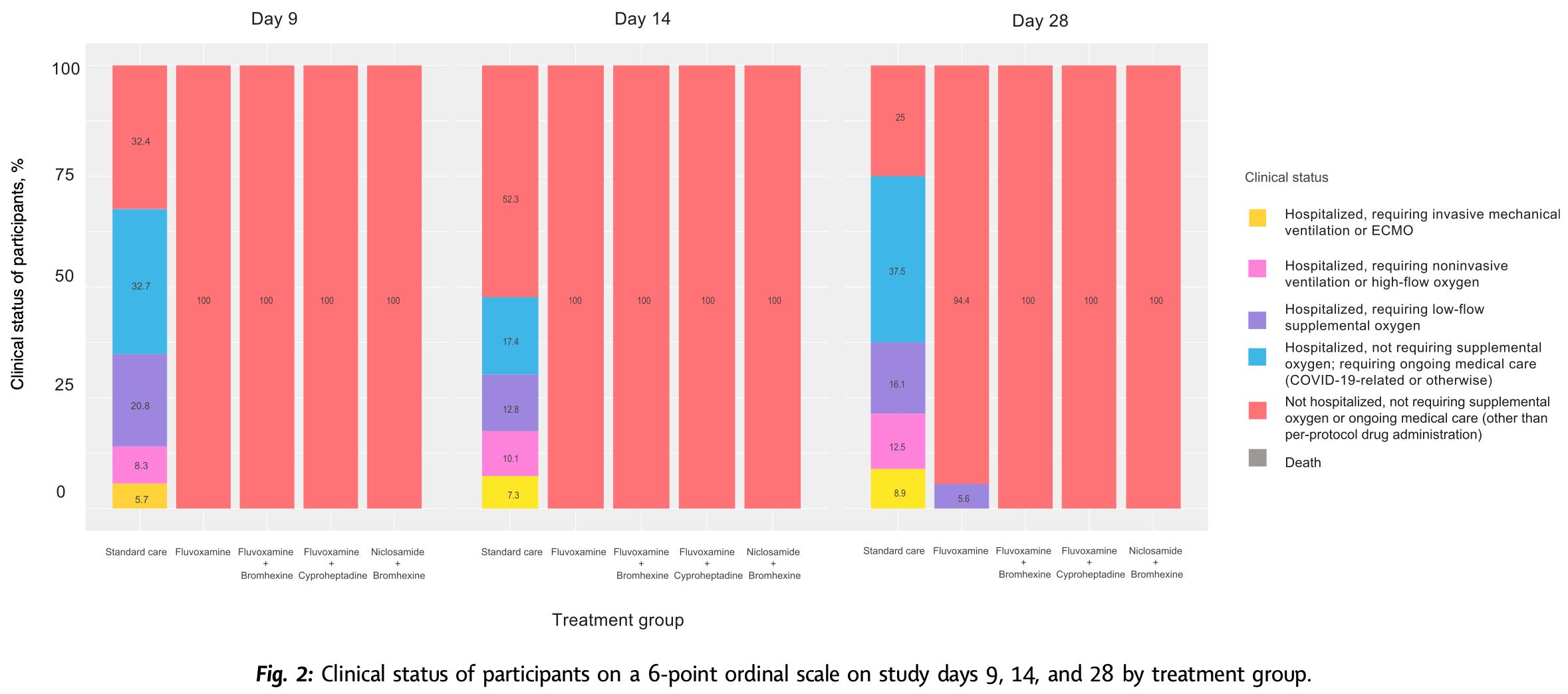
Early treatment with fluvoxamine, bromhexine, cyproheptadine, and niclosamide to prevent clinical deterioration in patients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
et al., eClinicalMedicine, 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102517, NCT05087381, Mar 2024
RCT 995 outpatients showing significantly lower progression with early treatment within 48 hours using fluvoxamine, fluvoxamine+bromhexine, fluvoxamine+cyproheptadine, and niclosamide+bromhexine.
70% of patients received treatment within 12 hours of symptom onset.
Treatments groups showed significantly lower long COVID (PASC). The combined treatment groups showed significantly lower viral load as early as day 3. The 3 combination arms were superior to fluvoxamine alone.
The study was open-label. 593 out of 1,900 randomized participants did not receive the treatment, mostly due to inability to confirm eligibility, however baseline characteristics were similar for these patients.
There was a very high hospitalization rate in the control arm. Authors note that the majority of cases were mild - the threshold for hospitalization may have been very low (in some places/times all cases were hospitalized). Authors also note that the patients requiring high flow oxygen all had the delta/alpha variants, and that the population has many health disparities.
Publication was over 500 days after the 90 day followup.
Bromhexine efficacy may vary depending on the degree of TMPRSS-dependent fusion for different variants1,2.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 98.5% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 32 of 336 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 98.2% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 27 of 336 (8.0%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 14.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 97.5% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 19 of 336 (5.7%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 9.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.7% lower, RR 0.003, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 171 of 336 (50.9%), NNT 2.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 28.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.7% lower, RR 0.003, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 150 of 336 (44.6%), NNT 2.2, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 14.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 99.6% lower, RR 0.004, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 117 of 336 (34.8%), NNT 2.9, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 9.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 98.5% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 32 of 336 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 98.2% lower, RR 0.02, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 27 of 336 (8.0%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 14.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 97.5% lower, RR 0.03, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 350 (0.0%), control 19 of 336 (5.7%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), combined bromhexine arms, day 9.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 55.1% lower, RR 0.45, p < 0.001, treatment 157 of 350 (44.9%), control 336 of 336 (100.0%), NNT 1.8, combined bromhexine arms, day 90.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Wannigama et al., 14 Mar 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Thailand, peer-reviewed, 29 authors, study period 1 October, 2021 - 21 June, 2022, average treatment delay 0.5 days, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with fluvoxamine/niclosamide) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial NCT05087381 (history).
Contact: Dhammika.L@chula.ac.th, Phatthranit.pha@mahidol.edu, gochi.akk@gmail.com.
wannigamab