Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468, Feb 2024
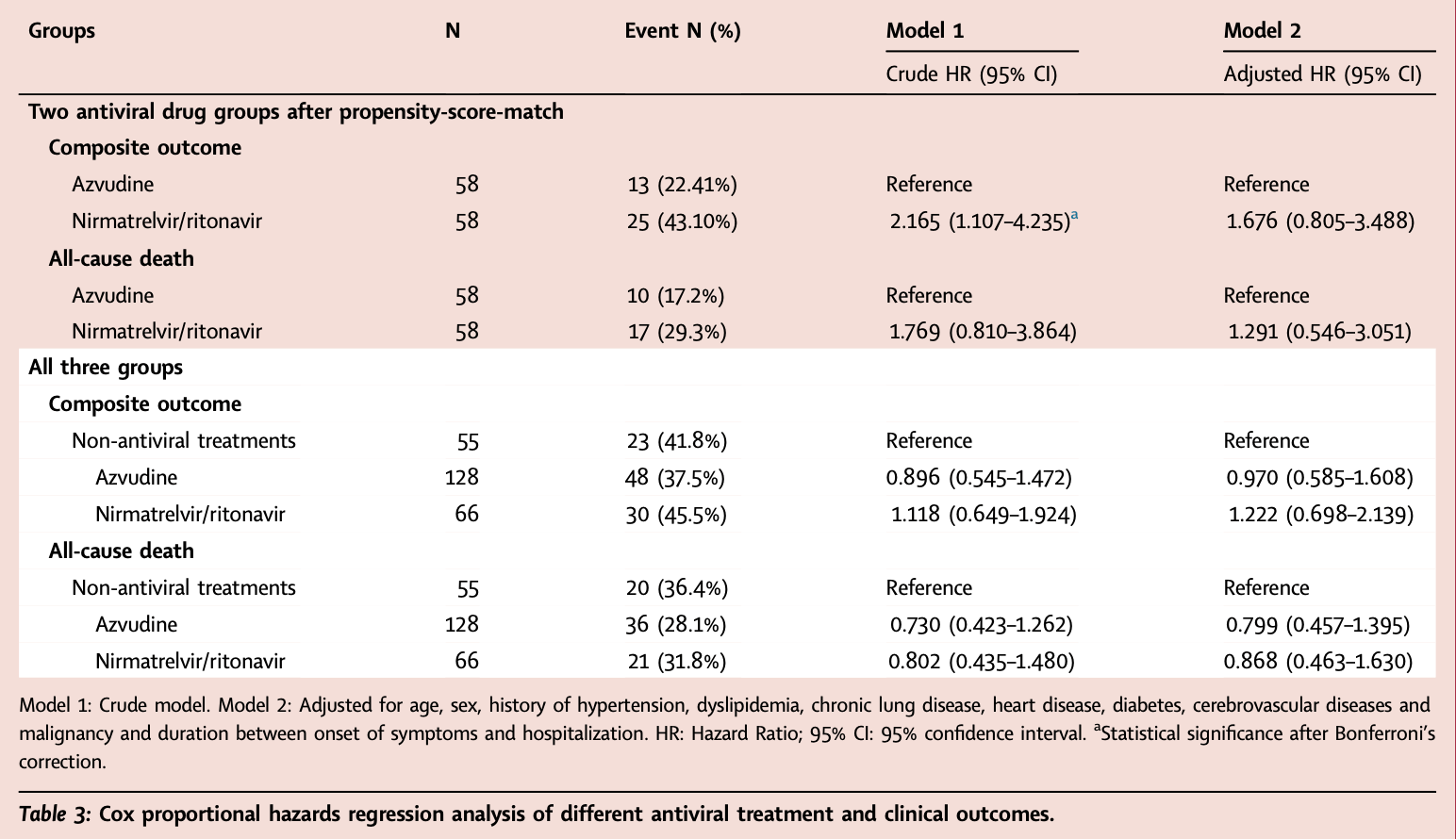
Retrospective 249 elderly patients with severe COVID-19, 128 treated with azvudine, 66 treated with paxlovid, and 55 receiving neither treatment, showing no significant differences for Ct value changes, progression, or survival for either treatment. Early viral decline was faster with paxlovid, without statistical significance.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers azvudine and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 13.2% lower, HR 0.87, p = 0.67, treatment 66, control 55, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 22.2% higher, HR 1.22, p = 0.49, treatment 66, control 55, adjusted per study, ICU, mechanical ventilation, or death, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Wang et al., 9 Feb 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 47 authors.
Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study
eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468
Background Azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir are approved to treat mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in adults with a high risk for progression to severe infection. We sought to compare the antiviral effectiveness and clinical outcomes of elderly severe patients with COVID-19 receiving these two antiviral agents. Methods In this observational study, we identified 249 elderly patients with severe COVID-19 infection who were admitted to the Second Medical Center of the People's Liberation Army General Hospital from December 2022 to January 2023, including 128 azvudine recipients, 66 nirmatrelvir/ritonavir recipients and 55 patients not received antiviral treatments. We compared the cycle threshold (Ct) value dynamic change of all three groups. The primary outcome was a composite outcome of disease progression, including all-cause death, intensive care unit admission, and initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation. The outcomes of all enrolled patients were followed up from the electronic medical record system. Kaplan-Meier and Cox risk proportional regression analyses were used to compare the clinical outcomes of all three groups. To more directly compare the effectiveness of the two antiviral drugs, we performed propensity-score matching between the two antiviral groups and compared antiviral efficacy and clinical outcomes in the matched population.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data related to this article can be found at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468.
References
Amani, Amani, Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a rapid review and meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Anesi, Maguire, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for ambulatory COVID-19: expanding evidence, expanding role, Ann Intern Med
Chen, Tian, Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Heliyon
Chuang, Wu, Liu, Efficacy of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir for post-acute COVID-19 sequelae beyond 3 months of SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Med Virol
Deng, Li, Sun, Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J Med Virol
Gao, Luo, Ren, Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Infect
Gentry, Nguyen, Thind, Kurdgelashvili, Williams, Characteristics and outcomes of US Veterans at least 65 years of age at high risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection with or without receipt of oral antiviral agents, J Infect
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Karita, Dong, Johnston, Trajectory of viral RNA load among persons with incident SARS-CoV-2 G614 infection (wuhan strain) in association with COVID-19 symptom onset and severity, JAMA Netw Open
Lamb, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval, Drugs
Liu, Pan, Zhang, Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac
Mannucci, Nobili, Multimorbidity and polypharmacy in the elderly: lessons from REPOSI, Internal Emerg Med
Moderbacher, Ramirez, Dan, Antigenspecific adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in acute COVID-19 and associations with age and disease severity, Cell
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients, Clin Infect Dis
Reis, Metzendorf, Kuehn, Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Shao, Fan, Guo, Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China, Microorganisms
Sun, Dian, Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Wan, Yan, Mok, Effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 : a target trial emulation study, Ann Intern Med
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvirritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Zhang, Li, Wang, Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct Targeted Ther
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: a retrospective study, Infect Drug Resist
Zheng, Yu, Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study, BMJ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468",
"ISSN": [
"2589-5370"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589537024000476"
],
"article-number": "102468",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "eClinicalMedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shuxia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Jin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Man",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qin",
"given": "Bangguo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7975-6702",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Miao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Nan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shengshu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Tingyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Cong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Xinli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bai",
"given": "Yongyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Geping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Suxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Fan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Jinling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Yajuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "An",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Wenhui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Ru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yin",
"given": "Xi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ao",
"given": "Qiangguo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Shuangtong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Haili",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Peng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Linggen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Wenning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Lining",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lei",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Keyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Zhijian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fang",
"given": "Xiangqun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Yao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Tianzhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0007-4161-1640",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"container-title-short": "eClinicalMedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-09T07:18:25Z",
"timestamp": 1707463105000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-18T09:15:51Z",
"timestamp": 1710753351000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012165",
"award": [
"2020YFC2008900"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Key Technologies Research and Development Program"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012166",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Key Research and Development Program of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100017548",
"award": [
"223-CXCY-N101-07-18-01"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Defense Science and Technology Innovation Fund of the Chinese Academy of Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-01T17:19:39Z",
"timestamp": 1711991979120
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709251200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1705622400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537024000476?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537024000476?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "102468",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib1",
"series-title": "China grants conditional approval for Pfizer’s oral COVID-19 drug",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib2",
"series-title": "Domestically developed drug joins virus battle",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Targeted Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib3",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of paxlovid in reducing severe coronavirus disease 2019 and mortality in high-risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e342",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib4",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28441",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a rapid review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Amani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib6",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib7",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib8",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib9",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"first-page": "e158",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib10",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19",
"author": "Reis",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib11",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1681",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib12",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.038",
"article-title": "Antigen-specific adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in acute COVID-19 and associations with age and disease severity",
"author": "Rydyznski Moderbacher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "996",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib13",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Characteristics and outcomes of US Veterans at least 65 years of age at high risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection with or without receipt of oral antiviral agents",
"author": "Gentry",
"first-page": "248",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib14",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3057",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 : a target trial emulation study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib15",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval",
"author": "Lamb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib16",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3427",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for ambulatory COVID-19: expanding evidence, expanding role",
"author": "Anesi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib17",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28750",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir for post-acute COVID-19 sequelae beyond 3 months of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Chuang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib18",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-014-1124-1",
"article-title": "Multimorbidity and polypharmacy in the elderly: lessons from REPOSI",
"author": "Mannucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "723",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Internal Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in Tibet: a retrospective study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6053",
"journal-title": "Infect Drug Resist",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib20",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1443",
"article-title": "Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1443",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib21",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42796",
"article-title": "Trajectory of viral RNA load among persons with incident SARS-CoV-2 G614 infection (wuhan strain) in association with COVID-19 symptom onset and severity",
"author": "Stankiewicz Karita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib22",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11071859",
"article-title": "Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Shao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib23",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study",
"author": "Liu",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102468_bib24",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2589537024000476"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral effectiveness and survival correlation of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in elderly severe patients with COVID-19: a retrospective real-world study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "69"
}
wang25