Role of intravenous vitamin C on outcomes in hospitalized patients with moderate or severe COVID-19: a real life data of Turkish patients
et al., Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7, Nov 2024
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
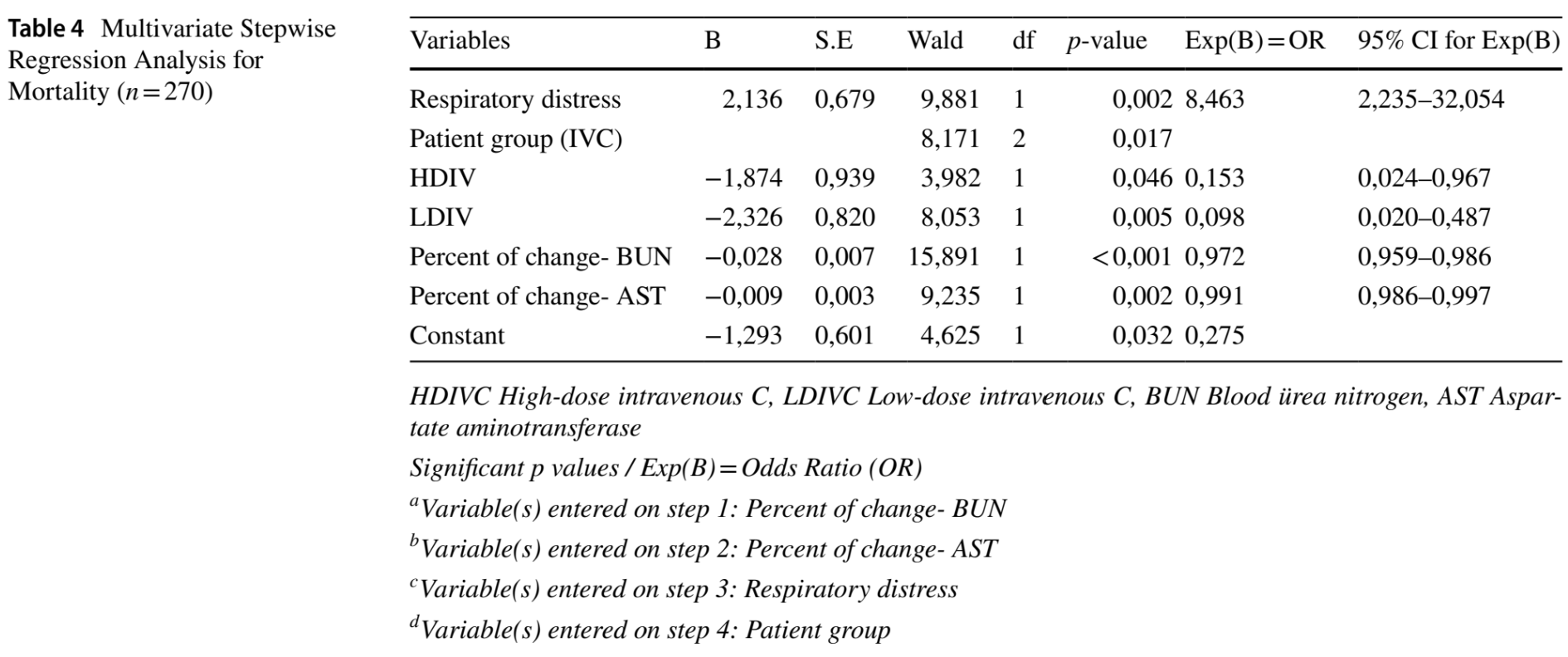
Retrospective 270 moderate/severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients, showing lower mortality with high (25 g/day) or low-dose (2 g/day) intraveneous vitamin C.
This is the 72nd of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0012.
|
risk of death, 84.2% lower, OR 0.16, p = 0.04998, treatment 41, control 46, adjusted per study, high dose, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death, 90.2% lower, OR 0.10, p = 0.004, treatment 183, control 46, adjusted per study, low dose, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Uz et al., 13 Nov 2024, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7",
"ISSN": [
"0925-4692",
"1568-5608"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7",
"alternative-id": [
"1597"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "17 October 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "1 November 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 November 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing Interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Ondokuz Mayıs University (13.04.2022/OMÜ KAEK 2022-167). In addition, this trial was approved by the Academic and Ethichs Committee of Medicana International Samsun Hospital (03.03.2022/2) and the General Directorate of Health Services at the Republic of Turkey Ministry of Health (16.03.2022)."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to publish",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "Our manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9326-4301",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uz",
"given": "Burak",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "İnce",
"given": "Özgür",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gümüş",
"given": "Can",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gökosmanoğlu",
"given": "Feyzi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Özgür",
"given": "Emrah Gökay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bekiroğlu",
"given": "Gülnaz Nural",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Inflammopharmacol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-13T12:23:46Z",
"timestamp": 1731500626000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-13T12:32:22Z",
"timestamp": 1731501142000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-14T05:22:45Z",
"timestamp": 1731561765911,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1731456000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1731456000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.5937/jomb0-27554",
"author": "M Ahnach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "500",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Med Biochem",
"key": "1597_CR1",
"unstructured": "Ahnach M, Zbiri S, Nejjari S, Ousti F, Elkettani C (2020) C-reactive protein as an early predictor of COVID-19 severity. J Med Biochem 39(4):500–507. https://doi.org/10.5937/jomb0-27554",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"author": "C Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Med Drug Discov",
"key": "1597_CR2",
"unstructured": "Arvinte C, Singh M, Marik PE (2020) Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically Ill COVID-19 patients of a north american community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: a pilot study. Med Drug Discov 8:100064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/1058813",
"author": "A Avila-Nava",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1058813",
"journal-title": "Oxid Med Cell Longev",
"key": "1597_CR3",
"unstructured": "Avila-Nava A, Pech-Aguilar AG, Lugo R, Medina-Vera I, Guevara-Cruz M, Gutiérrez-Solis AL (2022) Oxidative stress biomarkers and their association with mortality among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in mexico. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:1058813. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1058813",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1597_CR4",
"unstructured": "Belhadi, Chawki (2021) Acute Induced Scurvy: Implications for COVID-19 and the Cytokine Storm. Field Notes: A Journal of Collegiate Anthropology 12(4). Available at: https://dc.uwm.edu/fieldnotes/vol12/iss1/4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15163653",
"author": "LS Boerenkamp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3653",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1597_CR5",
"unstructured": "Boerenkamp LS, Gijsbers BLMG, Ververs EJ, Pijpers EMS, Spaetgens B, de Coninck A, Germeraad WTV, Wodzig WKWH, Wieten L, van Gorkom GNY, van Elssen CHMJ (2023) Low levels of serum and intracellular vitamin C in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 15(16):3653. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163653",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taaa011",
"author": "II Bogoch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Travel Med",
"key": "1597_CR6",
"unstructured": "Bogoch II, Watts A, Thomas-Bachli A, Huber C, Kraemer MUG, Khan K (2020) Potential for global spread of a novel coronavirus from China. J Travel Med. https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taaa011",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199603000-00006",
"author": "E Borrelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "1597_CR7",
"unstructured": "Borrelli E, Roux-Lombard P, Grau GE, Girardin E, Ricou B, Dayer J, Suter PM (1996) Plasma concentrations of cytokines, their soluble receptors, and antioxidant vitamins can predict the development of multiple organ failure in patients at risk. Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199603000-00006",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110102",
"author": "R Cecchini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110102",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "1597_CR8",
"unstructured": "Cecchini R, Cecchini AL (2020) SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression. Med Hypotheses 143:110102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110102",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"author": "L Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "1597_CR9",
"unstructured": "Chiscano-Camón L, Ruiz-Rodriguez JC, Ruiz-Sanmartin A, Roca O, Ferrer R (2020) Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care 24(1):522. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "HJS De Grooth",
"key": "1597_CR10",
"unstructured": "De Grooth HJS, Spoelstra-de Man AME, Oudemans-van Straaten HM (2014) Early plasma vitamin C concentration, organ dysfunction and ICU mortality. intensive care medicine. Springer, New York",
"volume-title": "Early plasma vitamin C concentration, organ dysfunction and ICU mortality. intensive care medicine",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2018.02.025",
"author": "HJ de Grooth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1368",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "1597_CR11",
"unstructured": "de Grooth HJ, Manubulu-Choo WP, Zandvliet AS, Spoelstra-de Man AME, Girbes AR, Swart EL, Oudemans-van Straaten HM (2018) vitamin C pharmacokinetics in critically Ill Patients: a randomized trial of four IV regimens. Chest 153(6):1368–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.02.025",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102887",
"author": "P Domingo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102887",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "1597_CR12",
"unstructured": "Domingo P, Mur I, Pomar V, Corominas H, Casademont J, de Benito N (2020) The four horsemen of a viral Apocalypse: The pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). EBioMedicine 58:102887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102887",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020615",
"author": "M Doseděl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "615",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1597_CR13",
"unstructured": "Doseděl M, Jirkovský E, Macáková K, Krčmová LK, Javorská L, Pourová J, Mercolini L, Remião F, Nováková L, Mladěnka P, Oemonom OBOT (2021) Vitamin C-sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, use, toxicity, and determination. Nutrients 13(2):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020615",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2009.08.015",
"author": "R Evans-Olders",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1070",
"issue": "11–12",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "1597_CR14",
"unstructured": "Evans-Olders R, Eintracht S (2010) Hoffer LJ (2010) Metabolic origin of hypovitaminosis C in acutely hospitalized patients. Nutrition 26(11–12):1070–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2009.08.015",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-022-01254-8",
"author": "H Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "1597_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E (2023) Abrupt termination of vitamin C from ICU patients may increase mortality: secondary analysis of the LOVIT trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 77(4):490–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-022-01254-8",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "1597_CR16",
"unstructured": "https://covid19.saglik.gov.tr/TR-66301/covid-19-rehberi.html. Accessed 03 June 2024"
},
{
"key": "1597_CR17",
"unstructured": "https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Accessed 16 October 2024"
},
{
"key": "1597_CR18",
"unstructured": "https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed 16 October 2024"
},
{
"author": "EP Hudson",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Resusc",
"key": "1597_CR19",
"unstructured": "Hudson EP, Collie JT, Fujii T, Luethi N, Udy AA, Doherty S, Eastwood G, Yanase F, Naorungroj T, Bitker L, Abdelhamid YA, Greaves RF, Deane AM, Bellomo R (2019) Pharmacokinetic data support 6-hourly dosing of intravenous vitamin C to critically ill patients with septic shock. Crit Care Resusc 21(4):236–242",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-021-00490-1",
"author": "S JamaliMoghadamSiahkali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "1597_CR20",
"unstructured": "JamaliMoghadamSiahkali S, Zarezade B, Koolaji S, SeyedAlinaghi S, Zendehdel A, Tabarestani M, Sekhavati Moghadam E, Abbasian L, Dehghan Manshadi SA, Salehi M, Hasannezhad M, Ghaderkhani S, Meidani M, Salahshour F, Jafari F, Manafi N, Ghiasvand F (2021) Safety and effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a randomized open-label clinical trial. Eur J Med Res 26(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-021-00490-1",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/jccm-2022-0013",
"author": "T Karaaslan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "156",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures)",
"key": "1597_CR21",
"unstructured": "Karaaslan T, Karaaslan E (2022) Predictive value of systemic immune-inflammation index in determining mortality in COVID-19 patients. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures) 8(3):156–164. https://doi.org/10.2478/jccm-2022-0013",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-023-01200-5",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3357",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "1597_CR22",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Hasan SS, Ramachandram DS (2023) The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflammopharmacology 31(6):3357–3362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01200-5",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.11779",
"author": "P Kumari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e11779",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "1597_CR23",
"unstructured": "Kumari P, Dembra S, Dembra P, Bhawna F, Gul A, Ali B, Sohail H, Kumar B, Memon MK, Rizwan A (2020) The role of vitamin C as adjuvant therapy in COVID-19. Cureus 12(11):e11779. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.11779",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0022-4804(02)00083-5",
"author": "CL Long",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "144",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Surg Res",
"key": "1597_CR24",
"unstructured": "Long CL, Maull KI, Krishnan RS, Laws HL, Geiger JW, Borghesi L, Franks W, Lawson TC, Sauberlich HE (2003) Ascorbic acid dynamics in the seriously ill and injured. J Surg Res 109(2):144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-4804(02)00083-5",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.explore.2023.06.009",
"author": "L Mahjoub",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "95",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Explore (NY)",
"key": "1597_CR25",
"unstructured": "Mahjoub L, Youssef R, Yaakoubi H, Salah HB, Jaballah R, Mejri M, Sekma A, Trabelsi I, Nouira S, Khrouf M, Soltane HB, Mezgar Z, Boukadida L, Zorgati A, Boukef R (2024) Melatonin, vitamins and minerals supplements for the treatment of Covid-19 and Covid-like illness: a prospective, randomized, double-blind multicenter study. Explore (NY) 20(1):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2023.06.009",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816",
"author": "N Majidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "717816",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1597_CR26",
"unstructured": "Majidi N, Rabbani F, Gholami S, Gholamalizadeh M, BourBour F, Rastgoo S, Hajipour A, Shadnoosh M, Akbari ME, Bahar B, Ashoori N, Alizadeh A, Samipoor F, Moslem A, Doaei S, Suzuki K (2021) The effect of vitamin C on pathological parameters and survival duration of critically Ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a randomized clinical trial. Front Immunol 12:717816. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1597_CR27",
"unstructured": "NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guideliness, https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed 03 June 2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14194217",
"author": "M Olczak-Pruc",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1597_CR28",
"unstructured": "Olczak-Pruc M, Swieczkowski D, Ladny JR, Pruc M, Juarez-Vela R, Rafique Z, Peacock FW, Szarpak L (2022) Vitamin C supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194217",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10020257",
"author": "J Pincemail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "A Pilot Study Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "1597_CR29",
"unstructured": "Pincemail J, Cavalier E, Charlier C, Cheramy-Bien JP, Brevers E, Courtois A, Fadeur M, Meziane S, Goff CL, Misset B, Albert A, Defraigne JO, Rousseau AF (2021) Oxidative stress status in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit for severe pneumonia. A Pilot Study Antioxidants (Basel) 10(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020257",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.19902",
"author": "K Ried",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e19902",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Randomized Trial Cureus",
"key": "1597_CR30",
"unstructured": "Ried K, BinJemain T, Sali A (2021) Therapies to prevent progression of COVID-19, including hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, zinc, and vitamin D3 with or without intravenous vitamin C: an international, multicenter. Randomized Trial Cureus 13(11):e19902. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.19902",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2024.102145",
"author": "R Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102145",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Curr Dev Nutr",
"key": "1597_CR31",
"unstructured": "Sharma R, Patel A, Ojha T, Pablo LA, Vosoughi T, Ziegler C, Sivapragasam K, Pinto AD, Jenkins D, Hosseini B (2024) Role of antioxidant therapy in the treatment and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr Dev Nutr 8(5):102145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdnut.2024.102145",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11081580",
"author": "T Sinnberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1580",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "1597_CR32",
"unstructured": "Sinnberg T, Lichtensteiger C, Hill-Mündel K, Leischner C, Niessner H, Busch C, Renner O, Wyss N, Flatz L, Lauer UM, Hoelzle LE, Nohr D, Burkard M, Marongiu L, Venturelli S (2022) Vitamin C deficiency in blood samples of COVID-19 patients. Antioxidants (Basel) 11(8):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081580",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16091345",
"author": "A Sinopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1597_CR33",
"unstructured": "Sinopoli A, Sciurti A, Isonne C, Santoro MM, Baccolini V (2024) The efficacy of multivitamin, vitamin A, vitamin B, vitamin C, and vitamin D supplements in the prevention and management of COVID-19 and long-COVID: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutrients 16(9):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091345",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S402206",
"author": "SW Smail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "1597_CR34",
"unstructured": "Smail SW, Babaei E, Amin K (2023) Hematological, inflammatory, coagulation, and oxidative/antioxidant biomarkers as predictors for severity and mortality in COVID-19: a prospective cohort-study. Int J Gen Med 16:565–580. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S402206",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuad105",
"author": "L Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1056",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "1597_CR35",
"unstructured": "Sun L, Zhao JH, Fan WY, Feng B, Liu WW, Chen RQ, Ban C, Dang AG, Wang M, Luo KT, Zhou GY, Yu FF, Ba Y (2024) Therapeutic effects of high-dose vitamin C supplementation in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Nutr Rev 82(8):1056–1068. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuad105",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s42506-021-00095-w",
"author": "MS Uddin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Egypt Public Health Assoc",
"key": "1597_CR36",
"unstructured": "Uddin MS, Millat MS, Baral PK, Ferdous M, Uddin MG, Sarwar MS, Islam MS (2021) The protective role of vitamin C in the management of COVID-19: a review. J Egypt Public Health Assoc 96(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42506-021-00095-w",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10122022",
"author": "LE van Eijk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2022",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "1597_CR37",
"unstructured": "van Eijk LE, Tami A, Hillebrands JL, den Dunnen WFA, de Borst MH, van der Voort PHJ, Bulthuis MLC, Veloo ACM, Wold KI, Vincenti González MF, van der Gun BTF, van Goor H, Bourgonje AR (2021) Mild coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is marked by systemic oxidative stress: a pilot study. Antioxidants (Basel) 10(12):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10122022",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10715760100301401",
"author": "VM Victor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "907",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Free Radic Res",
"key": "1597_CR38",
"unstructured": "Victor VM, Guayerbas N, Puerto M, De la Fuente M (2001) Changes in the ascorbic acid levels of peritoneal lymphocytes and macrophages of mice with endotoxin-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 35(6):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760100301401",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504",
"author": "AP Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106504",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "1597_CR39",
"unstructured": "Yang AP, Liu JP, Tao WQ, Li HM (2020) The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients. Int Immunopharmacol 84:106504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"author": "J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "1597_CR40",
"unstructured": "Zhang J, Rao X, Li Y, Zhu Y, Liu F, Guo G, Luo G, Meng Z, De Backer D, Xiang H, Peng Z (2021) Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Ann Intensive Care 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10787-024-01597-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Role of intravenous vitamin C on outcomes in hospitalized patients with moderate or severe COVID-19: a real life data of Turkish patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}
