In vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone iodine nasal spray (Nasodine) at clinically relevant concentrations and timeframes using tissue culture and PCR based assays
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.31.426979 , Feb 2021
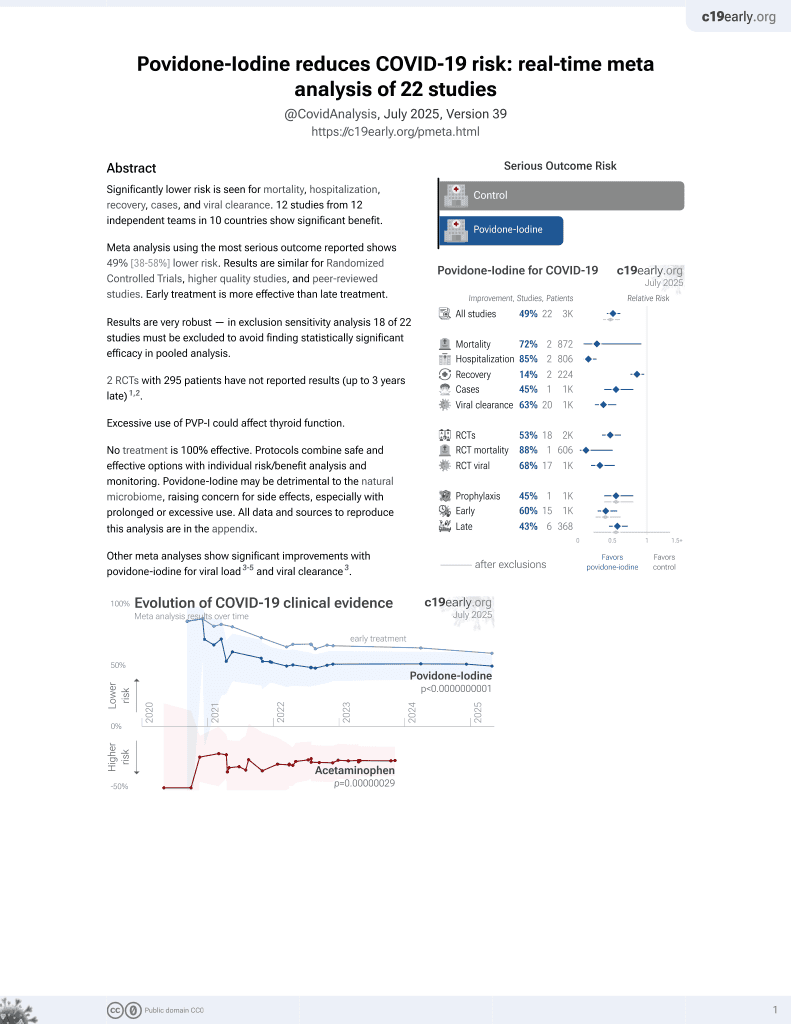
PVP-I for COVID-19
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.000000000016 from 22 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing that PVP-I eliminated the viability of SARS-CoV-2 with short exposure times. Authors find that PCR alone may not be adequate for viral quantification and recommend incorporating cell culture to assess viral viability.
9 preclinical studies support the efficacy of povidone-iodine for COVID-19:
1.
Xu et al., Differential Effects of Antiseptic Mouth Rinses on SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity In Vitro, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10030272.
2.
Tucker et al., In vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone iodine nasal spray (Nasodine) at clinically relevant concentrations and timeframes using tissue culture and PCR based assays, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.31.426979.
3.
Pelletier et al., Efficacy of Povidone-Iodine Nasal and Oral Antiseptic Preparations Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, doi:10.1177/0145561320957237.
4.
Frank et al., In Vitro Efficacy of a Povidone-Iodine Nasal Antiseptic for Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3053.
5.
Meister et al., Virucidal Efficacy of Different Oral Rinses Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa471.
6.
Anderson et al., Povidone-Iodine Demonstrates Rapid In Vitro Virucidal Activity Against SARS-CoV-2, The Virus Causing COVID-19 Disease, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00316-3.
7.
Hassandarvish et al., Povidone iodine gargle and mouthwash, British Dental Journal volume, doi:10.1038/s41415-020-1794-1.
Tucker et al., 1 Feb 2021, preprint, 6 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
In vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone iodine nasal spray (Nasodine) at clinically relevant concentrations and timeframes using tissue culture and PCR based assays
doi:10.1101/2021.01.31.426979
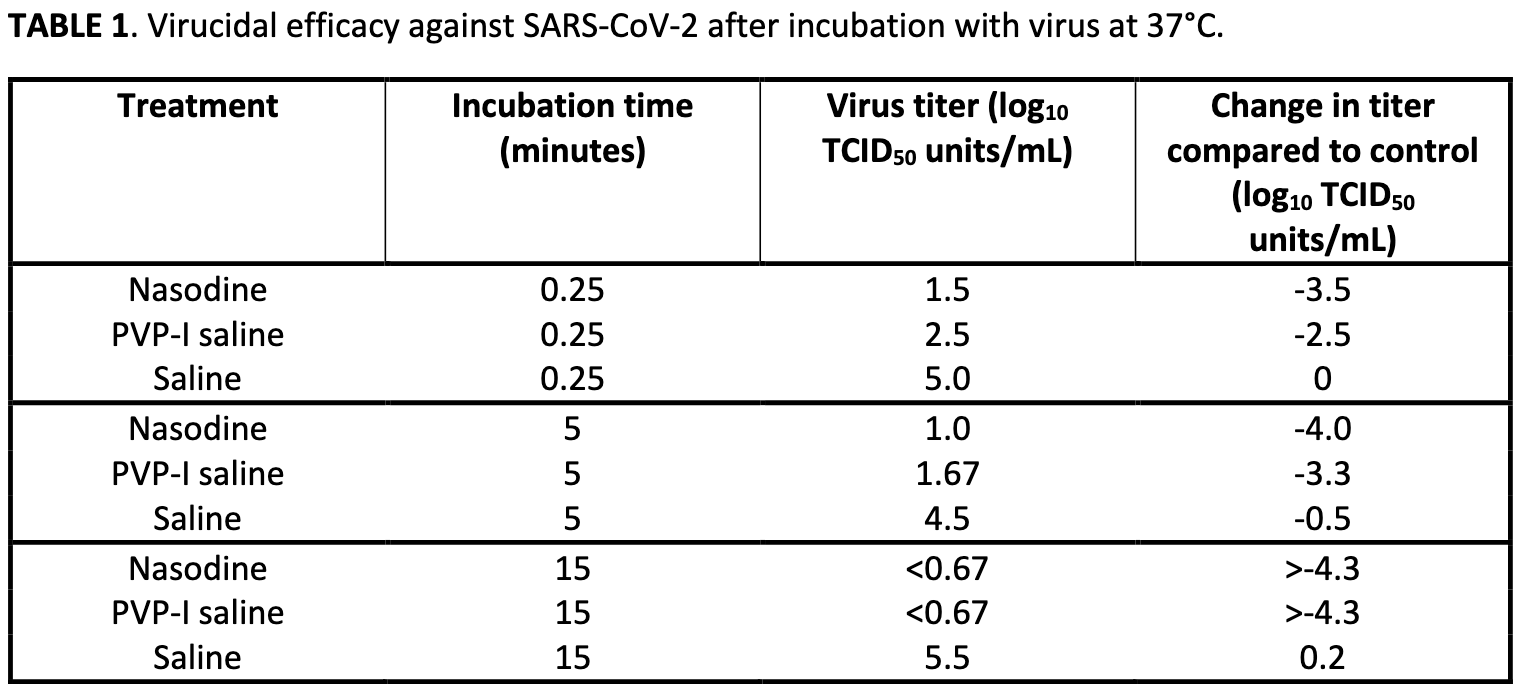
BACKGROUND There has been considerable speculation regarding the potential of PVP-I nasal disinfection as an adjunct to other countermeasures during the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Nasodine is a commercial formulation of 0.5% PVP-I that has been evaluated for safety and efficacy in human trials as a treatment for the common cold, including a Phase III trial (ANZCTR: ACTRN12619000764134). This study presents the first report of the in vitro efficacy of this formulation against SARS-CoV-2.
METHODS We conducted in vitro experiments to determine if the PVP-I formulation inactivated SARS-CoV-2 using two independent assays and virus isolates, and incorporating both PCR-based detection and cell culture methods to assess residual virus after exposure to the formulation.
RESULTS Based on cell culture results, the PVP-I formulation was found to rapidly inactivate SARS-CoV-2 isolates in vitro in short timeframes (15 seconds to 15 minutes) consistent with the minimum and maximum potential residence time in the nose. The Nasodine formula was found to be more effective than 0.5% PVP-I in saline. Importantly, it was found that the formulation inactivated culturable virus but had no effect on PCR-detectable viral RNA.
CONCLUSIONS The PVP-I formulation eliminated the viability of SARS-CoV-2 virus with short exposure times consistent with nasal use. PCR alone may not be adequate for viral quantification in nasal PVP-I studies; future studies should incorporate cell culture to assess viral viability. Nasal disinfection with PVP-I may be a useful intervention for newly-diagnosed COVID-19 patients to reduce transmission risk and disease progression to the lower respiratory tract.
Address reprint requests to Dr. Tucker at sptucker@firebrickpharma.com
References
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Frank, Brown et al., Rapid In-Vitro Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Using Povidone-Iodine Oral Antiseptic Rinse, J Prosthodont
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Frank, Brown et al., Rapid In-Vitro Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Using Povidone-Iodine Oral Antiseptic Rinse, Journal of Prosthodontics
Campbell, SARS-CoV-2 and the nose: Risks and implications for primary care, Australian Journal of General Practice
Challacombe, Kirk-Bayley, Sunkaraneni, Combes, Povidone iodine, Br Dent J
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill
De, Kang, Povidone-Iodine Demonstrates Rapid In Vitro Virucidal Activity Against SARS-CoV-2, The Virus Causing COVID-19 Disease, Infect Dis Ther
Eggers, Eickmann, Zorn, Rapid and Effective Virucidal Activity of Povidone-Iodine Products Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara (MVA), Infectious diseases and therapy
Eggers, Infectious Disease Management and Control with Povidone Iodine, Infect Dis Ther
Frank, Brown, Capriotti, Westover, Pelletier et al., In Vitro Efficacy of a Povidone-Iodine Nasal Antiseptic for Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Gallo, Locatello, Mazzoni, Novelli, Annunziato, The central role of the nasal microenvironment in the transmission, modulation, and clinical progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Mucosal Immunol
Hou, Okuda, Edwards, SARS-CoV-2 Reverse Genetics Reveals a Variable Infection Gradient in the Respiratory Tract
Kawana, Kitamura, Nakagomi, Inactivation of human viruses by povidone-iodine in comparison with other antiseptics, Dermatology
Kim, Rimmer, Mrad, Ahmadzada, Harvey, Betadine has a ciliotoxic effect on ciliated human respiratory cells, J Laryngol Otol
Lachapelle, Co, Casado, Antiseptics in the era of bacterial resistance: a focus on povidone iodine, Future Med
Lepelletier, Maillard, Pozzetto, Simon, Povidone Iodine: Properties, Mechanisms of Action, and Role in Infection Control and Staphylococcus aureus Decolonization, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Ma, Inventor, Prevention Of Infection By Highly Pathogenic Viruses Using Topical Application Of Povidone-iodine On Mucous Membranes2020
Mady, Kubik, Baddour, Snyderman, Rowan, Consideration of povidoneiodine as a public health intervention for COVID-19: Utilization as "Personal Protective Equipment" for frontline providers exposed in high-risk head and neck and skull base oncology care, Oral Oncol
Martinez Lamas, Dios, Rodriguez, Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo tests, Oral Dis
Naqvi, Citardi, Cattano, Ostrosky-Zeichner, Knackstedt et al., Povidoneiodine solution as SARS-CoV-2 prophylaxis for procedures of the upper aerodigestive tract a theoretical framework, J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Pelletier, Tessema, Frank, Westover, Brown et al., Efficacy of Povidone-Iodine Nasal and Oral Antiseptic Preparations Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Ear Nose Throat J
Ramezanpour, Smith, Psaltis, Wormald, Vreugde, In vitro safety evaluation of a povidone-iodine solution applied to human nasal epithelial cells, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Sato, Miyake, Hazama, Omori, Ramezanpour et al., Povidone-iodine-induced cell death in cultured human epithelial HeLa cells and rat oral mucosal tissue, International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology
Sungnak, Huang, Bécavin, Berg, SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes Are Most Highly Expressed in Nasal Goblet and Ciliated Cells within Human Airways
Zamora, Chemical and microbiologic characteristics and toxicity of povidone-iodine solutions, Am J Surg
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.31.426979",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.31.426979",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>BACKGROUND</jats:title><jats:p>There has been considerable speculation regarding the potential of PVP-I nasal disinfection as an adjunct to other countermeasures during the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Nasodine is a commercial formulation of 0.5% PVP-I that has been evaluated for safety and efficacy in human trials as a treatment for the common cold, including a Phase III trial (ANZCTR: ACTRN12619000764134). This study presents the first report of the <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic> efficacy of this formulation against SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>METHODS</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic> experiments to determine if the PVP-I formulation inactivated SARS-CoV-2 using two independent assays and virus isolates, and incorporating both PCR-based detection and cell culture methods to assess residual virus after exposure to the formulation.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>RESULTS</jats:title><jats:p>Based on cell culture results, the PVP-I formulation was found to rapidly inactivate SARS-CoV-2 isolates <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic> in short timeframes (15 seconds to 15 minutes) consistent with the minimum and maximum potential residence time in the nose. The Nasodine formula was found to be more effective than 0.5% PVP-I in saline. Importantly, it was found that the formulation inactivated culturable virus but had no effect on PCR-detectable viral RNA.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>CONCLUSIONS</jats:title><jats:p>The PVP-I formulation eliminated the viability of SARS-CoV-2 virus with short exposure times consistent with nasal use. PCR alone may not be adequate for viral quantification in nasal PVP-I studies; future studies should incorporate cell culture to assess viral viability. Nasal disinfection with PVP-I may be a useful intervention for newly-diagnosed COVID-19 patients to reduce transmission risk and disease progression to the lower respiratory tract.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tucker",
"given": "S.P.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodall",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Julander",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mendenhall",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Friedland",
"given": "P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molloy",
"given": "P.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-02T21:12:18Z",
"timestamp": 1612300338000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-03T09:36:23Z",
"timestamp": 1612344983000
},
"group-title": "Microbiology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-30T15:52:54Z",
"timestamp": 1680191574132
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "bioRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.01.31.426979",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.31128/AJGP-05-20-5452",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.1",
"unstructured": "Campbell RG . SARS-CoV-2 and the nose: Risks and implications for primary care. Australian Journal of General Practice;49."
},
{
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.2",
"unstructured": "Hou YJ , Okuda K , Edwards CE , et al. SARS-CoV-2 Reverse Genetics Reveals a Variable Infection Gradient in the Respiratory Tract."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41385-020-00359-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.3",
"unstructured": "Gallo O , Locatello LG , Mazzoni A , Novelli L , Annunziato F . The central role of the nasal microenvironment in the transmission, modulation, and clinical progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mucosal Immunol 2020."
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes Are Most Highly Expressed in Nasal Goblet and Ciliated Cells within Human Airways",
"journal-title": "LID",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00682-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.5",
"unstructured": "Lepelletier D , Maillard JY , Pozzetto B , Simon A . Povidone Iodine: Properties, Mechanisms of Action, and Role in Infection Control and Staphylococcus aureus Decolonization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2020;64."
},
{
"article-title": "Antiseptics in the era of bacterial resistance: a focus on povidone iodine",
"first-page": "579",
"journal-title": "Future Med",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000246027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-019-00260-x",
"article-title": "Infectious Disease Management and Control with Povidone Iodine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "581",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00316-3",
"article-title": "Povidone-Iodine Demonstrates Rapid In Vitro Virucidal Activity Against SARS-CoV-2, The Virus Causing COVID-19 Disease",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40463-020-00474-x",
"article-title": "Povidone-iodine solution as SARS-CoV-2 prophylaxis for procedures of the upper aerodigestive tract a theoretical framework",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.10",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.25.20110239",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.11",
"unstructured": "Pelletier JS , Tessema B , Frank S , Westover JB , Brown SM , Capriotti JA . Efficacy of Povidone-Iodine Nasal and Oral Antiseptic Preparations Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Ear Nose Throat J 2020:145561320957237."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41415-020-1589-4",
"article-title": "Povidone iodine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "656",
"journal-title": "Br Dent J",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.12",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104724",
"article-title": "Consideration of povidone-iodine as a public health intervention for COVID-19: Utilization as “Personal Protective Equipment” for frontline providers exposed in high-risk head and neck and skull base oncology care",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104724",
"journal-title": "Oral Oncol",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.13",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3053",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.14",
"unstructured": "Frank S , Brown SM , Capriotti JA , Westover JB , Pelletier JS , Tessema B . In Vitro Efficacy of a Povidone-Iodine Nasal Antiseptic for Rapid Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jopr.13209",
"article-title": "Rapid In-Vitro Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Using Povidone-Iodine Oral Antiseptic Rinse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "J Prosthodont",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.15",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.16",
"unstructured": "Goodall Ma , inventor Prevention Of Infection By Highly Pathogenic Viruses Using Topical Application Of Povidone-iodine On Mucous Membranes 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9610(86)90477-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22575",
"article-title": "In vitro safety evaluation of a povidone-iodine solution applied to human nasal epithelial cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "Int Forum Allergy Rhinol",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.18",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Betadine has a ciliotoxic effect on ciliated human respiratory cells",
"first-page": "S45",
"journal-title": "J Laryngol Otol",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.19",
"volume": "129 Suppl 1",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/01480545.2013.846364",
"article-title": "Povidone-iodine-induced cell death in cultured human epithelial HeLa cells and rat oral mucosal tissue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Drug Chem Toxicol",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.20",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22575",
"article-title": "In vitro safety evaluation of a povidone-iodine solution applied to human nasal epithelial cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.21",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.22",
"unstructured": "Corman VM , Landt O , Kaiser M , et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 2020;25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/odi.13526",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.23",
"unstructured": "Martinez Lamas L , Diz Dios P , Perez Rodriguez MT , et al. Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo tests. Oral Dis 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-015-0091-9",
"article-title": "Rapid and Effective Virucidal Activity of Povidone-Iodine Products Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara (MVA)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "Infectious diseases and therapy",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.24",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jopr.13209",
"article-title": "Rapid In-Vitro Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Using Povidone-Iodine Oral Antiseptic Rinse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "Journal of Prosthodontics",
"key": "2021020301300670000_2021.01.31.426979v1.25",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.01.31.426979"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "In vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone iodine nasal spray (Nasodine) at clinically relevant concentrations and timeframes using tissue culture and PCR based assays",
"type": "posted-content"
}