Iodine increases pulmonary type I interferon responses and decreases covid-19 disease severity: Results from an open label randomized clinical trial
et al., PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0341126, EudraCT2020-001852-16, Feb 2026
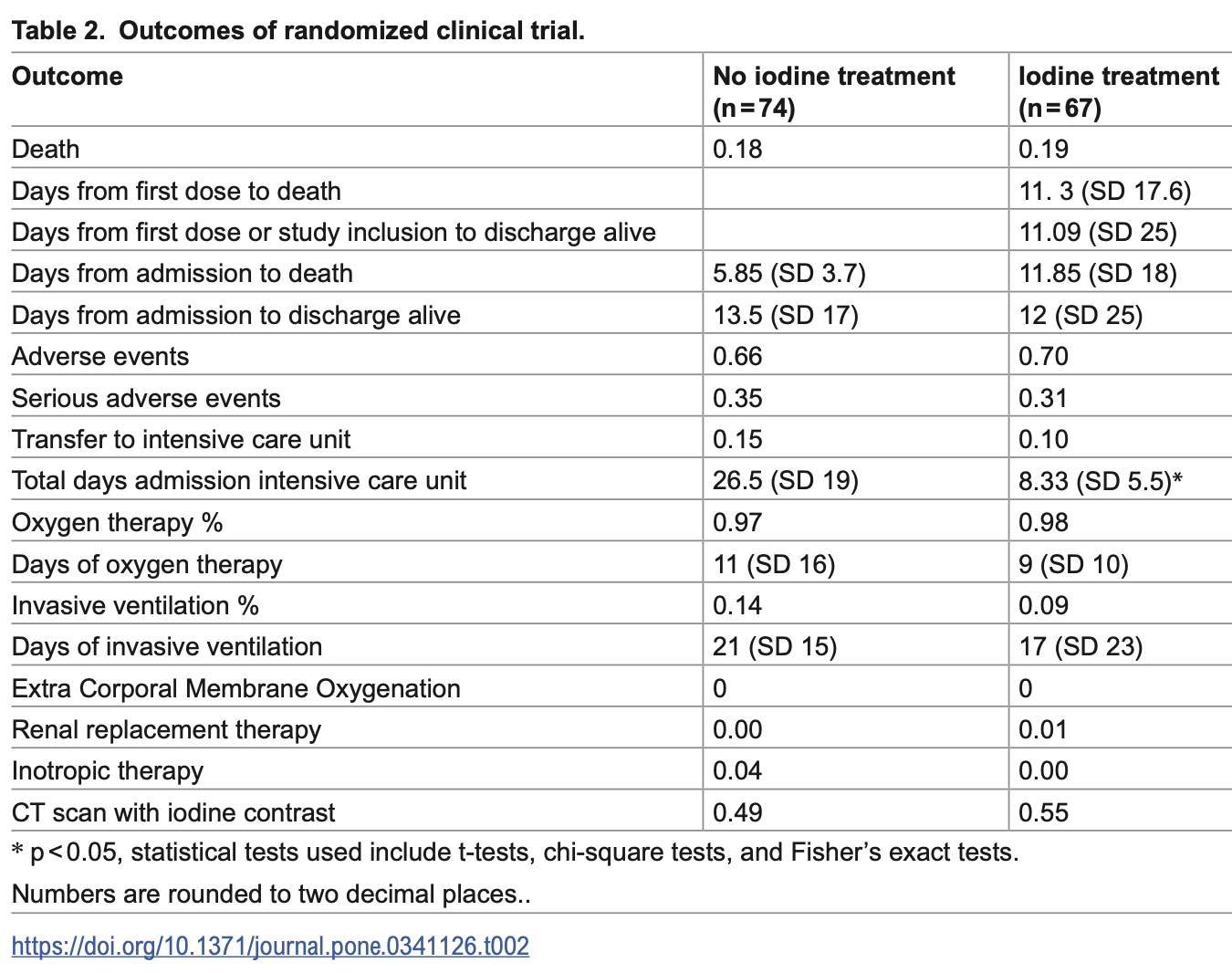
RCT 141 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in mortality or ICU admission with 12.5 mg daily oral iodine for 8 days. Exploratory analysis found patients receiving iodine had significantly shorter ICU stays.
|
risk of death, 10.4% higher, RR 1.10, p = 0.83, treatment 13 of 67 (19.4%), control 13 of 74 (17.6%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 33.7% lower, RR 0.66, p = 0.44, treatment 6 of 67 (9.0%), control 10 of 74 (13.5%), NNT 22.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 29.7% lower, RR 0.70, p = 0.46, treatment 7 of 67 (10.4%), control 11 of 74 (14.9%), NNT 23.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Traksel et al., 2 Feb 2026, Randomized Controlled Trial, Netherlands, peer-reviewed, mean age 70.4, 7 authors, study period 1 October, 2020 - 1 April, 2022, trial EudraCT2020-001852-16.
Contact: r.traksel@mmc.nl.
Iodine increases pulmonary type I interferon responses and decreases covid-19 disease severity: Results from an open label randomized clinical trial
PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0341126
Objective To investigate whether oral treatment with 12.5 mg iodine additional to standard of care is effective in reducing mortality and clinical deterioration of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Methods We performed a single center, randomized clinical trial (EudraCT 2020-001852-16) in which patients with severe covid-19 in need of hospitalization were randomized in two groups. The first group received 12.5 mg oral iodine for 8 days, the second group did not receive iodine next to the standard of care. Primary endpoints were deterioration of disease defined as transfer from the ward to the intensive care unit (ICU) or death. Next to these parameters we collected parameters in line with the recommendations made by the WHO in the early days of the pandemic. On these additional datasets we performed an exploratory analysis and investigated possible confounders and trends. The inclusion phase of the study was between October 2020 and April 2022. Finally, in vitro validations were performed.
Results Outcomes from 141 participants were analyzed, revealing no significant differences in mortality or transfers to intensive care between the iodine-treated group (67 patients) and the control group (74 patients). In an exploratory analysis we found that patients randomized to receive oral iodine had a significantly shorter stay at the ICU (p = 0.016). In vitro validations proved increased virus-induced type I interferon responses upon iodine administration in pulmonary cells.
Conclusion These findings suggest that while iodine does not reduce mortality or ICU admissions, it may enhance antiviral immunity through increased type I interferon responses, contributing to shorter ICU stays in COVID-19 patients. The role of iodine in enhancing IFN-I mediated antiviral immunity warrants future research.
References
Alexopoulou, Holt, Medzhitov, Flavell, Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3, Nature, doi:10.1038/35099560
Anderson, Sivalingam, Kang, Ananthanarayanan, Arumugam et al., Povidone-iodine demonstrates rapid in vitro virucidal activity against SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19 disease, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00316-3
Blum, Iodine a specific germicide in respiratory affections: preliminary report, Cal State J Med
Derscheid, Van Geelen, Berkebile, Gallup, Hostetter et al., Increased concentration of iodide in airway secretions is associated with reduced respiratory syncytial virus disease severity, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, doi:10.1165/rcmb.2012-0529OC
Diamond, Farzan, The broad-spectrum antiviral functions of IFIT and IFITM proteins, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri3344
Dijck-Brouwer, Muskiet, Verheesen, Schaafsma, Schaafsma et al., Thyroidal and extrathyroidal requirements for iodine and selenium: a combined evolutionary and (Patho) physiological approach, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14193886
Hadjadj, Yatim, Barnabei, Corneau, Boussier et al., Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc6027
Ivashkiv, Donlin, Regulation of type I interferon responses, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri3581
Iwasaki, Grubaugh, Why does Japan have so few cases of COVID-19?, EMBO Mol Med, doi:10.15252/emmm.202012481
Kawka, Fabacher, Sauleau, Coury, Arnaud, Factors associated with severity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with connective tissue diseases and rheumatoid arthritis: a nation-wide, population-based analysis of the French national medico-administrative SNDS database, Joint Bone Spine, doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105818
Lim, Teng, Ng, Bao, Tambyah et al., Repurposing povidone-iodine to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission: a narrative review, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2076902
Markou, Georgopoulos, Kyriazopoulou, Vagenakis, Iodine-Induced hypothyroidism, Thyroid, doi:10.1089/105072501300176462
Menon, The 1957 pandemic of influenza in India, Bull World Health Organ
Nauman, Wolff, Iodide prophylaxis in Poland after the Chernobyl reactor accident: benefits and risks, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/0002-9343(93)90089-8
Niu, Farrell, Li, Reffsin, Jain et al., Piscis: a novel loss estimator of the F1 score enables accurate spot detection in fluorescence microscopy images via deep learning, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.01.31.578123
Park, Iwasaki, Type I and type III interferons -induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe
Raj, Van Den Bogaard, Rifkin, Van Oudenaarden, Tyagi, Imaging individual mRNA molecules using multiple singly labeled probes, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.1253
Seyedalinaghi, Karimi, Barzegary, Mojdeganlou, Vahedi et al., COVID-19 mortality in patients with immunodeficiency and its predictors: a systematic review, Eur J Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00824-7
Sinopoli, Sciurti, Isonne, Santoro, Baccolini, The efficacy of multivitamin, Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D supplements in the prevention and management of COVID-19 and Long-COVID: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16091345
Stringer, Wang, Michaelos, Pachitariu, Cellpose: a generalist algorithm for cellular segmentation, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/s41592-020-01018-x
Van Eyndhoven, Singh, Tel, Decoding the dynamics of multilayered stochastic antiviral IFN-I responses, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2021.07.004
Verheesen, Traksel, Iodine, a preventive and curative agent in the COVID-19 pandemic?, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109860
Verhelst, Parthoens, Schepens, Fiers, Saelens, Interferon-inducible protein Mx1 inhibits influenza virus by interfering with functional viral ribonucleoprotein complex assembly, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01682-12
Wilson, Mckillop, Jenkins, Thomson, In vivo and in vitro studies into the immunological changes following iodine 131 therapy for Graves' disease, Eur J Nucl Med, doi:10.1007/BF00186651
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0341126",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0341126",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n <jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To investigate whether oral treatment with 12.5 mg iodine additional to standard of care is effective in reducing mortality and clinical deterioration of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n We performed a single center, randomized clinical trial (EudraCT 2020-001852-16) in which patients with severe covid-19 in need of hospitalization were randomized in two groups. The first group received 12.5 mg oral iodine for 8 days, the second group did not receive iodine next to the standard of care. Primary endpoints were deterioration of disease defined as transfer from the ward to the intensive care unit (ICU) or death. Next to these parameters we collected parameters in line with the recommendations made by the WHO in the early days of the pandemic. On these additional datasets we performed an exploratory analysis and investigated possible confounders and trends. The inclusion phase of the study was between October 2020 and April 2022. Finally,\n <jats:italic>in vitro</jats:italic>\n validations were performed.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n Outcomes from 141 participants were analyzed, revealing no significant differences in mortality or transfers to intensive care between the iodine-treated group (67 patients) and the control group (74 patients). In an exploratory analysis we found that patients randomized to receive oral iodine had a significantly shorter stay at the ICU (\n <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>\n = 0.016).\n <jats:italic>In vitro</jats:italic>\n validations proved increased virus-induced type I interferon responses upon iodine administration in pulmonary cells.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>These findings suggest that while iodine does not reduce mortality or ICU admissions, it may enhance antiviral immunity through increased type I interferon responses, contributing to shorter ICU stays in COVID-19 patients. The role of iodine in enhancing IFN-I mediated antiviral immunity warrants future research.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>\n Registration of trial: EudraCT Number: 2020-001852-16.\n <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2020-001852-16\" xlink:type=\"simple\">https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2020-001852-16</jats:ext-link>\n </jats:p>\n <jats:p>\n Sponsor name: Maxima Medical Center. Date of Registration: April 1\n <jats:sup>st</jats:sup>\n 2020.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Traksel",
"given": "René",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4344-3157",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Broen",
"given": "Jasper",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van Henten",
"given": "Arjen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Königs",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raj",
"given": "Arjun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7230-1134",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "van Eyndhoven",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Verheesen",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS One",
"container-title-short": "PLoS One",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-02T18:23:23Z",
"timestamp": 1770056603000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-02T18:23:27Z",
"timestamp": 1770056607000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Cheorl-Ho",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"N/A"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"N/A"
]
}
],
"name": "Maxima Medical Center Innovation Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-03T06:32:04Z",
"timestamp": 1770100324259,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1769990400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0341126",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0341126",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16091345",
"article-title": "The efficacy of multivitamin, Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D supplements in the prevention and management of COVID-19 and Long-COVID: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials",
"author": "A Sinopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref001",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109860",
"article-title": "Iodine, a preventive and curative agent in the COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "RH Verheesen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109860",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref002",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The 1957 pandemic of influenza in India",
"author": "IG Menon",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "Bull World Health Organ",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref003",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1959"
},
{
"article-title": "Iodine a specific germicide in respiratory affections: preliminary report",
"author": "S Blum",
"journal-title": "Cal State J Med",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref004",
"year": "1914"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14193886",
"article-title": "Thyroidal and extrathyroidal requirements for iodine and selenium: a combined evolutionary and (Patho) physiological approach",
"author": "DAJ Dijck-Brouwer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3886",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref005",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2022.2076902",
"article-title": "Repurposing povidone-iodine to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission: a narrative review",
"author": "N-A Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1488",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Med",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref006",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00316-3",
"article-title": "Povidone-iodine demonstrates rapid in vitro virucidal activity against SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19 disease",
"author": "DE Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref007",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2012-0529OC",
"article-title": "Increased concentration of iodide in airway secretions is associated with reduced respiratory syncytial virus disease severity",
"author": "RJ Derscheid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref008",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00186651",
"article-title": "In vivo and in vitro studies into the immunological changes following iodine 131 therapy for Graves’ disease",
"author": "R Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nucl Med",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref009",
"volume": "18",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012481",
"article-title": "Why does Japan have so few cases of COVID-19?",
"author": "A Iwasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref010",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "pone.0341126.ref011",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation. COVID-19 case report form core Version 8. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.1253",
"article-title": "Imaging individual mRNA molecules using multiple singly labeled probes",
"author": "A Raj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "877",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Methods",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref012",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-020-01018-x",
"article-title": "Cellpose: a generalist algorithm for cellular segmentation",
"author": "C Stringer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Methods",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref013",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Piscis: a novel loss estimator of the F1 score enables accurate spot detection in fluorescence microscopy images via deep learning",
"author": "Z Niu",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref014",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/35099560",
"article-title": "Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3",
"author": "L Alexopoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732",
"issue": "6857",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref015",
"volume": "413",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008",
"article-title": "Type I and type III interferons - induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19",
"author": "A Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref016",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3581",
"article-title": "Regulation of type I interferon responses",
"author": "LB Ivashkiv",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref017",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6027",
"article-title": "Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "J Hadjadj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "718",
"issue": "6504",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref018",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01682-12",
"article-title": "Interferon-inducible protein Mx1 inhibits influenza virus by interfering with functional viral ribonucleoprotein complex assembly",
"author": "J Verhelst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13445",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref019",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3344",
"article-title": "The broad-spectrum antiviral functions of IFIT and IFITM proteins",
"author": "MS Diamond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref020",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2021.07.004",
"article-title": "Decoding the dynamics of multilayered stochastic antiviral IFN-I responses",
"author": "LC Van Eyndhoven",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "824",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref021",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/105072501300176462",
"article-title": "Iodine-Induced hypothyroidism",
"author": "K Markou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "501",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Thyroid",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref022",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9343(93)90089-8",
"article-title": "Iodide prophylaxis in Poland after the Chernobyl reactor accident: benefits and risks",
"author": "J Nauman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "524",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Med",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref023",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-022-00824-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality in patients with immunodeficiency and its predictors: a systematic review",
"author": "S SeyedAlinaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref024",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105818",
"article-title": "Factors associated with severity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with connective tissue diseases and rheumatoid arthritis: a nation-wide, population-based analysis of the French national medico-administrative SNDS database",
"author": "L Kawka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105818",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Joint Bone Spine",
"key": "pone.0341126.ref025",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2025"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0341126"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Iodine increases pulmonary type I interferon responses and decreases covid-19 disease severity: Results from an open label randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "21"
}